|
|

This document provides information about a new series of features for CiscoSecure Access Control Server (ACS) 2.1 for UNIX that became available after the user guide was printed. Use this document in conjunction with the CiscoSecure Access Control Server User Guide publication.
This document contains the following sections:
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more up to date than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription.
You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com, http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com. From here, you can send Cisco your comments on any document by clicking the Feedback button, selecting MarketPlace, and clicking Enter the feedback form.
If you have questions or need help, refer to the section "Cisco Connection Online" at the end of this document.
The CiscoSecure Access Control Server software now includes an updated user interface that includes User Administration, a group of options for managing and sorting CiscoSecure users. This graphical user interface (GUI) is easier to use and offers several new options that enable system administrators to:
In addition to new options, the interface has been rewritten and redesigned to run more quickly than previous versions.
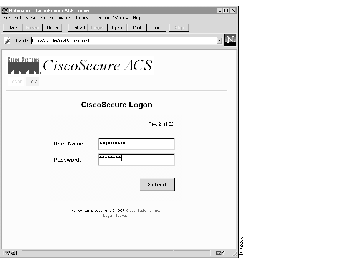
Users log on as in previous versions. See Figure 1. Depending on user privileges, users see the CSUser screen or the CiscoSecure Main menu.
The Main menu opens only if the user provides a name and password with Administrator privilege level. See Figure 2. This screen enables the administrator with to:
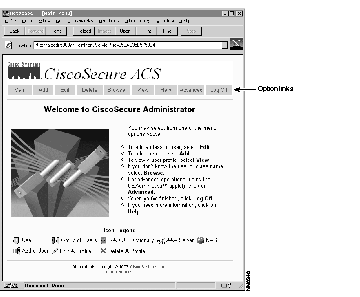
Several options appear at the top of the page:
Each of these options appears on every menu and form throughout the User Administration Functions program, so there is no need to return to the Main menu to access a new function.
The following sections provide instructions on how to use each of these options.
This section describes the tasks you can perform using the User Administration functions.
At any point during the course of the User Administration program, click Main to return to the Main menu.
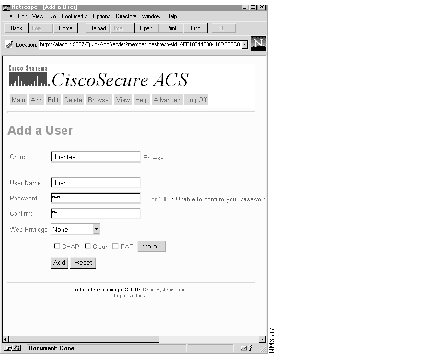
To add a user to the database for CiscoSecure, use the Add a User function:
Step 1 Click Add from anywhere within the User Administration program. The Add a User menu shown in Figure 3 opens.
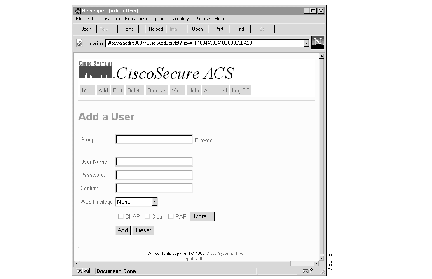
Step 2 Specify the group to which this user will belong.
If you need to search the database for the correct group, click Browse... to the right of the field. The Browse screen opens. For more information on using the Browse function, refer to the section "Browse Option."
Step 3 Tab to or click in the User Name field.
Step 4 Enter the new user's name in the User Name field.
Step 5 Tab to or click the Password field.
Step 6 Enter a password for this user. An asterisk appears in place of each letter.
Step 7 Tab to or click the Confirm field and enter the password again.
The Password and Confirm entries must agree. If the entry in the Password field does not agree with the entry in the Confirm field, you are prompted to retype your entry.
Step 8 Click any of the three check boxes to indicate the type of password error handling you require for this user:
Step 9 Specify the privilege level this user can exercise using the Web Privilege scroll box. There are three levels:
Step 10 Click More to access more authentication options for this user. The Add a User menu changes to offer more options, as shown in Figure 4.
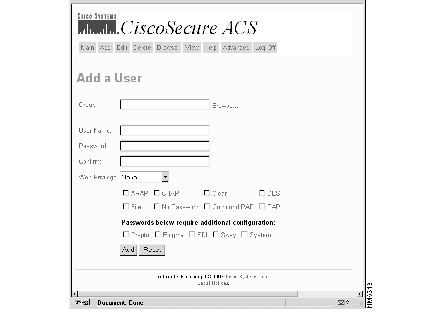
The additional fields in this version of the Add a User menu include several new authentication methods:
Each of these encryption types require custom configurations. For more information on S/Key, refer to "Carrying Out Advanced Management Operations" in the CiscoSecure ACS 2.1.2 for UNIX User Guide. For more on CRYPTOCard, Secure Computing, and SDI, refer to "Token Server Support."
Step 11 Select one or more of the check boxes if any of the additional protocols are required.
Step 12 When you have finished, click one of the following:
To edit the parameters or attributes for a user in the CiscoSecure database, use the Edit a User function:
Step 1 Click the Edit button from anywhere within the User Administration program. The initial Edit a User window opens. See Figure 6.
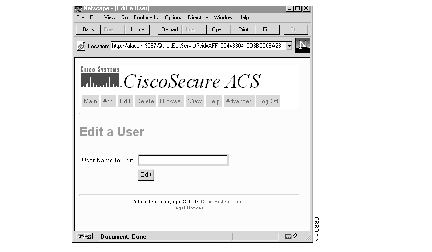
Step 2 At the User Name to Edit field, enter the name of the user whose password and privilege you want to edit. If you do not know the name of the user you want to edit, click Browse at the top of the menu.
Step 3 When the name you need appears in the User Name to Edit field, click Edit.
Editing can also be done by clicking Browse, then clicking the pencil icon next to a specified user profile. For more on this, see the section "Browse Option."
The full Edit a User menu opens. See Figure 7.
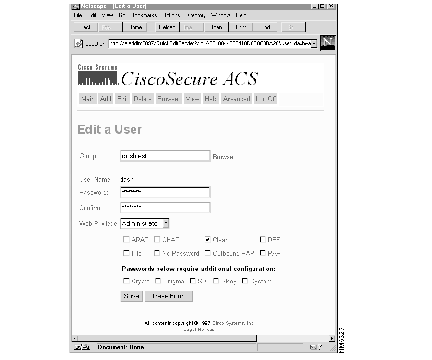
Step 4 Specify the group to which this user belongs, if required. If the specified user is a member of another group, the user is reassigned to the group you have just specified.
If you need to search the database for the correct group, click Browse to the right of the field. The Browse screen opens.
Step 5 Tab to or click the Password field.
Step 6 Enter a password for this user. An asterisk appears for each letter you enter.
Step 7 Tab to or click the Confirm field and enter the password again.
The Password and Confirm entries must agree. If the entry in the Password field does not agree with the entry in the Confirm field, you are prompted to enter the password again.
