CiscoWorks network management software lets you monitor complex internetworks that use Cisco devices and helps you plan, troubleshoot, and analyze your network. CiscoWorks uses the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to monitor and control any SNMP device on the network.
CiscoWorks works directly with your SNMP network management platform, allowing CiscoWorks applications to be integrated with the features and applications of your platform.
CiscoWorks provides a fully integrated relational database that is based on the Sybase relational database.
This chapter contains the following sections:
The following new or changed features have been made to CiscoWorks and are reflected by information in this manual:
- Online Help System--CiscoWorks now includes a new form of online help based upon help systems supplied with Windows-based platforms. It provides online information contained in this guide. The online help system allows you to access different levels of information by clicking on underlined text. The underlined text opens additional help windows. This enables instant access to screen information. The online help system provides overviews, related information, procedures, and glossary data. It also allows users to search for keywords or phrases within the help text.
- For more information on how to use the online help system, see Using Help in the online help system.
- NETSYS Integration--CiscoWorks integration with NETSYS applications includes the following capabilities:
- Scripts that pull router configuration files from the CiscoWorks Sybase database
- Scripts that send configuration file changes to routers through the Configuration Management or nmconfig applications
- Updates to Configuration Management that check user permissions in Security Manager before continuing with configuration changes
- Integration of NETSYS applications into the network management platform menu structure along with CiscoWorks applications.
- Both CiscoWorks and NETSYS maintain their own databases. CiscoWorks does not include the NETSYS Connectivity Toolkit. Only the above scripts and feature improvements are included.
- MIB Support--Additional MIB support in this release includes support for Cisco IOS Version 10.3 and 11.0 software. A list of the RFC and Cisco Private MIB files included in this CiscoWorks release can be found in the $NMSROOT/contrib/mibs and $NMSROOT/etc/mibs directories, or in the CiscoWorks Reference Guide. Access CCO for the most up-to-date and complete MIB information.
- CiscoWorks Toolbox--The CiscoWorks Toolbox launches CiscoWorks applications without requiring you to navigate through network management platform menu structures. CiscoWorks applications are grouped by their functions.
- Access the CiscoWorks online help system by placing your cursor over a CiscoWorks icon in the Toolbox and pressing F1. For more details, refer to the online help for the CiscoWorks Toolbox.
- Upgrade to Sybase 10.1--The upgrade to Sybase Release 10.1 includes the following significant changes:
- Single Sybase database structure is split into two databases (nms and polldb)
- Changes to database administration scripts and report-writing functions
- Replacement of Sybase Data WorkBench (DWB) with Sybase ESQR (Easy SQR) reporting tool.
- Environmental Monitor Upgrade--Environmental Monitor now supports the Cisco 7000 router as well as continuing to support the AGS+ router.
- Your environmental monitor card must be a Revision 4 ENVM card (Microcode Version 2.0) or later.
The following features have been modified or removed from CiscoWorks:
- Software Management Application and Sybase Database Tables--The suite of software management applications and the nmadd portion of Device Management have been altered to support the following enhancements:
- Support for multiple-subset Cisco IOS version images for the Device Software Manager application
- Support for Cisco 4500, Cisco 7010, and Cisco 7500 products
- Removal of the microcode upgrade features and toggle switch from windows
- Removal of the controller table from the database
- Use of MIB variables to get config-register values
- Log Manager and Event Daemon Removed (nmeventd)--With this release of CiscoWorks, event logging and message logging are no longer performed by Log Manager and the Event daemon (nmeventd). These functions have been removed from CiscoWorks and can be performed by your network management system (NMS) platform tool.
- CiscoWorks events are written to the platform's log file by the CiscoWorks centralized log and are no longer written to the Sybase table. Therefore, the Sybase log table is no longer used and has been removed.
- The Log Manager daemon (nmlogd) now collects messages from nmslog and writes them to the platform logging tool. Use your platform's log application to view CiscoWorks events. For more information on your platform's logging capabilities, refer to the event or message logging sections in your platform's documentation set.
