|
|

78-4671-02
Product Numbers: AS53-12-M-56K=
This document describes how to install 56K 12-port modem modules in Cisco AS5300 universal access servers, and includes the following sections:
Use this document with the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information publication that shipped with the Cisco AS5300.
The 56K 12-port modem module (Figure 1) uses Rockwell's K56Flex technology. The modem can send data at up to 56 kbps and receive data at up to 33.6 kbps. However, the actual speed that you can achieve with the modem depends on the condition of your local telephone network.
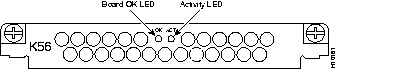
The following prerequisites apply to the 56K 12-port modem module:
Follow these guidelines to ensure general safety:
Safety warnings appear throughout this publication in procedures that, if performed incorrectly, may harm you. A warning symbol precedes each safety warning.
 | Warning This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device. |
Waarschuwing Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in deze publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informatie over naleving van veiligheids- en andere voorschriften) raadplegen dat bij dit toestel is ingesloten.
Varoitus Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten käännökset löydät laitteen mukana olevasta Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information -kirjasesta (määräysten noudattaminen ja tietoa turvallisuudesta).
Attention Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des traductions d'avertissements figurant dans cette publication, consultez le document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformité aux règlements et consignes de sécurité) qui accompagne cet appareil.
Warnung Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen Warnhinweise finden Sie im Dokument Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informationen zu behördlichen Vorschriften und Sicherheit), das zusammen mit diesem Gerät geliefert wurde.
Avvertenza Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La traduzione delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nel documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformità alle norme e informazioni sulla sicurezza) che accompagna questo dispositivo.
Advarsel Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Hvis du vil se oversettelser av de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Overholdelse av forskrifter og sikkerhetsinformasjon) som ble levert med denne enheten.
Aviso Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis acidentes. Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação, consulte o documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informação de Segurança e Disposições Reguladoras) que acompanha este dispositivo.
¡Advertencia! Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. Para ver una traducción de las advertencias que aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el documento titulado Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Información sobre seguridad y conformidad con las disposiciones reglamentarias) que se acompaña con este dispositivo.
Varning! Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. Se förklaringar av de varningar som förkommer i denna publikation i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Efterrättelse av föreskrifter och säkerhetsinformation), vilket medföljer denna anordning.
 | Warning Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. |
 | Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
 | Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment. |
 | Warning To ensure your safety and the safety of others, be sure the power is OFF and the power cord is unplugged before working on the router. |
 | Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
Follow these guidelines when working on equipment powered by electricity:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic printed circuit cards are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures. Always follow ESD prevention procedures when removing and replacing cards. Ensure that the chassis is electrically connected to earth ground. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted surface of the chassis frame to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis.
 | Caution For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap, which should be between 1 and 10 megohm (Mohm). |
The use of 56K modems introduces a new step for installing and configuring modem software. To use 56K modems, you must first install the modem code file into the Cisco AS5300 system Flash memory. The following steps provide an overview of the installation process:
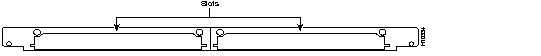
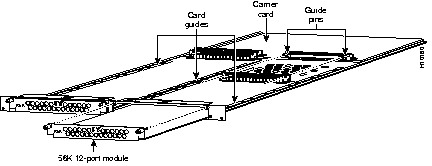
You must install 56K 12-port modem modules in a Microcom carrier card, which is not included with this kit. The carrier card, shown in Figure 2, is a wide card with two slots in which you can install up to two 56K 12-port modem modules (or other supported port modules). You can install 56K 12-port modem modules with any combination of other supported port modules.
You will need the following tools:
To install the 56K 12-port modem module, refer to Figure 3 and take these steps:
Step 1 Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap.
Step 2 Power OFF the access server.
 | Caution The modem modules are not hot-swappable (that is, you cannot remove or install them when the access server power is ON). Be sure to power OFF the access server before installing or removing modem modules. Failure to do so can damage the access server. |
Step 3 Remove all interface cables from the back panel of the access server.
Step 4 Remove the blank cover or modem module installed in the carrier card.
Step 5 Remove the 56K 12-port modem module from the ESD-preventive shipping material.
Step 6 Slide the 56K 12-port modem module into the carrier card slot until it is seated completely.