Step 8 If required, select from among these check box options:
Step 9 If required, select and deselect one or more of these check box options:
Each of these encryption types requires custom configurations. For more information on S/Key, refer to "Carrying Out Advanced Management Operations" in the CiscoSecure ACS 2.1.2 for UNIX User Guide. For more on CRYPTOCard, Secure Computing, and SDI, refer to "Token Server Support in the CiscoSecure ACS 2.1.2 for UNIX User Guide."
Step 10 When you have finished, click one of the following:
If you select Save, a confirmation of the edit appears. See Figure 8.
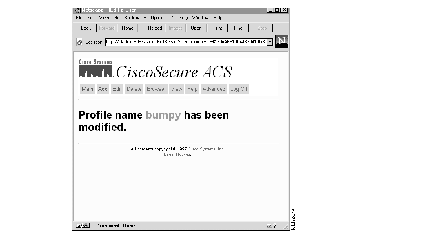
Step 11 Continue to edit users as required or click Main to return to the Main menu.
To delete a user from the CiscoSecure database, use the Delete a User function.
Step 1 Click Delete from anywhere within the User Administration program. The Delete a User window opens. See Figure 9.
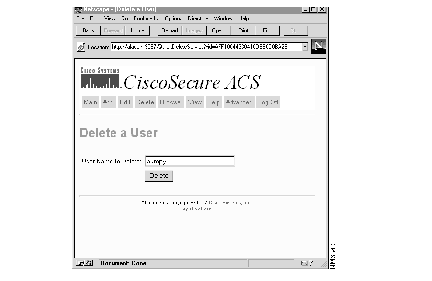
At the User Name field, enter the name of the user whose profile you want to delete.
If you do not know the name of the user you want to delete, click Browse at the top of the menu and delete the user through that option.
Step 2 When the name you need appears in the User Name field, click Submit.
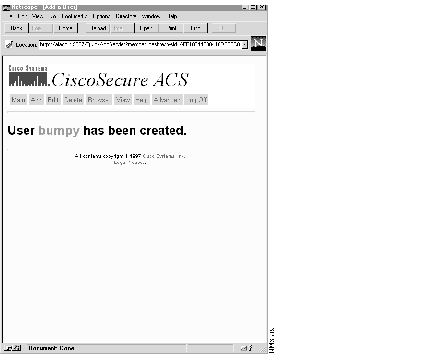
If you click Submit, a message appears (similar to Figure 10) indicating that the name has been deleted.
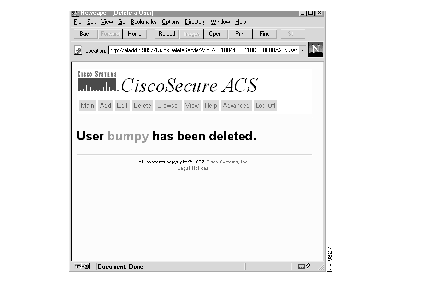
Step 3 Continue to delete users as required.
Step 4 When you are finished, click Main to return to the Main menu.
The Browse option can be used to view both users and groups in the CiscoSecure database. Through this option, you can:
To access a user or group directly, use the View option (refer to the section "View Option").
To browse the CiscoSecure database:
Step 1 Click Browse from anywhere within the User Administration program. The User Quick Browse menu opens, as shown in Figure 11.
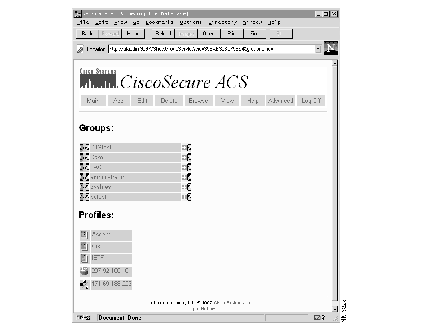
This screen consists of two sections:
In addition to names, each section contains several symbols. The names to the right of these icons serve as links to other menu options within the program. The icons commonly found in the Groups section are described below.
| Icon | Definition and Function |
 | A group. Click this symbol to access the Profile and member information for the specified group. |
 | A user. Click this symbol to access the Profile information for the specified user. |
 | Add a user to the specified group. This is another way to access the Add a User screen. |
 | This represents one of the RADIUS dictionaries stored in the database. These include IETF, Cisco, and Ascend. The HTML-based GUI is not designed to edit these dictionaries. |
| This represents a Network Access Server (NAS). All values to the right of this indicate the NAS configuration. The HTML-based GUI is not designed to edit this information. |

| This represents a AAA Server (one type of which is a CiscoSecure ACS). All values to the right of this indicate the AAA configuration. The HTML-based GUI is not designed to edit this information. |
 | Edit the specified user. This is another way to access the Edit a User screen. |
 | Delete the specified user. This is another way to access the Delete a User screen. |
Step 2 To view the profile for a specific group or user, click the group/user name. Alternatively, click the icon to the left of the name.
A group or user profile for the selected item appears as in the sample group profile shown in Figure 12.
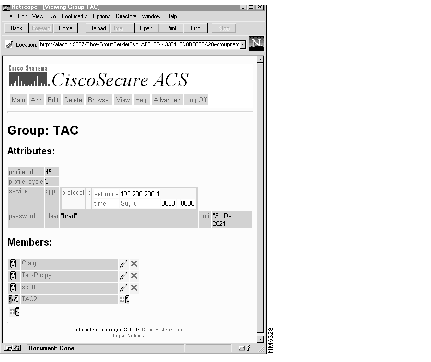
Several new icons appear on this screen. These icons are described below.
| Icon | Definition and Function |
 | Edit the specified user. This is another way to access the Edit a User screen. |
 | Delete the specified user. This is another way to access the Delete a User screen. |
For more on deciphering the meaning of the terms and statistics appearing in the profiles, refer to the section "View Option."
Step 3 Click the icons indicated above to add users to a specific group, edit a specific user profile, or delete a user from the database.
Step 4 Review data and perform operations as required. To return to the Main menu, click Main.
The profiles appearing on these screens are sometimes complex. To help you interpret the attributes which are displayed in a profile, refer to the section "View Option."
Use the View option to see the profile for a selected user or group. Depending on the complexity of the values assigned to a particular user or group, the profile can contain many different attributes, each of which is defined in this section. To view a selected profile:
Step 1 Click View. A screen similar to the one shown in Figure 13 opens.
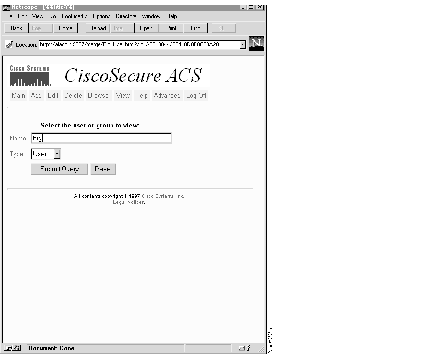
Step 2 If this is a user, make sure User is selected from the option list below the Name field.
