|
|

This chapter describes the CiscoWorks features that help you manage the performance level of your network, including managing individual devices, lines, and interfaces. This chapter also describes how to monitor CiscoWorks performance by:
Several CiscoWorks applications help manage the performance of the SNMP devices in your network. A brief description of each application discussed in this chapter follows:
Use these applications to collect network data as a baseline before your network develops problems. These applications are discussed in detail in the following sections.
This section describes how to set up a customized polling table (or table group) for devices and interfaces on the internetwork using Device Polling.
CiscoWorks allows you to probe and extract information about the condition of your networks by using the polling feature. Information acquired from these polls is stored in the database for further analysis. The construction and use of polling configurations allow you to compare relative performance and status of devices and interfaces on the network. You can poll devices individually, in groups, or poll all devices at once based on your disk space availability. Use multiple polls to collect a wide range of data at varying polling interval rates.
For consistency, this publication uses the term object as a replacement for such terms as Management Information Base (MIB) variables, MIB object instances, and so on. These terms are used interchangeably in this guide.
You must have CiscoWorks security privileges to read and write to the Device Polling window. If you do not have write privileges, you might not be able to apply or delete table changes. You can use the Change Domain command to change to a different domain in order to access other devices for polling. You can use the Change User command to change to a username with different privileges. Use the Security>Privilege command on the Security menu to check your privileges for Device Polling.
The polling process consists of the following general procedures. Each task is described in greater detail later in this chapter.
Step 1 Create a polling table (or polling group) in Device Polling that contains the polling configuration components or use one of the sample polling tables provided with CiscoWorks. (When you complete construction of the table, select Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon of these changes.)
Step 2 View the polling table in the Polling Summary application and start or stop polling the devices defined in the polling table (if you have not yet done so). Use the Polling Summary application to view the collected data in a preconfigured report, export the data, and start or stop the polling.
The MIB objects selected in the table are read by the polling table and written to the database where they are retained for future use. Subsequent data polls do not overwrite previous polled data. Data is stacked with all collected information available for analysis. Data segments are listed in Polling Summary.
To browse poll data in a text or graph format, select the data segment and use the Browse Data command.
This command sends the data segment to the Results Browser application.
Step 3 While browsing the data segment, you can view text or convert the data to a graph using the SNM Results Browser. You cannot move the polling data to the HP OpenView grapher.
Step 4 Use the Polling Summary Tools menu to export polling data or create reports. You can use Easy SQR to create reports or use the preconfigured reports in Polling Summary.
Figure 3-1 illustrates the device polling concept. The polling daemon CiscoWorks uses, nmpolld, queries and stores information in the Sybase database. Both the Device Polling and Polling Summary applications use the polling daemon.
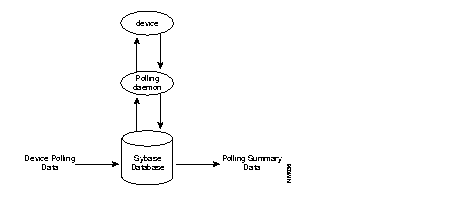
A Device Polling table consists of the following elements: a polling frequency, a set of MIB objects, and a list of devices. The information specified in the table is collected during the polling process. A collection of information from the polling process is called a data segment. A segment is defined as the data selected from the start of polling to the stop of polling, regardless of the frequency used to sample. For instance, if you start polling at 1:00 p.m. and stop at 2:00 p.m. on the same day, the data segment will contain one hour of polling data. If you had set a polling frequency of 1 minute, you would have obtained 60 samples in the segment. Data segments are also broken down by day,
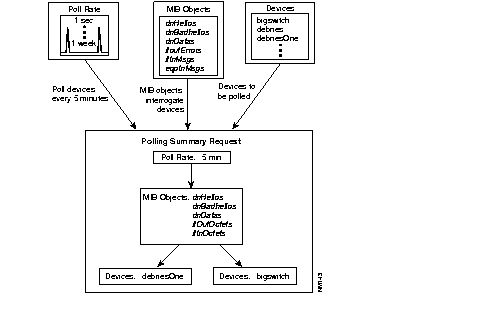
Figure 3-2 illustrates the polling table construction concept. You can select MIB objects to collect information on a device and choose a polling interval for the poll. The polling interval has a significant impact on the amount of data collected in a given time frame.
 | Caution The amount of data collected varies depending upon the type and number of queries made, so be sure to monitor the disk space available for storage of polled information. For additional information on database and transaction log space, refer to the "Database Administration" chapter. |
Before you can begin polling devices for data, you must set up your polling table in the Device Polling window.