- Although CiscoConnect appears on some CiscoWorks 3.2 menus, you should use Cisco Connection Online (CCO) instead. CCO lets you access to up-to-date product and customer information. For information about using CCO, see "Cisco Connection Online" in About This Guide.
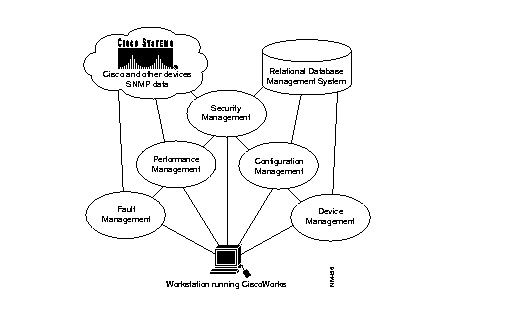
Figure 1-1 illustrates the general relationship of CiscoWorks functions.
Figure 1-1: CiscoWorks Functional Diagram
CiscoView is a separately-bundled graphical network management application that provides a physical view of a Cisco device, its cards, and its ports. Available device data includes SNMP error messages; system status information; hardware type and software version number; and device, card, and port status. With CiscoView you can configure your Cisco devices, monitor network performance, quickly access vital device information, and troubleshoot minor network problems.
Additional networking tools can be started from CiscoView. Additional device support is available on the Cisco Connection Online (CCO) or by ordering the Network Management Support CD.
For more information about CiscoView, see "Using CiscoView" in the online help system.
CiscoWorks applications target five network management functional areas: fault management, performance management, configuration management (which includes device management), accounting management (which is included in performance management applications), and security management.
The following sections describe the tasks you can perform in each functional area.
You can use CiscoWorks fault management functions to do the following:
- Access specific device information on Cisco routers to monitor router environment and interface information using the Device Monitor application (available on SNM only).
- Emulate router EXEC show commands on Cisco routers using the Show Commands application.
- Display a dynamic graphical routing path from a source device to a destination device using the Path Tool application.
- Analyze a graphical routing path for link utilization and error rate information using the Path Tool application.
- Access the Cisco AGS+ and 7000 router environmental monitor cards for temperature and voltage information using the Environmental Monitor application.
- Access device information from the Health Monitor application, which includes Show Commands and Real-Time Graphs application data.
- Quickly access administrative and maintenance personnel associated with devices on the network using the Contacts application.
With CiscoWorks, you can retrieve status and administrative information about the network devices and display the information for multiple devices concurrently so that you can act on the changing needs of your internetwork environment.
You can use CiscoWorks performance management functions to do the following:
- Compare device statistics dynamically using the Polling Summary and Real-Time Graphs applications.
- Display historical data over a selected timeframe using the Polling Summary and Real-Time Graphs applications.
- Dynamically graph real-time router information including data on router health, interface health, and protocol traffic using the Real-Time Graphs application.
- Emulate router EXEC show commands on Cisco routers using the Show Commands application.
- Specify MIB objects to continually monitor from selected devices in your network using the Device Polling application.
- Display the polled information of network variable statistics in a graphic plot format, to monitor and compare network component performance using the Polling Summary application.
- Start a Sybase Easy SQR application to run a database report and print polling table information gathered in the Polling Summary application.
- Create a custom report format for any data element collection that is available in the database, using standard Structured Query Language (SQL) or Visual Query Language (VQL) commands in the Sybase Easy SQR application.
Accounting management is a subset of the performance management functional area: the applications used to generate accounting management information are located in those areas. The following list describes the functions you can perform for accounting management:
- Emulate Cisco router EXEC show commands for information on Internet Protocol (IP) accounting checkpoint using the Show Commands application.
- Access Cisco private Management Information Base (MIB) object information using the Device Polling application.
You can use CiscoWorks configuration management functions to do the following:
- Dynamically access the configuration parameters of remote Cisco Systems devices on your network using the Configuration Management application.
- Edit and browse device configuration files that can be loaded to the Cisco device. Scroll through and search for text strings in a configuration file using the Configuration Management application.
- Identify a Cisco device, select the appropriate configuration command script, and invoke the load operation using the Configuration Management application.