Step 3 If this is a group, select Group from the option list.
Step 4 Enter the user or group name in the Name field.
If you cannot remember the name, click Browse to look through the entire database.
Step 5 Click Submit Query. A screen similar to the one shown in Figure 14 opens.
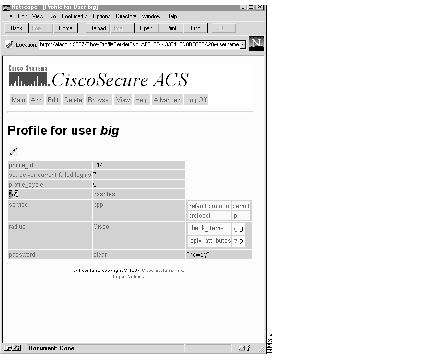
This provides a profile of the selected user or group. While the example profile above is relatively simple, the profile can contain a great deal of information on the attributes and values assigned to the selected user or group.
To learn more about an attribute, click the attribute word. Each attribute word is linked to its definition. For more on this, see "Profile Attributes and Values" below.
Step 6 When you are finished reviewing the profile, select View to see another profile, or click another button to access another function.
The profile on the View screen can contain information on any number of attributes assigned to a selected user or group. Attributes are derived from several internetworking protocols, including Terminal Access/ Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) and Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS).
Attributes are normally arranged by rows with greater levels of detail arranged in columns from left to right. So, for example, the Password attribute usually follows the rows identifying the profile_id, profile_cycle, and group name. In the password row, there are a number of columns that define (from left to right): the attribute name, the password type, the password value, and the beginning and ending dates when this password is effective.
The most common attributes and their meanings are shown in the table:
| Attribute | Definition | Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| profile_id | ID number assigned to the profile by the database. This number is generated internally and cannot be edited by the user. | |||||||
| profile_cycle | This number starts at 1 and is incremented by one each time the profile is modified. This number is generated internally and cannot be edited by the user. | |||||||
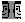 | If this is a user profile, the group to which the user is currently assigned. Groups can also be members of other groups. | |||||||
| password | Type of password; this is followed by the actual password in quotation marks, followed by the beginning and ending dates during which this password is effective. | CHAP, PAP, clear, and so on | ||||||
| privilege | Whether this profile is Web-enabled and what the privilege level is. There are three privilege levels.
Only valid when Privilege = Web. |
|
In many cases, the profile won't be more complicated than this. There are occasions, however, when profiles can be far more complex, particularly when a large number of authentication and response attributes have been assigned for a particular user or group. In such cases, the profile might look more like the example in Figure 15.
As the above example shows, a great deal of diverse information can be contained in a profile:
For complex profiles, it is usually better to put most of the attributes into a group, and create users in that group. It is far more common to have many users with nearly identical attributes (like protocol specifications) than to have a group with many diverse individuals. Since groups can be nested within other groups, additional detail can be layered in by creating sub-groups to hold families of users. For example, you might put all the common security information in a group called "Acme Sprockets" then create a group for Acme Sprockets employees in San Raphael to handle specifics of their locale. The San Raphael group would be a member of Acme, the San Raphael employees would be a member of San Raphael.
Many possible authentication attributes are defined below:
TACACS+ Attributes
The attributes and values for TACACS+ protocol are shown here:
| Attribute | Definition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| service | Indicates that this is an authorization request for starting a primary service. | slip, ppp, arap, shell |
| protocol | Network protocol that is a subset of the service. This attribute must be specified when the service is PPP to indicate that a protocol is being brought up as a secondary service. | lcp, ip, ipx, atalk, vines, unknown |
| cmd | Indicates the command name for a shell command that is to be run. | NULL = shell itself |
| cmd-arg | Indicates an argument for the shell command that is to be run. Multiple cmd-arg attributes can be specified and are order dependent. | |
| acl (access control list) | ASCII number representing a connection access list. Used only when service = shell and cmd = NULL. | |
| inacl | ASCII number for an interface input access list. | |
| outacl | ASCII number for an interface output access list. | |
| zonelist | A numeric zonelist value. Applicable to AppleTalk only. | |
| addr | A network address. | |
| addr-pool | The name of an address pool from which the NAS should assign an address. | |
| routing | Specifies whether routing information is to be propagated to and accepted from this interface. | Boolean value |
| route | Indicates a route that is to be applied to this interface. Values must be of the form:
dst_address mask routing_addr If routing_addr is missing, the current interface is used. | |
| timeout | Sets a value, in minutes, after which a session is terminated. Does not work for PPP. A value of zero indicates no timeout. This is NOT available on Cisco IOS Release 11.0, but is available on Cisco IOS Release 11.1 and Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Used for ARAP. | 0 - nn where
0 = no timeout |
| idletime | Sets a value, in minutes, after which an idle session is terminated. Does not work for PPP. A value of zero indicates no timeout. This is NOT available on Cisco IOS Release 11.0, but is available on IOS versions 11.1 and 11.2. | 0 - nn where
0 = no timeout |
| autocmd | An auto-command to run. Used only when service = shell and cmd = NULL. | |
| noescape | Prevents user from using an escape character. Used only when service = shell and cmd = NULL. | Boolean |
| nohangup | Do no disconnect after an automatic command. Used only when service = shell and cmd = NULL. | Boolean |
| priv_lvl | Privilege level to be assigned. | 1 - 15 |
| callback-dialstring | Number the NAS will call back. | NULL = dialstring |
| callback-line | Line the NAS uses to call back the user. | |
| callback-rotary | Rotary number to use for a callback. | |