Step 7 Tighten the two captive screws on the 56K 12-port modem module to secure it to the carrier card.
If you have questions or need assistance, refer to the section "Cisco Connection Online" at the end of this document. Otherwise, proceed to the section, "Configuring 56K 12-Port Modem Modules."
The 12-port module uses the following modem code images in a single-file format:
Modem code also resides on the access server: one version is bundled with Cisco IOS software, and another version can exist in system Flash memory. This modem code residing in the access server is a single file comprised of the modem firmware image combined with the DSP software image.
After power on, Cisco IOS software uses its bundled modem code file or the existing modem code file in system Flash memory to automatically update the DSP software and modem firmware on a given modem.
When you install a new 12-port module, Cisco IOS software examines the following versions of modem code:
Then, Cisco IOS software ensures that the system uses matching DSP software and modem firmware--which may include overriding the current firmware on the modem. In some circumstances you may decide to manually update the modem code after the automatic download process completes.
Because of the possibility of multiple versions of modem code and the way Cisco IOS software process these versions, Cisco suggests that you decide between the following two strategies:
To help with the decision, Figure 4 shows a hypothetical release process. We recommend that you use the modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software because it is the easier strategy and enables you to take advantage of new modem code whenever you upgrade your Cisco IOS software. You can also control the modem code by reverting to previous versions by using the copy command as discussed later.
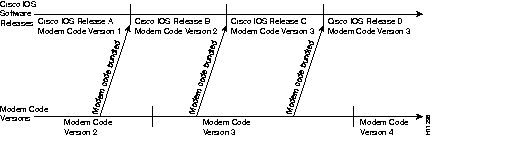
Table 1 provides some typical scenarios that occur when you add or replace a 12-port module. Table 2 provides scenarios that occur when you upgrade Cisco IOS software or modem code.
| Scenario | Update Process |
|---|---|
| You replace an existing 56K 12-port module with a module that contains newer modem code.1
Option 1--Accept the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. Option 2--Upgrade modem code to a different version. | Option 1--No action needed.
Option 2--Copy the desired version of the modem code file to system Flash memory, then copy that file to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. See "Using the Modem Code from an External File," page 12. |
| You replace a V.34 12-port module with a 56K 12-port module.2
Option 1--Accept the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software (this is the bundled version). Option 2--Upgrade the modem code to a different version. | Option 1--No action needed.
Option 2--Copy the desired version of modem code file to system Flash memory, then copy that file to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. See "Using the Modem Code from an External File," page 12. |
| No. | Scenario | Update Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide to use the version of modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
|
|
2 | You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide not to use the modem code selected by Cisco IOS software. |
|
|
3 | The modems are running a version of modem code from system Flash memory that is different than the version bundled with Cisco IOS software. You decide to revert to the bundled version. |
|
|
4 | Cisco releases new modem code, which is a later version than the version currently running on the modems. You decide to use Cisco's newest modem code.2 |
|
Figure 5 shows a location on the release timeline where updates might take place, and Table 3 explains the resulting versions of Cisco IOS software and modem code.
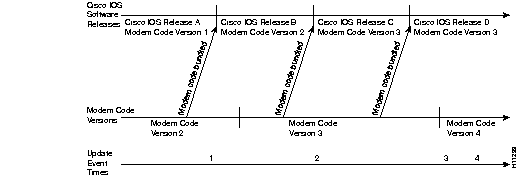
| Update Event Time | Update Event | Resulting Version of Cisco IOS Software and Modem Code |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release B.
|
|
|
2 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release C. (Cisco IOS software uses mapping from last copy command at Time 1).1 | Cisco IOS Release C Modem Mode Version 1 |
| You enter copy ios-bundled modem command. | Cisco IOS Release C Modem Mode Version 3 | |
| 3 | New Modem Code Version 4 is released, you copy the file to system Flash memory, enter copy flash modem and specify Modem Code Version 4. | Cisco IOS Release C Modem Mode Version 4 |
4 | You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release D. | Cisco IOS Release D Modem Mode Version 4 |
| You enter the copy ios-bundled modem command. | Cisco IOS Release D Modem Mode Version 3 |
Table 4 provides a list of terms and commands and a description of how they are used in the modem code update process.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Modem firmware | Modem controller firmware that resides in modem Flash memory. |
| DSP software | DSP controller software that resides in modem RAM. Cisco IOS software transfers a version of DSP software to modem RAM on each reboot. |
| Modem code | Two images:
These images reside separately in the modems and as a single-file version in the access server's system Flash memory. System Flash memory can contain several versions of modem code: a version bundled with Cisco IOS software and multiple versions that resulted from previous copy tftp flash commands. |
| copy tftp flash mcom-modem-code-x.x.x.bin command | Places a copy of the modem code in system Flash memory. |
| copy flash modem command | Transfers the copy tftp flash version of modem code to the modems. This command transfers the modem firmware file to modem Flash memory and the DSP software file to modem RAM.
