|
|

Product Number DOC-CSACUG2.1=
This document provides new information that became available after the user guide was printed for the CiscoSecure Access Control Server (ACS) 2.1.
This document contains the following sections:
This section lists and describes the latest information about this version of the CiscoSecure Access Control Server User Guide. Information is updated immediately prior to release of the software.
The filename for CiscoSecure ACS was changed after the user guide was printed. The installation filename in the user guide is incorrect.
Instead, enter the following new installer command at the command prompt:
pkgadd -d /cdrom/csus212
The following list contains requirements for hardware and system configuration.
In order to protect data transfers (which can include passwords) between the CiscoSecure ACS graphical user interface (GUI) and your web browser, you should enable the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol. SSL is a security protocol created by Netscape Communications Corporation. This protocol ensures that data is encrypted before being transferred over the network.
CiscoSecure ACS software provides security for remote access and SSL provides security for data transfer between the Netscape FastTrack web server and browser.
The CiscoSecure ACS GUI communicates with the Netscape FastTrack web server, and the web server in turn communicates with the CiscoSecure ACS database. By employing CiscoSecure ACS and enabling SSL, you can provide secure data transfer into and within your network.
SSL works by requiring Netscape Navigator to only authenticate a server that has a key that is signed by either Netscape or VeriSign. VeriSign will sign your keys for a fee, provided you comply with certain requirements.
To enable SSL on your web server, follow these steps:
Step 1 Log into the FastTrack server as the administrator (root privileges).
http://name of your FastTrack server:64000
You are prompted for a username and password.
Step 2 Enter the username and password, for example:
admin
password>
You see the Netscape Server Selector window.
Step 3 Click the name of your Netscape FastTrack Server.
Step 4 From the command buttons at the top of the window, click Encryption.
Step 5 On the left side of the window, click Generate Key.
You see a help window called Generating a key pair.
Step 6 Follow the online instructions to generate a server key pair.
Step 7 Click Request Certificate.
You see the online form called Request a Server Certificate.
Step 8 Complete the online form, then click OK.
Step 9 Request a certificate from a Certification Authority (such as VeriSign at www.verisign.com) and obtain a signed key.
Step 10 When you receive the server certificate, click Install Certificate from the Server Manager window.
You see the online form called Install a Server Certificate.
Step 11 Complete the online form, then click OK to install the server certificate.
Step 12 On the left side of the window, click On/Off to enable encryption.
The security of your network can be compromised in many ways beyond the data exchange between the network access server and the CiscoSecure server. This section is designed to identify areas that are potential security hazards and give you advice on what you can do to protect these key areas, or security holes, against potential intruders.
Keep your CiscoSecure server and network access servers in a locked room. Restrict access to that room and the servers within it.
Unless physically protected, intruders can attack your network at several points. Perhaps most damaging is the possibility that an intruder can approach a security server and remove its disk drive for later analysis. Also, when security servers are physically accessible, intruders can potentially boot the server from a CD or floppy disk, then mount the hard disk from the system, and finally change the root password. With a new root password known only to the intruder, the potential for damage is limitless.
In other cases, the intruder might disrupt service by turning off the server, or disconnecting it from the network. A "denial of service" attack might even involve destroying the security server or its disk; this is another scenario where keeping good backups can reduce downtime.
If at all possible, keep the local telephone closet locked. When the telephone lines going into a network access server are adequately secured, wire-tapping of telephone lines or monitoring of keystrokes becomes difficult (although not impossible).
Keep remote access to security servers as restrictive as possible. Even with security servers physically locked down, attacks can be launched remotely by intruders if they can access the servers through the network. Many software bugs have eventually turned out to be security holes. For this reason, you should avoid using any unnecessary services on the security server that might potentially have as yet unknown security holes.
Most networks have large numbers of unencrypted passwords and other data flowing over them. As such, local users are able to "snoop," or easily extract, data flowing over broadcast technology networks such as Ethernet. At the very least, consider using secure methods of logging in and manipulating security configurations (for example, use Kerberized and encrypted rlogin access, SSL browsers, or dedicated and physically secured serial lines).
