|
|
The IPX supports a wide range of narrowband and broadband applications for both enterprise networks and service provider networks. In a multiservice environment, the IPX allows you to easily and cost-effectively launch new services and expand system capacity to meet growing demands. Similarly, as technologies evolve and WAN bandwidth increases, the IPX provides you with seamless growth and migration.
The IPX, IGX, and BPX Service Node share many of the same core capabilities and advanced networking features including the following:
The IPX lets you migrate from narrowband speed to broadband ATM on the same platform, providing unmatched WAN investment protection.
Figure 11-3 shows a front view of the IPX 8, Figure 11-4 shows a front view of the IPX 16, and Figure 11-5 shows a rear view of the IPX 32.
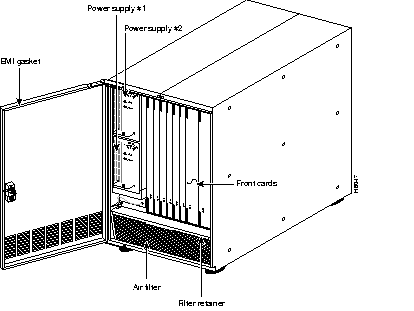
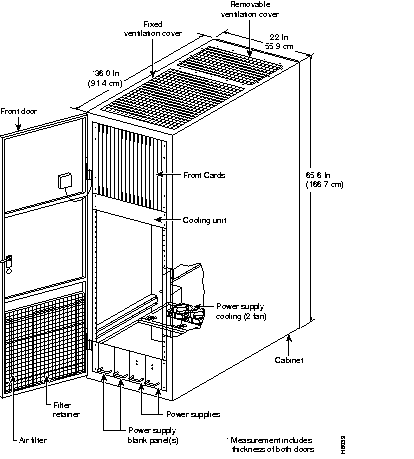
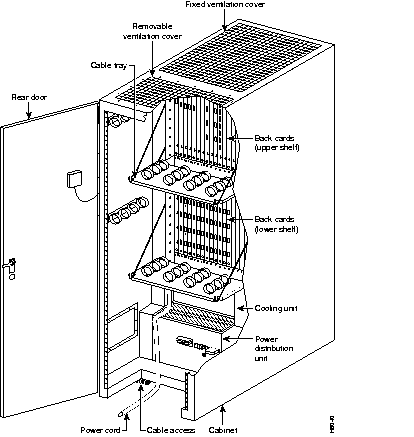
Hardware, firmware, and software are designed for maximum availability, even while routine maintenance functions are being performed on the IPX. Design features, common to all switching systems, include the following:
All switches use a midplane design with front cards performing processing functions and back cards providing interfacing and physical connectivity. This allows most system maintenance to be performed at the front cards, without disconnecting interface cables.
The IPX has a processor card group that controls communication between the cards in the node and the system bus. This card group also controls communication to other nodes in the network, and performs system timing, network control, and status reporting functions.
Processor Card Group
The processor card group consists of the nodal processor card, the system clock card, and the alarm relay card.
IPX systems provide efficient, high-quality voice connectivity to digital PABX through standard interfaces. The IPX uses both voice compression and silence suppression. The following voice services are supported by the IPX:
Circuit-switched data services include the following features:
Standards-compliant Frame Relay services from IPX systems achieve high-throughput, low delay, and low discard connectivity for LAN interconnect and legacy FRAD traffic. Port speed options range from 56 kbps to 2.048 Mbps. A port concentrator shelf (PCS) can be used in conjunction with the IPX for higher-density, lower-speed Frame Relay ports. (For more information on the PCS, see the "Port Concentrator Shelf" section later in this chapter). Standard interfaces include V.35, X.21, and channelized T1 and E1 for up to 31 logical ports per physical port.
Frame Relay services on the IPX include the following features:
The IPX trunk modules include the network trunk card, ATM internetworking trunk, and FastPAD trunk card.
The modular PCS hardware lets you tailor each IPX node for specific applications. Modules are available with V.24/V.28, V.11, or V.35 DCE and/or DTE interfaces. For applications requiring multiple types of interfaces, interface daughter boards can be mixed and matched on a per-interface basis. You can insert up to four PCS modules into a PCS shelf. Modules can be hot-swapped without affecting service to other ports on the shelf.
