|
|

This appendix provides selected port and cable assembly pinouts for the Cisco AccessPath Integrated Access System. Further details can be found in the hardware documentation specific to each shelf of the AccessPath system. If you need more information, refer to the documents listed in the table "Related and Referenced Documents" in the chapter "About This Guide."
The appendix includes the following cable assembly and pinout information:
In addition, the appendix includes the following information on cable connections:
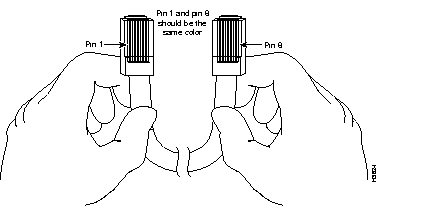
You can identify a rollover cable by comparing the two modular ends of the cable. Holding the cables side-by-side, with the tab at the back, the wire connected to the pin on the outside of the left plug should be the same color as the wire connected to the pin on the outside of the right plug. (See Figure B-1.) If your cable was purchased from Cisco Systems, pin 1 will be white on one connector, and pin 8 will be white on the other (a rollover cable reverses pins 1 and 8, 2 and 7, 3 and 6, and 4 and 5).
Each Access Server Shelf comes with a console cable preconnected to the console port on the Failsafe/Console Management Shelf (these console cables may also be connected to an ASCII terminal or PC running terminal emulation software). An auxiliary cable kit includes cables for connecting to T1 lines and to peripherals such as modems. The Access Server Shelf cable assemblies and pinouts include the following:
For console connections, proceed to the section "Access Server Shelf Console Port Signals and Pinouts" later in this appendix; for modem connections, proceed to the section "Auxiliary Port Signals and Pinouts" later in this appendix.
Use the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and RJ-45-to-DB-9 female DTE adapter (labeled Terminal) to connect the console port to a PC running terminal emulation software. Figure B-2 shows how to connect the console port to a PC. Table B-1 lists the pinouts for the asynchronous serial console port, the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable, and the RJ-45-to-DB-9 female DTE adapter (labeled Terminal).
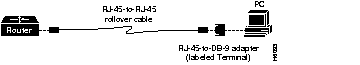
| Console Port (DTE) | RJ-45-to-RJ-45 Rollover Cable | RJ-45-to-DB-9 Terminal Adapter | Console Device | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal | RJ-45 Pin | RJ-45 Pin | DB-9 Pin | Signal |
| RTS | 11 | 8 | 8 | CTS |
| DTR | 2 | 7 | 6 | DSR |
| TxD | 3 | 6 | 2 | RxD |
| GND | 4 | 5 | 5 | GND |
| GND | 5 | 4 | 5 | GND |
| RxD | 6 | 3 | 3 | TxD |
| DSR | 7 | 2 | 4 | DTR |
| CTS | 81 | 1 | 7 | RTS |
Use the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter (labeled Terminal) to connect the console port to a terminal. Figure B-3 shows how to connect the console port to a terminal. Table B-2 lists the pinouts for the asynchronous serial console port, the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable, and the RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter (labeled Terminal).
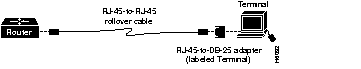
| Console Port (DTE)1 | RJ-45-to-RJ-45 Rollover Cable | RJ-45-to-DB-25 Terminal Adapter | Console Device | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal | RJ-45 Pin | RJ-45 Pin | DB-25 Pin | Signal |
| RTS | 12 | 8 | 5 | CTS |
| DTR | 2 | 7 | 6 | DSR |
| TxD | 3 | 6 | 3 | RxD |
| GND | 4 | 5 | 7 | GND |
| GND | 5 | 4 | 7 | GND |
| RxD | 6 | 3 | 2 | TxD |
| DSR | 7 | 2 | 20 | DTR |
| CTS | 81 | 1 | 4 | RTS |
Four serial cables are available from Cisco Systems for connecting the E1 PRI card ports. All four have DB-15 connectors on the E1 end and either BNC, DB-15, twinax, or RJ-45 connectors on the network end. Figure B-4, Figure B-5, Figure B-6, and Figure B-7 show the E1 interface cables. Table B-3 lists the pinouts for the E1 interface cables connecting to the Dual E1 PRI card.




| CE1 End | Network End | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB-151 | BNC | DB-15 | Twinax | RJ-45 2 | RJ-45/NT3 | |||||
| Pin | Signal4 | Signal | Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
| 9 | TX Tip | TX Tip | 1 | TX Tip | TX-1 | TX Tip | 4 | RX Tip | 1 | TX Tip |
| 2 | TX Ring | TX Shield | 9 | TX Ring | TX-2 | TX Ring | 5 | RX Ring | 2 | TX Ring |
| 10 | TX Shield | - | 2 | TX Shield | Shield | TX Shield | 6 | RX Shield | 3 | TX Shield |
| 8 | RX Tip | RX Tip | 3 | RX Tip | RX-1 | RX Tip | 1 | TX Tip | 4 | RX Tip |
| 15 | RX Ring | RX Shield | 11 | RX Ring | RX-2 | RX Ring | 2 | TX Ring | 5 | RX Ring |
| 7 | RX Shield | - | 4 | RX Shield | Shield | RX Shield | 3 | TX Shield | 6 | RX Shield |
Use the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and RJ-45-to-DB-25 male DCE adapter (labeled Modem) to connect the auxiliary port to a modem. Figure B-8 shows how to connect the auxiliary port to a modem. Table B-4 lists the pinouts for the asynchronous serial auxiliary port, the RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable, and the RJ-45-to-DB-25 male DCE adapter (labeled Modem).