| nocallback-verify | Indicates a connection doesn't require authentication after callback. | 1 |
RADIUS Attributes
If the RADIUS protocol is specified, a list of attributes is displayed to the right of the RADIUS column. The access request attributes and values for the RADIUS protocol are shown here. Because RADIUS and Ascend share many attributes in common, both are represented here. Where nomenclature or values differ, those differences are noted:
| Attribute (number) | Definition | Value(s) |
|---|---|---|
| User-Name (1) | Indicates the name of the user to be authenticated. Only used in Access-Request packets. | |
| User-Password (2) | The user's name. Only used in Access-Request packets. | |
| CHAP-Password (3) | The user's CHAP password if CHAP is specified and a password challenge is permitted. Only used in Access-Request packets. | |
| NAS-IP-Address (4) | Indicates the identifying IP address. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| NAS-Identifier (4) | IP address of the MAX authenticating the user. Only used in Ascend Access-Request packets. | |
| NAS-Port (5) | Specifies the port on the MAX handling the user session. Only used in Access-Request packets. | 0 = no port calculated |
If the attribute values submitted to the RADIUS server match the user profile, the server authenticates the call and returns an Access-Accept packet containing a list of attributes for the authenticated user. These attributes appear to the right of the RADIUS and Access Response columns. The possible access response attributes are shown here:
| Attribute (number) | Definition | Value(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Callback-Number (19) | Indicates a dialing string to be used for callback. Can be used as a hint to the server that a callback service is desired. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Callback-Id (20) | Indicates the name of a place to be called as interpreted by the NAS. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Caller-Id (31) | The calling party number indicating the phone number of the user connected to this MAX. | |
| CHAP-Challenge (60) | Contains the CHAP challenge sent by the NAS to a PPP CHAP user. | |
| Class (25) | A value sent to the client from the server. In Ascend, value should be sent as part of an authentication-acceptance message. In RADIUS, value should be sent unmodified to accounting server as part of Accounting-Request packet. | |
| Called-Station-ID or Client-Port-DNIS (30) | The called party number, indicating the phone number dialed by the user to connect to this NAS using Dialed Number Identification (DNIS). | |
| Calling-Station-Id (31) | Allows the NAS to send in the Access-Request packet the phone number that the call came from, using Automatic Number Identification (ANI). Use for RADIUS. | |
| Filter-Id (11) | Indicates the name of the filter list for this user. Use for RADIUS. | |
| Framed-Address (8) | IP address of the user. Use for Ascend version of RADIUS. Field is four octets. | |
| Framed-AppleTalk- Link (37) | Indicates the AppleTalk network number that should be used for the serial link to the user (which should be another AppleTalk router). Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Framed-AppleTalk- Network (38) | Indicates the AppleTalk network number the NAS should probe to allocate an AppleTalk node for the user. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Framed-AppleTalk- Zone (39) | Name of the default AppleTalk Zone for this user. | |
| Framed-Compression (13) | Indicates compression protocol to use for the link. Use for RADIUS. | 0 = none 1 = VJ TCP/IP header 2 = IPX header |
| Framed-IP-Address (8) | IP address of the user. Use for RADIUS. Field is four octets. | |
| Framed-IP-Netmask (9) | Indicates the IP netmask to be configured for the user when the user is a router to a network. Use for RADIUS. | |
| Framed-IPX-Network (23) | Indicates the unique, internal IPX network number to be configured for the user. | 0xFFFFFFFFE = NAS should select an IPX network for the user. All other values used as IPX network for link. |
| Framed-MTU (12) | Indicates the Maximum Transmission Unit to be configured for the user when it is not negotiated by some other means, such as PPP. Use for RADIUS only. | 64 - 65535 |
| Framed-Protocol (7) | Indicates framing to be used for framed access. | ppp, slip, arap, mpp, euraw, euui, comb, fr |
| Framed-Route (22) | A static route when User-Service = Dialout-Framed User | IP_addr gateway_addr metric [private] [RADIUS profile] |
| Framed-Routing (10) | Indicates the routing method for the user when the user is a router to a network. Only used in Access-Accept packets with RADIUS. | 0 = none 1 = send routing pkts 2 = listen for rtg pkts 3 = send and listen |
| Idle-Timeout (28) | Sets the maximum time (in seconds) idle connection is allowed to the user before termination of the session or prompt. | |
| Login-Host (14) | The host to which the Login-User connects on login. | |
| Login-LAT-Group (36) | Contains a string identifying the LAT group codes this user is authorized to use. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Login-LAT-Node (35) | Indicates the node with which the user is to be automatically connected by the LAT. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Login-LAT-Port | Indicates the port with which the user is to be connected by LAT. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Login-LAT-Service (34) | Indicates the system the user is going to be connected to. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Login-Service (15) | The type of terminal server session. | 0 = Telnet 1 = Rlogin 2 = TCP Clear 3 = PortMaster 4 = LAT |
| Login-TCP-Port (16) | The port number to which a TCP session connects. | 0 - 65535 23 = default |
| NAS-Identifier (32) | Contains a string identifying the NAS originating the Access-Request packet. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| NAS-IP-Address (32) | The IP address of the MAX. | |
| NAS-Port-Type (61) | Indicates the type of physical port for the NAS authenticating the user. Can be used in addition to or instead of NAS-Port (5). Use for RADIUS only. | 0 = Async 1 = Sync 2 = ISDN Sync 3 = ISDN Async v.120 4 = ISDN Async v.110 5 = Virtual |
| Port-Limit (62) | Sets the maximum number of ports to be provided to the user by the NAS. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Proxy-State (33) | Available to be sent by a proxy server to another server when forwarding an Access-Request and must be returned unmodified. This attribute should be removed by the proxy server before the response is forwarded to the NAS. Use for RADIUS only. | |
