|
|
This appendix contains useful information about using the FastHub in Ethernet networks and contains the following sections:
There are two types of ports on the FastHub: network ports and an uplink port. These ports have different pinouts and should be cabled accordingly.
Table B-1 is a summary of the ports on the FastHub 112T and FastHub 124T.
| Model | Network Ports | Uplink Port |
|---|---|---|
| FastHub 112T | 1x through 12x | 12 |
| FastHub 124T | 1x through 24x | 24 |
Network ports are internally crossed. Use an Ethernet crossover cable of the following type to connect any of these ports to another network device, such as a workstation, server, hub, switch, or router:
Table B-2 lists the pinouts for FastHub network ports.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | RD+ |
| 2 | RD- |
| 3 | TD+ |
| 4 | NC |
| 5 | NC |
| 6 | TD- |
| 7 | NC |
| 8 | NC |
The uplink port is not internally crossed. Use an Ethernet straight-through cable of the following type to connect one of these ports to another FastHub network port or to a network port on another hub, switch, or router:
Figure B-1 is a schematic of the two types of cable (crossover and straight-through) used to connect the hub to network devices.
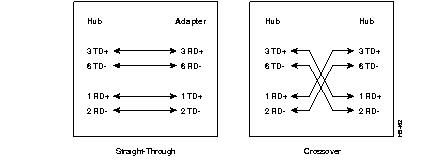
The IEEE 802.3u standard defines two different classes of Ethernet repeaters, Class I and Class II.
The FastHub 112T and FastHub 124T are Class II repeaters. Following are the advantages of Class II repeaters:
Table B-3 describes some guidelines when creating Ethernet networks with multiple repeaters. Exact figures could vary, depending on the manufacturer of the network equipment.
| Specification | 10BaseT | 100BaseTX |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum segment length | 100 | 100 |
| Maximum number of segments per network | 5 |
|
|
Maximum number of hops1 | 4 |
|
|
Maximum number of stations per segment | 1024 | 1024 |
| Cable type supported | UTP Category 3, 4, or 5 | UTP Category 5 |
|
|