|
|

December 29, 1997
This document contains instructions for installing, configuring, and using the Catalyst 5000 series switches Token Ring module (product number: WS-X5030). This document is divided into the following sections:
 | Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment. |
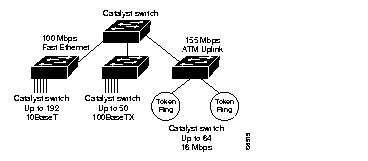
The Catalyst 5000 series switch provides high-density switched Ethernet and Fast Ethernet for both wiring closet and data center applications. The switch includes a single, integrated 1.2-Gbps switching backplane that supports switched Ethernet with repeater connections, Fast Ethernet with backbone connections, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), Copper Distributed Data Interface (CDDI), Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), and 4- and 16- Mbps Token Ring. The Catalyst 5000 provides switched connections to individual workstations, servers, LAN segments, backbones, or other Catalyst 5000 switches using shielded twisted-pair (STP), unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), and fiber-optic cable. Figure 1 is an example of a configuration using the Catalyst 5000 series switch.
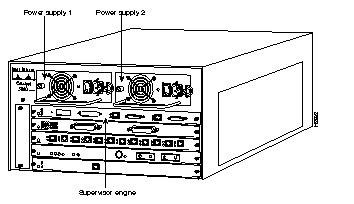
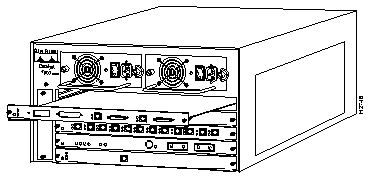
Depending on the Catalyst 5000 series switch model that you are using, there are up to 11 interface slots available on the switch. Regardless of the Catalyst 5000 series switch, interface slot 1 supports a supervisor engine module, which provides Layer 2 switching, local and remote management, and dual Fast Ethernet interfaces. Slot 13 on the Catalyst 5500 switch is reserved for the ATM Switch Processor (ASP) module. The remaining slots are used for any combination of modules for additional Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, CDDI/FDDI, ATM, and Token Ring connections. Figure 2 shows the rear view of the Catalyst 5000 series switch, which provides access to the supervisor engine, all switching modules, power supplies, and fan assembly.
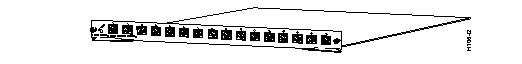
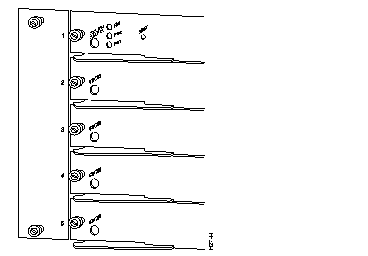
The Token Ring module, shown in Figure 3 has 16 shielded RJ-45 connectors for Token Ring connections. These ports allow full or half duplex connections to other switches, hubs, or end nodes.
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module provides the following features:
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module applies the IEEE 802.5 annex K models of Concentrator Relay Functions (CRFs) and Bridge Relay Functions (BRFs). The Token Ring Concentrator Relay Function (TrCRF) and the Token Ring Bridge Relay Function (TrBRF) models support for the following bridging modes:
For more information about bridging modes, please see the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" section. For more information on TrBRFs and TrCRFs, see the "Token Ring VLANs" section.
Each of the 16 Token Ring ports on the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module can operate in one of the following modes:
The mode of operation can be configured, or it can be automatically sensed when equipment is connected to the port. The media speed (4 or 16 Mbps) can also be configured or automatically sensed in all port modes.
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module supports 4- and 16-Mbps Token Ring transmission speeds. You can configure ports on the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module to operate at one of these speeds or to automatically sense the speed of the ring to which it is connected. However, with Token Ring technology, a transmission speed cannot be changed without closing and reopening the port, therefore the following rules apply:
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module supports a new token passing standard called Dedicated Token Ring (DTR). DTR is the IEEE 802.5R standard that:
DTR is particularly useful for providing improved access to central resources, such as network servers. for servers can be directly attached to a switch.
To address the needs of delay-sensitive data, such as multimedia data, each port on the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module has two data queues: high-priority and low-priority.
The queue for a frame is determined by the value of the priority field in the frame control (FC) byte of the frame. If the FC priority is above the user-defined priority level (the default is 3), the frame is put in the high-priority queue and is transmitted using the frame priority. If the FC priority is at or below the user-defined priority level, then the frame is sent to the low-priority queue.
For information on defining a priority level, see the "Setting the Frame Priority Levels" section.
Many bridged networks today use filtering to reduce broadcast traffic, block protocols, and provide basic security. The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module provides filtering capabilities for the same purpose.
You can filter frames based on the following:
MAC address filters can be configured for only input ports. DSAP/SNAP filters can be configured for both input and output ports. You can configure up to 16 MAC address or DSAP/SNAP filters for each port on the Token Ring module.
To filter data based on MAC address, you specify an address and indicate whether you want to block or allow frames that contain the address as a source or destination address. To filter data based on protocol, specify either a DSAP or SNAP and specify whether to permit or deny frames with that protocol.
For information on configuring filters, see the "Configuring Filters" section.
For parallel SRB or SRT backbones, All-Routes Explorer reduction ensures that the number of all-routes explorer frames generated by the switch does not overwhelm the network.
The IEEE 802.1d SRT standard specifies two optional ways of reducing the all-routes explorer explosion. The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module discards any all-routes explorer frames that have already been on a ring that is attached to the switch.
This mechanism is configurable and ensures that only one all-routes explorer frame is received on each ring within each VLAN. The number of all-routes explorer frames is equal to the number of external parallel paths between the rings. If a port on the switch fails, or is disabled, the switch will no longer check for this ring number in the Routing Information Field (RIF). This bypass allows frames to travel on alternate paths.
By default, All-Routes Explorer Reduction is enabled.
For information on enabling and disabling All-Routes Explorer Reduction, see the "Enabling and Disabling All-Routes Explorer Reduction" section.
With a VLAN, logical rings can be formed by defining port groups that have the same ring number. The IEEE standard calls such a Token Ring port group a TrCRF. Within the TrCRF, source-route switching is used for forwarding based on either MAC addresses or route descriptors (RDs). If desired, you may configure the entire VLAN to operate as a single ring (for example, a single TrCRF).
Multiple logical rings or TrCRFs can be interconnected via a single TrBRF. The TrBRF provides either the SRB or SRT switching mode. For source routing, the switch, or network of switches, appears as a single bridge between the logical rings. If SRB is used, duplicate MAC addresses can be defined on different logical rings.
For more information on Token Ring VLANs, see the "Token Ring VLANs" section. For information on configuring a VLAN, see the "Configuring VLANs" section.
When creating a fault-tolerant internetwork, a loop-free path must exist between all nodes in a network. A spanning-tree algorithm is used to calculate the best loop-free path through a Catalyst 5000 series switched network. Spanning-tree packets are sent and received by switches in the network at regular intervals. The packets are not forwarded by the switches participating in the Spanning-Tree Protocol, but are instead used by the switches to identify the loop-free path. Spanning-Tree Protocols perform this function for Catalyst 5000 series switches.
