|
|

This chapter shows you how to configure ISDN-capable access servers, such as a Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server, to accept ISDN and analog calls so that remote clients can access network resources.
You can configure a Cisco AS5200 to accept calls from routers such as the Cisco 753 and Cisco 1004 by performing the steps outlined in the following sections:
A comprehensive configuration example is provided at the end of this chapter. Commands that are not specific to remote dialin and dialout access for the listed devices are described in previous chapters. Figure 6-1 shows a typical Cisco AS5200 dialin scenario.
If you are configuring a Cisco 753 or Cisco 1004 router to dial in to a Cisco AS5200 access server and need configuration information, you can receive a fax-back document from Cisco's Technical Assistance Center at 800 553-2447 or 408 526-7209 or call directly into the fax-on-demand service at 415 596-4408.
The configuration information in this chapter builds on preceding configurations from previous chapters and assumes you understand group asynchronous interfaces, basic asynchronous modem configuration, and autoselect. Users dialing in must also be running one of the following applications:
For each of the following configuration examples, dialin users are assumed to belong to one subnet. In this way, all the remote clients appear to belong to one Ethernet segment from the Cisco AS5200's perspective.
This section includes the base configuration to enable IP clients to access network resources by dialing through the Cisco AS5200. Configure remote IP dialin before you enter any commands for IPX or AppleTalk, even if you are setting up an IPX- or AppleTalk-only network.
Enter the following Cisco AS5200 configuration sequentially, first entering the commands featured in the "Entering Configuration Mode" section. Enter your own addresses, host names, and passwords where appropriate.
This section assumes that you have already switched on your access server and typed no at the following system prompt:
Would you like to enter the initial dialog? [yes]: no
The following system prompt appeared:
Router>
To enter configuration mode at this point, issue the following commands:
Router>enableRouter#configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
At this point, you can change the name of the access server and assign an enable password to secure unauthenticated access to enable mode.
Router(config)#hostname AS5200AS5200(config)#enable password irongate
Proceed to the "Configuring Security" section.
To set up basic security using a local authentication database, enter the commands in the following list (substitute the usernames in this example with the appropriate usernames):
AS5200(config)#aaa new-modelAS5200(config)#aaa authentication login default localAS5200(config)#aaa authentication login console noneAS5200(config)#aaa authentication ppp default if-needed localAS5200(config)#username jojackso password <password>AS5200(config)#username wmays password <password>AS5200(config)#username bruth password <password>AS5200(config)#username hwilliam password <password>
For more information, refer to the "Configuring Access Service Security" chapter earlier in this guide.
At this point, proceed to the "Configuring the T1 Controllers" section.
To configure the T1 controllers, which accept and send incoming and outgoing calls through ISDN PRI interfaces, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enable the T0 controller.
controller T1 0
Step 2 Set the framing and line code type. The framing and line code you configure must match your telco's offering, which in most cases is esf and b8zs.
framing esf
linecode b8zs
Step 3 Configure one T1 line to serve as the primary or most stable clock source line. (The other T1 line is configured as the secondary clock source line, which you enter later in this example.)
clock source line primary
Most T1 lines provide stable clocking, so choosing the correct primary and secondary clock source is not a vital part of the configuration. However, do not configure the clock source as internal unless you are performing back-to-back advanced testing between two routers in a network simulated environment such as in a router lab.
Step 4 Specify how you want to configure all 24 channels. To configure all channels for ISDN, enter the following command.
pri-group timeslots 1-24
exit
If you are not running ISDN but want to configure a channelized T1 to accept voice calls, substitute the pri-group timeslots 1-24 command with the cas-group 1 timeslots 1-24 command on both T1 controllers. This command configures the E&M analog signal on each timeslot.
cas-group 1 timeslots 1-24
exit
Alternatively you can configure a channelized T1 that is not running ISDN with the channel-group 1 timeslots 1-24 command on both T1 controllers.
channel-group 1 timeslots 1-24
exit
Step 5 Set the facilities data link exchange standard for the CSU on the Cisco AS5200's T1 controllers by entering the fdl controller interface command.You must configure this command on both T1 controllers if you want to support the CSU functionality. However, you must use the same facilities data link exchange standard as your service provider.
fdl ansi
Step 6 Configure the T1 controller. This controller's configuration is identical to the one you entered on the T0 controller except that it is used as the secondary clock source line.
controller T1 1
framing esf
linecode b8zs
clock source line secondary
pri-group timeslots 1-24
fdl ansi
exit
At this point, proceed to the "Configuring the ISDN D-Channel Serial Interfaces" section.