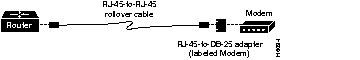
| AUX Port (DTE) | RJ-45-to-RJ-45 Rollover Cable | RJ-45-to-DB-25 Modem Adapter | Modem | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal | RJ-45 Pin | RJ-45 Pin | DB-25 Pin | Signal |
| RTS | 1 | 8 | 4 | RTS |
| DTR | 2 | 7 | 20 | DTR |
| TxD | 3 | 6 | 3 | TxD |
| GND | 4 | 5 | 7 | GND |
| GND | 5 | 4 | 7 | GND |
| RxD | 6 | 3 | 2 | RxD |
| DSR | 7 | 2 | 8 | DCD |
| CTS | 8 | 1 | 5 | CTS |
Two options exist for connecting the T1 port on an Access Server Shelf to the T1 patch panel. The patch panel will accommodate one of the following configurations, depending on what you ordered:
Table B-5 lists the T1 PRI card port pinouts.
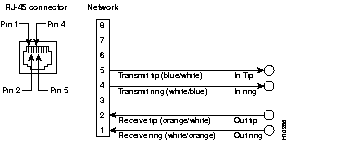
| RJ-48C8 Pin1 | Telco Side Description | T1 Patch Panel Description | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Receive ring from telco | Out ring | White/Orange |
| 2 | Receive tip from telco | Out tip | Orange/White |
| 4 | Transmit ring to telco | In ring | White/Blue |
| 5 | Transmit tip to telco | In tip | Blue/White |
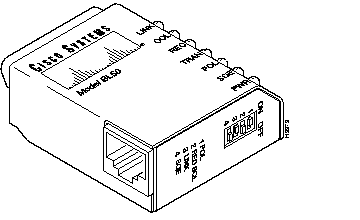
Each of the Access Server Shelves uses a Model BL50 10BaseT IEEE 802.3 Transceiver to connect from its Ethernet LAN port to the Router Shelf. These transceivers should already have been installed before the AccessPath system was shipped. See Figure B-10.
The Failsafe/Console Management Shelf uses a Model BL50R 10BaseT IEEE 802.3 Transceiver. This transceiver should already have been installed before the AccessPath system was shipped. See Figure B-11.
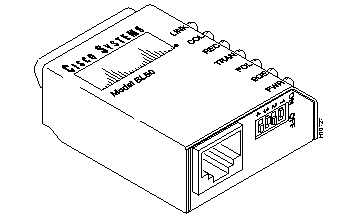
The 10BaseT transceivers (both models BL50 and BL50R) have four switch settings and seven diagnostic lights. The switches should be kept at the factory settings (shown in Figure B-10), unless changes to the switch settings are recommended by Cisco-certified maintenance personnel.
For information on the factory switch settings, refer to Table B-6.
For information on the diagnostic lights, refer to Table B-7.
For information on pinouts, refer to Table B-8.
| Switch | Function | Setting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automatically corrects reversed polarity. | On | ||
| Allows a connection to be used on a Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) network by reducing STP squelch. | Off | ||
| Disables the transceiver from working with legacy equipment that does not conform to 10BaseT specifications. | On | ||
| Enables the 10BaseT SQE test. | Off |
| Light | Function |
|---|---|
| Link (Green) | Indicates that the transceiver is connected to the Router Shelf, and that the twisted pair circuit between them is complete. |
| Col (Yellow) | This light will flash if there is a collision detected on the network. If the light stays on, the MAU is jabber protected. |
| Rec (Green) | This light flashes when an Ethernet packet is received from the network. The speed of the flashing reflects the density of the Ethernet traffic. |
| Tran (Green) | This light flashes when Ethernet packets are transmitted to the network. |
| Pol (Yellow) | Indicates that packets of reversed polarity are being received when the reverse polarity slide switch Pol is set to the ON position. |
| Sqe (Yellow) | Indicates that squelch reduction is on. The connection can be used on a Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) network. See Red Sql in Table B-6. |
| Pwr (Green) | This light will be on continuously while power is being supplied to the transceiver from the DTE. |
| RJ-45 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | TD+ |
| 2 | TD- |
| 3 | RD+ |
| 4 | No connection |
| 5 | No connection |
| 6 | RD- |
| 7 | No connection |
| 8 | No connection |
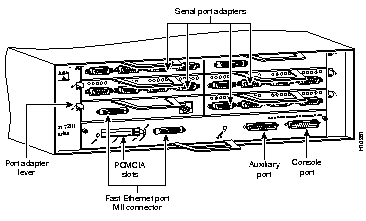
The instructions for connecting the cables for each port adapter installed in the Cisco 7206 are contained in the respective configuration note for each port adapter. For example, if you are connecting the cables for a Token Ring port adapter, refer the configuration note PA-4R Token Ring Port Adapter Installation and Configuration (Document Number 78-2661-xx). This configuration note accompanies every Token Ring port adapter that is shipped from the factory as an installed item in a Cisco 7206 or as a FRU. The document is also available on the Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series CD, and on Cisco Connection Online (CCO).