The Catalyst 5000 series switch uses the IEEE 802.1D or Cisco Spanning-Tree protocols on all TrCRFs. The IBM or IEEE Spanning-Tree protocol is used on all TrBRFs. For more information on the Spanning-Tree Protocols running on TrCRFs and TrBRFs, see the "Configuring Spanning-Tree Protocol" section. The default configuration has all Spanning-Tree Protocols enabled.
For more information on Spanning-Tree Protocols, see the "Configuring Spanning-Tree Protocol" "Understanding Token Ring Switching" sections.
With the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, you can preform the following tasks:
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module can be managed via an SNMP manager (such as CiscoView). The Token Ring module supports nine Management Information Bases (MIBs). Six of the MIBs are standard MIBs, which are defined by RFCs and are included with most SNMP management applications. Three of the MIBs are Cisco proprietary MIBs and can be obtained from CCO. See the "Cisco Connection Online" section for access to CCO information.
In addition to the standard MIBs supported the Catalyst 5000 series switch, the Token Ring module supports the following additional MIBs:
The proprietary MIBs supported are:
Most user configurable variables are supported in either the standard MIBs or private MIBs. Configuration settings, such as port attributes, and operational information, such as address tables, are fully accessible through SNMP. Certain other settings, such as passwords and console settings, cannot be viewed or modified via SNMP for security reasons.
CiscoView is a graphical user interface device management software application that provides dynamic status, statistics, and comprehensive configuration information for Cisco System's switched and internetworking products. CiscoView allows you to display configuration and performance information, and perform minor troubleshooting tasks.
RMON is an industry-standard method for providing network statistics monitoring using SNMP. It also collects fault, performance, and configuration statistics. RMON can monitor continuously, even when communication with the management station is not possible or efficient. It can then notify the management station when an exceptional condition occurs.
In typical SNMP management, the SNMP manager has to continuously poll the Catalyst 5000 series switch for fault, performance, and configuration information while waiting for the value to change. This causes increased traffic through the network. With RMON, you can have the switch monitor a particular statistic internally, and when the statistic reaches a threshold the Catalyst 5000 series switch will send a trap to the client. This monitoring method reduces traffic between the SNMP manager and the Catalyst 5000 series switch.
As an option, the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module provides RMON support statistics, history, alarms, and events. It also provides support for the following groups of the Token Ring extensions to the Remote Network Monitoring MIB (RFC 1513):
You can use an external RMON probe for full RMON support.
Access to RMON data is available only via an SNMP management application that supports RFC 1757 and RFC 1513. You cannot access RMON via the Catalyst 5000 series switch console interface; however, the console statistics provide similar information. For full utilization of RMON data, you should use Cisco's TrafficDirector.
This section lists sources of additional information that may be helpful in using the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
These documents can be obtained through Cisco Connection Online. For information on Cisco Connection Online, see the "Cisco Connection Online" section of this configuration note.
Before installing a Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, ensure that your existing system components meet the following minimum requirements for compatibility:
The following are the technical specifications for the 16-port Token Ring module:
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 1.17 x 14.4 x 16.0 in (2.9 x 36.58 x 40.64 cm) |
| Weight | 3.9 lb (1.45 kg) |
Environmental Conditions
|
32 to 104° (0 to 40°C) -40 to 167°F (-40 to 75°C) 10 to 90%, noncondensing |
| Connectors | 16 RJ-45 IEEE 802.5 Token Ring UTP/STP |
| Frame processing | Source-route, source-route transparent, source-route switching |
| Network management | SNMP2 agent |
| Agency Approvals: Safety EMI2
| UL 1950, CSA-C22.2 No. 950, IEC 950, EN 60950 FCC 15J Class A, VCCI CE II, CE Mark, EN 55022 Class B, CISPR 22 Class B |
Depending on the Catalyst 5000 series switch model that you are using, there are up to 11 interface slots available on the switch. Regardless of the Catalyst 5000 series switch, interface slot 1 supports a supervisor engine module. Slot 13 on the Catalyst 5500 switch is reserved for the ATM Switch Processor (ASP) module. All other slots support any combination of network interface switching modules or provides maximum port densities of up to 176 Token Ring interfaces.
Light emitting diodes (LEDs) are located on the Token Ring module and on each of the 16 RJ-45 female connectors. The module LED indicates the status of the module. The port LEDs indicate the status and any activity occurring on a port.
The LED that indicates the status of the module is located on the left side of the front of the module. A green module LED indicates that the module is operational. It does not, however, indicate the operational status of the individual ports.
Table 2 lists the meanings of the Token Ring Module LED.
| LED | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Green | Switch has performed a series of self-tests and diagnostics tests and all which passed. |
| Red | Test other than an individual port test has failed or the power supply is bad. |
| Orange | System is starting up, performing self-test diagnostics, or the module is disabled. |
| Off | System is off. |
The port LEDs are integrated into each of the 16 RJ-45 female connectors of the Token Ring module. The port LEDs indicate the status or activity occurring on a specific port.
Figure 4 illustrates an RJ-45 connector as seen from the outside of the unit and identifies the approximate LED locations and designations.

Table 3 lists the meanings of the Token Ring module port LEDs.
| LED | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Status | Off Green Orange Orange (Flashing repeatedly) Orange | No signal is detected. Port is operational (a signal is detected). Link has been disabled by software. Link is bad and has been disabled because of a hardware failure. Card is coming up and synergy diagnostics are running a test on each port. |
| Activity | Off Green | Port activity is idle. Port is receiving or transmitting a packet. |
Before installing the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, read this section carefully, it contains information on pre-installation planning.
This section discusses the following topics:
When preparing your site for network connections to the switch, you need to consider a number of factors related to each type of interface:
Before installing the switch, have all additional external equipment and cables on hand. If you intend to build your own cables, refer to the cable pinouts in the "Token Ring Cabling Recommendations" section. For ordering information, contact a customer service representative.
The following tables contain the maximum supported lobe lengths. The maximum lengths reflect the longest lengths supported by the transmission characteristics of IEEE 802.5-compliant adapters.
The recommended distances for the various cable types are set by North American and international commercial building wiring standards. These standards state that standards-compliant horizontal copper cabling shall not exceed 295 feet (90 m) leaving 33 feet (10 m) total for required patch cabling in both the office and telecommunications closet. It is good practice to follow the cabling standards guidelines when installing building cabling to help ensure a longer useful life for your cabling infrastructure, migration to new technologies, and maximum flexibility for the network configuration.
Table 4 lists distance limits guidelines for planning your network connections before installation.
| Cable Type | Impedance |
|---|---|
| 1 and 1A | 150 ohms |
| 2 and 2A | 150 ohms |
| 8 | 150 ohms |
| 9 | 150 ohms |
| 3 | 100 ohms |
| Category 3 | 100 and 120 ohms |
| Category 4 | 100 and 120 ohms |
| Category 5 | 100 and 120 ohms |
The IBM Token Ring network dedicated-media connections support only one attached entity per connection.