Figure 3-3 illustrates the Device Polling window.
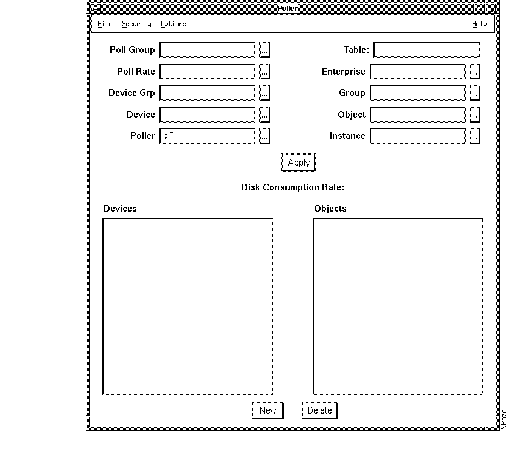
Table 3-1 describes the components of the Device Polling window.
As each object is selected, the Disk Consumption Rate field is adjusted to reflect an estimate of how fast the disk space will be consumed in order to store the polled data. The algorithm uses the poll rate, number of devices, and number of objects currently selected in the table to estimate the space required to hold one day (24 hours) of polling. The result of the calculation is reflected as whole kilobytes required per day.
Multiply the disk space consumption rate by the length of time you plan to poll. This equals the number you compare with the available disk space. If you do not want to change the polling table, you might have to increase your database space allocation. Before deciding to adjust disk space, review the polling interval and duration and the number of objects to determine if any values can be adjusted. To learn how to increase the database space, refer to the "Database Administration" chapter.
Note that if you fill up the disk, Sybase could become unusable. Refer to your Sybase documentation and to "Monitoring Transaction Log and Disk Space" in Chapter 7.
If you are creating a new polling table, you must enter data in the Table, Enterprise, Group, and Object fields. The Instance field is optional. If you use a sample table (such as sample_load or sample_traffic), it is automatically populated with MIB objects. You can add MIB objects to those already listed.
In order to set up polling, access the Device Polling window and complete the necessary information. If you are not familiar with MIB objects, using Device Polling will be more difficult. Contact your network administrator for more information on MIB objects.
To access the Device Polling window to set up a new polling table, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select Device Polling.
On SNM, select Tools>CW - Device Polling.
On HP OpenView, select Monitor>CW - Device Polling.
The Device Polling window appears. (See Figure 3-3.)
For a description of the device polling fields, refer to Table 3-1.
Step 2 Create a new poll group by clicking on New.
If you want to use one of the sample tables as a template, open the Poll Group chooser list and choose a sample table.
Step 3 Create the new poll group name by entering the name in the Poll Group field.
Only one poll group is used with each data configuration. The Poll Group field defines what tables are in the poll groups.
CiscoWorks includes several sample poll group tables in the chooser list called sample. You can use these tables as templates. Modify them to your specific polling needs, but rename the poll group to describe the type of polling you are performing.
Step 4 To use a sample template to create a new poll table, select the sample table and rename it by entering a new group and table name and click on Apply.
If you overwrite or delete one of the sample tables, you can recreate it using the makesample program. The makesample script adds the sample files back to your directory structure. Refer to the "Database Administration" chapter for information on the makesample script.
Step 5 Create the new table name or use the poll group name as the table name by default. To create a new table name, enter the name in the Table field.