The console and auxiliary ports for the Router Shelf are located on the I/O controller. The I/O controller also has an optional Fast Ethernet port (refer to Figure B-12.) This section contains connection equipment and pinout information for the console, auxiliary, and Fast Ethernet ports on the I/O controller.
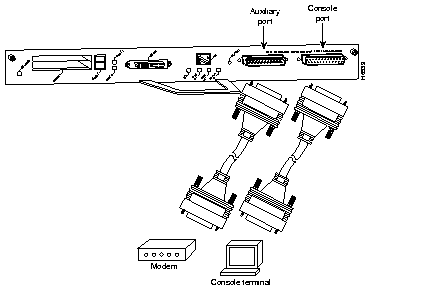
The I/O controller has two EIA/TIA-232 ports: a DCE-mode console port and a DTE-mode auxiliary port. The console port is a DCE DB-25 receptacle for connecting a data terminal, which you will use to configure the interfaces and bring up the router. The auxiliary port is a DTE DB-25 plug for connecting a modem or other DCE device (such as a CSU/DSU or other router) to the Router Shelf (refer to Figure B-13).
Before connecting a terminal to the console port, configure the terminal to match the router console port as follows: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (9600 8N1). You need an EIA/TIA-232 DCE console cable to connect the terminal to the console port. After you establish normal router operation, you can disconnect the terminal.
You must supply your own interface cable between the auxiliary port and the equipment you are connecting. For console and auxiliary port pinouts, refer to the following sections "Console Port Signals" and "Auxiliary Port Signals."
Both Data Set Ready (DSR) and Data Carrier Detect (DCD) signals are active when the system is on. The Request To Send (RTS) signal tracks the state of the Clear to Send (CTS) input. The console port does not support modem control or hardware flow control. Table B-9 lists the signals used on the console port. The console port requires a straight-through EIA/TIA-232 cable.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | - | Ground |
| 2 | TxD | <-- | Transmit Data |
| 3 | RxD | --> | Receive Data |
| 6 | DSR | --> | Data Set Ready (always on) |
| 7 | GND | - | Ground |
| 8 | DCD | --> | Data Carrier Detect (always on) |
Table B-10 lists the signals used on the auxiliary port. The auxiliary port supports hardware flow control and modem control.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | TxD | --> | Transmit Data |
| 3 | RxD | <-- | Receive Data |
| 4 | RTS | --> | Request To Send (used for hardware flow control) |
| 5 | CTS | <-- | Clear To Send (used for hardware flow control) |
| 6 | DSR | <-- | Data Set Ready |
| 7 | Signal Ground | - | Signal Ground |
| 20 | DTR | --> | Data Terminal Ready (used for modem control only) |
The Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller has a single MII, 40-pin, high-density D-shell type connector that is configurable for 100 megabits per second (Mbps). The MII connector supports IEEE 802.3u interfaces compliant with the 100BASE-X and 100BASE-T standards. The single MII connection requires an external transceiver that permits connection to multimode fiber for 100BaseFX or 100BaseT4 physical media (refer to Figure B-14).
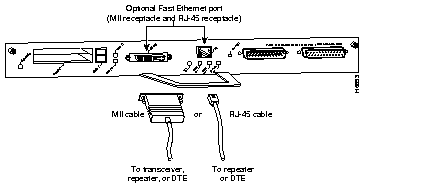
Depending on the type of media you use between the MII connection and your switch or hub, the network side of your 100BaseT transceiver should be appropriately equipped with ST-type connectors (for optical fiber), BNC connectors, and so forth.
Figure B-15 shows the pin orientation of the female MII receptacle on the Fast Ethernet port.
The MII receptacle uses 2-56 screw-type locks, called jackscrews, to secure the cable or transceiver to the MII port. MII cables and transceivers have knurled thumbscrews that you fasten to the jackscrews on the MII connector and tighten with your fingers. Use the jackscrews to secure your MII cable to the MII receptacle.
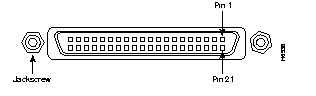
Table B-11 lists the pinouts and signals for the I/O controller MII receptacle.
| Pin1 | In | Out | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14-17 | - | Yes | - | Transmit Data (TxD) |
| 12 | Yes | - | - | Transmit Clock (Tx_CLK)2 |
| 11 | - | Yes | - | Transmit Error (Tx_ER) |
| 13 | - | Yes | - | Transmit Enable (Tx_EN) |
| 3 | - | Yes | - | MII Data Clock (MDC) |
| 4-7 | Yes | - | - | Receive Data (RxD) |
| 9 | Yes | - | - | Receive Clock (Rx_CLK) |
| 10 | Yes | - | - | Receive Error (Rx_ER) |
| 8 | Yes | - | - | Receive Data Valid (Rx_DV) |
| 18 | Yes | - | - | Collision (COL) |
| 19 | Yes | - | - | Carrier Sense (CRS) |
| 2 | - | - | Yes | MII Data Input/Output (MDIO) |
| 22-39 | - | - | - | Common (ground) |
| 1, 20, 21, 40 | - | - | - | +5.0V |
Each of the Router Shelves in a dual Router Shelf configuration uses a Model BL-6000 MII-to-MII Crossover IEEE 802.3u Adapter to connect from its Fast Ethernet MII port in Slot 0 to the corresponding port on the other Router Shelf.