When you configure the T1 controller, two corresponding D-channel serial interfaces are instantly created. Serial interface 0:23 is the D channel for the T0 controller, and serial interface 1:23 is the D channel for the T1 controller. You must configure each serial interface to receive incoming and send outgoing modem signaling.
To configure the ISDN D-channel serial interfaces, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Specify the D channel of the first primary rate interface (PRI).
interface Serial 0:23
Step 2 Configure all incoming voice calls to go to the modems.
isdn incoming-voice modem
Because some telcos charge more for ISDN data calls, you might want to configure the isdn incoming-voice data command to process ISDN calls as voice calls, which provides you with data service at a voice billing rate. However, incoming modem calls will not be passed to the modems with this command enabled.
Native ISDN calls are directed like a protocol.
Step 3 Combine these configurations under the umbrella of a dialer interface, which modularizes the configuration. The dialer interface serves as the parent interface that contains additional protocol characteristics.
dialer rotary-group 1
This command also creates one interface with one address, which is helpful for the hunt group provided by the phone company.
Step 4 Specify the D channel for the second PRI and give it the same channel configurations you set for the first PRI interface.
interface Serial 1:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer rotary-group 1
exit
At this point, proceed to the "Creating Interfaces for Asynchronous and ISDN Dialin Services" section.
This section describes how to configure the Cisco AS5200 interfaces that enable dialin clients to make remote asynchronous and ISDN connections to the Cisco AS5200 access server.
To configure remote services, you must configure three interrelated interfaces on the Cisco AS5200. The loopback interface essentially makes the network appear as if the dialin users exist on one Ethernet segment. The loopback interface has the following four types of neighboring interfaces used for dialin operations: ISDN interface, dialer interface, group asynchronous interface, and asynchronous interface. Figure 6-2 shows an internal view of the components used to process incoming ISDN and analog calls on a Cisco AS5200.
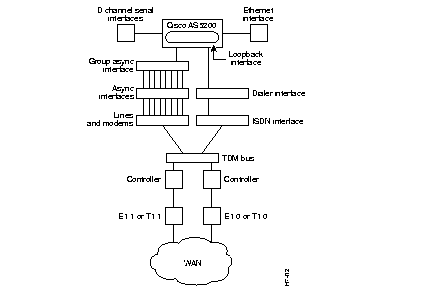
All dialin users exist on one dialin subnet. Remote asynchronous users dial in through the group asynchronous interface to the Cisco AS5200. Remote ISDN users dial in through the ISDN dialer interface to the Cisco AS5200. Figure 6-3 shows an external view of how remote users dial in to the Cisco AS5200.
The loopback 0 interface is a virtual IP interface carrying all the dialin users, and it exists only in the access server. You assign an IP network number to the loopback interface, then let each asynchronous interface borrow this network number.
To configure the loopback and Ethernet interface, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Create interface loopback 0, which is the logical IP subnet containing all the dialin users' addresses.
interface loopback 0
Step 2 Give the loopback interface an IP addresses using an existing subnet reserved for asynchronous dialin users (such as subnet 172.16.254.254).
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0
exit
Step 3 Configure Ethernet interface 0 and assign it an IP address from the subnet address on the network to which you are enabling dialin access.
interface Ethernet 0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
exit
At this point, proceed to the "Creating the Group Asynchronous Interface" section.
As described in the "Configuring Asynchronous Ports" section in the earlier chapter "Working with your Access Server for the First Time," a group asynchronous interface is the parent interface that applies specified protocol characteristics to specified asynchronous ports.
To create a group asynchronous interface, enter the following commands, a process which is described in the earlier chapter "Enabling Dialin to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk Networks."