Maps the system Flash memory version to the modems. |
| copy ios-bundled command | Instructs the modems to use the version of modem code bundled with Cisco IOS software. This command does not affect any existing versions of modem code that reside in system Flash memory.
After one copy ios-bundled modem command, future Cisco IOS upgrades will potentially result in the downloading of new Cisco IOS bundled firmware to the modems. (If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same modem code as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the modems.) Maps the bundled Cisco IOS software version to the modems. |
| Mapping | The copy commands map a specific version of modem code to a group of modem slots/ports. The copy ios-bundled modem command maps the slots/ports to the bundled version, and the copy flash modem command maps the slots/ports to a specific modem code file located in system Flash memory. Cisco IOS software uses the mapping to determine which version of modem code should be downloaded to the modems. If Cisco IOS software finds no mapping or invalid mapping, it downloads the bundled version. |
Use the procedures in this section to transfer modem code from Cisco Connection Online (CCO) to the integrated modems on the 12-port module. The procedure consists of the following tasks:
You can download the single file (mcom-modem-code-x.x.x.bin) to a TFTP server on your LAN two ways:
Log in to Cisco's Software Center at the following URL to download the modem code file. You must log in as a Cisco registered user. (If you are not a registered user, note that Cisco provides modem code on a disk when are updates are necessary. This disk is shipped with the 12-port module.)
After downloading to your desktop computer, you must transfer it to a TFTP server on your network using an FTP application.
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/56K
Alternatively, you can access Cisco at http://www.cisco.com, login, and take the following path to the file:
Take the following steps to download the modem code file from Cisco's FTP server using an FTP client application. These steps assume that you want to download both the modem firmware and the DSP software.
Step 1 Log in to Cisco System's CCO FTP server, which is called cco.cisco.com:
ftp cco.cisco.com
Step 2 Enter your CCO registered username and password (for example, harry and letmein):
harry
letmein
Step 3 Specify the directory that holds the Modem Code file, which is /cisco/access/5300:
cd /cisco/access/5300
Step 4 View the contents of the directory with the ls command:
ls
Step 5 Specify a binary image transfer:
binary
Step 6 Copy the modem code file from the server to your local environment with the get command. The filename is mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin.
The following example downloads the modem code file:
get mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
Step 7 Quit your terminal session:
quit
Step 8 Verify that you successfully transferred the modem code file to your local directory:
ls -al
pwd
Step 9 If you have not already done so, transfer this file to a local TFTP server that your Cisco AS5300 can access.
The procedure for copying the modem code file from your local TFTP server to the access server system Flash memory is a two-step process. First, transfer the code to the access server. Then, transfer the code to the modems.
These two steps are performed only once. After you copy the modem code file into system Flash memory for the first time and map that file to a specific modem using the copy flash modem command, you do not have to perform these steps again. Because the DSP software runs from modem RAM, the Cisco IOS software must automatically copy the DSP software to each modem each time the access server power cycles.
Step 1 Copy the modem code file from your TFTP server to the access server's system Flash memory using the copy tftp flash command. Cisco IOS software prompts you with a sequence of questions such as name/address of the TFTP server and the filename to be copied. Answer all of the prompts according to your configuration. The following example shows a typical download.
Step 2 Copy the modem code file to the modems by entering the copy flash modem Privileged EXEC command.
mcom-modem-code-3.1.30.bin
yes
If you want to verify that the DSP software and modem firmware copied to the modems, use the show modem version command. In this example, modems 2/12 through 2/23 are loaded with the modem controller firmware and DSP software:
show modem version
Now the modems are equipped with code. The modems are configured to transmit at speeds up to 56 kbps. Each time the access server is power cycled, Cisco IOS software automatically loads the modems with the modem code in system Flash memory. If you erase the modem code file from system Flash memory, the Cisco IOS default modem code (that is, the bundled modem code) will be automatically downloaded to the modem.