The female MII connector on the Router Shelves is in an idle state, compliant to IEEE 802.3u, until cables are attached.
The Router Shelf software configuration must contain the following lines:
interface FastEthernet0/0 ! full-duplex no keepalive
The inclusion of these lines stops the Router Shelf from sending out packets it will expect to see returned, otherwise it will shut down the line.
These transceivers should already have been installed before the AccessPath system was shipped.
The adapters have four diagnostic lights. For information on the diagnostic lights, refer to Table B-12.
The adapters use the pinouts required by the Router Shelf MII receptacle. For information on these pinouts, refer to Table B-11.
| Light | Function |
|---|---|
| Link/Activity (Green) | Indicates that the adapter is connected to the Router Shelf, that the circuit between the two Router Shelves is complete, and that data is being received. |
| Power (Green) | This light will be on continuously while power is being supplied to the transceiver from the MII receptacle on the Router Shelf. |
The illustrations and tables in this section provide assembly drawings and pinouts for the EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21 data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communications equipment (DCE) cables, which are used with the five-in-one synchronous serial WAN port.
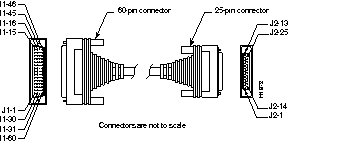
Figure B-16 shows the EIA/TIA-232 cable assembly. Table B-13 lists the DTE pinouts. Table B-14 lists the DCE pinouts. Arrows indicate signal direction: a right arrow (-->) indicates DTE to DCE, and a left arrow (<--) indicates DCE to DTE.
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 25 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-50 J1-51 J1-52 | MODE_0 GND MODE_DCE | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield GND | Single | - | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-41 Shield | TxD/RxD - | Twisted pair no. 5 | --> - | J2-2 Shield | TxD - |
| J1-36 Shield | RxD/TxD - | Twisted pair no. 9 | <-- - | J2-3 Shield | RxD - |
| J1-42 Shield | RTS/CTS - | Twisted pair no. 4 | --> - | J2-4 Shield | RTS - |
| J1-35 Shield | CTS/RTS - | Twisted pair no. 10 | <-- - | J2-5 Shield | CTS - |
| J1-34 Shield | DSR/DTR - | Twisted pair no. 11 | <-- - | J2-6 Shield | DSR - |
| J1-45 Shield | Circuit GND - | Twisted pair no. 1 | - - | J2-7 Shield | Circuit GND - |
| J1-33 Shield | DCD/LL - | Twisted pair no. 12 | <-- - | J2-8 Shield | DCD - |
| J1-37 Shield | TxC/NIL - | Twisted pair no. 8 | <-- - | J2-15 Shield | TxC - |
| J1-38 Shield | RxC/TxCE - | Twisted pair no. 7 | <-- - | J2-17 Shield | RxC - |
| J1-44 Shield | LL/DCD - | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> - | J2-18 Shield | LTST - |
| J1-43 Shield | DTR/DSR - | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> - | J2-20 Shield | DTR - |
| J1-39 Shield | TxCE/TxC - | Twisted pair no. 6 | --> - | J2-24 Shield | TxCE - |
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 25 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-50 J1-51 | MODE_0 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield GND | Single | - | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-36 Shield | RxD/TxD - | Twisted pair no. 9 | <-- - | J2-2 Shield | TxD - |
| J1-41 Shield | TxD/RxD - | Twisted pair no. 5 | --> - | J2-3 Shield | RxD - |
| J1-35 Shield | CTS/RTS - | Twisted pair no. 10 | <-- - | J2-4 Shield | RTS - |
| J1-42 Shield | RTS/CTS - | Twisted pair no. 4 | --> - | J2-5 Shield | CTS - |
| J1-43 Shield | DTR/DSR - | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> - | J2-6 Shield | DSR - |
| J1-45 Shield | Circuit GND - | Twisted pair no. 1 | - - | J2-7 Shield | Circuit GND |
| J1-44 Shield | LL/DCD - | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> - | J2-8 Shield | DCD - |
| J1-39 Shield | TxCE/TxC - | Twisted pair no. 7 | --> - | J2-15 Shield | TxC - |
| J1-40 Shield | NIL/RxC - | Twisted pair no. 6 | --> - | J2-17 Shield | RxC - |
| J1-33 Shield | DCD/LL - | Twisted pair no. 12 | <-- - | J2-18 Shield | LTST - |
| J1-34 Shield | DSR/DTR - | Twisted pair no. 11 | <-- - | J2-20 Shield | DTR - |
| J1-38 Shield | RxC/TxCE - | Twisted pair no. 8 | <-- - | J2-24 Shield | TxCE - |
Figure B-17 shows the EIA/TIA-449 cable assembly. Table B-15 lists the DTE pinouts. Table B-16 lists the DCE pinouts. Arrows indicate signal direction: a right arrow (-->) indicates DTE to DCE, and a left arrow (<--) indicates DCE to DTE.