PCS ports offer the following features:
The common operating system across the Cisco product line provides common multiband/ATM network-wide support for advanced networking features, including the following:
Table 11-17 lists IPX specifications.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Platforms | IPX 8
8-slot unit, rack-mount or freestanding 32-Mbps cell switching bus CISPR B EMI certified IPX 16 16-slot unit, freestanding 32-Mbps cell switching bus CISPR B EMI certified IPX 32 32-slot unit, freestanding 32-Mbps cell switching bus CISPR B EMI certified |
| Power | Distributed 48V DC power conversion on modules 220/240 VAC AC-DC converter, 1: redundant |
| Control processors | Nodal processor card (NPC)
System clock card, internal or external clocking |
| Alarm modules | Alarm relay card (ARC)
8 normally open contacts 6 normally closed contacts |
| Voice service modules | Channelized data PAD (CDP)
32-, 24-, and 16-kbps ADPCM voice compression (ITU G.721, G.723, and G.726) Voice activity detection Integrated FAX/high-speed modem detection and optional echo cancellation Supports T1, E1, Japanese J1 trunk interfaces |
| Circuit switched data service modules | Synchronous data PAD (SDP)
Up to 4 channels, each up to 1.344 Mbps Supports EIA/TIA-232, V.35, EIA/TIA-422, EIA/TIA-449, and X.21/V.36 interfaces Repetitive pattern suppression to 128 kbps Low-speed data PAD (LDP) Up to 8 channels Supports EIA/TIA-232 interface Repetitive pattern suppression to 56 kbps |
| Frame Relay service modules | All Frame Relay service modules conform to the following:
CCITT 1.122 (ANSI T1/S1) T1.606--Services description of Frame Relay bear service T1.606 addendum--Congestion management T1.617 (Annex D)--Signaling specification for Frame Relay T1.618--Core aspects of Frame Relay Includes fully standard handling of DE, FECN, and BECN bits Frame Relay PAD (FRP) Up to four channels, totaling 2.048 Mbps Supports V.35, EIA/TIA-422, EIA/TIA-449, X.21/V.36, and T1/E1 (channelized and nonchannelized) interfaces Frame Relay PAD (FRP-31) Up to 31 logical ports Frame Relay PAD (FRP-6) Up to 6 logical ports Frame Relay PAD (FRP-2) T1/E1 (channelized and nonchannelized) interfaces X.21 I/F for port concentrator shelf |
| Network trunking modules | Network trunk card (NTC)
Trunk speeds from 128 kbps to 2.048 Mbps Supports T1/E1, Japanese Y trunk interfaces ATM internetworking trunk (AIT) ITU 53-byte cell standard Supports T3/E3 and HSSI interfaces Multipoint logical trunking over ATM service FastPAD trunk card (FTC) FastDLC, FrameClass, Frame Relay service compatible, protocol FastPAD trunk speeds from 9.6 kbps to 512 kbps Supports V.35, T1, E1, and X.21 interfaces |
This section describes the software available for the IPX.
The IPX requires system software for each node. Table 11-18 lists the system software product numbers. Optional software packages include the following:
Standard System Software
Optional System Software
The IPX is supported by Cisco's ATM network management tools.
StrataSphere network management provides the unique capabilities required for managing ATM WANs. StrataSphere distributes the logical management intelligence throughout the network through a set of building blocks, or modules. By distributing network management functionality, service management and process automation can be tightly integrated--simplifying management of even the most complex WANs and providing a comprehensive end-to-end management solution.
StrataSphere is an SNMP-based multiprotocol management environment designed specifically for ATM WANs. It provides integrated service management and process automation to simplify management of even the most complex networks. StrataSphere lets you easily monitor usage, provision connections, prototype services, optimize traffic flow, model network design, and track network statistics. See the "Cisco StrataSphere ATM Network Management" chapter for additional information about StrataSphere.