| Reply-Message (18) | Indicates texts which might be displayed to the user. (Message text sent from the RADIUS server to the MAX.) | |
| Service-Type (6) | Indicates the type of service the user has requested. Use for RADIUS only. | Login, Framed, Callback Login, Callback Framed, Outbound, Administrative, NAS Prompt, Authenticate Only, Callback NAS Prompt |
| Session-Timeout (27) | Sets the maximum time (in seconds) service is provided to the user before termination of the session or prompt. | |
| Termination-Action (29) | Indicates what action the NAS should take when the specified service is completed. Use for RADIUS only. | 0 = Default 1 = RADIUS-Request |
| User-Service (6) | Specifies whether this is a framed or unframed call. Use for Ascend extension of RADIUS. | Framed-User, Login-User, Dialout-Framed-User |
| Vendor-Specific (26) | Value enables vendors to support their own extended attributes not suitable for general usage. |
RADIUS Ascend Attributes
In addition to RADIUS access response attributes, there are a group of attributes specific to Ascend. These are defined only in the Ascend RADIUS dictionary file and require the Ascend RADIUS daemon. Ascend attributes appear to the right of the 'RADIUS' and 'Ascend' columns. A list of these is shown here:
| Attribute (number) | Definition | Value(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Ascend-Authen-Alias (203) | Sets this MAX's login name during PPP authentication. | |
| Ascend-Callback (245) | Enables or disables callback. | |
| Ascend-Call-Filter (243) | Defines a call filter. | |
| Ascend-Data-Filter (242) | Defines a data filter. | |
| Ascend-FR-Direct (219) | Specifies whether the Connection Profile operates in Frame Relay redirect mode. | |
| Ascend-FR-Direct- DLCI (221) | Specifies the DLCI that carries this connection to the Frame Relay switch. | |
| Ascend-FR-Direct- Profile (220) | Specifies the name of the Frame Relay Profile that carries this connection to the Frame Relay switch. | |
| Ascend-Handle-IPX (222) | Specifies how the MAX handles NCP watchdog requests on behalf of IPX clients during IPX bridging. | |
| Ascend-Home-Agent-IP (183) | The IP address of the home agent under ATMP (Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol) operation. | |
| Ascend-Home-Agent-Password (184) | The password that the foreign agent sends to the home agent during ATMP operation. | |
| Ascend-Home-Agent-UDP-Port (186) | The UDP port number to use when the foreign agent sends ATMP messages to the home agent. | |
| Ascend-Home-Agent- Network-Name (185) | The name of the Connection Profile by which the home agent sends all packets it receives from the mobile node during ATMP operation. | |
| Ascend-IP-Direct (209) | The IP address to which the MAX redirects packets from the user. | |
| Ascend-IPX-Alias (224) | An IPX network number to use when connecting to IPX routers that require numbered interfaces. | |
| Ascend-Menu-Item (206) | Defines a single menu item for a user profile. | |
| Ascend-Menu- Selector (205) | Specifies a string as a prompt for user input in the terminal server menu interface. | |
| Ascend-Netware- timeout (223) | The number of minutes the MAX responds to NCP watchdog requests on behalf of IPX clients on the other side of an offline IPX bridging or routing connection. | |
| Ascend-PPP-Address (253) | The IP address reported to the calling unit during PPP IPCP negotiations. | |
| Ascend-PPP-Async-Map (212) | Gives the Ascend PPP code the async control character map for the PPP session. | |
| Ascend-PPP-VJ-1172 (211) | Instructs the Ascend PPP code to user the 0x0037 value for the VJ compression packets. | |
| Ascend-PPP-VJ-Slot-Comp (210) | Instructs the Ascend PPP code not to use slot compression when sending VJ-compressed packets. | |
| Ascend-PW- Expiration (21) | An expiration date for the user's password. | mmmddyyyy (such as oct021997) |
| Ascend-PW-Lifetime (208) | Specifies on an individual user basis the number of days that a password is valid. | |
| Ascend-Require-Auth (201) | Specifies whether additional authentication is required for CLID-authenticated calls. | |
| Ascend-Receive- Secret (215) | A value received from a dial-in user and used to verify an encrypted password. | |
| Ascend-Route-IPX (229) | Enables IPX routing. | |
| Ascend-Send-Auth (231) | Specifies the protocol to use for name-password authentication following CLID authentication. | PAP, CHAP |
| Ascend-Send-Secret (214) | When used in place of Ascend-Send-Passwd attribute, the password is encrypted when passed between the RADIUS server and the MAX. | |
| Ascend-Third-Prompt (213) | An additional prompt for user input after the login and password prompts. | |
| Ascend-Token- Expiry (204) | Sets the lifetime of a cached token - that is, the lifetime of hand-held security card authentication. | |
| Ascend-Token-Idle (199) | The maximum length of time in minutes a cached token can remain alive between authentications if a call is idle. | |
| Ascend-Token- Immediate (200) | Establishes how RADIUS treats the password received from a login-user when the user's file entry specifies a hand-held security card server. |
An additional pair of Ascend attributes explain connection and request states:
These attributes contain return values that explain the cause of the connection or disconnection.
| Attribute | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Ascend-Disconnect- Cause (195) | unknown (2) clidAuthFail(4) noModemNoCarrier(10) noModemLossCarrier(11) noModemResultCodes(12) tsUserExit(20) tsIdleTimeout(21) tsExitTelnet(22) tsNoIPAddr(23) tsExitTcp(24) tsPassWordFail(25) tsRawTCPDisable(26) tsControlC(27) tsDestroyed(28) pppLcpTimeout(40) pppLcpNegotiateFail(41) pppPAPAuthFail(42) pppCHAPAuthFail(43) pppRemoteAuthFail(44) pppRcvTerminate(45) pppCloseEvent(46) sessTimeOut(100) sessFailSecurity(101) sessCallback(102) invalidProtocol(120) | Reason unknown Failure to authenticate calling-party number No carrier detected Loss of carrier Failure to detect modem result codes User exited terminal server Timeout waiting for user input Disconnect due to exiting Telnet session Could not switch to SLIP/PPP. Remote has no IP address Disconnect due to exiting raw TCP Bad passwords Raw TCP disabled Control-C detected Terminal server destroyed PPP LCP negotiation timed out PPP LCP negotiation failed PPP PAP authentication failed PPP CHAP authentication failed PPP remote authentication failed PPP received Terminate Request from remote end Upper layer requested session close Session timed out Session failed for security reasons Session terminated due to callback Call refused because detected protocol is disabled |