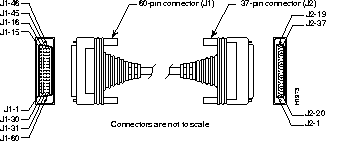
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 37 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-49 J1-48 | MODE_1 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-51 J1-52 | GND MODE_DCE | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | _ | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-11 J1-12 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 6 | --> --> | J2-4 J2-22 | SD+ SD- |
| J1-24 J1-23 | TxC/RxC+ TxC/RxC- | Twisted pair no. 9 | <-- <-- | J2-5 J2-23 | ST+ ST- |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 11 | <-- <-- | J2-6 J2-24 | RD+ RD- |
| J1-9 J1-10 | RTS/CTS+ RTS/CTS- | Twisted pair no. 5 | --> --> | J2-7 J2-25 | RS+ RS- |
| J1-26 J1-25 | RxC/TxCE+ RxC/TxCE- | Twisted pair no. 10 | <-- <-- | J2-8 J2-26 | RT+ RT- |
| J1-1 J1-2 | CTS/RTS+ CTS/RTS- | Twisted pair no. 1 | <-- <-- | J2-9 J2-27 | CS+ CS- |
| J1-44 J1-45 | LL/DCD Circuit_GND | Twisted pair no. 12 | --> _ | J2-10 J2-37 | LL SC |
| J1-3 J1-4 | DSR/DTR+ DSR/DTR- | Twisted pair no. 2 | <-- <-- | J2-11 J2-29 | DM+ DM- |
| J1-7 J1-8 | DTR/DSR+ DTR/DSR- | Twisted pair no. 4 | --> --> | J2-12 J2-30 | TR+ TR- |
| J1-5 J1-6 | DCD/DCD+ DCD/DCD- | Twisted pair no. 3 | <-- <-- | J2-13 J2-31 | RR+ RR- |
| J1-13 J1-14 | TxCE/TxC+ TxCE/TxC- | Twisted pair no. 7 | --> --> | J2-17 J2-35 | TT+ TT- |
| J1-15 J1-16 | Circuit_GND Circuit_GND | Twisted pair no. 9 | - - | J2-19 J2-20 | SG RC |
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 37 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-49 J1-48 | MODE_1 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | - | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 11 | <-- <-- | J2-4 J2-22 | SD+ SD- |
| J1-13 J1-14 | TxCE/TxC+ TxCE/TxC- | Twisted pair no. 7 | --> --> | J2-5 J2-23 | ST+ ST- |
| J1-11 J1-12 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 6 | --> --> | J2-6 J2-24 | RD+ RD- |
| J1-1 J1-2 | CTS/RTS+ CTS/RTS- | Twisted pair no. 1 | <-- <-- | J2-7 J2-25 | RS+ RS- |
| J1-24 J1-23 | TxC/RxC+ TxC/RxC- | Twisted pair no. 9 | --> --> | J2-8 J2-26 | RT+ RT- |
| J1-9 J1-10 | RTS/CTS+ RTS/CTS- | Twisted pair no. 5 | --> --> | J2-9 J2-27 | CS+ CS- |
| J1-29 J1-30 | NIL/LL Circuit_GND | Twisted pair no. 12 | --> - | J2-10 J2-37 | LL SC |
| J1-7 J1-8 | DTR/DSR+ DTR/DSR- | Twisted pair no. 4 | --> --> | J2-11 J2-29 | DM+ DM- |
| J1-3 J1-4 | DSR/DTR+ DSR/DTR- | Twisted pair no. 2 | <-- <-- | J2-12 J2-30 | TR+ TR- |
| J1-5 J1-6 | DCD/DCD+ DCD/DCD- | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> --> | J2-13 J2-31 | RR+ RR- |
| J1-26 J1-25 | RxC/TxCE+ RxC/TxCE- | Twisted pair no. 10 | <-- <-- | J2-17 J2-35 | TT+ TT- |
| J1-15 J1-16 | Circuit_GND Circuit_GND | Twisted pair no. 8 | _ _ | J2-19 J2-20 | SG RC |
Figure B-18 shows the V.35 cable assembly. Table B-17 lists the DTE pinouts. Table B-18 lists the DCE pinouts. Arrows indicate signal direction: a right arrow (-->) indicates DTE to DCE, and a left arrow (<--) indicates DCE to DTE.