In a Token Ring network, the section of cable that attaches a device to an access unit is called a lobe.
For all supported cable types except optical fiber, the recommended maximum cable lobe length is 625 feet (190 m) plus a 33 feet (10 m) total allowance for the patch cords in the office and the telecommunications closets. For optical fiber, the recommended maximum cable lobe length is 2000 m (6562 feet).
Table 5and Table 6 specify the maximum supported lobe lengths for the following types of cables. An additional 10 m (33 feet) per lobe length is allowed to accommodate patch cables, unless otherwise specified.
| Ring Speed | Types 1 and 1a, Types 2 and 2a | Type 8 | Type 9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Mbps | 2460 feet (750 m) | 1234 feet (376 m) | 1640 feet (500 m) |
| 16 Mbps | 952 feet (290 m) | 480 feet (146 m) | 656 feet (200 m) |
| Ring Speed | 100-ohms Type 3 | 100-ohms Category 3 | 100- or 120-ohms Category 4 | 100- or 120-ohms Category 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Mbps | 328 feet (100 m) | 820 feet (250 m) | 1148 feet (350 m) | 1148 feet (350 m) |
| 16 Mbps | Not Supported | 328 feet (100 m) | 656 feet (200 m) | 656 feet (200 m) |
The types of cables that can be used are the same as those described above for dedicated-media segments. The acceptable distances are defined by the hub or concentrator attached to the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module port.
A Token Ring network supports up to 260 attached devices or nodes on a single network when using 150-ohms shielded media (type 1, 1A, 2, or 2A). When cable segments in the network are 100 or 120 ohms, this number is decreased to 132 (72 if using any 4-Mbps-only adapters or filters).
When connecting devices to the Token Ring ports on the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module, you must use a straight-through 100-ohms or 120-ohms cable.
The Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module RJ-45 connector makes ground available on the shield and on pins 1, 2, 7, and 8. Shielded cables provide continuity for the ground-to-any shielded connector on the other end of the cable.
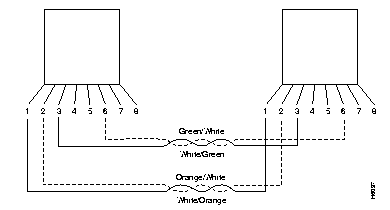
Figure 5 and Figure 6 illustrate the straight-through 100-ohms and 120-ohms cable and the 150-ohms data connector-to-RJ-45 straight-through cable.
To connect to a Token Ring network, use RJ-45 male connectors (Figure 7).
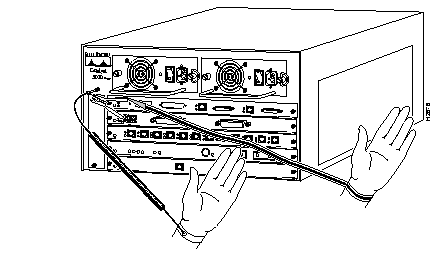
Before you begin installing the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module, review the safety and electrostatic (ESD)-prevention guidelines in this section to avoid injuring yourself or damaging the equipment.
Follow these guidelines when working with any equipment powered by electricity:
|
| Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
 | Warning Unplug the power cord before you work on a system that does not have an on/off switch. |
ESD damage occurs when electronic devices or components are improperly handled. This damage results in complete or intermittent failures. The supervisor engine and switching modules each consist of a printed circuit board fixed in a metal carrier. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, connectors, and a handle are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps protect modules from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap when you handle the supervisor engine or switching modules. Hold the carriers by the handles and the carrier edges only; never touch the modules or connector pins.
 | Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use. |
Guidelines for preventing ESD damage are the following:

The Catalyst 5000 series switching modules support hot swapping. The hot-swapping feature enables you to install, remove, replace, and rearrange the switching modules without turning off the system power. When the Catalyst 5000 series switch detects that a switching module has been installed or removed, it automatically runs diagnostic and discovery routines, acknowledges the presence or absence of the switching module, and resumes the system operation without any operator intervention.
The supervisor engine module and each switching module contain a bus-type connector that connects with the system backplane. Each card connector consists of a set of tiered pins, in three lengths. The pins send specific signals to the system as they make contact with the backplane of the Catalyst 5000 series switch. The system assesses the signals it receives and the order in which it receives them to determine what event is occurring and what task it needs to perform, such as reinitializing new interfaces or shutting down removed interfaces.
For example, when inserting your Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, the longest pins make contact with the backplane first and the shortest pins make contact last. The system recognizes the signals and the sequence in which it receives them. The system expects to receive signals from the individual pins in this logical sequence, and the ejector levers help to ensure that the pins mate in this sequence.
When you remove or insert a switching module, the backplane pins send signals to notify the system. The system then:
When you insert a new switching module, the system runs a diagnostic test on the new interfaces and compares them to the existing configuration. If this initial diagnostic test fails, the system remains off line for another 15 seconds while it performs a second set of diagnostic tests to determine whether or not the switching module is faulty and if normal system operation is possible.
If the second diagnostic test passes, which indicates that the system is operating normally and the new switching module is faulty, the system resumes normal operation but leaves the new interfaces disabled. If the second diagnostic test fails, the system crashes, which usually indicates that the new switching module has created a problem in the bus and should be removed.
 | Caution To avoid erroneous failure messages, allow at least 15 seconds for the system to reinitialize and note the current configuration of all interfaces before you remove or insert another switching module. |
Use the ejector levers (Figure 9) to align and seat the card connectors in the backplane. Failure to use the ejector levers and insert the switching module properly can disrupt the order in which the pins make contact with the backplane.
Before installing the Token Ring module, review the instructions in the "Installing the Token Ring Module" and "Removing Switching Modules or Module Fillers" sections carefully. Also review the following list of examples of incorrect insertion practices and results that you want to avoid when installing the Token Ring module.
When installing the Token Ring module:
It is also important to use the ejector levers when removing a switching module to ensure that the card connector pins disconnect from the backplane in the logical sequence expected by the system. Any supervisor engine module or switching module that is only partially connected to the backplane can hang the bus. Detailed steps for correctly performing hot swap are included in the "Installing the Catalyst 5000 Series Token Ring Module" section.
 | Caution All Catalyst 5000 series switching modules support hot swapping. The supervisor engine module is a required system component. Removing a supervisor engine module while the system is operating will cause the system to halt. |
This section explains the process you should follow to install the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
Before installing the Token Ring module, ensure that you have read the information in the "Planning for Installation" section of this configuration note.