Your poll group name and table name will default to the same name. You may want to change the table name.
 | Caution You can enter a table name only prior to pressing the Apply button. After you press Apply, the table is created, and the table name cannot change. |
Step 6 Select the poll rate for this poll. There are two methods of selecting a poll rate:
Use seconds, minutes, days, or weeks as the unit of measure. If you enter 21 days in the field, the data will be converted to 3 weeks, the largest unit of measure for the integer interval entered.
Step 7 Select the Poller field and pull down the chooser list to one of the poller options.
The default is ;0. If you use the ;0 default, the first poller starts working on that machine.
Step 8 Select the Enterprise field and select one of the enterprise MIB objects from the chooser list.
For example, if you are using the sample table, pull down to cisco.
Step 9 Select the Group field and pull down the chooser list to one of the MIB groups. Select a MIB object.
Step 10 Select the Object field and pull down the chooser list to select one of the MIB objects you want to include in this poll group. For example, if you are using a sample table, pull down to ifInOctets.
The Object field lists all the MIB objects that are available. To select multiple objects for the object poll group, click on Apply and then select another object.
The objects selected apply to the last table name entered. If you want an object to apply to a different table name, select the table first.
Step 11 If you have fewer than 60 devices in your device group (the domain you are currently working in), continue to the next step.
If you have more than 60 devices in your device group, select the Device Group field and open the chooser list to select one of the listed device group options you want to include in this poll.
By selecting a specific device group, your Device field list becomes more defined. For example, if you choose the group of devices from X to Z, your device list will include only those devices beginning with the letters X, Y, and Z.
Step 12 Select the Device field and use the chooser list to select one of the devices you want to include in this poll.
This list contains all devices in alphabetical order that are present in the CiscoWorks database. To select multiple devices for this poll group, click on Apply and select another device.
Step 13 After you select the devices from the Device field, select the Instance field and open the chooser list to select an instance associated with the device.
If you are using tables, for example if_tables, select the instance from the chooser list.
For SunNet Manager only:
If you are not using if_tables, you must know the format of Sun MIB object tables found in the schema file to enter the instance values. If you do not know the format, skip the Instance field. This causes the poll group to poll all instances. Only objects in a table need or can have an instance. You can skip this field if your object does not belong to an object table.
Step 14 When you click on Apply, all data is sent to the database. The scroller windows display what appears in the database.
Step 15 Select Options>Activate Changes to send the changes to the polling daemon.
If you have chosen a poll rate, the Activate Changes command informs the polling daemon (nmpolld) to start polling this poll table.
 | Caution Activate Changes occurs automatically when you exit Device Polling using the File>Exit command. |
This completes the process of creating a new polling table.
An instance defines which row to go to in a particular MIB table. Use the default instance selection in Device Polling to poll all objects on all devices. If you want to select specific devices and MIB objects to limit your poll group, add an instance to a device and object pair.
If you want to add an instance to a device and object pair, add the instance in the Device Polling window.
To add an instance to a device and object pair, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Device Polling.
Step 2 Specify the device and object pair. To select a device and object pair, select the device name and then the object in the scroll windows.
Step 3 For if_tables, select an instance using the chooser list.
For all other keys, enter the key manually. If you do not know your key, contact your network administrator.
Step 4 Click on Apply.
The new table with the instance added is now available for polling. The device will now be polled for this specific object and specific instance. An I marks the device and object pair you selected for polling. An asterisk (*) marks the polled instance in the instance list.
Step 5 Select Options>Activate Changes to send the changes to the polling daemon.
Step 6 Repeat Steps 1 through 4 for each instance you want to add to a device and object pair.
Device polling has the following limitations:
To delete an object, delete the poll group and start again.
To modify an existing poll group table effectively, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Device Polling.
Step 2 From the Poll Group chooser list, select the poll group name.
When an existing table name is selected, the configuration appears in the window. If you selected the table to change a data element, such as the polling interval, perform the necessary changes.
Step 3 Save your changes to the database by clicking on Apply.
Step 4 Select Options>Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon (nmpolld) of changes.
If you do not perform this step, any changes you have made are unknown to nmpolld and cannot be polled for.
