This chapter describes how to power ON the Cisco AS5300 universal access server and configure it using the prompt-driven setup script. The following sections are included:
If you prefer to configure the access server manually, proceed to the next chapter "Cisco IOS Software Survival Skills" to familiarize yourself with the command-line interface (CLI) and then proceed to the next chapter "Basic Configuration" for step-by-step instructions.
Before you turn on the access server and begin to use the setup script (also called the initial configuration dialog), make sure you have:
- Already connected the cables to the access server.
- Configured your PC terminal emulation program for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 2 stop bits.
All configuration will be performed from your PC terminal emulation program window.
Take these steps:
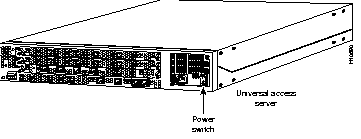
Step 1 Power ON the access server. The power switch is on the rear panel of the access server, at the lower right corner near the power cord.
Figure 1-1: Power Switch Location
Messages will begin to appear in your terminal emulation program window.
 | Caution Do not press any keys on the keyboard until the messages stop. Any keys pressed during this time are interpreted as the first command typed when the messages stop, which might cause the access server to power off and start over. It will take a few minutes for the messages to stop. |
The messages look similar to the following:
Note The messages vary, depending on the Cisco IOS software release and feature set you selected. The screen displays in this section are for reference only and might not exactly reflect the messages on your console.
System Bootstrap, Version 11.X(X)P, RELEASED SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1994-1997 by cisco Systems, Inc.
AS5300 processor with 32768 Kbytes of main memory
rommon 1 b f
program load complete, entry point: 0x80008000, size: 0xef4e0
Self decompressing the image : ###############################################
[OK]
Notice: NVRAM invalid, possibly due to write erase.
program load complete, entry point: 0x80008000, size: 0x415b20
Self decompressing the image : ################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################[OK]
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - Restricted
Rights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph
(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.
cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, California 95134-1706
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 5300 Software (C5300-JS-M), Experimental Version 11.2(19970619:020846) [ppalleti-DVT_08 102]
Copyright (c) 1986-1997 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 18-Jun-97 22:25 by ppalleti
Image text-base: 0x600088A0, data-base: 0x60738000
cisco AS5300 (R4K) processor (revision A) with 32768K/8192K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID 04614954
R4700 processor, Implementation 33, Revision 1.0 (Level 2 Cache)
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software.
Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.0.
Backplane revision 1
Manufacture Cookie is not programmed.
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
1 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
48 terminal line(s)
4 Channelized T1/PRI port(s)
128K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)
4096K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write)
Notice: NVRAM invalid, possibly due to write erase.
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Note At any time during the setup script (initial configuration dialog), you can exit and begin again by pressing
Ctrl-C and entering
setup at the enable mode prompt (#).
Step 2 When the following message appears, press Return to accept the default entry (yes) in square brackets:
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]:
Step 3 When the following message appears, press Return to see the current interface summary:
First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]:
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 unassigned NO unset up up
FastEthernet0 unassigned NO unset up down
Step 4 Enter a host name for the access server:
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [Router]: 5300
The enable secret is a one-way cryptographic secret used
instead of the enable password when it exists.
Step 5 Enter an enable secret password. This password is encrypted (more secure) and cannot be seen when viewing the configuration:
Enter enable secret: lab
The enable password is used when there is no enable secret
and when using older software and some boot images.
Step 6 Enter an enable password. This password is not encrypted (less secure) and can be seen when viewing the configuration:
Enter enable password: guessme
Step 7 Enter the virtual terminal password, which is used for remote console access:
Enter virtual terminal password: guessagain
Step 8 Respond to the following prompts as appropriate for your network:
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]:
Community string [public]:
Configure LAT? [no]:
Configure AppleTalk? [no]: yes
Multizone networks? [no]: yes
Configure DECnet? [no]:
Configure IP? [yes]:
Configure IGRP routing? [yes]:
Your IGRP autonomous system number [1]: 15
Configure CLNS? [no]:
Configure IPX? [no]: yes
Configure Vines? [no]:
Configure XNS? [no]:
Configure Apollo? [no]:
Configure bridging? [no]:
Step 9 Configure the asynchronous serial lines for the integrated modems on the modules installed in the access server:
Async lines accept incoming modems calls. If you will have
users dialing in via modems, configure these lines.
Configure Async lines? [yes]:
Async line speed [115200]:
Note We recommend that you keep the speed at 115200.
Will you be using the modems for inbound dialing? [yes]:
Would you like to configure group async interface? [yes]:
Note If your asynchronous interfaces will be using the same basic configuration parameters, we recommend that you group them so that they can be configured as a group. Otherwise, you will need to configure each interface separately.
Configure for Dynamic IP addresses? [no]:
Configure for TCP header compression? [yes]:
Configure for routing updates on async links? [no]:
Enter the starting address of IP local pool? [X.X.X.X]: 172.20.30.40
Enter the ending address of IP local pool? [X.X.X.X]: 172.20.30.88
Note Make sure the starting and ending addresses of the IP pool are in the same subnet.