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
This section discusses the following topics:
 | Warning Do not touch the power supply when the power cord is connected. For systems with a power switch, line voltages are present within the power supply even when the power switch is off and the power cord is connected. For systems without a power switch, line voltages are present within the power supply when the power cord is connected. |
To install the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module, you will need the following tools:
If a switching module or filler (blank) module exists in the slot in which you are planning to install the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module, remove the existing item before installing the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module. If there is no switching module or switching module filler in the slot in which you are planning to install the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module, proceed to the "Installing the Token Ring Module" section.
 | Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
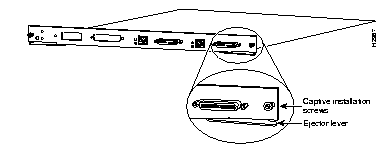
 | Caution Do not completely loosen one captive installation screw at a time. Attempting to completely loosen one captive installation screw at a time will cause damage to the thread. Always alternate between loosening the left screw and then loosening the right screw. |
To remove the existing module or module filler:
Step 1 Put on an ESD-preventive wrist or ankle strap and connect the equipment end of the strap to the metal case of the Catalsyt 5000 Series switch in which you are installing the module.
Step 2 Determine the slot for the Token Ring module and ensure that there is enough clearance to accommodate any interface equipment that you connect directly to the Token Ring module ports. If possible, place the switching module between empty slots that contain only switching module filler plates.
Using a flat-blade screw driver, turn the captive installation screw on the left side of the carrier counter-clockwise for two full turns.
 | Caution Always use the ejector levers (Figure 9 shows the ejector levers) when installing or removing switching modules. A module that is partially seated in the backplane will cause the system to halt and subsequently crash. |
Step 4 Using a flat-blade screw driver, turn the captive installation screw on the right side of the carrier counter-clockwise two full turns.
Step 5 Repeat steps 3 and 4 until you have completely loosened the captive installation screws.
Step 6 Place your thumbs on the left and right ejector levers and simultaneously push both the left and right levers to release the switching module or module filler from the backplane connector.
Step 7 Grasp the switching module or module filler with one hand and place your other hand under the carrier to support and guide the module out of the slot.
Step 8 Keeping the module or module filler at a 90-degree orientation to the backplane, carefully pull the module or module filler straight out of the slot, keeping your other hand under the carrier to guide it.
Step 9 If you have removed a switching module, place the removed module on an antistatic mat or antistatic foam, or immediately install it in another slot.
If you are not installing a switching module in the empty slot immediately, install a switching module filler (part number 800-00292-01) to keep dust out of the chassis and to maintain proper airflow through the switching module compartment.
 | Caution Never leave a switching module slot empty. Always ensure that a switching module or a switching module filler is installed in an empty slot to maintain the proper flow of cooling air across the modules. |
You can install the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module in any of the module slots except slot 1, which is reserved for the supervisor engine module or slot 13 on the Catalyst 5500 switch which is reserved for the ASP module. Depending on the model of the Catalyst 5000 series switch you are using, the module slots are numbered 1 through 13 from the top to bottom when viewing the Catalyst 5000 series switch from the rear (Figure 10).
Slot 1 contains the supervisor engine module, which is a required system component, and if you are using a Catalyst 5500 switch, slot 13 is reserved for the ASP module. Switching modules or switching module fillers, which are blank switching module carriers, are installed in the slots without modules to maintain consistent airflow through the switching module compartment.
 | Caution When installing the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, handle the module by the carrier edges only to prevent ESD damage. Make sure to avoid touching the card or connector pins. |
To install the Token Ring module:
Step 1 Hold the switching module handle with one hand and place your other hand under the carrier to support the switching module. Avoid touching the card.
Step 2 Aligning the notch on the sides of the switching module with the grooves in the slot, place the back of the switching module in the slot (Figure 11).
Keep the module at a 90-degree angle to the backplane and carefully slide the switching module into the slot until the module faceplate makes contact with the ejector levers.
 | Caution Do not force the Token Ring module into the slot. If the module does not slide in easily, make sure that it is properly aligned. |
Step 4 Using the thumb and forefinger of each hand, simultaneously push in the left and right levers to fully seat the module in the backplane connector.
Step 5 Using a flat-blade screwdriver, turn the captive installation screw on the left side of the carrier clockwise two full turns.
With the screwdriver, turn the captive installation screw on the right side of the carrier clockwise two full turns.
 | Caution Completely tightening one captive installation screw at a time will cause damage to the thread. Always alternate between turning the left screw and turning the right screw. |
Step 7 Repeat steps 5 and 6 until the captive installation screws are tight. Do not use excessive force to tighten the screws.
Step 8 Attach network interface cables or other devices to the interface ports.
Step 9 Use the set interface command facility to configure the new interfaces. This configuration does not have to be done immediately, but the interfaces will not be available until you configure them. For information on configuring the new interfaces, see the Catalyst 5000 Series Advanced Software Configuration Guide.
When you remove and replace the Catalyst 5000 series switching modules, the system provides status messages on the console screen. These messages are for information use only.
In the following display example, using the show system and show module commands, you can follow the events that are logged by the system when a switching module is removed from slot 4. When the show port command is used to query the module, the system reports notconnect. When the module is reinserted, the system marks the module as ok.
Console> (enable) show system
PS1-Status PS2-Status Fan-Status Temp-Alarm Sys-Status Uptime d,h:m:s Logout
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------
none ok ok off ok 0,01:32:56 none
PS1-Type PS2-Type Modem Baud Traffic Peak Peak-Time
---------- ---------- ------- ----- ------- ---- -------------------------
none WS-C5008 disable 9600 0% 0% Tue Oct 14 1997, 06:56:34
System Name System Location System Contact
------------------------ ------------------------ ------------------------
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) show module
Mod Module-Name Ports Module-Type Model Serial-Num Status
--- ------------------- ----- --------------------- --------- --------- -------
1 2 100BaseTX Supervisor WS-X5509 002258491 ok
2 48 4 Segment 10BaseT Eth WS-X5020 004859753 ok
3 16 Token Ring ws-x5030 900000002 ok
Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw
--- ---------------------------------------- ------ ------- ----------------
1 00-40-0b-8f-88-00 thru 00-40-0b-8f-8b-ff 0.214 3.1(113 3.1(143)
2 00-60-2f-36-86-70 thru 00-60-2f-36-86-87 2.4 1.1 3.1(143)
3 00:05:77:01:bb:0e thru 00:05:77:01:bb:1e 1.0 1.0(108 1.0(1)
Mod Sub-Type Sub-Model Sub-Serial Sub-Hw
--- -------- --------- ---------- ------
1 EARL 1+ WS-F5511 0003633671 0.202
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) show port 3/10
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------
3/10 notconnect 1003 normal auto auto TokenRing
Last-Time-Cleared
--------------------------
Tue Oct 14 1997, 06:56:34
Console> (enable)
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module is shipped with default configuration parameters and can function with these defaults. Therefore, you may not have to configure the module for it to work in your network. However, if you want or need to alter the configuration of the Token Ring module, you can do so.
This section describes how to use the command-line interface (CLI) to configure the ports on the Token Ring switching module. This section also contains information about Spanning-Tree Protocols and Token Ring VLANs. For additional information on the CLI, refer to the Catalyst 5000 Series Command Reference.