If you already have a version of modem code in the Flash memory on your access server, and you upgrade to a Cisco IOS release that includes newer modem firmware, only the modems that are mapped to the bundled Cisco IOS version are updated. In order to set the modem firmware mapping to the firmware version bundled with Cisco IOS software, enter the following command:
5300# copy ios-bundled modem
As a result of the copy ios-bundled modem command, future Cisco IOS upgrades will potentially result in the mapping of new Cisco IOS bundled firmware to the modems. (If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same modem code as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the modems.)
During the modem code download process, you may receive an error message if the download fails.
| Error Message | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| %%ERROR: Modem | The specified modem firmware is not compatible with the target modem. For example, V.34 modems cannot be upgraded with 56K firmware. If you have a bank of non-56K modems in the access server and specify the all option in the copy tftp modem command, this error message will appear and not download 56K firmware where appropriate. | Verify that you are copying 56K modem firmware to 56K modems. Also use the show modem command to verify that you specified the correct slot/port or range. |
| %%ERROR: Modem | The modem code is currently downloading to the 56K modems. | The first download will containue without interruption, and the second download is aborted. |
| %%ERROR: Modem | The modem code cannot be downloaded to the specified modem. | Use the show modem command to verify that you are downloading to a supported 56K modem. |
| %%ERROR: Modem | The specified modem is held in reset mode. The DSP software will not download to this modem. | Take the modem out of reset mode, then copy the DSP software again. |
| %%ERROR: NVRAM write for DSP download filename entry failed. | There is an NVRAM table problem. | Reissue the copy tftp flash command and copy the DSP file again. |
This section describes how to configure the 56K 12-port modem modules.
If you are experienced with Cisco IOS software, refer to the "Configuration Example" section at the end of the following task tables for a working configuration example. Or take the steps described in the following task tables to configure the access server:
| Step | Command | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5300> enable
Password: <password> | Enter enable mode.
Enter the password. You have entered enable mode when the prompt changes to |
| 2 | 5300# config term
| Enter global configuration mode. You have entered global configuration mode when the prompt changes to 5300(config)#.
|
| 3 | 5300(config)# interface group-async 1
5300(config-if)# | Place all asynchronous interfaces in a single group, so that you configure the same parameters quickly on all interfaces at one time. |
| 4 | 5300(config-if)# ip unnumbered ethernet 0
| To conserve IP addresses, configure the asynchronous interfaces as unnumbered and assign the IP address of the Ethernet interface to them. |
| 5 | 5300(config-if)# encapsulation ppp
| Enable PPP1 to run on the set of interfaces in the group. |
| 6 | 5300(config-if)# async mode interactive
| Configure interactive mode on the asynchronous interface. |
| 7 | 5300(config-if)# ppp authentication chap pap
| Enable CHAP2 and PAP3 authentication on the interface. |
| 8 | 5300(config-if)# peer default ip address pool default | Support dial-in PC clients. At the global level, define the pool of addresses |
| 9 | 5300(config-if)# group-range 1 48
Building configuration... | Define the group range of the interface. The number you use with the group-range command depends on the number of asynchronous interfaces you have on your access server. That is, if your access server has 48 asynchronous interfaces, you can specify group-range 1 48. If 60, specify group-range 1 60. |
| Step | Command | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5300(config-if)# line 1 48
| Enter the number of modem lines to configure. If you have 48 modems, enter line 1 48. If 60, enter line 1 60.