Step 5 To switch from one table to another in the Device Polling window, pull down the Poll Group selection and select a new table.
After you finish with a poll group and want to remove it from the database, delete it from the Device Polling window. Note that you must change the poll rate to "no polling" before deleting a poll group.
To delete a poll group, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Device Polling.
Step 2 When the Poller window appears, click on the button next to the Poll Group field.
Step 3 When the Poll Group window appears, select a polling group name from the list of poll groups.
Step 4 Click on OK.
Step 5 Select Options>Destroy Table.
A confirmation window appears asking you to confirm the deletion.
Step 6 Click on OK.
Step 7 Select Options>Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon (nmpolld) of changes.
The Poll Group is now deleted from the Polling Summary table and the database.
To delete a particular device from a poll group, delete the device from the Device Polling window.
To delete a device from a poll group, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Device Polling.
Step 2 When the Poller window appears, click on the button next to the Poll Group field.
Step 3 When the Poll Group window appears, select a polling group name from the list of poll groups.
Step 4 Click on OK.
Step 5 Select a device from the Devices list in the Poller window.
Step 6 Change the Poll Rate to "no polling."
Step 7 Click on Delete.
The new table with the device removed is now available for polling.
Step 8 Select Options>Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon (nmpolld) of changes.
The device is now deleted from the poll group.
If you want to delete a particular instance from a poll group, delete the instance from the Device Polling window.
To delete an instance association from a poll group:
Step 1 Select CW - Device Polling.
Step 2 When the Poller window appears, select a device and object pair by selecting a device name and then selecting the associated object from the Devices and Objects scrolling lists.
Step 3 Click on the button next to the Instance field.
Step 4 When the Instance window appears, select the instance data you want to delete from the list of instances.
You can only delete instances with asterisks (*) next to their names. You can only delete one instance association at a time.
Step 5 Click on OK.
Step 6 Click on Delete.
The new table with the instance removed is now available for polling.
Step 7 Select Options>Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon (nmpolld) of changes.
The instance is now deleted from the poll group.
Step 8 Repeat Steps 2 through 7 for each instance you want to delete from the device polling group.
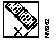
The Polling Summary application enables you to perform the following tasks:
These tasks are described in the following sections.
If you run polls using the sample poll groups supplied with CiscoWorks in Device Polling, the easiest way to view the poll data is to run the preconfigured reports supplied with CiscoWorks in Polling Summary. These reports sort the data by various categories and are available from the Polling Summary Tools menu. You have to write your own Sybase SQL or Easy SQR reports if you want to view sorted data returned by custom poll groups. You can always view the raw data returned by any poll by exporting polling intervals to an ASCII file.
Some of the automated reports do not require you to run a poll to return data to you about the network. Reports, such as the Device Inventory Report, use network data already in the Sybase database, including what devices are part of the network and information on those devices. Refer to "Viewing Polling Data Using the Polling Summary Tools" later in this chapter for more information on the automated reports and which poll groups' data they use.
You can also view poll interval data in a graphical format if you are using SunNet Manager as your network management platform. Refer to "Viewing Polling Data Using the SunNet Manager Browser or Grapher," later in this chapter for more information.
The Polling Summary window is the interface used to stop, start, browse and export poll data, and run reports.
Figure 3-4 illustrates the Polling Summary window. Table 3-2 describes its components.
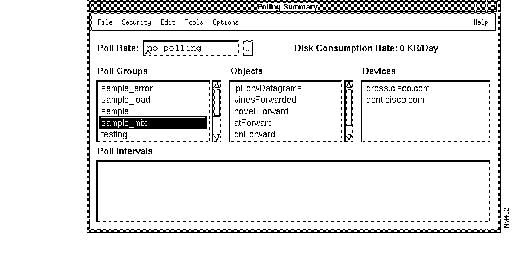
After you set your polling criteria in the Device Polling window, you can access the Polling Summary application to turn polling off, start additional polling tables, view poll data, and so on.
To start or stop polling your poll group table, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Polling Summary.