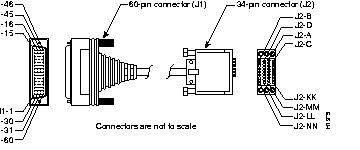
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 34 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-49 J1-48 | MODE_1 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-50 J1-51 J1-52 | MODE_0 GND MODE_DCE | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-53 J1-54 J1-55 J1-56 | TxC/NIL RxC_TxCE RxD/TxD GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | - | J2-A | Frame GND |
| J1-45 Shield | Circuit_GND - | Twisted pair no. 12 | - - | J2-B Shield | Circuit GND - |
| J1-42 Shield | RTS/CTS - | Twisted pair no. 9 | --> - | J2-C Shield | RTS - |
| J1-35 Shield | CTS/RTS - | Twisted pair no. 8 | <-- - | J2-D Shield | CTS - |
| J1-34 Shield | DSR/DTR - | Twisted pair no. 7 | <-- - | J2-E Shield | DSR - |
| J1-33 Shield | DCD/LL - | Twisted pair no. 6 | <-- - | J2-F Shield | RLSD - |
| J1-43 Shield | DTR/DSR - | Twisted pair no. 10 | --> - | J2-H Shield | DTR - |
| J1-44 Shield | LL/DCD - | Twisted pair no. 11 | --> - | J2-K Shield | LT - |
| J1-18 J1-17 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 1 | --> --> | J2-P J2-S | SD+ SD- |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 5 | <-- <-- | J2-R J2-T | RD+ RD- |
| J1-20 J1-19 | TxCE/TxC+ TxCE/TxC- | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> --> | J2-U J2-W | SCTE+ SCTE- |
| J1-26 J1-25 | RxC/TxCE+ RxC/TxCE- | Twisted pair no. 4 | <-- <-- | J2-V J2-X | SCR+ SCR- |
| J1-24 J1-23 | TxC/RxC+ TxC/RxC- | Twisted pair no. 3 | <-- <-- | J2-Y J2-AA | SCT+ SCT- |
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 34 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-49 J1-48 | MODE_1 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-50 J1-51 | MODE_0 GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-53 J1-54 J1-55 J1-56 | TxC/NIL RxC_TxCE RxD/TxD GND | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | - | J2-A | Frame GND |
| J1-45 Shield | Circuit_GND - | Twisted pair no. 12 | - - | J2-B Shield | Circuit GND - |
| J1-35 Shield | CTS/RTS - | Twisted pair no. 8 | <-- - | J2-C Shield | RTS - |
| J1-42 Shield | RTS/CTS - | Twisted pair no. 9 | --> - | J2-D Shield | CTS - |
| J1-43 Shield | DTR/DSR - | Twisted pair no. 10 | --> - | J2-E Shield | DSR - |
| J1-44 Shield | LL/DCD - | Twisted pair no. 11 | --> - | J2-F Shield | RLSD - |
| J1-34 Shield | DSR/DTR - | Twisted pair no. 7 | <-- - | J2-H Shield | DTR - |
| J1-33 Shield | DCD/LL - | Twisted pair no. 6 | <-- - | J2-K Shield | LT - |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 5 | <-- <-- | J2-P J2-S | SD+ SD- |
| J1-18 J1-17 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 1 | --> --> | J2-R J2-T | RD+ RD- |
| J1-26 J1-25 | RxC/TxCE+ RxC/TxCE- | Twisted pair no. 4 | <-- <-- | J2-U J2-W | SCTE+ SCTE- |
| J1-22 J1-21 | NIL/RxC+ NIL/RxC- | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> --> | J2-V J2-X | SCR+ SCR- |
| J1-20 J1-19 | TxCE/TxC+ TxCE/TxC- | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> --> | J2-Y J2-AA | SCT+ SCT- |
Figure B-19 shows the X.21 cable assembly. Table B-19 lists the DTE pinouts. Table B-20 lists the DCE pinouts. Arrows indicate signal direction: a right arrow (-->) indicates DTE to DCE, and a left arrow (<--) indicates DCE to DTE.