Note: There are 12 modems on each 56K module. |
| 2 | 5300(config-line)# modem autoconfigure type 56k
| Configure the access server modems to use a default configuration string (chat script). A string of modem configuration commands is sent to the modem each time it is reset. |
| 3 | 5300(config-line)# transport input all
| Allow all protocols to be used when connecting to the line. |
| 4 | 5300(config-line)# autoselect ppp
| Enable remote IP users running a PPP application to dial in, bypass the EXEC facility, and connect directly to the network. |
| 5 | 5300(config-line)# modem inout
| Enable both incoming and outgoing calls. |
| 6 | 5300(config-line)# flowcontrol hardware
| Enable hardware flow control. |
| 7 | 5300(config-line)# exit
| Exit to global configuration mode. |
| Step | Command | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5300(config)# isdn switch-type primary-5ess | Enter your telco's switch type. The following switch types are available: primary-4ess, primary-5ess, primary-dms100, primary-net5, primary-ntt, and primary-ts014. |
| 2 | 5300(config)# controller t1 0[or]controller e1 0
| Enter controller configuration mode to configure your controller port. The controller ports are labeled 0 through 3 on the quad T1/PRI and quad E1/PRI cards. |
| 3 | 5300(config-controller)# framing esf
| Enter your telco's framing type. The following framing types are available: esf, sf, crc4, and nocrc4. |
| 4 | 5300(config-controller)# linecode b8zs
| Enter your telco's line code type. The following line code types are available: ami, b8zs, and hdb3. |
| 5 | 5300(config-controller)# clock source line primary
| Enter the clock source for the line. Configure one line as the primary or most stable clock source line. Configure the other line as the secondary clock source line. |
| 6 | 5300(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-24[or]pri-group timeslots 1-31
| Configure all channels for ISDN. Enter pri-group timeslots 1-24 for T1. If E1, enter pri-group timeslots 1-31. |
| 7 | 5300(config-controller)# controller t1 1[or]controller e1 0
| Repeats steps 2 to 6 to configure the second controller. Note that the controller number is 1, instead of 0. And the clock source is secondary, instead of primary. |
| Step | Command | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5300(config-controller)# interface serial0:23
5300(config-if)# | Enter serial interface configuration mode. After you have configured the controller, a corresponding D channel serial interface is created instantly. Serial interface 0:23 is the D channel for controller 0. You must configure each serial interface to receive incoming and send outgoing modem signaling. |
| 2 | 5300(config-if)# ip address 172.16.253.254 255.255.255.0
| Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface. |
| 3 | 5300(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice modem
| Configure all incoming voice calls to go to the modems. |
| 4 | 5300(config-if)# end 5300#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console < | Return to privileged EXEC mode.
|
| 5 | 5300# copy running-config startup-configBuilding configuration...[OK] | Save the configuration changes to NVRAM. |
The following example shows the output of the show config command for a system configured with 56K 12-port modem modules. If you are experienced with Cisco IOS software, you might find this a useful reference for configuration.
5300# show config
Using 1888 out of 126968 bytes
!
version 11.2
service timestamps debug uptime
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname 5300
!
enable secret 5 $1$60L4$X2JYOwoDc0.kqa1loO/w8/
enable password lab
!
username modem password 7 020A0559
username smith-t1 password 7 060A0E23
partition flash 2 8 8
!
no ip domain-lookup
ip host jurai 223.255.254.254
ip host brios 223.255.254.253
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
chat-script dial "" "ATDT\T" TIMEOUT 120 CONNECT \p
!
controller T1 0
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
controller T1 1
framing esf
clock source line secondary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 1.18.0.99 255.255.0.0
hold-queue 512 in
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial0:23
ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
encapsulation ppp
no keepalive
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer idle-timeout 2147483
dialer map ip 20.0.0.2 name as5300-uut broadcast 8940166
dialer load-threshold 50 either
dialer-group 1
no fair-queue
ppp authentication chap
!
interface Serial1:23
ip address 21.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
encapsulation ppp
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer idle-timeout 2147483
dialer map ip 21.0.0.2 name as5300-uut broadcast 4341608
dialer load-threshold 50 either
dialer-group 1
no fair-queue
ppp authentication chap
!
interface Group-Async1
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
async default routing
async mode interactive
no peer default ip address
no fair-queue
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap
group-range 1 48
!
no ip classless
ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 1.18.0.1
snmp-server community public RW
!
line con 0
line 1 48
exec-timeout 0 0
autoselect ppp
modem InOut
transport input all
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password lab
login
!
end
This concludes the procedure for configuring the access server for use with the 56K 12-port modem module. If you have questions or need assistance, refer to the section "Cisco Connection Online" at the end of this document.
The equipment described in this document generates and may radiate radio-frequency energy. If it is not installed in accordance with Cisco's installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc. could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.

|
|