|
|

This chapter covers the following information:
This section describes the cabling requirements and provides sample configurations. Each port type has its own cabling requirements, including the kind of cable and devices you can connect to the ports and the length and type of wiring you can use:
The following cabling guidelines apply to a 10BaseT or 100BaseT network:
The 100BaseT standard specifies that individual cable lengths do not exceed an overall cable budget. To determine your cable budget, use the following formula:
For example, in a network with two repeaters, R= 2; the maximum cable length between two nodes is 400 - (2 x 90) = 220 meters.
When connecting to other devices, identify the type of port on the other device to which the BMM will connect. If the port on the other device is marked with an X (such as a 100BaseTX-compatible hub, switch, or router) use a crossover cable. If the port on the other device is not marked with an X (such as a server or workstation), use a straight-through cable. Pinouts for the BMM connectors are described in the appendix "Connectors and Cables."
This section describes possible network configurations using a FastHub with a BMM. One BMM is required per four interconnected FastHubs. One BMM is also required in each cascaded FastHub. Refer to the FastHub 300 Series Installation and Configuration Guide for a description of the difference between interconnected and cascaded FastHubs and additional FastHub network configuration examples.
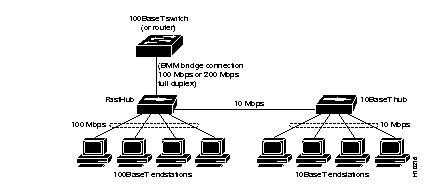
The BMM can connect 10BaseT devices (such as hubs, switches, and routers) and at the same time interconnect to 10BaseT and 100BaseT networks. Figure 2-1 shows how the BMM can provide a connection between a 10BaseT device and a 100BaseT switch or router. In this example, the FastHub has a distance between end-nodes of up to 100 meters.
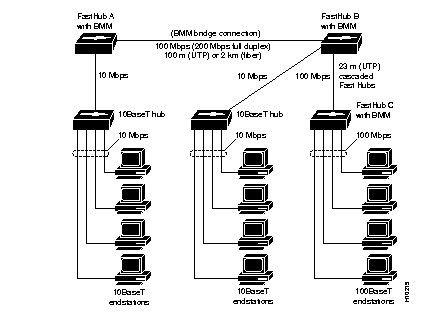
The BMM can interconnect two or more FastHubs or FastHub stacks in cases where wiring closets are further apart than the allowable distance defined by Class II repeater configuration guidelines. In the following example of this configuration (see Figure 2-2), each FastHub is a standalone unit.
FastHubs A and B each contain a BMM and can be linked with a 100BaseT connection either at a distance of 100 meters (using UTP) or 2 kilometers (using full-duplex fiber-optic cabling). FastHubs A and B also connect to 10BaseT environments and can support 100BaseT nodes (not shown). FastHubs B and C are cascaded (to a maximum of 23 meters) by using the 100BaseT uplink port.
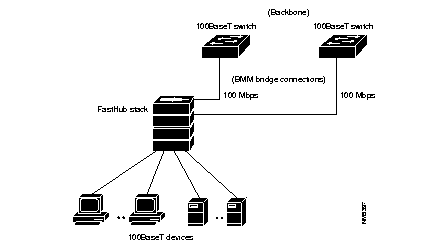
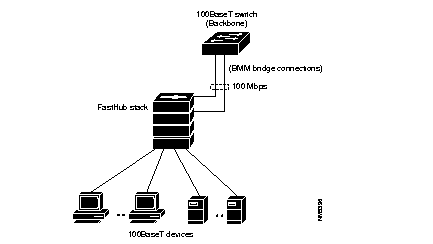
Using a BMM, 100BaseT devices can be connected to a backbone of 100BaseT switches. BMMs in a FastHub stack can be connected to separate backbone switches (see Figure 2-3) or redundantly connected to the same backbone switch (see Figure 2-4).
Follow these steps to unpack the BMM:
Step 1 Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
Step 2 Return all packing materials to the shipping container and save it.
Step 3 Ensure that all packing-list items are included in the shipment. The packing list is provided in the "Package Contents" section of the "Fast Install Guide" chapter. Check each item for damage.
Translated versions of the following safety warnings are provided in the "Translated Safety Warnings" appendix of this guide.
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
 | Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
 | Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment. |
 | Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
Follow these steps to install the BMM.
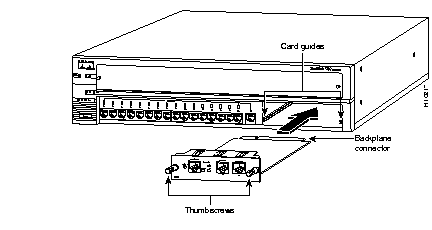
Step 1 Remove the slot cover from the lower, right FastHub slot by loosening the thumbscrews on each side.
Step 2 Unpack the BMM.
 | Caution To prevent ESD damage, handle the BMM by its front panel or board edges only. |
Step 3 Hold the BMM by its front panel, align the sides of the BMM with the card guides in the slot, and carefully slide it into the slot until the BMM faceplate is flush with the FastHub front panel (see Figure 2-5).