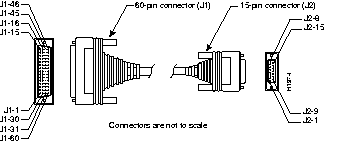
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 15 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-48 J1-47 | GND MODE_2 | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-51 J1-52 | GND MODE_DCE | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | - | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-11 J1-12 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> --> | J2-2 J2-9 | Transmit+ Transmit- |
| J1-9 J1-10 | RTS/CTS+ RTS/CTS- | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> --> | J2-3 J2-10 | Control+ Control- |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 6 | <-- <-- | J2-4 J2-11 | Receive+ Receive- |
| J1-1 J1-2 | CTS/RTS+ CTS/RTS- | Twisted pair no. 1 | <-- <-- | J2-5 J2-12 | Indication+ Indication- |
| J1-26 J1-25 | RxC/TxCE+ RxC/TxCE- | Twisted pair no. 5 | <-- <-- | J2-6 J2-13 | Timing+ Timing- |
| J1-15 Shield | Control_GND - | Twisted pair no. 4 | - - | J2-8 Shield | Control GND - |
| 60 Pin | Signal | Description | Direction | 15 Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-48 J1-47 | GND MODE_2 | Shorting group | - | - | - |
| J1-46 | Shield_GND | Single | - | J2-1 | Shield GND |
| J1-28 J1-27 | RxD/TxD+ RxD/TxD- | Twisted pair no. 6 | <-- <-- | J2-2 J2-9 | Transmit+ Transmit- |
| J1-1 J1-2 | CTS/RTS+ CTS/RTS- | Twisted pair no. 1 | <-- <-- | J2-3 J2-10 | Control+ Control- |
| J1-11 J1-12 | TxD/RxD+ TxD/RxD- | Twisted pair no. 3 | --> --> | J2-4 J2-11 | Receive+ Receive- |
| J1-9 J1-10 | RTS/CTS+ RTS/CTS- | Twisted pair no. 2 | --> --> | J2-5 J2-12 | Indication+ Indication- |
| J1-24 J1-23 | TxC/RxC+ TxC/RxC- | Twisted pair no. 4 | --> --> | J2-6 J2-13 | Timing+ Timing- |
| J1-15 Shield | Control_GND - | Twisted pair no. 5 | - - | J2-8 Shield | Control GND - |
This section lists the pinouts for ports on the supervisor engine module of the AccessPath system Switch Shelf. All pins not specifically listed are not connected. Following is a list of the signal summaries contained in this section:
The console port on the supervisor engine module does not support modem control or hardware flow control. Both data set ready (DSR) and data carrier detect (DCD) signals are active when the system is running. The Request To Send (RTS) signal tracks the state of the Clear To Send (CTS) input. Table B-21 lists the signals used on the console port for all supervisor engine module types.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground | |
| 2 | RxD | --> | Receive data |
| 3 | TxD | <-- | Transmit data |
| 4 | CTS | <-- | Clear to send |
| 5 | RTS | --> | Return to send |
| 7 | GND | Ground | |
| 8 | DTR | --> | Data terminal ready |
| 20 | DCD | <-- | Data carrier detect |
Most Ethernet transceivers require a transceiver cable to connect an Ethernet transceiver to the supervisor engine module Ethernet ports. For descriptions of Ethernet transceivers, connectors, and cables, refer to the section "Connecting the Switch" in the Chapter 3 "Installing the Switch" in the Catalyst 5000 Hardware Installation and Maintenance Guide.
Table B-22 lists the signals for the supervisor engine module 40-pin MII Fast Ethernet connector.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | +5V |
| 2 | MDIO |
| 3 | MDC |
| 4 | RxD<3> |
| 5 | RxD<2> |
| 6 | RxD<1> |
| 7 | RxD<0> |
| 8 | Rx_DV |
| 9 | Rx_Clk |
| 10 | Rx_Er |
| 11 | Tx_Er |
| 12 | Tx_Clk |
| 13 | Tx_En |
| 14 | TxD<0> |
| 15 | TxD<1> |
| 16 | TxD<2> |
| 17 | TxD<3> |
| 18 | Col |
| 19 | CRS |
| 20 | +5V |
| 21 | +5V |
| 22 | Common |
| 23 | Common |
| 24 | Common |
| 25 | Common |
| 26 | Common |
| 27 | Common |
| 28 | Common |
| 29 | Common |
| 30 | Common |
| 31 | Common |
| 32 | Common |
| 33 | Common |
| 34 | Common |
| 35 | Common |
| 36 | Common |
| 37 | Common |
| 38 | Common |
| 39 | Common |
| 40 | +5V |
Table B-23 lists the signals for the Switch Shelf supervisor engine module Fast Ethernet MDI X ports.
| Pin | Signal | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RxD+ | <-- | Receive data + |
| 2 | RxD- | <-- | Receive data - |
| 3 | TxD+ | --> | Transmit data + |
| 4 | NC | No connection | |
| 5 | NC | No connection | |
| 6 | TxD- | --> | Transmit data - |
| 7 | NC | No connection | |
| 8 | NC | No connection |
The AccessPath system ships precabled for data connectivity. However, if you need to replace data cabling, or if you add or remove AccessPath system shelves, you may need to refer to the following tables to connect the data cables.
Asynchronous cabling for the Failsafe/Console Management Shelf is outlined in Table B-24.
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf Connection | Access Server Shelf Connection |
|---|---|
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 1 | Access Server Shelf 1, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 2 | Access Server Shelf 2, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 3 | Access Server Shelf 3, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 4 | Access Server Shelf 4, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 5 | Access Server Shelf 5, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 6 | Access Server Shelf 6, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 7 | Access Server Shelf 7, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 1-8, 8 | Access Server Shelf 8, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 9 | Access Server Shelf 9, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 10 | Access Server Shelf 10, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 11 | Access Server Shelf 11, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 12 | Access Server Shelf 12, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 13 | Spare |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 14 | Router Shelf 2, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-16, 15 | Router Shelf 1, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Async 9-18, 16 | Switch Shelf, Console |
| Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 5/3 (single Router Shelf) or Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/3 (dual Router Shelf) |
Data cabling for the AccessPath system Access Server Shelves is outlined in Table B-25 (serial) and Table B-28 (T1 PRI).