On SNM, select Tools>CW - Polling Summary.
On HP OpenView, select Monitor>CW - Polling Summary.
The Polling Summary window appears. (See Figure 3-4.)
Step 2 From the Poll Groups scroll window, select a group you want to poll.
Step 3 If the table is not being polled currently, select a polling frequency. Then select Options>Activate Changes.
While the polling daemon (nmpolld) starts polling your devices in the background based on your entries in the Device Polling window, you can continue to work with the Device Polling window.
If your table is currently being polled, continue to the next step.
Step 4 After you collect the necessary data, stop the polling activity on this group from the poll rate chooser list by selecting No Polling.
Step 5 To signal the polling daemon to stop polling, select Options>Activate Changes to notify the polling daemon5 (nmpolld) of changes or exit the Polling Summary window.
After you complete your polling activity, you can examine your data in text, graph, or report form. Data is retrieved from the polled information segments obtained in polling operations. To view polling data, use the SNM Results Browser and Grapher on SunNet Manager or the grapher on HP OpenView. To view your polling data on the HP grapher, you need to export the data to a spreadsheet and then import it into the grapher.
You can also run reports using the Polling Summary Tools menu. For more information on the automated reports that are shipped with Polling Summary, refer to "Viewing Polling Data Using the Polling Summary Tools," later in this section.
With the SunNet Manager (SNM) Results Browser and Grapher features, you can review your data report information. You can browse text information using the Results Browser. From the Results Browser, you can send data to the SNM Grapher.
For example, you can compare input broadcast packets against the total number of input packets to identify broadcast storms, as well as review and analyze interface performance or traffic patterns by observing in and out packets over specific periods.
Refer to your SNM documentation for more information on using the Results Browser and Grapher features.
To view your polling data using the browser or grapher, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Polling Summary.
Step 2 Select a poll group.
Selecting a poll group updates the devices and interfaces in the Devices scroll window that will be available and, in turn, data segments that can be viewed or graphed. A graph can consist of multiple segment columns and multiple devices.
For example, CiscoWorks ships several sample tables with the Device Polling application. Click on a sample table.
Step 3 To modify the poll rate interval, select the poll rate you want from the chooser list, or enter the poll rate in the field and press Return.
Step 4 To view the data collected in your poll, from the Polling Summary window select the data report in the Polling Intervals scroller.
Step 5 Select Options>Browse Data.
The SNM Results Browser window appears with the data report (also known as the data stream in SNM) listed in the scroller. For more information on the Results Browser, refer to the SunNet Manager Reference Guide.
Step 6 To view the text of the data report, click on the report name.
The data report text appears in the lower portion of the results browser.
Step 7 To view the data report in a graph format, click on the report name and from the popup menu, select Graph. Continue to pull the Graph menu to the right and pull down to the specific graphing options you want.
For this exercise, select All Attributes. An SNM Grapher window appears with the data report name in the scroller. Seconds later, a graph appears.
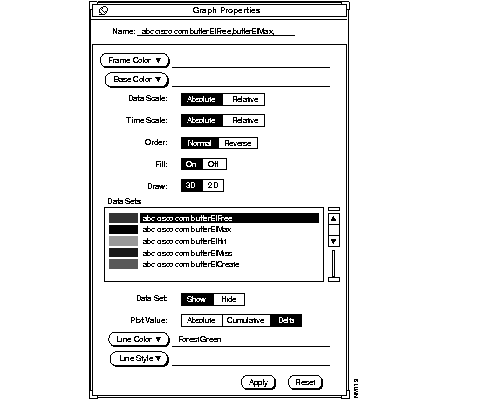
Step 8 To change the properties on your graph, return to the Results Grapher window, select the report name, and click on Properties. (See Figure 3-5.)
For more detailed information on customizing the SNM Graph Properties window, refer to your SunNet Manager Reference Guide.
The Device Polling application allows you to probe and extract data about the condition of devices on your network. In general, device polling stores data in polling tables. You can then graph the data with your platform grapher.