- Change individual parameters in a Cisco device configuration while the device is on line by reading and editing the loaded configuration using the Configuration Management application.
- Compare loaded configurations with stored configurations using the Configuration Management application.
- Import a configuration script file from a directory on your UNIX workstation and store it in the database using the Configuration Management application.
- Create and send global or snap-in commands to manage your network and schedule command execution during network downtime using the Global Command Manager or Configuration Snap-In Manager applications.
- Use the AutoInstall Manager application to bring up a new router remotely from the network management workstation.
- Manage the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) users in your network using the TACACS Manager application to revise passwords, manage account expiration, and perform other duties.
- Upgrade system software or microcode for Cisco devices via the Device Software Manager application.
- Use the concept of domains, or loosely grouped devices, to manage your network using several CiscoWorks applications.
Device management is a subset of the configuration management function. Following are the major management functions you can perform:
- Create, modify, and maintain a complete inventory of the network--hardware, software, release levels of operational components, responsible individuals involved in the network, and associated locations. Enter data into the database tables for network devices, interfaces, contacts, and so on.
- Synchronize the information in the CiscoWorks Sybase database with the information in the NMS database using the Sync w/Sybase application. You can also synchronize the platform database or add individual devices to the CiscoWorks Sybase database.
- Quickly access administrative and maintenance personnel associated with devices on the network using the Contacts application.
- Organize devices into domains or logical device groups that allow certain users access for maintenance and administrative purposes, while other users can only monitor these devices. This organization is set up in the Security Manager application, but is retained as part of the device information that each CiscoWorks application uses.
You can use CiscoWorks security management functions to do the following:
- Set up authority checking for selected CiscoWorks applications.
- Set up security privileges for selected users according to their group/domain and restrict access to device configuration files, network management processes, device database information, and network activity information.
- Create domains, or loosely grouped devices, that aid in the security of your network.
- Modify or delete user permissions for CiscoWorks network management application use.
On the SunNet Manager platform (SNM), you access CiscoWorks applications either from the Tools menu or the Glyphs menu. Figure 1-2 shows the CiscoWorks applications available on the Tools menu.
Figure 1-2: CiscoWorks Applications on the SunNet Manager Tools Menu

SNM also has a menu that appears when you click on an icon. On SNM, icons are called glyphs, and the menu that appears is called the Glyph menu (Figure 1-3).
Figure 1-3: CiscoWorks Applications on the Glyph Menu

Table 1-1 and Table 1-2 describe each of the CiscoWorks applications in the Tools and Glyph menus.
Table 1-1: CiscoWorks Tools Menu Applications
| Application
| Overview of Tasks
|
|---|
| Application Help
| CiscoWorks online help system that allows you to investigate different levels of details within the online help system by selecting highlighted text to open additional windows. The online help system provides overview, related information, procedures, and glossary data on the CiscoWorks applications and features. It allows both keyword and full-text searches to enable users to search for specific text.
|
| AutoInstall Mgr
| Remotely deploys a new router using a neighbor router. Perform AutoInstall tasks remotely via the workstation running CiscoWorks instead of running a Telnet session.
|
| CiscoView
| This option appears only if you have installed CiscoView separately. CiscoView allows you to view the front and rear panels of Cisco devices. You can display configuration and performance information for the device, its cards, and its ports. You can use this information to monitor network performance, quickly access vital device information, and troubleshoot minor network problems.
|
| Config Management
| Analyze or edit configuration files of local and remote Cisco Systems devices in your network. Compare the contents of two configuration files in the database or compare the configuration currently running on the device and the configuration that represents the last time you performed a Database to Device command.
|
| Configuration Snap-In Mgr
| Create and execute system commands on a device or group of devices at any time via the Global Command Scheduler application.
|
| Device Mgmt
| Create and maintain a database that holds a complete inventory of your network--hardware, software, release levels of operation components, individuals responsible for maintaining the devices, and associated locations. Enter or change data in the database tables for network devices, networks, interfaces, contacts, vendors, and so on.