| Ascend-Connect- Progress (196) | prUnknown(2) prCallUp(10) prModemUp(30) prModemWaitDCD(31) prModem Wait Codes(32) prTermSvrStarted(40) prLanSessionUp(60) prOpeningLCP(61) prOpeningCCP(62) prOpeningIPNCP(63) prOpeningBNCP(64) prLCPOpened(65) prCCPOpened(66) prIPNCPOpened(67) prBNCPOpened(68) prLCPStateInitial(69) prLCPStateStarting(70) prLCPStateClosed(71) prLCPStateStopped(72) prLCPStateClosing(73) prLCPStateStopping(74) prLCPStateReqSent(75) prLCPStateAckRecd(76) prLCPStateAckSent(77) | Progress unknown Call up Modem up Waiting for DCD Waiting for result codes Terminal server session started up LAN session up LCP negotiations allowed CCP negotiations allowed IP NCP negotiations allowed Bridging NCP negotiations allowed LCP in open state CCP in open state IP NCP in open state Bridging NCP in open state LCP in initial state LCP in starting state LCP in closed state LCP in stopped state LCP in closing state LCP in stopping state LCP in request sent state LCP in ACK received state LCP in ACK sent state |
Cross Reference of Attributes by Number
| Number | Cisco Attribute Name | RADIUS/Ascend Attribute Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | User-Name | User-Name |
| 2 | User-Password | User-Password |
| 3 | CHAP-Password | Challenge-Response |
| 4 | NAS-IP-Address | NAS-Identifier |
| 5 | NAS-Port | NAS-Port |
| 6 | Service-Type | User-Service |
| 7 | Framed-Protocol | Framed-Protocol |
| 8 | Framed-IP-Address | Framed-Address |
| 9 | Framed-IP-Netmask | Framed-Netmask |
| 10 | Framed-Routing | Framed-Routing |
| 11 | Filter-Id | Framed-Filter |
| 12 | Framed-MTU | Framed-MTU |
| 13 | Framed-Compression | Framed-Compression |
| 14 | Login-IP-Host | Login-Host |
| 15 | Login-Service | Login-Service |
| 16 | Login-TCP-Port | Login-TCP-Port |
| 17 | Change-Password | |
| 18 | Reply-Message | Reply-Message |
| 19 | Callback-Number | Callback-Number |
| 20 | Callback-Id | Callback-Name |
| 22 | Framed-Route | Framed-Route |
| 23 | Framed-IPX-Network | Framed-IPX-Network |
| 24 | State | |
| 25 | Class | Class |
| 26 | Vendor-Specific | |
| 27 | Session-Timeout | |
| 28 | Idle-Timeout | |
| 29 | Termination-Action | |
| 30 | Called-Station-Id | Client-Port-DNIS |
| 31 | Calling-Station-Id | Caller-Id |
| 32 | NAS-Identifier | NAS-IP-Address |
| 33 | Proxy-State | |
| 34 | Login-LAT-Service | |
| 35 | Login-LAT-Node | |
| 36 | Login-LAT-Group | |
| 37 | Framed-AppleTalk-Link | |
| 38 | Framed-AppleTalk-Network | |
| 39 | Framed-AppleTalk-Zone | |
| 40 | Acct-Status-Type | |
| 41 | Acct-Delay-Time | |
| 42 | Acct-Input-Octets | |
| 43 | Acct-Output-Octets | |
| 44 | Acct-Session-Id | |
| 45 | Acct-Authentic | |
| 46 | Acct-Session-Time | |
| 47 | Acct-Input-packets | |
| 48 | Acct-Output-packets | |
| 60 | CHAP-Challenge | |
| 61 | NAS-Port-Type | |
| 62 | Port-Limit | |
| 63 | Login-LAT-Port | |
| 183 | Ascend-Home-Agent-IP-Addr | |
| 184 | Ascend-Home-Agent-Password | |
| 185 | Ascend-Home-Network-Name | |
| 186 | Ascend-Home-Agent-UDP-Port | |
| 187 | Ascend-Multilink-ID | |
| 188 | Ascend-Num-In-Multilink | |
| 189 | Ascend-First-Dest | |
| 190 | Ascend-Pre-Input-Octets | |
| 191 | Ascend-Pre-Output-Octets | |
| 192 | Ascend-Pre-Input-packets | |
| 193 | Ascend-Pre-Output-packets | |
| 194 | Ascend-Maximum-Time | |
| 195 | Ascend-Disconnect-Cause | |
| 196 | Ascend-Connect-Progress | |
| 197 | Ascend-Data-Rate | |
| 198 | Ascend-PreSession-time | |
| 199 | Ascend-Token-Idle | |
| 200 | Ascend-Token-Immediate | |
| 201 | Ascend-Require-Auth | |
| 202 | Ascend-Number-Sessions | |
| 203 | Ascend-Authen-Alias | |
| 204 | Ascend-Token-Expiry (not supported) | |
| 205 | Ascend-Menu-Selector | |
| 206 | Ascend-Menu-Item | |
| 208 | Ascend-PW-Lifetime | |
| 209 | Ascend-IP-Direct | |
| 210 | Ascend-PPP-VJ-Slot-Comp | |
| 211 | Ascend-PPP-VJ-1172 | |
| 212 | Ascend-PPP-Async-Map | |
| 213 | Ascend-Third-Prompt | |
| 214 | Ascend-Send-Secret | |
| 215 | Ascend-Receive-Secret | |
| 216 | Ascend-IPX-Peer-Mode | |
| 217 | Ascend-IP-Pool-Definition | |
| 218 | Ascend-Assign-IP-Pool | |
| 219 | Ascend-FR-Direct | |
| 220 | Ascend-FR-Direct-Profile | |
| 221 | Ascend-FR-Direct-DLCI | |
| 222 | Ascend-Handle-IPX | |
| 223 | Ascend-Netware-Timeout | |
| 224 | Ascend-IPX-Alias | |
| 225 | Ascend-Metric | |
| 226 | Ascend-PRI-Number-Type | |
| 227 | Ascend-Dial-Number | |
| 228 | Ascend-Route-IP | |
| 229 | Ascend-Route-IPX | |
| 230 | Ascend-Bridge | |
| 231 | Ascend-Send-Auth | |
| 232 | Ascend-Send-Passwd | |
| 233 | Ascend-Link-Compression | |
| 234 | Ascend-Target-Util | |
| 235 | Ascend-Maximum-Channels | |
| 236 | Ascend-Inc-Channel-Count | |
| 237 | Ascend-Dec-Channel-Count | |
| 238 | Ascend-Seconds-Of-History | |
| 239 | Ascend-History-Weigh-Type | |
| 240 | Ascend-Add-Seconds | |
| 241 | Ascend-Remove-Seconds | |
| 242 | Ascend-Data-Filter | |
| 243 | Ascend-Call-Filter | |
| 244 | Ascend-Idle-Limit | |
| 245 | Ascend-Preempt-Limit | |
| 246 | Ascend-Callback | |
| 247 | Ascend-Data-Svc | |
| 248 | Ascend-Force-56 | |
| 249 | Ascend-Billing-Number | |
| 250 | Ascend-Call-By-Call | |
| 251 | Ascend-Transit-Number | |
| 252 | Ascend-Host-Info | |
| 253 | Ascend-PPP-Address | |
| 254 | Ascend-MMP-Idle-Percent |
Click Help to display information on the currently displayed screen.
The Advanced Configurator is the main mechanism for defining the attributes and groups which the User Administration GUI observe. For more on this function, refer to the CiscoSecure Access Control Server User Guide. To access the CiscoSecure Advanced Configurator:
Step 1 Click Advanced. A screen similar to the one shown in Figure 16 opens.
Step 2 To access the Advanced Configurator, click the Continue link. A menu similar to the one shown in Figure 17 opens.
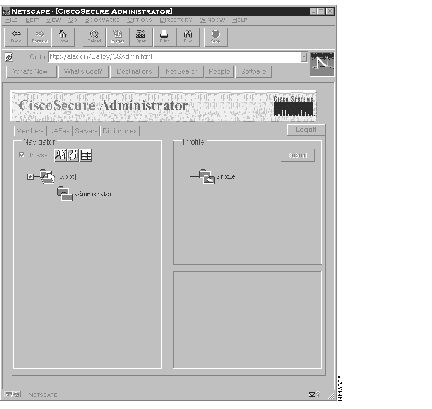
Step 3 To return to the User Administration functions, click Back on your browser.
Click Logoff to log off CiscoSecure. A message similar to the one in Figure 18 appears:
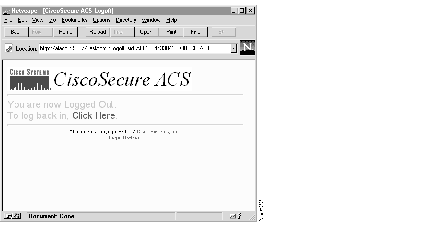
Step 4 To log back on, click the Click Here link.
If at any time, you either enter incorrect data or an illegal operation occurs, an error message appears in a window near the currently active field, as in the example in Figure 19.
These error messages are linked to more detailed explanations. To access the more detailed version of these error messages, click on the hyperlinked word or phrase in the displayed message. The error message list opens with the full description displayed.