Table 11-18 lists the product numbers you can use to order IPX products, accessories, and spares. If a product number ends with an equal sign (=), the item can be ordered only as a spare. If a product number does not end with an equal sign, the item can be ordered as a spare or as a configurable part of a system order
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| IPX Cabinets | |
| IPX 8, 8-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (North America) | IPX8-NA |
| IPX 16, 16-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (North America) | IPX16-NA |
| IPX 32, 32-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (North America) | IPX32-NA |
| IPX 8/CEPT, 8-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (international) | IPX8-INTL |
| IPX 16/CEPT, 16-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (international) | IPX16-INTL |
| IPX 32/CEPT, 32-slot, NPC, SCC, local bus (international) | IPX32-INTL |
| IPX Local Buses | |
| SCC/NPC local (utility) bus for IPX 8/16 (2 slots wide) | IPX-550058= |
| SCC/NPC local (utility) buses for IPX 32 (1 slot wide) | IPX-550059= |
| Local bus, 1 slot | IPX-6297A= |
| Local bus, 1 slot, ARC only | IPX-512019= |
| Local bus, 1 slot, SDP only | IPX-5096B= |
| IPX Processor Group | |
| Network processor card--32-MB DRAM | IPX-NPC-550051 |
| Redundant network processor card--32-MB DRAM | IPX-NPC-550051-R |
| Network processor card--32-MB DRAM (spare) | IPX-NPC-550051= |
| SCC-B with Ethernet back card in IPX 8, IPX 16 or dual (spare) | IPX-SCC-6235= |
| SCC-B with Ethernet and LEC back card in IPX 32 (spare) | IPX-SCC-6236= |
| IPX Alarm Relay Group | |
| Alarm relay card with IPX-512019 local bus | IPX-ARC-512010 |
| Alarm relay interface back card | BC-512011 |
| IPX Trunk Groups | |
| FastPAD trunk card with IPX-6297A local bus | IPX-FTC-6350 |
| FastPAD V.35 back card (FPC-V.35) | BC-6351A-V35 |
| FastPAD T1 back card (FPC-T1) | BC-6352A-T1 |
| FastPAD E1 back card (FPC-E1) | BC-6353A-E1 |
| FastPAD X.21 back card (FPC-X21) | BC-6354A-X21 |
| IPX8 network trunk card, model E, 6297A local bus | IPX8-NTC-6161E |
| IPX8/16/32 network trunk card, model E, 6297A local bus | IPX-NTC-6161E |
| Back card/T1 (BC-T1) | BC-6271A-T1 |
| Back card/subrate (BC-SR) | BC-6083A-SR |
| Back card/E1 (BC-E1) | BC-6171A-E1 |
| Back card/Y1 (BC-Y1) | BC-550150-Y1 |
| ATM interworking trunk card (AIT), 6297A local bus | IPX-AIT-571000 |
| T3 back card for broadband trunk module | BC-571110A-T3 |
| E3 back card for broadband trunk module | BC-571210A-E3 |
| E2 back card for broadband trunk module | BC-571310A-E2 |
| HSS1 backcard for broadband trunk module | BC-571410A-HSS1 |
| IPX Port Groups | |
| Synchronous data PAD, 5096B local bus | IPX-SDP-5080C |
| HDM back card/V.35 (SDI-V.35) | BC-5082A-V35 |
| HDM back card/RS449 (SDI-RS449) | BC-5083A-RS449 |
| HDM back card/RS232D (SDI-RS232D) | BC-5084B-RS232 |
| Low speed data pad (LDP), 6297A local bus | IPX-LDP-5285C |
| LDM back card/4-port/RS232C (LDI4) | BC-5286A-RS232 |
| LDM back card/8-port/RS232C (LDI8) | BC-5287A-RS232 |
| CDP ADPCM, 6297A local bus | IPX-511475 |
| IPX8 CDP ADPCM, T1 echo canceler, 6297A local bus | IPX8-T1-511477 |
| IPX 8 CDP ADPCM, E1 echo canceler, 6297A local bus | IPX8-E1-511478 |
| CDP ADPCM, T1 echo canceler, 6297A local bus | IPX-T1-511477 |
| CDP ADPCM, E1 echo canceler, 6297A local bus | IPX-E1-511478 |
| Back card/E1 (BC-E1) | BC-6171A-E1 |
| Back card/T1 (BC-T1) | BC-6271A-T1 |
| Back card/J1 (BC-J1) | BC-550100-J1 |
| IPX 8 Frame Relay PAD (FRP), 6297A local bus | IPX8-FRP-6250D |
| IPX8/16/32 Frame Relay PAD (FRP) model D, 6297A local bus | IPX-FRP-6250D |
| IPX 8 Frame Relay PAD (FRP-6), 6 channels, 6297A local bus | IPX8-FRP6-6255E |
| Frame Relay PAD (FRP-6), 6 channels, 6297A local bus | IPX-FRP6-6255E |