|
| Device Monitor
| Monitor your network devices for information about environmental and interface statistics. Specify how often CiscoWorks should check this information and whether or not to log it into the Log Manager application.
|
| Device Polling
| Probe and extract information about the condition of your networks using a polling feature. Information acquired from polling is stored in the database for further evaluation and analysis. Compare the relative performance and status of devices and interfaces on the network.
|
| Domain Mgr
| Set up groups of devices, called domains, so CiscoWorks applications can access these device groups to accomplish network management tasks such as security, configuration, and device polling.
|
| Global Command Mgr
| Create and execute system commands on a device or group of devices at any time via the Global Command Scheduler application.
|
| Global Command Scheduler
| Schedules commands or other jobs at regularly scheduled times using the crontab utility. Invoked from the Global Command Manager application or the command line.
|
| Login
| Perform a generic login for all CiscoWorks applications that require user authentication so that you do not have to log in to each separate application.
|
| Logout
| Log out of secured CiscoWorks applications to ensure security for those applications with authority checking turned on.
|
| Path Tool
| View and analyze the path between two devices. Perform analysis on the path to collect utilization and error data. The display shows the devices encountered between the source and the destination device, the link speeds connecting these SNMP devices, and the interface names.
|
| Polling Summary
| Summarize the polling setup completed by the Device Polling application. Browse data, and stop and start polling.
|
| Process Mgr
| Start or stop CiscoWorks-related processes including the following daemons: Polling (nmpolld), and Device Monitor (nmdevmond). View status for the following daemons: System Log (syslogd), the Sybase Server (dataserver), and the TACACS (xtacacsd).
|
| SA Password
| Log in to the default Sybase database account to perform system administrator tasks.
|
| Security Mgr
| Set up authority checking procedures to protect selected CiscoWorks applications and your network devices from unauthorized individuals by setting up your CiscoWorks environment to require a login to access applications. This protection ensures that only users with a valid account and password can perform tasks such as configuring a router, deleting database device information, or defining polling procedures.
|
| Software Inventory Mgr
| Update the Sybase database to include current device software and hardware status. Sorts device information according to platform and software image and allows you to invoke Device Software Manager to update specific devices.
|
| Software Library Mgr
| Maintain the master storage (a list of available Cisco system software and microcode).
|
| Sync w/Sybase
| Synchronize both the SNM database and the Sybase database. CiscoWorks maintains data in the Sybase database, whereas the SNM maintains its own database. Sync w/Sybase ensures that device data from SNM database is in the Sybase database and vice versa. Generally, synchronize the databases whenever new devices are added to your network. This application includes Sync w/SNM.
|
| Sybase ESQR
| Use Sybase ESQR utilities to run and print reports on any table created with the Device Polling application.
|
| TACACS Mgr
| Maintain the TACACS password file on UNIX hosts that act as TACACS security servers. Create and update TACACS accounts and computer-generated passwords.
|
| Toolbox
| Allows you to start CiscoWorks applications directly, without using the menus on your network management platform. Click on an application's icon in the Toolbox window to start the application. You can also display help for each application from the Toolbox.
|
Table 1-2: CiscoWorks Glyph Menu Applications
| Application
| Overview of Tasks
|
|---|
| Contacts
| Obtain information about the contact person for a specific device including the complete name, telephone number, e-mail address, title, location, and address of the person responsible for the operation of the device.
|
| Device SW Mgr
| Automate the upgrade of a system software or microcode image on a Cisco device.
|
| Env. Monitor
| View the environmental status of a Cisco AGS+ or Cisco 7000 router including temperature and voltage statistics. This function can be performed only on AGS+ or 7000 routers running at least System Software Release 9.0 with an environmental monitor card running ENVM Microcode Version 2.0 software.
|
| Health Monitor
| View information about the status of a device, including buffers, CPU load, memory available, and protocols and interfaces being used. Quickly accesses the Show Commands and Real-Time Graphs windows through the Health Monitor window.
|
| Path Tool
| View and analyze the path between two devices. Perform analysis on the path to collect utilization and error data. The display shows the devices encountered between the source and the destination device, the link speeds connecting these SNMP devices, and the interface names.