Do not allow local users to access security servers, even if the local users lack any privileges to change the configurations. This helps prevent exploitation of potential security holes that might exist but are generally not known.
Construct passwords that are fairly long (at least 8 characters) and consist of letters (uppercase and lowercase) and numbers. Confirm that the password cannot be easily guessed by people with familiarity with the local organization or personnel. Password-guessing attacks are the easiest and most common type of network intrusion. The easier a password is to guess, the faster an attacker can gain access to protected data.
Even well-chosen passwords are easily captured if sent in cleartext over broadcast media (such as Ethernet). Normally, protocols such as Telnet and rlogin do not encrypt passwords that are sent over the network although the destination system might encrypt those passwords upon arrival.
Use different passwords for the security servers and other systems, especially ones that can be accessed through unencrypted protocols. Some protocols, such as Kerberized Telnet, do not send the password over the network in cleartext, but subsequent data is still unencrypted. Consequently, while these protocols limit exposure, they do not entirely restrict exposure.
Confirm that your installation of CiscoSecure ACS is conducted in one session. Do not interrupt the installation. Similarly, do not leave your server unattended if you are conducting subsequent configurations such as adding new users or support for a new one-time password card. An intruder can potentially gain sensitive information during configurations and use the information later.
Do not install CiscoSecure ACS over an unsecure network; instead, install CiscoSecure ACS at the system console.
When providing configuration information to anyone (even technical support personnel), remove sensitive information such as passwords. Replace sensitive information such as password strings with "XXXXXX."
Do not use the Netscape FastTrack server software (that came bundled with CiscoSecure ACS) to serve any web pages that are not part of CiscoSecure ACS.
Use SSL for encrypted connections to the Netscape FastTrack server. This provides a high degree of security. Users can change their own web browsers to connect to the CiscoSecure ACS database to change their own passwords. As such, all of the data traffic is vulnerable and should be encrypted.
This section describes how to restore your SQL Anywhere database from backup media generated by the dbBackup program.
Two files are required for the restore operation: the database file (csecure.db) and the transaction log file (csecure.log). The backup of your SQL Anywhere database contains both of these files. Depending on the extent of damage to your SQL Anywhere database, you perform the restore operation by copying one or both of these files according to the three conditions that follow:
cd name of database directory
dbeng50 csecure.db -a csecure.log
cd name of database directory
dbeng50 csecure.db -f
New TACACS+ and RADIUS support for caller ID allows you to base profiles on the calling number, rather than the username being passed. Identifying users by their telephone number is especially useful for accounting purposes because you can directly bill charges according to the calling number.
To configure support for caller ID, create a new user profile and enter a designated telephone number instead of a username.
The following example shows a user profile configured for caller ID:
user =5551212password =chap01
In this case, if an unknown user dials into the network access server, it passes the user's information including "rem_addr (5551212)" to CiscoSecure ACS. CiscoSecure ACS first attempts to authenticate the user based on the user field but in this case, the user is not in the CiscoSecure ACS database. However, because the user profile contains the caller ID, CiscoSecure ACS uses the rem_addr 5551212 to index into the database.
You can take advantage of the CiscoSecure ACS feature that supports the use of one-time password cards (token cards) at any time. The easiest way is to specify which token cards you want to support when initially prompted by the CiscoSecure ACS installer. However, if you declined to specify token card support when you initially installed CiscoSecure ACS, you can still add support for Secure Computing (formerly Enigma Logic) or Security Dynamics (SDI) token cards by editing a configuration file, as described in the following steps:
Step 1 Locate the CSU.cfg file as shown in the following example:
cd $BASEDIR (where $BASEDIR is the directory where CiscoSecure ACS is installed)
ls
cd config
ls
Step 2 Make a copy of the CSU.cfg file. You can use this copy in case problems arise after editing the file.