This section discusses the following topics:
The default values of the Token Ring module features are:
Before you can customize certain parameters of the Token Ring module, you must invoke the privilege mode of the Catalyst 5000 series switch. When in privilege mode, you can issue commands to configure or troubleshoot the system.
To enter privileged mode:
Step 1 From the Console> prompt, type enable. You are prompted for your password.
Step 2 Type your password and press Enter. The Console> prompt now indicates that you are in enable mode by displaying (enable) next to the console prompt.
For more information on configuring the Token Ring interface parameters, see the "Configuring Token Ring Port Parameters" section.
This section contains information on the following topics:
By default, no names are assigned to the ports on the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module. However, you can assign names to each of the ports on your Token Ring module using the set port name command.
To assign a name to a port on the Token Ring module, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set port name mod_num/port_num nameAfter entering the set port name command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable)set port name 4/1 Print-1st FloorPort 4/1 name set. Console> (enable)set port name 4/2 Server 1Port 4/2 name set.
There are two types of frame priorities that you can set for a port.
To set the frame priority levels for a port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring priority mod_num/port_num {threshold 0-7 | minxmit 0-6}After entering the set tokenring priority command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable)set tokenring priority 4/2 threshold 6Port 2 priority threshold set to 6. Console> (enable)set tokenring priority 4/2 minxmit 5Port 2 priority minxmit set to 5.
The speed of the port is in megabits per second (Mbps). The Token Ring module ports can be set to 4 or 16 Mbps transmission speeds. The default speed, auto, enables the interfaces to automatically configure themselves to operate at the proper speed (4 or 16 Mbps). However, you can configure the port speed if necessary.
To set the transmission speed for a Token Ring module port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set port speed mod_num/port_num {4 | 16 | auto}After entering the set port speed command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable)set port speed 4/1 4Port 4/1 speed set to 4Mbps. Console> (enable)set port speed 4/2 16Port 4/2 speed set to 16Mbps. Console> (enable)set port speed 4/3 autoPort 4/3 speed set to auto detect. Console> (enable)
The ports of the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module are capable of operating in half duplex mode or full duplex mode. The port can behave as either a concentrator port or an end station. The default mode, auto, enables the port to detect the transmission mode it needs to use. However, you can configure the mode if necessary.
To set the transmission mode being used by a port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring portmode mod_num/port_num {auto | fdxcport | hdxcport | fdxstation |After entering the set tokenring portmode command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set tokenring portmode 4/2 fdxcport Port 3/2 mode set to fdxcport Console> (enable)
The Token Ring module interface ports support early token release when transmitting frames. Early token release is a technique used in Token Ring networks that allows a station to release a new token onto the ring immediately after transmitting, instead of waiting for the first frame to return. Early token release increases the total bandwidth on the ring. All ports, by default, are enabled to use Early Token Release.
To enable or disable the early token release feature on a Token Ring module ports, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring etr mod_num/port_num {enable | disable}After entering the set tokenring etr command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable)set tokenring etr 4/1 enablePort 4/1 Early Token Release enabled. Console> (enable)set tokenring etr 4/2 disablePort 4/2 Early Token Release disabled.
You can specify whether the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit should be set unconditionally on repeated source-routed Logical Link Control (LLC) frames. These include source-routed frames with a RIF length greater than 2 and all spanning-tree explorer and all-routes explorer frames. The default is disable. If this parameter is set to disable, the setting of these bits is based on whether the frame was actually forwarded.
To set the AC bits for a port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring acbits mod_num/port_num {enable | disable}After entering the set tokenring acbits command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set tokenring acbits 4/4 enable Port 4/4 acbits enabled. Console> (enable) set tokenring acbits 4/4 disable Port 4/4 acbits disabled.
Configuration loss occurs when a port completes a connection, allows data traffic to flow, and subsequently closes. The configuration loss threshold is used to control the number of configuration losses that can occur within a specified time. When the threshold is exceeded, the port is disabled and must be enabled using the set port enable command or an SNMP manager. The valid range for the configuration loss threshold is 1 through 100. The default is 8.
To set and verify the configuration loss threshold for a port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring configloss mod_num/port_num {threshold <1..100> | interval <1..9999>}After entering the set tokenring configloss command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set tokenring configloss 4/2 threshold 50
Port 4/2 configloss threshold set to 50.
Console> (enable) set tokenring configloss 4/2 interval 20
Port 4/2 configloss interval set to 20.
After configuring the Token Ring ports, you can verify the configuration using the following commands:
After entering the show port command and specifying the module and port number, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) show port 3/2 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 3/2 inactive 1003 normal fdx auto TokenRing Last-Time-Cleared -------------------------- Wed Oct 15 1997, 18:09:47 Console> (enable)
Table 7 describes the information returned by the show port command.
| Field | Description |
| Port | Module and port number. |
| Name | Name (if configured) of the port. |
| Status | Status of the port (connected, notconnect, connecting, standby, faulty, inactive, shutdown, disabled, monitor, activeflt). |
| Vlan | VLANs to which the port belongs. |
| Level | Setting level for the port (normal or high). |
| Duplex | Duplex setting for the port (auto, full, fdx, half, hdx, a-half, a-full, a-fdx, a-hdx). |
| Speed | Speed setting for the port (auto, 10, 100, 155, a-10, a-100, 4, 16, a-4, a-16). |
| Type | Port type (10BaseT, 10BaseFL MM, 100BaseTX, 100BaseT4, 100BaseFX MM, 100BaseFX SM, 10/100BaseTX, TokenRing, FDDI, CDDI, MLT3 CDDI, SDDI, SMF-FDDI, PreStd CDDI, SCF FDDI, OC3 MMF ATM, OC3 SMF ATM, OC3 UTP ATM, Route Switch). |
After entering the show tokenring command and specifying a module and port number, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) show tokenring 3/2
Ports Crf/Brf Ring# Port-Mode Early-Token AC-bits
----- --------- ----- ------------- ----------- --------
3/2 1003/1005 3276 fdx-cport enabled disabled
Ports Prior-Thresh Min-Xmit MAC-Address
----- ------------ -------- -----------------
3/2 6 5 00:40:0b:01:bc:65
Ports Cfg-Loss-Thresh Cfg-Loss-Intvl Cfg-Loss-Count Cfg-Loss-Reason
----- --------------- -------------- -------------- ---------------
3/2 50 20 0 none
Console> (enable)
Table 8 describes the information returned by the show tokenring command issued with a module and port number specified.