|
| Real-Time Graphs
| View device information such as the router health (buffer space, CPU load, environment, free memory, and security), interface health (bits per second, bytes, errors, packets per second, packets, and queues), and protocol traffic such as IP, Internal Control Memory Protocol (ICMP), SNMP, Transfer Control Protocol (TCP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), AppleTalk, DECnet IV, Novell, VINES, and Xerox Network Systems (XNS) using the SNM Grapher utility.
|
| Show Commands
| View device data about any SNMP device, including Cisco routers and communication servers. This device data includes the software version, buffers, selected device interfaces, traffic mix, IP accounting checkpoint, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), and IP route. This application emulates the EXEC show commands for Cisco routers.
|
| Sync w/Sybase
| Synchronize a single device in both the SNM database and the Sybase database. Synchronize a device to ensure that both databases share the same device data. Generally, synchronize the databases whenever new devices are added to your network.
|
CiscoWorks is fully integrated with HP OpenView, so you can access CiscoWorks applications directly from the HP OpenView main window. (See Figure 1-4.)
Figure 1-4: HP OpenView Main Window
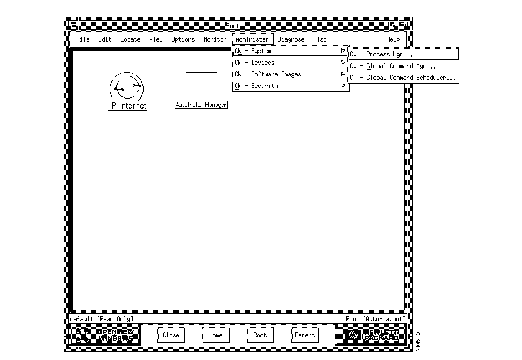
The CiscoWorks applications are available from the HP OpenView main menu. For example, to open the Device Management application, you would choose Administer, then Cisco Devices, then Device Mgmt (which would be represented as Administer>Cisco Devices>CW - Device Mgmt).
HP OpenView does not use glyphs or a Glyph menu, as SunNet Manager does. In HP OpenView, instead of using the Glyph menu to access device-dependent applications, you would perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select an object in your network map or submap.
Step 2 Select the specified CiscoWorks application from the object menu.
Table 1-3 briefly describes each of the CiscoWorks applications, and shows how to choose them from the HP OpenView menus.
Table 1-3: Accessing CiscoWorks Applications from HP OpenView
| Application
| Menu Location
| Overview of Tasks
|
|---|
| Application Help
| Help>CW - Application Help
| CiscoWorks online help system that allows you to investigate different levels of details within the online help system by selecting highlighted text to open additional windows. The online help system provides overview, related information, procedures, and glossary data on the CiscoWorks applications and features. It allows both keyword and full-text searches to enable users to search for specific text.
|
| AutoInstall Manager
| Administer>Cisco Devices>AutoInstall Manager
| Remotely deploys a new router using a neighbor router. Performs AutoInstall tasks remotely via the workstation running CiscoWorks instead of running a Telnet session.
|
| Configuration Management
| Administer>Cisco Devices>ConfigurationManagement
| Access configuration files of local and remote Cisco Systems devices in your network to analyze or edit them as necessary. Compare the contents of two configuration files in the database or compare the configuration currently running on the device and the configuration that represents the last time you performed a Database to Device command.
|
| Configuration Snap-In Manager
| Administer>Cisco Devices>ConfigurationSnap-In Manager
| Create and execute system commands on a device or group of devices at any time via the Global Command Scheduler application.
|
| Contacts
| Monitor>Description>Contacts
| Obtain information about the contact person for a specific device including the complete name, telephone number, e-mail address, title, location, and address of the person responsible for the operation of the device.
|
| Device Management
| Administer>Cisco Devices>Device Management
| Create and maintain a database that holds a complete inventory of your network--hardware, software, release levels of operation components, individuals responsible for maintaining the devices, and associated locations. Enter or change data in the database tables for network devices, networks, interfaces, contacts, vendors, and so on.