Step 3 Use a text editor, such as vi, to edit the CSU.cfg file:
# vi CSU.cfg
Step 4 Update the CSU.cfg for one of the following supported token card servers:
AUTHEN config_external_authen_symbols = {
{
"./libsdi.so",
"sdi"
}
,
}
"./libenigma.so",
"enigma"
}
02 SafeWord Authen. Server Name: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 0 0 7482
Step 5 Save the file and exit from your text editor.
Step 6 Stop CiscoSecure ACS by entering the following command:
/etc/rc0.d/K80CiscoSecure
Step 7 Restart CiscoSecure ACS by entering the following command:
/etc/rc2.d/S80CiscoSecure
Support for the token cards you specified is now available.
To increase GUI performance from an Oracle database, use the database management system (DMBS)-provided tools (such as sqlplus) to create an index in the member column of the cs_profile table, as follows:
Step 1 Log into the DBMS using the appropriate account name (confirm that the account name is the same one that was specified when you installed CiscoSecure ACS).
Step 2 Enter the following Oracle statement:
create index cs_profile_member on cs_profile (member)
storage (initial 5M next 5M pctincrease 0)
To increase GUI performance from an SQL Anywhere database, use the database management system (DBMS)-provided tools (such as isql) to create an index in the member column of the cs_profile table, as follows:
Step 1 Log into the DBMS using the appropriate account name, as shown in the following example:
DBA
SQL
Step 2 Enter the following SQL statement at the command prompt:
create index cs_profile_member on cs_profile (member)
Use the following procedures to increase GUI performance on Netscape Navigator.
Step 1 Select the Netscape Navigator Options menu.
Step 2 From the dropdown menu, select Network Preferences.
Step 3 Click the Cache tab.
You see the Memory Cache dialog box.
Step 4 In the Memory Cache field, increase the number from the default (1024 kilobytes) to 8000.
Step 5 In the Disk Cache field, increase the number the default (5000 kilobytes) to 20000.
Step 6 Click OK.
The increased memory and disk cache take effect immediately.
Step 1 Select the Netscape Navigator Options menu.
Step 2 From the dropdown menu, select Network Preferences.
Step 3 Click the Cache tab.
You see the Memory Cache dialog box.
Step 4 Click Clear Memory Cache Now.
Step 5 Click Clear Disk Cache Now.
Step 6 Click OK.
The memory and disk cache are cleared immediately.
A new control has been added to the dictionary that allows the assignment of a vendor identifier code. This value is used with the Vendor Specific attribute (26).
When a dictionary is created, it is assigned a vendor code through a control located on the bottom right corner of the dictionary page. This control can be used when the dictionary is being edited. Select this control to access a dialog box used to enter the vendor code. An updated dictionary page is illustrated in Figure 1.
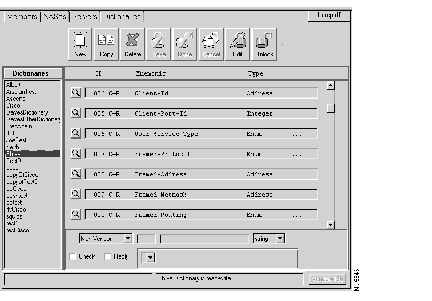
Additional changes to the Dictionary page that did not make it into the user guide include:
The migration tool has been enhanced to import DES encrypted passwords. When the migration tool encounters this password type in the RADIUS user's file, it DES encrypts the password and sets the password type for that user to DES. For example:
msmart DESPASSWORD = "agent86" Framed-Protocol = PPP, ...