To view polling data using your platform grapher, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Export your polling data using Polling Summary.
For information on exporting polling data, refer to the section "Exporting Polling Data to ASCII Files," later in this section.
Step 2 Refer to your HP OpenView documentation on how to import ASCII data into the SnmpCollect data collector.
Step 3 With your network map open, select Monitor>CW - MIB Values from the menu.
Step 4 Select Graph Collected Data>SNMP>All.
During polling, CiscoWorks stores any poll data in segments referred to as polling intervals. If you use polling extensively, you may need to delete polling data as a way to maintain disk space on your workstation. Instructions on how to delete selected polling intervals or entire sets of polling data follow.
The following caution applies when using CiscoWorks on any platform.
In order to delete polling data (or intervals), perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Polling Summary.
Step 2 From the Polling Summary window, select a poll group.
Selecting a poll group updates the objects, devices, and polling intervals that are available with the selected poll group.
Step 3 Select a poll interval to delete by clicking on the data segment in the Polling Intervals scroller.
If you do not select a poll interval, you will receive an error message when you attempt to delete the poll interval.
Step 4 Select Edit>Delete Poll Interval.
A confirmation box appears asking you to confirm the deletion.
Step 5 To confirm the deletion of the selected poll interval, click on OK. To cancel the deletion, click on Cancel.
If you deleted the poll interval, the Polling Summary window no longer displays the data segment and removes the information from the database.
In order to delete all polling data (or intervals) associated with a poll group, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Polling Summary.
Step 2 From the Polling Summary window, select a poll group.
Selecting a poll group updates the objects, devices, and polling intervals that are available with the selected poll group.
Step 3 Select Edit>Delete All Data.
A confirmation box appears asking you to confirm the deletion.
Step 4 To confirm the deletion of the selected poll interval, click on OK. To cancel the deletion, click on Cancel.
If you deleted all polling data, the Polling Summary window no longer displays the data segment and removes the information from the database.
The Tools menu in the Polling Summary application contains several utilities including an export tool and automated SQL reports. The reports.nmstool file in the $NMSROOT/lib directory contains the details of each report.
If you have an overabundance of polling data, use the $NMSROOT/etc/nmpollsummarize utility. The nmpollsummarize utility creates a summary table that summarizes data in a polling interval into averages. A poll table using a 10-second poll rate can be summarized into hourly records for a more compact file that saves storage space. For more information on nmpollsummarize, refer to the UNIX manual page.
 | Caution Do not edit the reports.nmstool file. If you need to alter this file, copy it first and edit your custom file. |
These automated reports help you display a variety of information including:
If you want to display polling data in some other format, such as a spreadsheet, the Polling Summary application offers an option that allows you to export polling data into an ASCII flat file. You can then import the ASCII file into other applications, such as a spreadsheet application, that displays your data in a more tabular format.
To export polling data to an ASCII file, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select CW - Polling Summary.
Step 2 From the Polling Summary window, select a poll group.
Selecting a poll group updates the objects, devices, and polling intervals that are available with the selected poll group.
Step 3 Select a poll interval to export by clicking on the data segment in the Polling Intervals scroller.
If you do not select a poll interval, you will receive an error message when you attempt to export the poll interval data.
Step 4 Select Tools>Export Data.
The Export Data window appears. (See Figure 3-6.)
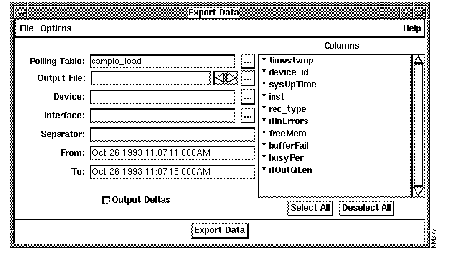
Step 5 To toggle between exporting polling or summary tables, select Options>Export Poll Table or Options>Export Summary Table.
The Export Data window appears again with the appropriate field change.
Step 6 To toggle between exporting data to a UNIX file, select Options>To UNIX File.
Step 7 Enter data into the fields required.