|
| Device Polling
| Monitor>Device Polling
| Probe and extract information about the condition of your networks using a polling feature. Information acquired from polling is stored in the database for further evaluation and analysis. Compare the relative performance and status of devices and interfaces on the network.
|
| Device Software Manager
| Administer>
CiscoWorks Software Images>Device Software Manager
| Automate the upgrade of system software on a Cisco device.
|
| Domain Manager
| Administer> Security>
Domain Manager
| Set up groups of devices called domains so that CiscoWorks applications can access these device groups to accomplish network management tasks such as security, configuration, and device polling.
|
| Environmental Monitor
| Monitor>
Environmental Monitor
| View the environmental status of a Cisco AGS+ or Cisco 7000, including temperature and voltage statistics. This function can be performed only on AGS+ or 7000 routers running System Software Release 9.0 or later with an environmental monitor card running ENVM Microcode Version 2.0 or later software.
|
| Global Command Manager
| Administer>
CiscoWorks System>
Global Command Manager
| Create and execute system commands on a device or group of devices at any time via the Global Command Scheduler application.
|
| Global Command Scheduler
| Administer>
CiscoWorks System>Global Command Scheduler
| Schedule commands or other jobs at regularly scheduled times using the crontab utility.
|
| Health Monitor
| Monitor>Health Monitor
| View information about the status of a device, including buffers, CPU load, memory available, and protocols and interfaces being used. Enables you to access the Show Commands and Real-Time Graphs windows through the Health Monitor window.
|
| Login
| Misc>Login
| Perform a generic login for all CiscoWorks applications that require user authentication so that you do not have to log into each separate application.
|
| Logout
| Misc>Logout
| Log out of secured CiscoWorks applications to ensure security for those applications with authority checking turned on.
|
| Path Tool
| Diagnose>Network
Connectivity>Path Tool
| View and analyze the path between two devices. Perform analysis on the path to collect utilization and error data. The display shows the devices encountered between the source and the destination device the link speeds connecting these SNMP devices, and the interface names.
|
| Polling Summary
| Monitor>Polling Summary
| Summarize the polling setup completed by the Device Polling application. Browse data, and stop and start polling.
|
| Process Manager
| Administer>
CiscoWorks System>Process Manager
| Start or stop CiscoWorks-related processes including the following daemons: Log (nmlogd), Polling (nmpolld). View status for the following daemons: System Log (syslogd), the Sybase Server (dataserver), and the TACACS (xtacacsd).
|
| Real-Time Graphs
| Monitor>Real-Time Graphs
| View device information such as the router health (buffer space, CPU load, environment, free memory, and security), interface health (bits per second, bytes, errors, packets per second, packets, and queues), and protocol traffic (IP, ICMP, SNMP, TCP, UDP, AppleTalk, DECnet IV, Novell, VINES, and XNS) using the xnmgraph utility.
|
| SA Password
| Administer>Security>SA Password
| Log in to the default Sybase database account to perform system administrator tasks.
|
| Security Manager
| Administer>Security>Security Manager
| Set up authority checking procedures to protect selected CiscoWorks applications and your network devices from unauthorized individuals by setting up your CiscoWorks environment to require a login to access applications. This protection ensures that only users with a valid account and password can perform tasks such as configuring a router, deleting database device information, or defining polling procedures.
|
| Show Commands
| Diagnose>Show Commands
| View device data about any SNMP device, including Cisco routers and communication servers. This device data includes the software version, buffers, selected device interfaces, traffic mix, IP accounting checkpoint, ARP, and IP route. This application emulates the EXEC show commands for Cisco routers.
|
| Software Inventory Manager
| Administer>
CiscoWorks Software Images>Software Inventory Manager
| Update the Sybase database to include current device software and hardware status. Sort device information according to platform and software image and invoke Device Software Manager to update specific devices.
|
| Software Library Manager
| Administer>
CiscoWorks Software Images>Software Library Manager
| Maintain the master storage (a list of all available Cisco system software and microcode).