Gets converted to and is represented within the CiscoSecure ACS 2.1 database as:
user = msmart {
password = DES "*&^@#*!&%" # encrypted "agent86"
radius = IETF {
reply_attributes {
Framed-Protocol = PPP
}
}
}
It is possible that a user's profile contains many password types. The RADIUS server applies the following rules when it comes to passwords (this is stated on page 5-16 of the user guide, and restated here for the purposes of this discussion):
|
NAS Sends Attribute | AAA Server Utilizes User's Profile Password |
| User-Password(2) | OTP, file, PAP |
| CHAP-Password(3) | CHAP |
| ARAP | Ascend-ARA-Password (181) |
There is no way to force the AAA server to apply the DES-assigned password established by the migration/import utility. As a result, the AAA server has been augmented with a command-line argument, -D, that forces the server to apply the DES password to authenticate users. When the -D option is applied, the RADIUS/AAA server will authenticate user's according to the following table (again, assuming no password in a radius subprofile):
| NAS Sends Attribute | AAA Server Utilizes User's Profile Password |
| User-Password(2) | DES |
| CHAP-Password(3) | CHAP |
| ARAP | Ascend-ARA-Password (181) |
When you exit Netscape, there is a delay of several seconds before Netscape exits because of GUI resource allocation.
When running the administration GUI under Netscape Navigator, the virtual memory used by Netscape constantly increases. There are no problems associated with this behavior.
$BASEDIR/utils/bin/AcctExport has been enhanced to remove the offline requirement for deleting accounting records from the database. Now the tool can be used while database accounting records are being added or modified. It will export and delete accounting records except ones for the active sessions.
This section includes a troubleshooting checklist for orderly problem resolution and identifies shortcomings of CiscoSecure ACS 2.1 that are expected to be addressed in a subsequent release, and related information.
CiscoSecure ACS operates in conjunction with many disparate systems, platforms, and devices. If you encounter a problem while using CiscoSecure ACS, you can quickly isolate the problem by performing the steps in the troubleshooting checklist that follows. A custom shell script is located at the end of the list. Depending on your needs, you can skip ahead to the shell script and run it as documented to make checking the processes more convenient.
Netscape Navigator 4.02 does not function correctly when running on the same Solaris machine on which the CiscoSecure ACS is installed. Netscape is working on these issues. [CSCdj28878]
The help text for the Command Line Interface needs to be more detailed and descriptive. For additional information read the CiscoSecure ACS User Administration Command Line Release Notes that are shipped with the CiscoSecure ACS 2.1.2 software. [CSCdj29749]
If a host is configured with more than one IP address and RADIUS is being used, CiscoSecure uses the first IP address found on the host when the 'ipconfig' command is executed. To avoid this problem use the Advanced Configurator to configure the specific server profile, including its IP address that you want to use with RADIUS. [CSCdj38601]
The timeout function between the User Administration Interface and the Advanced Administration Interface is not working. [CSCdj39532]
The privilege=web level can not be set at the group level from the User Administration Interface. Privilege=web must be assigned for individual users. [CSCdj35514]
The authentication methodology used by the one-time password cards from SDI differs somewhat from what is used by the CiscoSecure ACS. Whereas SDI authentication uses a single process, CiscoSecure ACS employs a multithreaded approach for improved performance. Although not seen in either laboratory or beta site, a large volume of simultaneous SDI-based authentications can theoretically generate unexpected failures. In this case, the authentication might fail although the username and password were correct. If users encounter this problem, advise them to wait a few moments, and then retry the operation. [CSCdj01541]
The default installation allows CiscoSecure ACS to communicate with any network access server with which it can connect. The default installation does not record a default name for network access servers. However, additional security can be added by specifying network access servers by name to limit communication with CiscoSecure ACS. You can modify the CSU.cfg file after installation to include specific network access server names.
To replace the default NAS_NAME value with the unique name of your network access server, follow these steps:
Step 1 Using a text editor, edit the CSU.cfg file to identify the location where the network access server name is stored:
vi $BASEDIR/CSU/CSU.cfg
Step 2 Find the line that includes the statement "NAS config_nas_config".
If you have accepted the default installation, you should see a line that looks like the following example.
"NAS_NAME", /* NAS name can go here */
Step 3 Replace NAS_NAME with the name of your NAS.
Step 4 Restart CiscoSecure.
You must have an individual statement for each NAS that you specify by name. The example below shows you the syntax and information that needs to be in the CSU.cfg file for each specified NAS.