AS5200(config)#interface Group-Async 1AS5200(config-if)#ip unnumbered Loopback 0AS5200(config-if)#ip tcp header-compression passiveAS5200(config-if)#encapsulation pppAS5200(config-if)#async mode interactiveAS5200(config-if)#ppp authentication chap papAS5200(config-if)#group-range 1 48Building configuration... AS5200(config-if)#
This section describes how to create an IP address pool that exists inside the access server. The name of the pool is default and the address range is 172.16.254.1 to 172.16.254.48.
Step 1 Assign dialin clients an IP address from the pool named default (the pool is defined later) by assigning it to the group asynchronous interface:
peer default ip address pool default
Step 2 Assign a pool of IP addresses (in this example, from 172.16.254.1 to 172.16.254.48), all of which are on the same IP subnet as loopback interface 0.
ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48
This section describes how to specify packets that keep an asynchronous link in the "up" state.
Step 1 Specify the packets that keep the asynchronous links up.
dialer-group 1
The dialer-group command derives its definition from to the dialer list command, which is configured in the "Configuring the ISDN Dialer Interface" section.
Step 2 Define the amount of time (in seconds) that a line is idle before it hangs up. The default is 5 minutes. This command derives its definition from to the dialer list command.
dialer idle-timeout 3600
exit
At this point, proceed to the "Configuring the ISDN Dialer Interface" section.
The ISDN dialer interface is the parent interface that holds the central protocol characteristics for the two ISDN D-channels that are part of dialer rotary-group 1. The previous section, "Configuring the ISDN D-Channel Serial Interfaces," described how to configure the ISDN D-channels on serial interfaces 0:23 and 1:23.
To configure the ISDN dialer interface, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enable both D channels to access their core protocol intelligence from interface dialer 1.
interface Dialer 1
Step 2 Associate all ISDN users with the subnet configured on loopback interface 0.
ip unnumbered Loopback 0
Step 3 Configure PPP on the dialer interface.
encapsulation ppp
Step 4 Assign a common IP address pool. PPP packets coming through an asynchronous line and an ISDN line share this common IP pool. The default address pool is specified in the "Creating the Group Asynchronous Interface" section.
peer default ip address pool default
Step 5 Enable the router to build dynamic mapping of IP addresses to the ISDN B channels.
dialer in-band
Step 6 Define which packets reset the idle timer. The idle timer default is 5 minutes.
dialer-group 1
Step 7 Define the number of seconds that a line is idle before it hangs up. The default is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
dialer idle-timeout 3600
The dialer list command defines the interesting traffic, which is the traffic that resets the idle-timeout or triggers a dial if the line is down and you have a number to send.
Step 8 Enable PPP multilink, which uses multiple bundled B channels from the remote user who is likely to be running BRI with two available B channels.
ppp multilink
Step 9 Enable CHAP and PAP authentication on dialer interface 1.
ppp authentication chap pap
exit
Step 10 Specify which packets reset the idle timer. In this case, any IP packet resets the timer. Ping packets cannot reset the idle timer with this configuration.
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Continue on to the "Configuring Modem Lines" section.
To configure the modem lines, issue the following series of commands, which were described in depth in the "Configuring Modems" chapter earlier in this guide:
AS5200(config)#line 1 48AS5200(config-line)#modem InOutAS5200(config-line)#modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdmsAS5200(config-line)#transport input allAS5200(config-line)#stopbits 1AS5200(config-line)#speed 57600AS5200(config-line)#flowcontrol hardwareAS5200(config-line)#autoselect during-loginAS5200(config-line)#autoselect pppAS5200(config-line)#login local
At this point, proceed to the "Defining a Routing Protocol and Domain Name" section.
To complete the configuration, you must define a routing protocol and a domain name. You also can specify a domain name server to resolve host names and IP addresses. To do so, issue the following commands, which are described in detail in the chapter "Enabling Dialin to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk Networks."
AS5200(config)#router eigrp 202AS5200(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0as5200(config-router)#exitAS5200(config)#ip domain-name cisco.comAS5200(config)#ip name-server 172.16.99.99
At this point, proceed to the "Enabling DNS and NBNS Services for PPP Users" section.
Dialin clients using PPP applications such as CiscoRemote and Windows 95 need domain name service (DNS) and NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) address information as described in RFC 1877. Enter the following parameters to enable Telnet users to gather this information transparently as part of the PPP negotiation.