| Field | Description |
| Ports | Module and port number. |
| Crf/Brf | TrCRF to which a port is assigned and the parent BRF associated with the TrCRF. |
| Ring | Logical ring number (in hexadecimal format) assigned to the TrCRF. Possible values are 01 through FFF. |
| Port-Mode | Operation mode of the port. Possible values are auto, fdx-cport, fdx-station, hdx-cport, hdx-station, passive, and riro. Only FDX and HDX modes can be automatically detected. The operation mode of riro applies to fiber ports only. |
| Early-Token | Indicates whether the port is enabled for Early Token Release. Possible values are enabled and disabled. The default is enabled. Early Token Release is valid for 16 Mbps media only. If the Early Token Release is enabled and the media speed is 4 Mbps, the switch will force Early Token Release to be disabled. |
| AC-bits | Indicates whether the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit should be set unconditionally on repeated source-routed LLC frames. These include source-routed frames with RIF length greater than 2 and all spanning-tree explorer and all-routes explorer frames. The default is no. If this parameter is set to no, the setting of these bits is based on whether the frame was actually forwarded. |
| Prior-Thresh | Highest Token Ring frame priority in the Frame Control field of the frame that the switch should place in the low-priority transmit queue. Possible values are 0 through 7. The default is 3. |
| Min-Xmit | Minimum reservation priority used when requesting a token on a busy ring. Possible values are 0 through 6. The default is 4. |
| MAC-Address | MAC address of the port. |
| Cfg-Loss-Thresh | Value used to control the number of configuration losses that can occur within the configuration loss sampling interval. Configuration loss occurs when a port completes a connection, allows data traffic to flow, and subsequently closes. When the threshold is exceeded, the port is disabled and must be enabled via this panel or an SNMP manager. Possible values are 1 through 100. The default is 8 |
| Cfg-Loss-Intvl | Sampling period (in minutes) used when measuring the number of configuration losses occurring. Possible values are 1 through 60. The default is 1. |
| Cfg-Loss-Count | Number of Token Ring configuration loss events after the port has completed the join process and then lost communication. |
| Cfg-Loss-Reason | Error code of the latest configuration loss event. Possible values are None, Wire Fault, Lobe Test Fail, TKP Frame Error, Heart Beat Fail, TXI New Station, TXI Prot Error, Speed Error, Remove Received. |
Check the following items to help isolate the possible causes for a port to be in a faulty state.
As explained in the "All-Routes Explorer Reduction" section, for parallel SRB or SRT backbones, All-Routes Explorer reduction ensures that the number of all-routes explorer frames generated by the switch does not overwhelm the network. Using the set tokenring reduction command, you can enable and disable All-Routes Explorer Reduction.
All-Routes Explorer Reduction ensures that only one all-routes explorer frame is received on each ring within each VLAN (TrBRF and TrCRF). The number of all-routes explorer frames is equal to the number of external parallel paths between the rings.
To enable All-Routes Explorer Reduction, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring reduction enableTo disable All-Routes Explorer Reduction, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set tokenring reduction disableA VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might be grouped as a department, such as engineering or accounting. If the end stations are located close to one another, they can be grouped into a LAN segment. If any of the end stations are on a different LAN segment, such as different buildings or locations, they can be grouped into a VLAN that has all the same attributes as a LAN even though the end stations are not all on the same LAN segment. The information identifying a packet as part of a specific VLAN is preserved across a Catalyst 5000 series switch connection to a router or another switch if connected via trunk ports (for example, ISL).
Any VLAN can participate in the Spanning-Tree Protocol. Once VLANs have been established, packets are forwarded between ports belonging to the same VLAN only, unless the VLANs are joined by the bridging function to other VLANs. You can partition the ports on a single Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module into multiple Token Ring VLANs.
Before configuring VLANs, ensure that a VTP management domain exists. For information on configuring management domains and VLANs, Catalyst 5000 Series Advanced Software Configuration Guide.
Within a Token Ring VLAN, logical rings can be formed by defining groups of ports that have the same ring number. In general, a TrCRF is limited to the ports in a Catalyst 5000 series switch. However, there is one exception to this rule, which is discussed in the "Adding or Changing TrCRF Parameters"section. Within the TrCRF, source-route switching is used for forwarding based on either MAC addresses or route descriptors. Frames can be switched between ports within a single TrCRF.
Multiple TrCRFs can be interconnected using a single TrBRF. The connection between the TrCRF and the TrBRF is referred to as a logical port. For source routing, the switch appears as a single bridge between the logical rings. The TrBRF can function as an SRB or SRT bridge running either the IBM or IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol. If SRB is used, duplicate MAC addresses can be defined on different logical rings.
Traditionally, one instance of Spanning-Tree Protocol is run for each VLAN to prevent loops in the bridge topology, however, Token Ring runs an instance of Spanning-Tree Protocol both at the TrCRF level and the TrBRF level. The Spanning-Tree Protocol running at the TrCRF level removes loops in the logical ring. The TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol functions similar to the Ethernet Spanning-Tree Protocol, interacting with external bridges to remove loops from the bridge topology.
 | Caution Certain parent TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol and TrCRF bridge mode configurations may result the logical ports (the connection between the TrBRF and the TrCRF) of the TrBRF being put in a blocked state. For more about these configurations, see the "Configuring Spanning-Tree Protocol" section of this configuration note. |
For more information about Token Ring VLANs, see the "Token Ring VLANs" section in the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" section.
Using the set vlan command, you can configure a new TrBRF or change an existing TrBRF.
When configuring a TrBRF, keep the following in mind:
To configure a new TrBRF, issue the following version of the set vlan command in privileged mode:
set vlan vlan_num [name name] type trbrf [state {active | suspend}] [mtu mtu]After entering the set vlan command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 999 name brf-999 type trbrf Vlan 999 configuration successful Console> (enable)
To change an existing TrBRF, issue the following command in privileged mode, changing the appropriate parameters as necessary:
set vlan vlan_num [name name] [state {active | suspend}] [mtu mtu] [bridge bridge_number]Using the set vlan command, you can configure a new TrCRF or change an existing TrCRF. There are two types of TrCRFs that you can configure in your network: undistributed and backup.
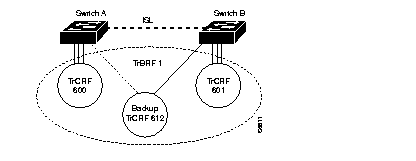
The undistributed TrCRF is the standard type of TrCRF in the Catalyst 5000 series switch. The undistributed TrCRF is located on one switch and has a logical ring number associated with it. Multiple undistributed TrCRFs located on the same or separate switches can be associated with a single parent TrBRF. The parent TrBRF acts as a multiport bridge, forwarding traffic between the undistributed TrCRFs. Figure 12 illustrates the undistributed TrCRF.
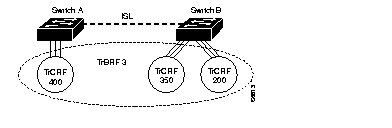
TrCRFs cannot be distributed across boxes as illustrated in Figure 13. Ports associated with a TrCRF must be located within the same Catalyst 5000 series switch. However, there is one exception to this rule and that is the default Token Ring VLAN configuration of the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
By default, the Token Ring VLAN configuration of the Token Ring module has all ports assigned to the default TrCRF (1003). The default TrCRF is associated with the default TrBRF (1005). In the situation where a user has not configured the ports of a Token Ring module to be associated with a new TrCRF, traffic will be passed between the default TrCRFs located on separate switches that are connected via ISL.