Step 4 Press firmly on the faceplate to ensure that the backplane connector is fully seated in the backplane.
Step 5 Tighten the thumbscrews on each side of the BMM.
Use the following module LED color indications to verify the operating status of the BMM:
| MOD LED Color | Module Status |
|---|---|
| Green | BMM running POST (approximately 30 seconds). |
| Green | POST completed; BMM operational and acting as primary supervisor. |
| Solid amber | BMM powered up and in standby mode (appears when multiple BMMs are in a FastHub stack). |
| Flashing amber | BMM failed POST. |
You can connect a PC, UNIX station terminal, or modem to the console port to access the FastHub management console. You can then manage a variety of FastHub and FastHub stack functions. When connecting a BMM 10BaseT port, 100BaseTX Port, or 100BaseFX port to the network, follow the guidelines described in the "Connecting 10BaseT and 100BaseTX Ports" and "Connecting the 100BaseFX Port" sections in this chapter.
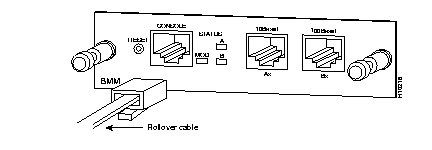
Use the thin, flat, RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and appropriate adapter, both supplied with the BMM, to connect the FastHub RJ-45 console port to a PC, terminal, or modem. Perform the following steps to connect the cable. See the "Console Cables and Adapters" section in the "Connectors and Cables" appendix for cable and adapter pinouts and to identify the rollover cable.
Step 1 Insert one end of the rollover cable into the BMM console port (see Figure 2-6).
Step 2 Attach one of the following adapters to a PC, terminal, or modem (see Figure 2-7):
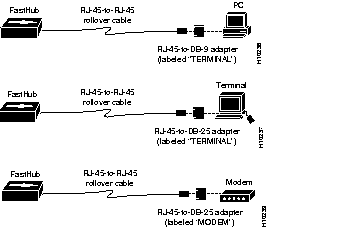
Step 3 Insert the other end of the rollover cable into the adapter.
Step 4 From the console terminal, boot the terminal emulation program. The BMM Log-In Security Menu is displayed.
The BMM console port must be configured to the same baud rate and character format as the PC, terminal, or modem. Although the match-baud-rate option (auto baud, configured through the Console Port menu) matches the baud rate when the BMM is answering an incoming call, the BMM does not change from its configured rate when dialing out. In addition, the BMM only matches a baud rate lower than its configured rate. When it completes a call and disconnects, the BMM always returns to the last configured baud rate.
Following are the default characteristics for the BMM console port:
Use the Console Port menu to change any defaults. Refer to the "Out-of-Band Management" chapter for details on using the BMM management console.
Always observe the following general rules when connecting devices: Use a straight- through cable to connect two ports when one of the ports is designated with an X; use a crossover cable to connect two ports when both ports are designated with an X. Use crossover or straight-through cabling, as required, to connect the BMM to the network (see Figure 2-8).
The 10BaseT RJ-45 connector requires Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cabling. The internally-crossed 10BaseT port is compatible with the 10BaseT IEEE-802.3 specification. Servers or workstations attached to the 10BaseT port must use a 10BaseT-compatible adapter.
The 100BaseTX RJ-45 connector requires Category 5 UTP cabling. The internally-crossed 100BaseTX port is compatible with the 100BaseTX IEEE-802.3u specification. Servers or workstations attached to the 100BaseTX port must use a 100BaseTX-compatible adapter.
 | Caution Connect the supplied rollover cable to the console port only. Do not connect it to the 10BaseT or 100BaseTX ports. |
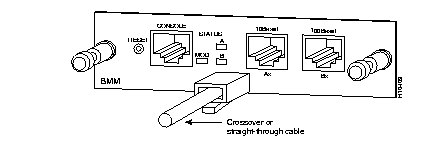
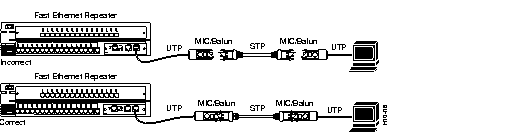
 | Caution To prevent potential loopback problems when using shielded twisted pair (STP) cable in a Token Ring network environment, make sure media interface connectors (MICs) and baluns are always connected when they are part of a link connected to a Fast Ethernet repeater (see Figure 2-9). |
The 100BaseFX SC-type connector requires fiber-optic cabling. The internally-crossed 100BaseFX port is compatible with the 100BaseFX IEEE-802.3u specification. Servers or workstations attached to the 100BaseFX port must use a 100BaseFX-compatible adapter.
The A and B port LEDs indicate port status as follows:
You can remove the BMM from the FastHub chassis without powering down the FastHub. Loosen the thumbscrews on each side of the module, and carefully slide it out of the FastHub.
 | Caution Always install a slot cover in an empty module slot to keep dust out of the unit, maintain the cooling air flow, and help prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI). |
 | Caution If you remove a FastHub with a BMM and there is no backup BMM in the FastHub stack, you lose manageability for the entire stack. |
|
|