|
|
This appendix provides further explanation of concepts related to the hub. It also provides information on how to use the hub in your network.
The hub supports a 10BaseT network segment and a 100BaseTX network segment. Each hub port can be in either the 10BaseT segment or the 100BaseTX segment, and each segment communicates with one another via an internal bridge as shown in Figure A-1.
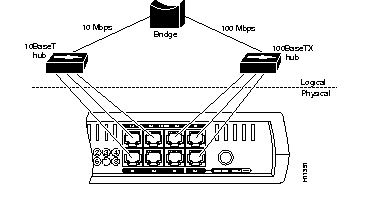
You cannot disable the autonegotiation of speed on the hub.
This section describes two common examples of how you can use the hub:
The hub can provide a connection between a compatible switch, router, or server and PCs or workstations as shown in Figure A-2. To be considered compatible, a switch, router, server, PC, or workstation must support either 10BaseT or 100BaseTX. For example, the Cisco 1548 Micro Switch 10/100 or any of the Cisco 1600 series routers are compatible devices.
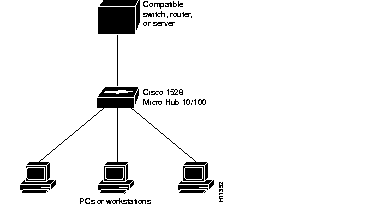
The speed of the connected network device and the type of cable determine the speed at which packets are transmitted for a particular port. For example, if the network device is running at 10 Mbps and the hub and the network device are connected by a 10BaseT Ethernet cable, this connection transmits packets at 10 Mbps. If the network device is running at 100 Mbps and the hub and the network device are connected by a 100BaseTX Ethernet cable, this connection transmits packets at 100 Mbps.
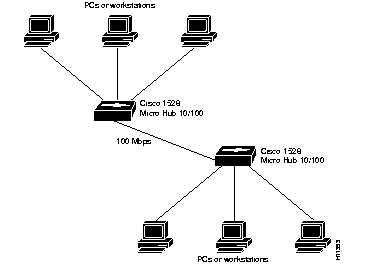
The hub can provide a connection to another Cisco 1528 Micro Hub 10/100 as shown in Figure A-3. In this example, the two hubs will autonegotiate the speed of the connection to 100 Mbps.
|
|