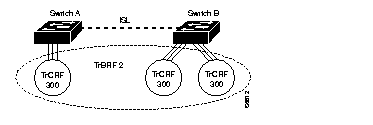
The backup TrCRF enables you to configure an alternate route for traffic between undistributed TrCRFs located on separate switches that are connected by a TrBRF, should the ISL connection between the switches become inactive. Only one port per switch can be configured as part of a backup TrCRF and only one backup TrCRF can be configure for a TrBRF.
To create a backup TrCRF, you assign one port on each switch that the TrBRF traverses to the backup TrCRF. Under normal circumstances, only one port in the backup TrCRF is active. If the ISL connection between the switches become inactive, the port that is a part of the backup TrCRF on each affected switch will automatically become active, rerouting traffic between the undistributed TrCRFs through the backup TrCRF. When the ISL connection is reestablished, all but one port in the backup TrCRF will once again be disabled. Figure 14 illustrates the backup TrCRF.
When configuring a TrCRF, keep the following in mind:
To configure a new TrCRF, issue the following version of the set vlan command in privileged mode, ensuring that you specify each of the parameters that applies to the type of TrCRF you are configuring:
set vlan vlan_num [name name] type trcrf [state {active | suspend}] [mtu mtu]After entering the set vlan command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 1000 name crf-1000 type trcrf ring 001 parent 999 Vlan 1000 configuration successful Console> (enable)
To change an existing TrCRF, issue the following command in privileged mode, changing the appropriate parameters as necessary:
set vlan vlan_num [name name] [state {active | suspend}] [mtu mtu] [ring ring_number]To specify that a TrCRF is a backup TrCRF, issued the following command in privileged mode:
set vlan vlan_num backupcrf onAfter entering the set vlan command and specifying on for the backupcrf parameter, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 1000 backupcrf on Vlan 1000 configuration successful.
 | Caution If the backup TrCRF port is attached to a Token Ring MAU, it will not provide a backup path unless the ring speed and port mode are set by another device. Therefore, it is recommended that ring speed and port mode be configured for the backup TrCRF. |
You can specify the maximum hop count for all-route and spanning-tree explorer frames for each TrCRF. This limits the maximum number of hops an explorer is allowed to traverse. If a port determines that the explorer frame it is receiving has traversed more than the number of hops specified, it does not forward the frame. The TrCRF determines the number of hops an explorer has traversed based on the number of bridge hops in the route information field.
If you are configuring maximum hop counts for a TrCRF, ensure that you specify values for the aremaxhop and stemaxhop parameters when issuing the set vlan command. Valid values are 1 to 14. The default is 7.
To specify the maximum number of bridge hops to be allowed in explorer packets for a TrCRF, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set vlan vlan_num aremaxhop hopcount stemaxhop hopcountAfter entering the set vlan command and specifying hopcount values, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 1000 aremaxhop 10 stemaxhop 10 Vlan 1000 configuration successful
A TrCRF created in a management domain remains unused until it is associated with ports on the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
To group Token Ring module ports into a TrCRF, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set vlan vlan_num mod/ports...After entering the set vlan command to group ports to a TrCRF, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 1000 3/1-3 VLAN 1000 modified.
To verify the Token Ring VLANs you have configured, issue the following command:
show vlan [vlan_number]After entering the show vlan command and specifying a TrBRF, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> show vlan 1005
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1005 trbrf 101005 4472 - - 0xf ibm - 0 0
VLAN AREHops STEHops Backup CRF
---- ------- ------- ----------
Console>
After entering the show vlan command and specifying a TrCRF, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) show vlan 1003
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1003 trcrf 101003 4472 1005 0xccc - - srb 0 0
VLAN AREHops STEHops Backup CRF
---- ------- ------- ----------
1003 7 7 off
Console> (enable)
Table 9 describes the information returned by the show vlan command.
| Field | Description |
| VLAN | VLAN number. |
| Name | Name of the VLAN (if configured). |
| Status | Status of the VLAN (active or suspend). |
| Mod/Ports, VLANs | Ports that belong to the VLAN. |
| Type | Media type of the VLAN. |
| SAID | Security Association ID value for the VLAN. |
| MTU | Maximum transmission unit size for the VLAN. |
| Parent | Parent VLAN, if a parent VLAN exists. |
| RingNo | Ring number for the TrCRF. |
| BrdgNo | Bridge number for the TrBRF. |
| Stp | Spanning-Tree Protocol type used on TrBRF. |
| BrdgMode | Bridging mode for this TrCRF. Possible values are SRB and SRT. The default is SRB. This field is valid only for TrCRFs. |
| Trans1 | First translational VLAN used to translate FDDI to Ethernet. |
| Trans2 | Second translational VLAN used to translate FDDI to Ethernet. |
| AREHops | Maximum number of hops for all-routes explorer frames. Possible values are 1 through 13. The default is 7. |
| STEHops | Maximum number of hops for spanning-tree explorer frames. Possible values are 1 through 13. The default is 7. |
| Backup CRF | Whether the TrCRF is a backup path for traffic. |
To clear the definition of a TrCRF or TrBRF, issue the following command while is privileged mode:
clear vlan vlan_numberAfter entering the clear vlan command and specifying a TrCRF, you will be notified that the command will deactivate the ports on the VLAN and be prompted to continue as seen in the following display:
Console> (enable) clear vlan 1000 This command will deactivate all ports on vlan 1000 in the entire management domain Do you want to continue(y/n) [n]?y Vlan 1000 deleted.
 | Caution When clearing a TrCRF, all the ports grouped to the TrCRF will become inactive and will remain inactive and associated with the TrCRF number until they are assigned to a new TrCRF. |
After entering the clear vlan command and specifying a TrBRF, you will see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) clear vlan 999 Vlan 999 deleted Console> (enable)
When creating fault-tolerant internetworks, a loop-free path must exist between all nodes in a network. The algorithm performed by a Spanning-Tree Protocol calculates the best loop-free path throughout a switched network. Spanning-tree packets are sent and received by switches in the network at regular intervals.
The packets are not forwarded by the switches participating in the Spanning-Tree Protocol, but are instead used by the switches to identify the loop-free path. Spanning-Tree Protocol performs this function for Catalyst 5000 series switches.
Traditionally, one instance of Spanning-Tree Protocol is run for each VLAN to prevent loops in the bridge topology, however, Token Ring runs an instance of Spanning-Tree Protocol both at the TrCRF level and the TrBRF level. The Spanning-Tree Protocol running at the TrCRF level removes loops in the logical ring. The TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol functions similar to the Ethernet Spanning-Tree Protocol, interacting with external bridges to remove loops from the bridge topology.