Step 1 Specify the list of available DNS servers, as shown in the following example.
async-bootp dns-server 172.16.10.100 172.16.39.67
Step 2 Specify the list of available NBNS servers, as shown in the following example.
async-bootp nbns-server 172.16.200.200 172.16.201.200
Step 3 Save the running configuration to startup configuration.
copy running-config startup-config
This completes the IP configuration.
Continue to the "Configuring the Cisco AS5200 to Accept Dialin Calls from the Cisco 753 and Cisco 1004" section if you want to enable ISDN and analog calls to enter the Cisco AS5200 from a Cisco 753 or Cisco 1004 router.
Perform the following steps to enable a remote ISDN user to dial in to a Cisco AS5200 access server through a Cisco 753 or Cisco 1004 on an IP network as shown in Figure 6-4.

The host names, user names, IP addresses, and passwords for the Cisco 753 and Cisco 1004 routers entered in this section match the device addressing schemes documented in the Configuring the Cisco 753 and Cisco 1004 to Dial in to a Cisco AS5200 Access Server publication.
This section describes the relationships between devices.
Step 1 Create a dialer map from the Cisco AS5200 to the Cisco 753-A router shown in Figure 6-4. The dialer map name (for example, 753-A) must match the device name entered in the username password command, which is configured in Step 3.
interface Dialer 1
dialer map ip 172.16.254.49 name 753-A
Dialer maps are needed even to receive calls. If you do not want to place calls, do not enter a phone number at the end of the dialer map.
Depending on your ISDN provider's setup offering, you may need to set the line speed to 56 kbps for long distance ISDN calls. In this case, you enter this replacement command:
dialer map ip 172.16.254.49 name 753-A speed 56
Likewise you enter the set speed 56 command under the user profile on the Cisco 753 router.
Step 2 If you want to accept dialin calls from a Cisco 1004, as shown in Figure 6-4, you must configure a dialer map to the Cisco 1004.
dialer map ip 172.16.254.50 name 1004
exit
As mentioned in Step 1, you may need to set the line speed to 56 kbps for long distance ISDN calls depending on your service provider's setup offering.
Step 3 In global configuration mode, configure a static route from the Cisco AS5200 to the Cisco 753-A as shown in Figure 6-4.
username 753-A password letmein
ip route 172.16.253.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.254.49
To reach network 172.16.253.1 at netmask 255.255.255.0, the Cisco AS5200 connects to the IP address 172.16.254.49, which is the Cisco AS5200's profile address configured on the Cisco 753-A router.
 | Caution The same password (for example, letmein) is entered in three places for successful authentication. It is entered at the set ppp secret client command on the Cisco 753-A, at the set ppp secret host command on the Cisco 753-A, and with the username global configuration command on the Cisco AS5200. This password is case sensitive on each device. |
Step 4 Configure a static route from the Cisco AS5200 to the Cisco 1004.
username 1004 password openup
ip route 172.16.252.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.253.50
Step 5 Save the new configuration to NVRAM, so that it becomes the next startup configuration at the next power up.
copy running-config startup-config
To enable IPX clients to access network resources by dialing through the Cisco AS5200 over ISDN, perform the following steps. Enter your own addresses where appropriate.
Step 1 Enter the following commands. (This process was described in the earlier chapter, "Enabling Dialin to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk Networks.")
ipx routing
interface loopback 0
ipx network FEFEFE
exit
interface ethernet 0
ipx network 123ABCD encapsulation SAP
exit
interface group-Async 1
group-range 1 48
ipx ppp-client Loopback 0
exit
Step 2 Create a dialer interface. This is the parent interface for all of the ISDN interfaces, which was set using the dialer rotary-group 1 command in the IP configuration.
interface dialer 1
ipx unnumbered loopback 0
Step 3 Create a dialer map for the single IPX network address that contains all the dialin users (for example, FEFEFE). The map for each IPX address differs and is activated by each dialin user's login sessions.
dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.1234 name jordan
dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.4567 name rodman
dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.89AB name kemp
exit
For IP configurations, dialer mapping is automatically constructed when the access server receives a user's name and address. However, when you use IPX configuration, you must statically configure each user name's IPX address.