| Frame Relay PAD (FRP-31), 31 channels for IPX 8 only | IPX8-FRP31-6260E |
| Frame Relay PAD (FRP-31), 31 channels model E for IPX 8/16/32 | IPX-FRP31-6260E |
| Frame Relay PAD (FRP-2), model A for port concentrator shelf | IPX-FRP2-6270A |
| Frame Relay interface (FRI-V.35) required back card | BC-6251B-V35 |
| Frame Relay interface (FRI-T1) | BC-6252A-T1 |
| Frame Relay interface (FRI -E1) | BC-6253A-E1 |
| Frame Relay interface X.21 for FRM-2 and PCS | BC-6355A-X21 |
| Frame Relay interface (FRI-X.21) required back card | BC-6254A-X21 |
| IPX Port Concentrator Shelf | |
| 110V, 44-port PCS unit with V.28 interfaces | PCS-NA-S-V28 |
| 110V, 44-port PCS unit with V.11 interfaces | PCS-NA-S-V11 |
| 110V, 44-port PCS unit with V.35 interfaces | PCS-NA-S-V35 |
| 220V, 44-port PCS unit with V.28 interfaces | PCS-INTL-S-V28 |
| 220V, 44-port PCS unit with V.11 interfaces | PCS-INTL-S-V11 |
| 220V, 44-port PCS unit with V.35 interfaces | PCS-INTL-S-V35 |
| 240V, 44-port PCS unit with V.28 interfaces | PCS-UK-S-V28 |
| 240V, 44-port PCS unit with V.11 interfaces | PCS-UK-S-V11 |
| 240V, 44-port PCS unit with V.35 interfaces | PCS-UK-S-V35 |
| PCS shelf only with 110 VAC power supply | PCS-NA |
| PCS shelf only with 220 VAC power supply | PCS-INTL |
| PCS shelf only with 240 VAC power supply | PCS-UK |
| 48VDC PCS shelf | PCS-DC |
| PCS module with 1 V.11 and 11 V.28 interfaces | PCS-V28 |
| PCS module with 12 V.11 interfaces | PCS-V11 |
| PCS module with 1 V.11 and 11 V.35 interfaces | PCS-V35 |
| V.24/V.28 interface module | ICARD-V28 |
| V11/RS-422/X.21 plug-in interface modules | ICARD-V11 |
| V35 plug-in interface modules | ICARD-V35 |
| RS232M25 - RS-23/2M25 cable | CABLE-V28 |
| RS232M25 - X.21/V.11 DB15/M cable | CABLE-V11 |
| RS232M25 - V.35/M34 cable | CABLE-V35 |
| RS232M25 - V.35/M34 cable | CABLE-SPV35 |
| RS232M25 - RS-422/M37 cable | CABLE-X21DTE |
| RS232M25 - RS-422/M37 cable | CABLE-X21DCE |
| IPX Power Cords | |
| IPX 8 power cord with CEE 7/7 ("Schuko") plug (Europe) (spare) | CAB-590061= |
| IPX 8 power cord with AS3112 plug (Australia and New Zealand) (spare) | CAB-590062= |
| IPX 8 power cord with BS1363 plug (Great Britain and Ireland) (spare) | CAB-590063= |
| IPX 8 power cord with CEI 23-16/VII plug (Italy) (spare) | CAB-590064= |
| IPX 8 power cord with IEC 320 style plug (spare) | CAB-590065= |
| IGX/IPX 16/32 power cord with CEI 23-16/VII plug (Italy) (spare) | CAB-590071= |
| IGX/IPX 16/32 power cord with CEE 7/7 plug (Europe) (spare) | CAB-590072= |
| IGX/IPX 16/32 power cord with AS3112 plug (Australia and New Zealand) (spare) | CAB-590073= |
| IGX/IPX 16/32 power cord with BS1363 plug (Great Britain and Ireland) (spare) | CAB-590074= |
| IGX/IPX 16/32 power cord with NEMA L6-20 twistlock plug (North America and Japan) (spare) | CAB-590076= |
| IPX Spares and Accessories | |
| North America IPX 8 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX8-AC-NA= |
| North America IPX 8 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX8-DC-NA= |
| North America IPX 16 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX16-AC-NA= |
| North America IPX 16 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX16-DC-NA= |
| North America IPX 32 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX32-AC-NA= |
| North America IPX 32 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX32-DC-NA= |
| International IPX 8 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX8-AC-INTL= |
| International IPX 8 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX8-DC-INTL= |
| International IPX 16 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX16-AC-INTL= |
| International IPX 16 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX16-DC-INTL= |
| International IPX 32 AC cabinet (spare) | IPX32-AC-INTL= |
| International IPX 32 DC cabinet (spare) | IPX32-DC-INTL= |