NAS config_nas_config = {
{
"NAS_NAME", /* NAS name can go here */
"SECRET", /* NAS/CiscoSecure secret key */
"", /* message_catalogue_filename */
1, /* username retries */
2, /* password retries */
1 /* trusted NAS for SENDPASS */
},
{
"NAME_OF_YOUR_NAS", /* NAS name can go here */
"SECRET123", /* NAS/CiscoSecure secret key */
"", /* message_catalogue_filename */
1, /* username retries */
2, /* password retries */
1 /* trusted NAS for SENDPASS */
},
{
"ANY_OTHER_NAS_NAME", /* NAS name can go here */
"SECRET456", /* NAS/CiscoSecure secret key */
"", /* message_catalogue_filename */
1, /* username retries */
2, /* password retries */
1 /* trusted NAS for SENDPASS */
}
};
Depending on the size of your database and the number of client/server transactions taking place, you might experience some processing delays, such as waiting a long time for GUI screens to refresh. Although these performance problems can be annoying, they do not result in system malfunction or loss of data.
Unlike other GUI-based applications that run locally on a given computer, CiscoSecure ACS is a network-based application and is therefore dependent on external data-transfer rates, such as what is provided by local telephone services. In addition, CiscoSecure ACS is a client/server product that includes a full relational database management system, so you might experience wait time as profiles are written to and from the database.
The max-sessions feature can only be applied to user logins. CiscoSecure ACS currently does not permit limiting the number connections based on a specific domain. [CSCdi90229]
On pages B-20 to B-22 of the CiscoSecure Access Control Server User Guide 2.1, the instructions for setting up max-sessions might be incomplete depending on your particular configuration. In addition to the steps provided on those pages, be sure to enable finger on the network access server as follows:
cisco-router>enablePassword:<password>cisco-router#conf termcisco-router(config)#service fingercisco-router(config)#end
For best performance, dedicate one computer exclusively for CiscoSecure ACS.
To change the username and password on your FastTrack web server, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Log into FastTrack as the administrator:
http://name of your CiscoSecure Server:64000
You see a screen requesting your username and password.
Step 2 Enter your administrator username and password to gain access to the Web Server Administration section.
Step 3 Click the Configure Administration box.
Step 4 Click on the Access Control line.
You see editable fields for username and password.
Step 5 Replace the username and password as necessary.
The following web browsers are currently supported for use with CiscoSecure ACS:
CiscoSecure allows the installation of up to 50 instances of the package on one machine. This limit means that there can be one original install and a maximum of 49 upgrades. After this limit is reached, all packages will have to be removed completely so that a new installation can be performed. If you decide to remove CiscoSecure ACS 2.x using the pkgrm command, you must remove all the remaining packages. If you do not remove all remaining packages, there will be incomplete packages and CiscoSecure will no longer function. This is caused by a limitation in the package operation involving files placed in the root directory.
The installation script requires the /etc/hosts file to contain the IP address of the local machine. Further, the name associated with the IP address (within the /etc/hosts file) must match what uname -n returns.
After clicking OK to a dialog box in IE, the focus will temporarily shift somewhere else, then shift back to IE.
The profile attribute Privilege - Web will accept a blank password field as valid.
Find results on systems configured with a more than 10 groups causes abnormal behavior in the browser pane. Scroll down the Navigator pane to the bottom so that Root is no longer showing. Use the Find button to find a user. You will now see a blank Navigator pane when the find completes. You must scroll back up to the top of the pane to view the find results.
This is documented incorrectly in the user guide. The config_max_failed_authentication is a GLOBAL value applied to all users. It is the number of consecutive failed logins a user can have before that user's account is disabled.
The "server current-failed-logins" is the given user's current number of consecutive failed logins. After the user authenticates successfully, this is reset to 0.
This section provides details about bug fixes included in CiscoSecure ACS 2.1.
Previously, CiscoSecure only performed double authentication, where the one-time passwords (OTP) were passed in the User Name field following the asterisk, and a PAP password was passed in the Password field.
User Name: Joe*1226PP1H Password: *****
In this example Joe is the username, the asterisk is used to delimit the username from the OTP, 1226PP1H is the OTP, and the asterisks in the Password field represent a PAP password.