A list of current error messages with brief explanations is shown below. Some troubleshooting information is also included.
| System Message | Meaning/Troubleshooting | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | No Such Error, Unsupported request, Invalid request data | There is a major problem between the application and the database, indicating that the application is not working properly. The user should never see these error messages. |
| 3 | Out of database connections | The current number of database requests has exceeded the ability of the application to service them. Wait for a moment and try again. |
| 4 | Request connection failed | The GUI application was unable to make a connection with the database server. Try again. If connection problems persist, contact your system administrator. |
| 5 | Request disconnection failed | When the user logs off, the disconnection failed due to server shutdown or some other disruption. If you can reconnect, there is no problem. |
| 6 | Request create record failed | User tried to create a record and the operation failed. This can be caused by severe problems in the database or a momentary problem reaching the database. Try the operation again. If it fails again, you might have to recreate your database. |
| 7 | Request delete record failed | User tried to delete a record and the operation failed. This can be caused by severe problems in the database or a momentary problem reaching the database. Try the operation again. If it fails again, you might have to recreate your database. |
| 8 | Request update record failed | User tried to update/edit a record and the operation failed. This can be caused by severe problems in the database or a momentary problem reaching the database. Try the operation again. If it fails again, you might have to recreate your database. |
| 9 | Request replace record failed | User tried to replace the entire record and the operation failed. This can be caused by severe problems in the database or a momentary problem reaching the database. Try the operation again. If it fails again, you might have to recreate your database. |
| 10 | Request get record failed | User tried to access a record and failed to get it. This can be caused by a bad connection to the database. Try reconnecting. If this doesn't work, the record might not exist or the database might be corrupted. |
| 11 | Request lock on record failed | User tried to lock a record and the operation failed. This could mean that the record is already locked. Try unlocking and relocking the record. If this fails, the record might not exist or the database might be corrupted. |
| 12 | Request unlock on record failed | User tried to unlock a record and the operation failed. This could mean that the record is already unlocked. Try locking the record. If this fails, the record might not exist or the database might be corrupted. |
| 13 | Request query record failed | User tried to access a query record and the operation failed. This can be caused by a bad connection to the database. Try reconnecting. If this doesn't work, the record might not exist or the database might be corrupted. |
| 14 | Accounting request insert failed | User tried to add an accounting record to the database and the operation failed. The connection to the database might be bad or the database might be corrupted. Try reconnecting and reinserting the record in the accounting database. |
| 15 | Accounting request get failed | User tried to access an accounting record from the database and the operation failed. The connection to the database might be bad or the database might be corrupted. Try reconnecting and reaccessing the record in the accounting database. |
| 16 | Administration request failed | Internal administrative error indicating that an administrative request failed. This indicates serious problems with the application and/or database. The user should never see this error. |
| 17 | Packet version number invalid | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 18 | Packet length incorrect | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 19 | Packet type value out of range | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 20 | Packet client identifier invalid | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 21 | Packet session identifier invalid | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 22 | Packet encryption type invalid | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 23 | Packet contains an invalid key | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 24 | Packet protocol data error | Internal application error. The client and server are not running the same version of this application. The user should never see this error. |
| 25 | Database: record locked by another user | User tried to lock a record which is already locked. Another user has previously locked this record. |
| 26 | Database: consistency error | Program has detected inconsistencies within the database. This usually indicates that the database has been corrupted and must be rebuilt. Contact your administrator. |
| 27 | Database: request data error | User requested data that is bad or invalid. Try the request again. If problems persist, there might be something wrong with the database. Contact your administrator. |
| 28 | Database: result generation error | Internal server error. The server could not generate a result for a received request. |
| 29 | Database: unable to delete record | The server was unable to delete a record despite a user request. Try deleting the record again. If the problem persists, the record might not exist or there might be internal errors with the database. In the latter case, contact your administrator. |
| 30 | CGI: Reserved for more errors | This message reserved for future use. |
| 31 | CGI: Configuration file open error | The program could not read its configuration file. This usually means the program was installed improperly or incompletely. Reinstall the program. |
| 32 | CGI: Configuration file missing | The program could not find the configuration file. This usually means the file was not copied properly during installation. Reinstall the program. |
| 33 | CGI: Configuration file incomplete | The program found an incomplete configuration file. This usually means the file was not copied properly during installation. Reinstall the program. |
| 34 | CGI: Installation directory invalid | The program detected that the installation directory was invalid. Try reinstalling the program. If this doesn't work, get a new installation disk and try again. |
| 35 | CGI: Port number invalid | The port number identifying the server location is invalid. Check the port number in the configuration file to make sure it matches the server's port number. It this doesn't work, reinstall the program, making sure to specify the correct port number for CGI-to-server communications. |
| 36 | CGI: Major release number invalid | The client release number doesn't match the server release number, so the two cannot communicate. Check the client and server program major release numbers to make sure they are the same. If they aren't, change the client configuration file or perform a complete reinstallation. |
| 37 | CGI: Minor release number invalid | The client release number doesn't match the server release number, so the two cannot communicate. Check the client and server program minor release numbers to make sure they are the same. If they aren't, change the client configuration file or perform a complete reinstallation. |
| 38 | CGI: Client ID invalid | The client ID sent to the server is not a trusted ID. This means the ID is either illegal or unauthorized. Contact your system administrator to make sure this client ID is correct. If it isn't, assign a new ID. |
| 39 | CGI: Session file name invalid | The server couldn't find the client-side file containing the record of all client-server sessions. Either manually replace the session file in its proper directory or reinstall at the client to automatically generate a new session file. |
| 40 | CGI: Log authentication errors value invalid | When the client tried to log in, the server did not accept the authentication values. Check the client program configuration files to make sure the authentication attributes and values are valid for this client. If they aren't, edit the file accordingly. |
| 41 | CGI: Server host entry invalid | The server host name is bad. Check the client configuration file to make sure the host name is correct. If it isn't, edit the file accordingly. |
| 42 | CGI: Invalid HTTP GET request | Invalid request came from the application. Try again. |
| 43 | CGI: Unsupported HTTP method | The application sent an unsupported request to the CGI. Try again. |
| 44 | CGI: Socket open failed | CGI couldn't open a socket. The server might be down or the network is not functioning properly. Check the network to make sure it and the server are functioning properly. |
| 45 | CGI: Socket bind failed | CGI couldn't bind a socket. The server might be down or the network is not functioning properly. Check the network to make sure it and the server are functioning properly. |
| 46 | CGI: Connect socket failed | The CGI tried to connect a socket to the server, but failed. The server might be down or the network is not functioning properly. Check the network to make sure it and the server are functioning properly. |
| 47 | CGI: Response error data malformed | CGI got bad data back from the server and couldn't parse the information correctly. Try the operation again and see if the error recurs. If this fails, the database might be corrupted. |
| 48 | CGI: Invalid web user | CGI detected that the user trying to log in to the server does not have proper web authorization. Make sure this user has proper clearance to work on this system. |
| 49 | CGI: Session file open failed | CGI could not find the session file. Either the file is corrupted or has been unintentionally deleted. Check to make sure the session file does exist. If it doesn't, create a new one in the proper directory. |