For information on Access Server Shelf console port cabling to the Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, refer to Table B-24.
| Access Server Shelf Connection | Connection in a Single Router Shelf Configuration | Connection in a Dual Router Shelf Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Access Server Shelf 1, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 2, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/1 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 3, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/2 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/1 |
| Access Server Shelf 4, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/3 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/1 |
| Access Server Shelf 5, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/2 |
| Access Server Shelf 6, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/1 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/2 |
| Access Server Shelf 7, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/2 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/3 |
| Access Server Shelf 8, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/3 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/3 |
| Access Server Shelf 9, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 10, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/1 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 3/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 11, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/2 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/2 |
| Access Server Shelf 12, Serial 0 | Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/3 | Router Shelf 2, Serial 3/1 |
Data cabling for the AccessPath system Router Shelves is outlined in Table B-26 and Table B-27.
| Connection on the Router Shelf | Connection on the Other Shelf |
|---|---|
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/0 | Access Server Shelf 1, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/1 | Access Server Shelf 2, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/2 | Access Server Shelf 3, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/3 | Access Server Shelf 4, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/0 | Access Server Shelf 5, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/1 | Access Server Shelf 6, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/2 | Access Server Shelf 7, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/3 | Access Server Shelf 8, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/0 | Access Server Shelf 9, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/1 | Access Server Shelf 10, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/2 | Access Server Shelf 11, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/3 | Access Server Shelf 12, Serial 0 |
| Router Shelf 1, Serial 5/3 | Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Serial 0 |
| First (Bottom) Router Shelf | Second (Top) Router Shelf |
|---|---|
| Access Server Shelf 1, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/0 | Access Server Shelf 2, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 3, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/1 | Access Server Shelf 4, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/1 |
| Access Server Shelf 5, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/2 | Access Server Shelf 6, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/2 |
| Access Server Shelf 7, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 2/3 | Access Server Shelf 8, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 2/3 |
| Access Server Shelf 9, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/0 | Access Server Shelf 10, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 3/0 |
| Access Server Shelf 11, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 4/2 | Failsafe/Console Management Shelf, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 1, Serial 3/3 |
| Access Server Shelf 12, Serial 0 --> Router Shelf 2, Serial 3/1 | - |
| Router Shelf 1, Fast Ethernet 0/0 --> Router Shelf 2, Fast Ethernet 0/0 | Router Shelf 1, Fast Ethernet 0/0 --> Router Shelf 2, Fast Ethernet 0/0 |
| Switch Shelf, Fast Ethernet 1/1 --> Router Shelf 1, Fast Ethernet 1/0 | Switch Shelf, Fast Ethernet 1/2 --> Router Shelf 2, Fast Ethernet 1/0 |
| Access Server Shelf Connection | Connection to the T1 Patch Panel |
|---|---|
| Access Server Shelf 1, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 1 |
| Access Server Shelf 1, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 2 |
| Access Server Shelf 2, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 3 |
| Access Server Shelf 2, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 4 |
| Access Server Shelf 3, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 5 |
| Access Server Shelf 3, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 6 |
| Access Server Shelf 4, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 7 |
| Access Server Shelf 4, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 8 |
| Access Server Shelf 5, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 9 |
| Access Server Shelf 5, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 10 |
| Access Server Shelf 6, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 11 |
| Access Server Shelf 6, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 12 |
| Access Server Shelf 7, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 13 |
| Access Server Shelf 7, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 14 |
| Access Server Shelf 8, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 15 |
| Access Server Shelf 8, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 16 |
| Access Server Shelf 9, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 17 |
| Access Server Shelf 9, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 18 |
| Access Server Shelf 10, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 19 |
| Access Server Shelf 10, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 20 |
| Access Server Shelf 11, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 21 |
| Access Server Shelf 11, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 22 |
| Access Server Shelf 12, PRI 0 | T1 Patch Panel, 23 |
| Access Server Shelf 12, PRI 1 | T1 Patch Panel, 24 |
AC power cabling is preconfigured before the AccessPath system is shipped. However, if you add or remove AccessPath system shelves, you will need to refer to the matrix in Table B-29.
Power supplies are connected to specific power receptacles in ways that simplify power connections and preserve redundant power by using different power strips for redundant power supplies.
| Power Receptacle (From Top to Bottom) | Shelf (From Top to Bottom) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Failsafe/Console Management Shelf |
| 2 | Access Server Shelf 1 |
| 3 | Access Server Shelf 2 |
| 4 | Access Server Shelf 3 |
| 5 | Access Server Shelf 4 |
| 6 | Access Server Shelf 5 |
| 7 | Access Server Shelf 6 |
| 8 | Access Server Shelf 7 |
| 9 | Access Server Shelf 8 |
| 10 | Access Server Shelf 9 |
| 11 | Access Server Shelf 10 |
| 12 | Access Server Shelf 11 |
| 13 | Access Server Shelf 12 |
| 14 | Router Shelf 2, Power Supply 2 |
| 15 | Router Shelf 1, Power Supply 2 |
| 16 | Switch Shelf, Power Supply 2 |
| 17 | Unused |
| 18 | Router Shelf 2, Power Supply 1 |
| 19 | Router Shelf 1, Power Supply 1 |
| 20 | Switch Shelf, Power Supply 2 |
|
|