| Power supply, AC-input, IPX 8/16/32 600W (black faceplates) | IPX-6027-AC |
| Power supply, DC-input, IPX 8/16/32 600W (black faceplates) | IPX-6228-DC |
| IPX faceplate--blank front | IPX-5055A= |
| Back plate/1 slot | IPX-5056A= |
| IPX 8 rack-mount kit 19 in. | IPX-590050= |
| Center mount rail kit (CISPR) short | IPX-5794A= |
| Center mount rail kit (CISPR) long | IPX-5795A= |
| IPX ISC V.34R modem 28.8, synchronous, asynchronous, with security | IPX-5941B= |
| IPX 8 system bus | IPX-590070= |
| IPX 8 PDU AC | IPX-590080= |
| IPX 8 PDU DC | IPX-590085= |
| IPX 8 cooling unit | IPX-590090= |
| IPX 8 air filter | IPX-590092= |
| IPX 8 power interface board | IPX-590075= |
| IPX 8 U.S. power cord | IPX-590060= |
| System bus, IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5090A= |
| Power supply blank panels for IPX 8 (black) | IPX-6059A= |
| Center cooling unit, IPX 32, AC (CISPR) | IPX-511013A= |
| IPX 16/32 air filter | IPX-511014= |
| Center cooling unit, IPX 32, DC (CISPR) | IPX-6226B-D= |
| Power distribution unit, IPX 16 and 32, AC (CISPR, T1) | IPX-511010A= |
| Adapter bracket set for 511010A and 6224B-D | IPX-511010AK= |
| Lower cooling unit/IPX 16 and 32/DC (CISPR) | IPX-6224B-D= |
| Lower cooling unit/IPX 16 and 32/AC (CISPR) | IPX-6224B-A= |
| Power supply shelf/IPX 32/AC (CISPR) | IPX-511011A= |
| Blank utility bus, 1 slot | IPX-5097A= |
| Adapter kit for 511011A and 6222B-D | IPX-511011AK= |
| PDU and DC power supply shelf IPX 16 (CISPR) | IPX-6221B-D= |
| PDU and DC power supply shelf IPX 32 (CISPR) | IPX-6222B-D= |
| IPX Upgrades | |
| IPX 16/AC to IPX 32 (CISPR) | IPX-6210B-A-B= |
| IPX 16/DC to IPX 32 (CISPR) | IPX-6210B-D= |
| IPX 16 to IPX 16 with SCC | IPX-5036A= |
| IPX 32 to IPX 32 with SCC | IPX-5037A= |
| IPX 32 to IPX 216, AC-input | IPX-5037-216= |
| IPX Card Upgrades | |
| PCC D, E, F to H | IPX-511406= |
| IPX Software Licenses | |
| System software license 7.0.7 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.707 |
| System software license 7.1.1 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.711 |
| System software license 7.2.8.1 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.7281 |
| System software license 7.2.8.4 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.7286 |
| System software license 8.0.2 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.802 |
| System software license 8.1.1.9 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.8119 |
| System software license 8.1.2.6 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.8126 |
| System software license 8.2.0.3 for IPX 8 | IPX8-5008E.8203 |
| System software license 7.0.7 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.707 |
| System software license 7.1.1 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.711 |
| System software license 7.2.8.1 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.7281 |
| System software license 7.2.8.4 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.7286 |
| System software license 8.0.2 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.802 |
| System software license 8.1.1.9 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.8119 |
| System software license 8.1.2.6 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.8126 |
| System software license 8.2.0.3 for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-5001E.8203 |
| IPX Feature Licenses | |
| Frame Relay ForeSight software license per card | IPX-530140 |
| Repetitive pattern suppression for IPX 8 only | IPX8-5005E |
| Repetitive pattern suppression software license for IPX 16/32 | IPX-5005E |
| Enhanced Frame Relay for IPX 8 only | IPX-530120-8 |
| Enhanced FR software license for IPX 16 and 32 | IPX-530120 |
| Configuration save and restore | IPX-740000 |
| Multiuser sessions | IPX-740001 |
|
|