What is the username of the test user? [user]:
What is the password of the test user? [passwd]:
Will you be using the modems for outbound dialing? [no]:
Configure for Async IPX? [yes]: no
Configure for Appletalk Remote Access (ARA)? [no]: yes
AppleTalk Network for ARAP clients [1]:
Zone name for ARAP clients [ARA Dialins]:
Allow ARAP "Guest" logins? [yes/no]: yes
Step 10 Configure the Ethernet 0 interface:
Configuring interface Ethernet0:
Is this interface in use? [yes]:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 172.21.40.10
Number of bits in subnet field [0]:
Class B network is 172.21.0.0, 0 subnet bits; mask is /16
Configure AppleTalk on this interface? [no]: yes
Extended AppleTalk network? [no]:
AppleTalk network number [0]: 10
AppleTalk zone name [myzone]: etherzone
Configure IPX on this interface? [no]: yes
IPX network number [1]:
Step 11 Configure the FastEthernet 0 interface:
Is this interface in use? [yes]:
Operate in full-duplex mode? [no]: yes
Operate at 100 Mbps speed? [yes]: yes
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: yes
IP address for this interface: 172.22.50.10
Number of bits in subnet field [0]:
Class B network is 172.22.0.0, 0 subnet bits; mask is /16
Configure AppleTalk on this interface? [no]: yes
Extended AppleTalk network? [no]: y
AppleTalk starting cable range [0]:
Configure IPX on this interface? [no]: yes
IPX network number [2]:
Step 12 Configure the interface Group-Async1:
Do you want to configure ISDN switch type? [yes]:
The following ISDN switch types are available:
[a] primary-4ess
[b] primary-5ess
[c] primary-dms100
[d] primary-net5
[e] primary-ntt
[f] primary-ts014
Enter the switch type [b]:
Step 13 Configure the controllers:
Note All incoming calls to the access server are handled by the controllers, which route calls to the appropriate place inside the access server for processing.
These controllers enable users to dial in via ISDN or analog modems.
Do you intend to allow users to dial in? [yes]:
There are 4 controllers on this access server. If you want to use the full capacity of the access server configure all controllers.
Controller T1 0,1,..etc in software corresponds to Port 0,1,..etc
on the back of the access server.
Configuring controller T1 0:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP? [yes]:
Note If you want to configure the access server for channelized T1, enter no to the above prompt.
Configuring controller T1 1:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP? [yes]:
Configuring controller T1 2:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP? [yes]:
Configuring controller T1 3:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP? [yes]:
When you have completed the initial configuration script, messages similar to the following appear:
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname 5300
enable secret 5 $1$zxxT$YZMzUP1/wQvyLn5cWeyPu.
enable password guessme
line vty 0 4
password guessagain
snmp-server community public
!
appletalk routing
no decnet routing
ip routing
no clns routing
ipx routing
no vines routing
no xns routing
no apollo routing
no bridge 1
!
line 1 48
speed 115200
flowcontrol hardware
login local
autoselect during-login
autoselect ppp
modem dialin
ip local pool setup_pool 172.20.30.40 172.20.30.88
!
username user password passwd
!
arap network 1 ARA Dialins
line 1 48
arap enable
autoselect arap
!
! Turn off IPX to prevent network conflicts.
interface Ethernet0
no ipx network
interface FastEthernet0
no ipx network
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 172.21.40.10 255.255.0.0
appletalk address 10.0
appletalk zone etherzone
ipx network 1
no mop enabled
!
interface FastEthernet0
duplex full
speed 100
ip address 172.22.50.10 255.255.0.0
appletalk cable-range 0-0 0.0
appletalk discovery
ipx network 2
no mop enabled
!
Interface Group-Async1
group-range 1 48
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap pap
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
!
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
!
controller T1 0
pri-group timeslots 1-24
framing esf
linecode b8zs
!
interface serial0:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
dialer-group 1
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 list 101
!
controller T1 1
pri-group timeslots 1-24
framing esf
linecode b8zs
!
interface serial1:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
dialer-group 1
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 list 101
!
controller T1 2
pri-group timeslots 1-24
framing esf
linecode b8zs
!
interface serial2:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
dialer-group 1
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 list 101
!
controller T1 3
pri-group timeslots 1-24
framing esf
linecode b8zs
!
interface serial3:23
isdn incoming-voice modem
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
dialer-group 1
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 list 101
!
router igrp 15
redistribute connected
network 172.21.0.0
network 172.22.0.0
!
end
Step 14 Enter yes to save the configuration or enter no to erase it:
Note Entering
No, returns you to the enable mode (#) prompt. At this point, you can restart the setup script and begin again.
Use this configuration? [yes/no]: yes
Building configuration...
Use the enabled mode 'configure' command to modify this configuration.
Press RETURN to get started!
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet0, changed state to up
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Ethernet0, changed state to up
<Additional messages omitted.>
Step 15 When the messages stop displaying on your screen, press Return to get the prompt:
5300>
%AT-6-ONLYROUTER: Ethernet0: AppleTalk port enabled; no neighbors found
Note If you see this message, it means that no other AppleTalk routers were found on the network attached to the port.
Step 16 Continue the configuration. The 5300> prompt indicates that you are now at the CLI and you have just completed a basic access server configuration. However, this is not a complete configuration. At this point you have two choices:
- Run the setup script again and create another configuration. Enter the following:
5300> enable
Password: <password>
5300# setup
- Modify the existing configuration or configure additional features with the CLI as described in the next chapter.
At this point you can proceed to:
- The next chapter "Cisco IOS Software Survival Skills" to learn how to use the CLI to configure additional features.
- The chapter "Access Service Security" to configure security on the access server.
- The Cisco IOS software configuration guide and command reference publications for more advanced configuration topics. These publications are available on the Documentation CD-ROM that came with your access server, on the World Wide Web from Cisco's home page, or you can order printed copies.