Step 4 Enable IPX packets to reset the idle timer.
dialer-list 1 protocol ipx permit
Step 5 Save the running configuration to NVRAM, so that it becomes the next startup configuration at the next power up.
copy running-config startup-config
This completes the configuration for IPX.
To enable dialin clients running PPP to access network resources by dialing through the Cisco AS5200 over ISDN, perform the following steps. Enter your own addresses where appropriate.
Step 1 Enable AppleTalk routing and set the AppleTalk zone ATCP on network 2 (substitute your own network number and zone name):
configure terminal
appletalk routing
appletalk virtual-net 2 ATCP Zone
All users that dial in to the system belong to the AppleTalk network 2 in the AppleTalk zone ATCP Zone. All the dialin users look as though they are on a single network. Links do not have their own network numbers. This applies to configurations using PPP instead of ARA encapsulation.
Step 2 Set the AppleTalk cable range and the AppleTalk zone on the Ethernet interface:
appletalk cable-range 1-1 1.120
interface ethernet 0
appletalk zone Ethernet
Step 3 Enable AppleTalk over PPP:
appletalk client-mode
Ctrl-z
Step 4 Save the running configuration to startup configuration to NVRAM, so that it becomes the startup configuration the next time you start up the access server.
copy running-config startup-config
This completes configuration for AppleTalk operation.
Refer to the chapter "Enabling Dialin to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk Networks" for more information.
This section includes a complete start up configuration for the Cisco AS5200. This configuration includes a comprehensive setup for dialing in to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk networks.
The following configuration establishes basic security using a local authentication database:
aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authentication login console none aaa authentication ppp default if-needed local username jojackso password username wmays password username bruth password username hwilliam password !
The following global configuration command sets the ISDN switch type:
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
The following commands configure the appropriate interfaces for IP dialin:
controller T1 0
framing esf
linecode b8zs
clock source line primary
pri-group timeslots 1-24
fdl ansi
!
controller T1 1
framing esf
linecode b8zs
clock source line secondary
pri-group timeslots 1-24
fdl ansi
!
interface Serial0:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer rotary-group 1
!
interface Serial1:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer rotary-group 1
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Group-Async1
ip unnumbered Loopback0
ip tcp header-compression passive
encapsulation ppp
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool default
dialer-group 1
dialer idle-timeout 3600
ppp authentication chap pap default
group-range 1 48
!
interface Dialer1
ip unnumbered Loopback0
encapsulation ppp
peer default ip address pool default
ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48
dialer in-band
dialer-group 1
dialer idle-timeout 3600
ppp multilink
ppp authentication chap pap default
The following example configures modem lines 1 to 48:
line 1 48 autoselect during-login autoselect ppp modem InOut modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdms transport input all stopbits 1 speed 57600 flowcontrol hardware login local
The following commands configure enhanced IGRP:
router eigrp 202 network 172.16.0.0
The following commands configure a range of IP addresses in an IP address pool, a domain name, and name servers:
ip domain-name cisco.com ip name-server 172.16.99.99 ! async-bootp dns-server 172.16.10.100 172.16.39.67 async-bootp nbns-server 172.16.200.200 172.16.201.200
The following commands enable IPX dialin:
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit ipx routing 0060.3ef1.6f74 interface Loopback0 ipx network FEFEFE interface Ethernet 0 ipx network 123ABCD encapsulation SAP interface Group-Async1 group-range 1 48 ipx ppp-client Loopback0 interface Dialer1 ipx unnumbered loopback 0 dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.1234 name stock dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.4567 name john dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.89AB name cisco dialer-list 1 protocol ipx permit
The following commands enable users running PPP applications to dial in to an AppleTalk network:
appletalk routingappletalk virtual-net 2 ATCP Zoneappletalk cable-range 1-1 1.120appletalk zone Ethernetappletalk client-mode
This example does not describe how to configure ARA dialin access. To configure a Cisco AS5200 access server to support ARA dialin, refer to the "Enabling Macintosh Users to Dial In and Access AppleTalk Resources" section in the "Enabling Dialin to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk Networks" chapter.
|
|