For information on the data fields, refer to Table 3-3.
Step 8 Select the type of output you want to export, absolute or deltas, by clicking on the Output Deltas toggle.
Step 9 To deselect columns that you do not want to be included in the output file, select an entry in the Columns scroll window.
To deselect all columns, click on Deselect All.
Step 10 To return selected columns to the output file, select the column names or to return all columns, click on Select All.
Step 11 Click on Export Data to export the data to a file.
The data from the Sybase database tables is exported to the file you designated. You can use this file to import information into other applications, for example, a spreadsheet application.
Table 3-3 describes the components of the Export Data window.
| Component | Subcomponent | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File | Print
Exit | Opens the screen capture facility for your system.
Opens the current window. |
| Options | Toggle Buttons:
Export Poll Table Export Summary Table To UNIX File To Sybase File | Allows you to select which export method to use:
The summary tables are created using the nmpollsummarize command. |
| Help | Displays help on the Export Data Window. | |
| Polling Table | Polling or Summary | Contains the polling or summary table name that contains the data. Allows you to change to a poll or summary table from the Chooser List. |
| Output File | Chooser List | Allows you to name the file that will contain the exported data. |
| Device | Chooser List | Restricts output to a specific device in the poll group. Enter the name of the device without the domain name or click on the chooser list. |
| Interface | Chooser List | Restricts output to a specific interface of a device. To use this field you must also name a device in the Device field. Enter the interface index (ifIndex) value of the interface or click on the chooser list. |
| Separator | Allows you to enter any character to replace the default Tab character that separates fields. | |
| From | Restricts output to be later than a specified date/time. Enter the date and time in the following format: Oct 26 1993 11:07 AM | |
| To | Restricts output to be earlier than a specified date/time. Enter the date and time in the following format: Oct 26 1993 11:07 AM | |
| Output Deltas toggle button | Causes counter and timetick values to be exported as delta values rather than absolute values. | |
| Columns list | Displays the columns in the poll table named in the Table field. An asterisk (*) to the left of the column name indicates that this column will be included in the output file. Clicking on an entry in the Columns list box toggles asterisk on and off. | |
| Select All | Returns all asterisks in the Columns list to on. | |
| Deselect All | Turns all asterisks in the Columns list off. Turning the asterisks off prevents the column from being included in the output file. | |
| Export Data | Turns all asterisks in the Columns list back on. Turning the asterisks off prevents the column from being included in the output file. |
When you use the Real-Time Graphs application to manage the performance of your network, you can observe real-time information via a two- or three-dimensional graph (depending on your platform grapher). CiscoWorks enables you to graph data about router health, interface, and traffic information.
Figure 3-7 illustrates the Real-Time Graphs window.
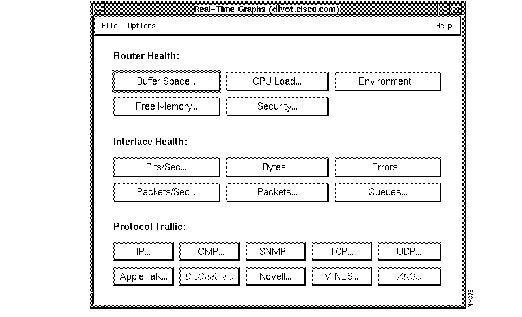
Table 3-4 describes the components of the Real-Time Graphs window.
| Component | Subcomponent | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File | Print
Exit | Prints a snapshot of the window.
Exits the current window. |
| Options | Set Polling Frequency | Changes polling rate. Frequency of analysis performance is represented in seconds. Can be set using slider or entering in the polling interval field. Default = 2 seconds. |
| Help | On Version
On Real-Time Graphs | Displays the CiscoWorks application version information.
Displays a manual page on the current window. |
| Router Health
Interface Health
Protocol Traffic1 | Refer to Table 3-5 for detailed descriptions of the router health buttons.
Refer to Table 3-6 for detailed descriptions of the interface health buttons. Refer to Table 3-7 for detailed descriptions of the protocol traffic buttons. |
The Real-Time Graphs application observes the behavior of devices suspected of being in degraded mode or introducing erratic behavior in traffic patterns, error status indications, or statistics.