| 50 | CGI: Session file lock failed | CGI detected that an attempt to lock the session file failed. This means that the file is already locked, the file is corrupted, or the file has been unintentionally deleted. Either replace the current session file or create a new one. |
| 51 | CGI: Session file unlock failed | CGI detected that an attempt to unlock the session file failed. This means that the file is already unlocked, the file is corrupted, or the file has been unintentionally deleted. Either replace the current session file or create a new one. |
| 52 | CGI: Session file not found | CGI could not find the session file. Either the file is corrupted or the file has been unintentionally deleted. Replace the session file or reinstall the client-side application to generate a new one. |
| 53 | CGI: Invalid user password | CGI detected that the user trying to log on to the server has an invalid password. Either issue the user a new password or check the configuration file to make sure it isn't corrupted. |
| 54 | CGI: Request type is out of range | The application sent a request type that the CGI found was out of acceptable range. Either replace the out-of-range value with an acceptable value by editing the configuration file or issue a new request type that is within range through the edit application. |
| 55 | CGI: System read error | The system (client or application) failed to read a message correctly. Retry the command or operation. If this problem persists, contact your system administrator. |
| 56 | CGI: Read data length invalid | The CGI detected a bad data length for the packet it just received from the client. Retry the operation. |
| 57 | CGI: Timeout parameter invalid | CGI detected that the current timeout parameter is invalid and out-of-range. Edit the configuration file to make sure the timeout value is within range or reinstall the application. |
| 58 | CGI: Unknown DB Server response | CGI detected a response from the database server that it did not recognize. This should not occur unless there is an internal program error. |
| 59 | CGI: Temporary file open error | CGI detected an error when the temporary file was opened. Retry the operation. If the error persists, create a new temp file. |
| 60 | The database currently does not support this request | The database server does not support this request. This is an internal programming error and should not occur. If it does, contact your system administrator. |
| 61 | Database connection has been closed unexpectedly, if this problem continues please see the database server's error log for details. | This usually indicates that a severe problem exists inside the database itself. If it recurs, contact your system administrator. |
| 62 | Profile data received contains illegal data format | Server received bad profile data from the application. This indicates some internal system error. Contact the system administrator. |
| 63 | A severe database SQL error occurred, please see the database server's error log for details | Server has detected a severe SQL runtime error from the application. Check the database server's error log for more information, then contact the system administrator. You might have to reboot the server or reinstall the application. |
| 64 | An unknown error occurred within the database server, please see the database server's error log for details | Server detected a runtime error while accessing/reading database files. Check the database server's error log for more information, then contact the system administrator. You might have to reboot the server or reinstall the application. |
| 65 | This profile name already exists, please choose a unique name | The profile name you are trying to add to the database already exists. Select a different name for this profile. |
| 66 | Illegal request, profile name or ID is required to process this request | Client generated an illegal request. Make sure the profile name and the ID are entered and valid for this request. If the problem persists, reinstall the application. |
| 67 | The number of available connections to the database has currently been reached. Please retry later. | The current number of requests to the database has exceeded the number of available connections. Wait for a moment and try again. |
| 68 | A severe internal database error has occurred, please see the database server's error log for details. | A severe database error has occurred affecting the database server. Check the database server's error log then contact the system administrator. This might require you to reboot the server or reinstall the application. |
| 69 | Requested profile either does not exist or is currently locked for a write update by the database. | The requested profile either does not exist or is currently being updated by the database. Check the database to make sure the profile exists. If it does but is locked, wait until the server is finished updating the profile, then try again. |
| 70 | Cannot delete group profiles that have existing member profiles | You cannot delete a group profile when individuals are still entered as members of the group. Delete the members of the group before deleting the group itself. |
| 71 | Invalid cycle number, you might want to get an updated copy of the profile | This profile is not current. Usually this means the data is currently being updated - either by the server or by another user. Wait a few seconds for the update to complete, then retry. |
| 72 | Cycle number is required to perform this request | Client application has not added a correct cycle number to this profile. Retry access. If this fails, restart the application. |
| 73 | The profile you requested was not found in the database | The profile you requested does not exist in the database. Either you have incorrectly identified the profile or the profile has been unintentionally deleted. |
| 74 | This QUERY request is not supported, try using GET request | The user has entered the wrong command arguments at the command line interface. Try using the GET request. |
| 75 | The group name specified does not exist. Must be a member of a pre-existing group | The group name you requested doesn't exist in the database. You cannot add a member to a nonexistent group. Either you have incorrectly identified the profile or the group profile has been unintentionally deleted. Either select an existing group or create a new group for this member. |
| 76- 79 | Database i/o message: reserved | These error messages have been reserved for future use. |
| 80 | Unable to perform this lock request due to an internal database error, please see the database server's error log for details | The server couldn't lock this data. A severe error has occurred to the database server. Please check the database server's log for details, then contact the system administrator. |
| 1000 | Unable to confirm your password, please enter your password again | The Confirm password entry did not match the initial password entry. Try entering the first password again at the Confirm field, or select a new password for the Password field and enter the same password at the Confirm field. |
| 1001 | Please enter your password twice to confirm | You have not entered the password for a second time. You must enter the password in both the Password and Confirm fields before it is valid. |
| 1002 | The profile you've modified is older than the one in the database, please select EDIT menu option to edit a new copy of the profile | The profile you are currently editing has already been updated by another person. Wait for a moment until the profile has been resubmitted to the database, then select EDIT again and select the profile. |
| 1003 | This profile only contains one-way encrypted password types. If another password type is added, please change the current password | The user has specified one of the encrypted password types - like DES or Crypto - as a password option. If a second or third password type is added which is unencrypted - like clear or PAP - then the same password cannot be understood by both the encrypted and unencrypted password types. Assign separate passwords for each type. |
| 1004 | Undefined internal error | This indicates a serious internal error has occurred. Try rebooting the client. If this message persists, contact the system administrator. |
| 1005 | Database server communication error | The database server is not responding to your communications requests. This can be caused by several things:
An administrative session expires after a configurable period of inactivity. If you can log back in, then the system is working properly. If you find your session expiring frequently, ask your system administrator to extend the time-out period. If you can't log back in, you might have a network or server problem. Contact your system administrator for assistance. |
| 1006 | Please enter a profile name | User must enter a unique user or group name to create a profile. |
| 1007 | You have entered a password but no password type | You have entered a password but have not checked a password type that requires a password value: Clear, PAP, CHAP, DES, File, Outbound PAP, PAP, WEB. Please select one of these password types. If you do not wish to add any of these password types, please clear the Password and the Confirm fields. |
| 1950 | Space not allowed | No spaces are allowed in the entry fields. If you want to enter a space, it must be surrounded by quotation marks. |
| 1951 | Maximum length exceeded | No entry can exceed 255 characters. |
| 1952 | Contains "{"or "}" | Curly brackets are not allowed as entry characters in these fields. |
| 1953 | Unbalanced quotes | There are more quotes on one side of the string than on the other, as in this example:
""unbalanced_string"
A string must be balanced like this: ""balanced_string"" |
| 1954 | Too many quotes | There are unnecessary quotes in this string. Remove the unnecessary marks. |
| 1955 | Missing begin or end quote | An ending or beginning quote is missing from this string, like this password example: badPassword" |
| 1956 | Not enough characters in the string | This field requires more characters than have been entered. For example, a password normally needs to be more than three characters long. |
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.

|
|