The PAP authentication model now supports the OTP being passed in the password field.
User Name: Joe Password: 1226PP1H
To enable PAP/OTP, where the OTP is passed in the password field, the user/group profile must be configured with the following password attributes (note: SDI can be replaced with Enigma, or crypto):
user = xxxx {
password = pap some-string-that-is-not-tested
password = SDI
}
CAVEAT:
This changes the previous behavior when OTP and PAP passwords reside in the user's profile.
Proper AAA server files were added for this release.
This section addresses errors in the CiscoSecure Access Control Server User Guide 2.1 and information that was not available before the user guide was printed.
In Chapter 6, "CiscoSecure Access Control Server Accounting," page 6-8, note the corrections regarding how to set group accounting:
In the CiscoSecure ACS GUI, the name of the attribute that enables group accounting is incorrectly documented as account = acct_member_fn. The correct name of the group accounting attribute is accounting_fn.
In Chapter 6, "CiscoSecure Access Control Server Accounting," page 6-6, note that the no_truncate switch is not required.
In Appendix B, "CiscoSecure Access Control Server File Formats and Syntax," pages B-2 and B-3, note the corrections to the example of a CiscoSecure server control file.
The following is an example CiscoSecure Access Control Server control file:
/*
* CiscoSecure Access Control Server Example Control File
*/
/* The license for this server. Multiple license keys may
* be specified, each separated by a comma.
*/
LIST config_license_key = {"061db8afcf66db981f3c" }; /* NAS License Key
goes here */
STRING config_update_log_filename = "/CiscoSecure/logfiles/passwd_chg.log";
NUMBER config_system_logging_level = 0x80;
NUMBER config_logging_configuration = 0x7e;
NUMBER config_warning_period = 20;
NUMBER config_expiry_period = 60;
NUMBER config_local_timezone = -8; /* set this for your timezone */
NUMBER config_record_write_frequency = 5; /* update frequency in
seconds */
NUMBER config_max_failed_authentication = 10; /* nmbr of authen fails
accepted */
/*before account is disabled. */
/*
* Per-NAS configuration records. The default encryption key is "arachnid"
* for all NAS except 'boggle', which is using "heliotrope".
*/
NAS config_nas_config = {
{
"", /* NAS name can go here */
"arachnid", /* NAS/CiscoSecure secret key */
"", /* message_catalogue_filename */
1, /* Authentication: username retries */
3, /* Authentication: password retries */
1 /* trusted NAS for SENDPASS */
},
{
"boggle", /* NAS name */
"heliotrope", /* NAS/CiscoSecure secret key */
"", /* message_catalogue_filename */
2, /* Authentication: username retries */
2, /* Authentication: password retries */
0 /* not a trusted NAS for SENDPASS */
}
};
AUTHEN config_external_authen_symbols = {
{
"./libskey.so",
"skey"
}
,
{
"./libsdi.so",
"sdi"
}
,
{
"./libenigma.so",
"enigma"
}
,
{
"./libcryptocard.so",
"crypto"
}
,
{
"./libpap.so",
"pap"
}
,
{
"./libchap.so",
"chap"
}
,
{
"./libarap.so",
"arap"
}
};
AUTHOR config_external_author_symbols = {
{
"./libargs.so",
"process_input_arguments",
"process_input_arguments_ok",
"process_input_arguments_fail",
"process_output_arguments",
"process_output_arguments_ok",
"process_output_arguments_fail"
}
};
ACCT config_external_acct_symbols = {
{
"./libargs.so",
"accounting_fn"
}
};
ADMIN config_external_admin_symbols = {
"./libadmin.so"
};
DB config_external_database_symbols = {
{
"./libdb.so",
"",
""
}
};
PARSER config_external_parser_symbols = {
"./libt+.so"
};
EVENT config_external_event_symbols = {
{
"./libdb.so",
"",
""
}
};
The following information supplements the copyright information in the user guide:
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, user documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.

|
|