|
| Sync w/Sybase
| Misc>Sync w/Sybase
| Synchronize both the NMS database and the Sybase database. CiscoWorks maintains data in the Sybase database, whereas HP OpenView maintains its own database. Sync w/Sybase ensures that device data from HP OpenView database is in the Sybase database (Sync w/Platform) and vice versa. Generally, synchronize the databases whenever new devices are added to your network. Use Sync Selected to add individual devices.
|
| Sybase ESQR
| Misc>Sybase ESQR
| Access Sybase ESQR utilities to run and print reports on any table created with the Device Polling application.
|
| TACACS Manager
| Administer>Security>TACACS Manager
| Maintain the TACACS password file on UNIX hosts that act as TACACS security servers. Create and update TACACS accounts and computer-generated passwords.
|
Toolbox allows you to start CiscoWorks tool or application directly, without using the menus on your network management platform. Clicking on an application's icon in the Toolbox window starts the application. You can also display the help for each application from Toolbox.
Use the Toolbox application to perform the following tasks:
- Starting CiscoWorks Tools from Toolbox
- Viewing CiscoWorks Online Help from Toolbox
- Exiting the Application
To start a CiscoWorks application from Toolbox:
Step 1 Select CW - Toolbox.
For SunNet Manager, select Tools>CW - Toolbox.
For HP OpenView, select Misc>CW - Toolbox.
Step 2 When the CiscoWorks 3.0 Toolbox window appears, click on the icon for the tool you want to run.
When your mouse pointer is positioned over a tool icon, a message appears at the bottom of the Toolbox window that indicates which tool you are starting.
The window for the application you select appears, unless you select one of the following applications: Environmental Monitor, Health Monitor, Real-Time Graphs, Show Commands, or Workgroup Director. If you select one of these applications, the Command Input window appears. You must select a device before you can run these applications.
Step 3 Enter a device name in the Device Name field.
Step 4 Enter the read community string for the device specified in the Device Name field in the Read Community field.
The read community string enables the retrieval of information using the SNMP protocol from the device. Toolbox uses the default read community string value, public, if the field is left blank.
Step 5 Click on OK to select a device and close the window.
The window for the application you select appears, showing data for the device you select.
You can leave Toolbox running while you use CiscoWorks, so you can start CiscoWorks applications easily at any time.
To view help for any CiscoWorks application from Toolbox:
Step 1 Select CW - Toolbox.
For SunNet Manager, select Tools>CW - Toolbox.
For HP OpenView, select Misc>CW - Toolbox.
Step 2 When the CiscoWorks 3.0 Toolbox window appears, point to a tool icon and press F1 instead of clicking on the icon.
The Help viewer appears and displays the Help Contents for that application. You can jump to any part of the help system from this viewer.
Note You can also start the Help viewer from Toolbox by selecting
Help>On Toolbox from the Toolbox window. The Help viewer opens to the Contents page for Toolbox help.
To quit the application, select File>Exit.
Exiting Toolbox only closes the Toolbox application. Other applications started from Toolbox continue to run.
This window has the following areas:
- Menu Bar--contains File and Help menus
- Buttons--Each button starts an application. Toolbox buttons are divided into the following categories:
- Fault Mgmt. Tools--Show Commands, Path Tool, Environmental Monitor, Real-Time Graphs, Health Monitor, WorkGroup Director
- Configuration Mgmt. Tools--Configuration Manager, Configuration Snap-In Mgr, Global Command Manager, Global Command Scheduler, Software Library Manager, Device Software Manager
- Inventory Mgmt. Tools--Device Manager, Domain Manager, Sync w/Sybase, Software Inventory Manager, Device Contacts
- Security Mgmt. Tools--Security Manager, TACACS Manager, Login, Logout
- Performance Mgmt. Tools--Polling Summary, Process Manager, Device Polling
This window has the following areas:
- Fields
- Device Name--Specify the name of the device from which you want to retrieve SNMP information in this field.
- Read Community--Enter the read community string for the device specified in the above field. The read community string enables the retrieval of information via the SNMP protocol from the device. Toolbox uses the default read community string value, public, if the field is left blank.
- Buttons
- OK--Applies your selection and closes the window.
- Cancel--Closes the window without applying your selection.




