|
|

August 15, 1997
These release notes describe the new features, modifications, and caveats for the Catalyst 2820 and the Catalyst 1900 version 5.35 firmware.
The product documentation for the Catalyst 2820 Series switches and Catalyst 1900 Series switches is as follows:
Catalyst 2820 Series and Catalyst 1900 Series Installation and Configuration Guide
Catalyst 2820 Modules User Guide
Catalyst 2820 Series and Catalyst 1900 Series MIB Reference Manual
This firmware version adds the following new features.
The switch Port Fast option is a simplified version of the Spanning-Tree Protocol that eliminates several of the normal spanning-tree states. The preforwarding states are bypassed to more quickly bring ports into the forwarding states. Port Fast is an option that you can enable on a per-port basis. It is recommended for end-station attachments only.
Use the Port Configuration Menu, shown in Figure 1, to disable or enable the Port Fast option.
Display this menu by pressing P on the Main Menu. The following prompt is displayed:
Identify port: 1 to 24, AUI,[A1],[B1] Select [1 - 24, AUI, A1, B1]:
Enter the number of the port you want to configure.
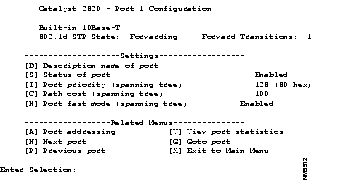
[H] Port fast mode (spanning tree)--Select this option to accelerate the time it takes for Spanning-Tree Protocol to bring a port into the forwarding state. Enter an E or D at the prompt and press Return.
When a Catalyst 2820 or 1900 receives a unicast packet with a destination address that it has not learned, the default is to flood it to all ports. However, on ports with only statically assigned addresses or with single stations attached, there are no unknown destinations, and flooding would serve no purpose. You can disable flooding in this case on a per-port basis.
You can also assign a single port, referred to as the Network Port, to act as the destination for all packets with unknown unicast addresses. This port is usually connected to a legacy network or backbone. A secured port cannot be the Network Port, and the Network Port does not learn addresses. Use the "System Menu" menu to define a port as the Network Port.
Use the System Configuration Menu, shown in Figure 2, to define a Network Port. Display this menu by entering S on the Main Menu.
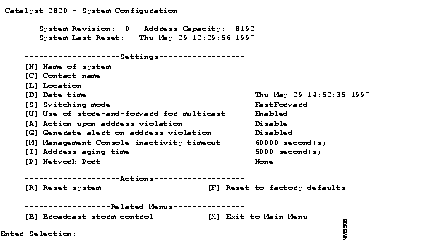
[P] Network Port--Use this option to specify the destination port for all packets with unknown unicast addresses. If you select a secure port to act as the Network Port, you are prompted to disable the security feature before continuing. Define a port according to the conventions in the prompt and press Return.
The following changes to the existing switch software are documented in the Catalyst 2820 Series and Catalyst 1900 Series Installation and Configuration Guide:
In addition, there are the following modifications:
This section lists possibly unexpected behavior by version 5.35.
The BOOTP protocol operates across the VLAN to which port 1 is assigned. By default, port 1 is assigned to VLAN 1.
Previous versions supported up to four switch IP addresses, each associated with a separate VLAN. With version 5.35, the switch has a single IP address that is associated with the management VLAN. When upgrading to version 5.35, the IP address of VLAN1 becomes the IP address of the switch and the management VLAN. IP addresses associated with the other VLANs in the earlier firmware version are dropped.
If you downgrade from version 5.35 to version 5.34, the switch IP address becomes the IP address of VLAN1. If there were other VLANs configured with their own IP addresses before the upgrade, the IP addresses assigned to the VLANs reappear after the downgrade.
When you upgrade to version 5.35, the VLANs and the ports that belong to them are preserved, unless there are overlapping VLANs. Overlapping VLANs are no longer supported with version 5.35. If there is a port that belongs to more than one VLAN, it is assigned to the VLAN with the highest number and dropped from the other VLAN definition.
If you downgrade from version 5.35 to an earlier version, any overlapping VLAN information that existed prior to the 5.35 upgrade is lost.
There should always be at least one port belonging to VLAN1. If there are no ports belonging to VLAN1, traffic can cross VLAN boundaries when the switch is reset.
If you have customized any version 5.25 parameters, the upgrade to version 5.34 or 5.35 resets these parameters to their factory default values. Reset them to your customized settings after the upgrade. (The 5.34 and 5.35 default values of the configurable parameters have not changed from version 5.25.)
The following parameters return to the listed factory default values when you upgrade to
version 5.34 or 5.35 from 5.25.
| Parameter | Default Value |
| Broadcast threshold (BCs received/sec) | 500 |
| Broadcast re-enable threshold | 250 |
| Spanning-Tree Protocol | Enabled |
| Generate alert on address violation | Enabled |
| Action upon address violation | Suspend |
| Switching mode | FastForward |
| Use of store-and-forward for multicast | Disabled |
| Capturing frames to the monitor | Disabled |
| Monitor port assignment | None |
| MIB object sysConfigHigherProtocolMonitor | Disabled |
| Authentication trap generation | Enabled |
| LinkUp/LinkDown trap generation | Enabled |
| Accept upgrade transfer from other hosts | Enabled |
| Action upon exceeding broadcast threshold | Ignore |
| Generate alert when threshold exceeded | Disabled |
| RS-232 data bits | 8 |
| RS-232 stop bits | 1 |
| RS-232 parity setting | None |
| RS-232 match remote baud rate (auto baud) | Enabled |
| RS-232 auto answer | Enabled |
| MIB object IP time to live | 255 |
| Help level setting of the management console | Novice |
| Overlapping of VLANs permitted | Disabled |
| Capture-time interval for the bandwidth-usage report | 24 hours |
| Status of an SNMP write manager | Enabled |
| Status of an SNMP trap manager | Enabled |
| Management console inactivity timeout | None |
| Password intrusion threshold | 3 attempts |
| Silent time upon intrusion detection | None |
| RS-232 baud rate | 9600 |
| Time delay between dial out attempts | 300 seconds |
| Address aging time | 300 seconds |
For service and support for a product purchased from a reseller, contact the reseller. Resellers offer a wide variety of Cisco service and support programs, which are described in the section "Service and Support" in the information packet that shipped with your product.
For service and support for a product purchased directly from Cisco, use CCO.
CCO is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. SMARTnet customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Please use CCO to obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades. If CCO is not accessible, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or cs-rep@cisco.com.

|
|