To create a graph with real-time device data, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Click on the device.
Step 2 Select Real-Time Graphs.
On SunNet Manager, select Tools>CW - Real-Time Graphs.
On HP OpenView, select Monitor>CW - Real-Time Graphs.
The Real-Time Graphs window appears. (See Figure 3-7.) As you can see from the figure, the device named divot does not have the DECnet IV or XNS protocols activated.
If you receive an SNMP error message, check the device's SNMP configuration under the Options menu. HP OpenView uses public as the default for the set community string. If you have a device or devices that use other community strings, you need to configure them appropriately using Options>SNMP Configuration.
On SNM, you can customize your current graph. For instructions, refer to your SunNet Manager User's Guide. The Grapher is an SNM feature and is not covered in this publication. On HP OpenView you can customize your graph using their platform grapher. Refer to your NMS documentation for more information.
Step 3 To gather data on interface health, click on the appropriate button. Table 3-6 describes the buttons and MIB object descriptions that are polled when you press the button.
Step 4 To gather data on router health, click on one of the button choices for data.
Table 3-5 describes the buttons and MIB object descriptions that are polled when you press the button. Refer to the Cisco MIB User Quick Reference for a description of MIB objects. MIB information is also available on CCO. You can access the following path: CCO>SW Image Library>MIBs>Support Lists. Then pick the device for which you want to view MIB information.
Step 5 To gather data on protocols, click on the appropriate button. Table 3-7 describes the buttons and MIB object descriptions that are polled when you press the button.
The real-time graphs you create will use the polling frequency that is set in the Polling Frequency window. You can enter a new polling frequency selecting Options>Set Polling Frequency, entering the new frequency in the window, and clicking on OK.
Step 6 After you click on a button, a grapher window appears.
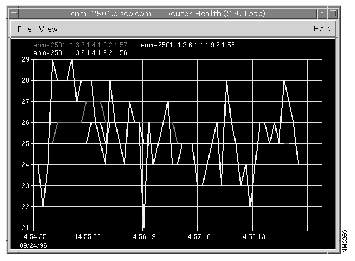
Real-time graphs on HP OpenView look like the one shown in Figure 3-8.
If you are using SNM, a Results Grapher window also appears (Figure 3-9), but is hidden behind the grapher window. The devices and objects you selected appear in the scroller window.
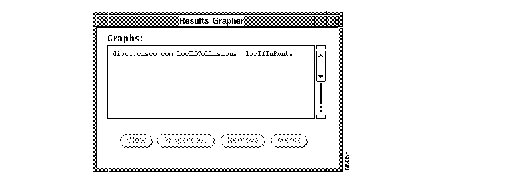
If you want to change the appearance of your real-time graph or delete the graph, use the SNM Results Grapher window. The following tasks can be performed using the SNM Results Grapher:
For more information on the SNM grapher, refer to the SunNet Manager User's Guide.
Table 3-5, Table 3-6, and Table 3-7 describe the command buttons in the Real-Time Graphs window. (See Figure 3-7.)

You can use the Show Commands application to monitor system status, IP information, and traffic information. This information helps you to determine how to change and improve the efficiency of your network environment.
For more detailed descriptions of all show commands, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication. Refer to Volume 1 for all but protocol-specific show traffic commands and show commands.
For detailed information on the Show Command window components, refer to "Using Show Commands to View Router Data," in the "Fault Management" chapter.
To use the Show Commands application, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Click on a network device.
Step 2 Select Show Commands.
On SNM, select Tools>CW - Show Commands.
On HP OpenView, select Diagnose>CW - Show Commands.
Figure 3-10 illustrates the Show Commands window.
Step 3 To request specific system status, IP information, or traffic information, click on the Show Command button you want.
Each show window is described in detail in the section "Using Show Commands to View Router Data," in the "Fault Management" chapter.
Step 4 To exit this window, select File>Exit.
|
|