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module supports the following Spanning-Tree Protocols:
The Catalyst 5000 series switch uses the IEEE 802.1D and IBM Spanning-Tree Protocols on TrBRFs. The Spanning-Tree Protocol running on the TrCRF is either the Cisco or IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol, depending on the bridging mode configured for the TrCRF using the set vlan command. The default configuration has all Spanning-Tree Protocols enabled.
 | Caution Certain TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol and TrCRF bridge mode configurations are incompatible and result in the TrCRFs of the configuration being put in a blocked state. For more about these configurations, see the "Setting the Port State" section of this configuration note. |
For more information on the Spanning-Tree Protocol activity at the TrBRF and TrCRF levels depending upon the TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol and the TrCRF bridge mode configuration, see "Spanning-Tree Protocol" in the "Understanding Token Ring Switching" section of this configuration note.
By default, Spanning-Tree Protocol is enabled for VLANs, however, if necessary, you can enable and disable Spanning-Tree Protocol for TrBRFs and TrCRFs.
To enable Spanning-Tree Protocol, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree enable [vlan]After enabling Spanning-Tree Protocol for a VLAN, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree enable 1005 VLAN1005 bridge spanning tree enabled Console< (enable)
To disable Spanning-Tree Protocol for a VLAN, enter the set spantree disable command:
set spantree disable [vlan]After disabling Spanning-Tree Protocol for a VLAN, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree disable 1005 VLAN1005 bridge spanning tree disabled Console< (enable)
You can configure the type of Spanning-Tree Protocol to be used by a TrBRF.
Note that the following Spanning-Tree Protocol and bridge mode configurations are incompatible and result in logical ports being placed in a blocked state:
For more information on these configurations and how to manually set the logical port state, see the "Setting the Port State" section.
To specifying a Spanning-Tree Protocol for a TrBRF, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set vlan vlan_num [stp {ieee | ibm}]After entering the set vlan command and specifying a Spanning-Tree Protocol, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set vlan 950 stp ieee Vlan 950 configuration successful Console> (enable) show vlan 950
Using the set spantree command, you can whether to use the bridge functional address instead of the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol address when a TrBRF is configured to use the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol.
To specify for a TrBRF running the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol to use the bridge functional address instead of the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol address, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree multicast-address vlan_num ibmEach logical port (the connection between the TrBRF and TrCRF) of a TrBRF on a switch using Spanning-Tree Protocol exists in one of the following five states:
The port states occur as follows:
When Spanning-Tree Protocol is enabled, every switch in the network goes through the blocking state and the transitory states at power up. If properly configured, the logical ports then stabilize to the forwarding or blocking state. However, with TrBRFs and TrCRFs, there are two exceptions to this rule that require you to manually set the state of a logical port of a TrBRF. The two exceptions are if the:
You can use the set spantree portstate command to manually set the state of a logical port to blocked or forwarding mode if either of the above configurations exists.
To manually set the state of a logical port of a TrBRF, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree portstate trcrf {auto | block | forward} [trbrf]After entering the set spantree portstate command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree portstate 950 forward Portstate successfully set for tokenring crf 950 Console> (enable)
The port (physical or logical) with the lowest priority value has the highest priority and will forward the spanning-tree frames. The possible priority range is 0 through 255 (decimal). The default is 128. If all ports have the same priority value, the lowest port number forwards the spanning-tree frames.
To configure the priority associated with a logical port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree portpri vlan_num priorityAfter entering the set spantree portpri command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree portpri 900 50 Token Ring 900 port priority set to 50. Console> (enable)
To configure the priority associated with a physical port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree portpri mod_num/port_num priorityAfter entering the set spantree portpri command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree portpri 3/4 10 Bridge port 3/4 port priority set to 10. Console> (enable)
The Spanning-Tree Protocol uses port path costs to determine which port (physical or logical) to select as a forwarding port. Therefore, lower numbers should be assigned to ports attached to faster media (such as full duplex), and higher numbers should be assigned to ports attached to slower media.The possible range is 1 to 65535. The default is 62. A rule of thumb for path cost is 1000 ÷ LAN speed in megabits per second.
To configure the cost associated with a physical port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree portcost mod_num/port_num costTo configure the cost associated with a logical port, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set spantree portcost trcrf costAfter entering the set spantree portcost command and specifying a module number and port number, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set spantree portcost 3/4 100 Spantree port 3/4 path cost set to 100. Console> (enable)
You can configure additional Spanning-Tree Protocol parameters using the set spantree command. Table 10 lists the types of spanning tree information you can configure and the command you use.
| Task | Command |
| Set the bridge forward delay for a VLAN. | set spantree fwddelay delay [vlan] |
| Set the bridge hello time for a VLAN | set spantree hello interval |
| Set the bridge maximum aging time for a VLAN. | set spantree maxage agingtime [vlan] |
| Set the bridge priority for a VLAN. | set spantree priority bridge_priority [vlan] |
| Configure a physical port that is connected to a single workstation or PC to start faster when it is connected. | set spantree portfast mod_num/port_num {enable | disable} |
You can display the Spanning-Tree Protocol configuration for a specific VLAN, switching module, or port.
To verify the Spanning-Tree Protocol configuration information for a TrBRF or TrCRF, issue the following command:
show spantree vlan_numAfter entering the show spantree command, you will see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) show spantree 1003
VLAN 1003
Spanning tree enabled
Designated Root 00-e0-1e-2f-6f-ea
Designated Root Priority 32768
Designated Root Cost 0
Designated Root Port 1/0
Root Max Age 20 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID MAC ADDR 00-e0-1e-2f-6f-ea
Bridge ID Priority 32768
Bridge Max Age 20 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Port Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Fast-Start Group-method
--------- ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ------------
3/1 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/2 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/3 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/4 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/5 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/6 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/7 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/8 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/9 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/10 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/11 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/12 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/13 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/14 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/15 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
3/16 1003 not-connected 250 32 disabled
Console> (enable)
Table 11 describes the information returned by the show spantree command.
| Field | Description |
| VLAN | VLAN for which spanning-tree information is shown. |
| Spanning tree | Indicates whether Spanning-Tree Protocol is enabled or disabled. |
| Designated Root | MAC address of the designated spanning-tree root bridge. |
| Designated Root Priority | Priority of the designated root bridge. |
| Designated Root Cost | Total path cost to reach the root. |
| Designated Root Port | Port through which the root bridge can be reached (shown only on non-root bridges). |
| Root Max Age | Amount of time a BPDU1 packet should be considered valid. |
| Hello Time | Indicates how often the root-bridge sends BPDUs (in seconds). |
| Forward Delay | Indicates how much time the port spends in listening or learning mode (in seconds). |
| Bridge ID MAC ADDR | Bridge MAC address. |
| Bridge ID Priority | Bridge priority. |
| Bridge Max Age | Bridge maximum age (in seconds). |
| Hello Time | Indicates how often the bridge sends BPDUs (in seconds). |
| Forward Delay | Indicates how much time the bridge spends in listening or learning mode (in seconds). |
| Port | Port number. |
| Vlan | VLAN to which the port belongs. |
| Port-State | Indicates spanning tree port state (disabled, inactive, not-connected, blocking, listening, learning [this state does not apply to the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol], forwarding, bridging). |
| Cost | Cost associated with the port. |
| Priority | Priority associated with the port. |
| Fast-Start | Indicates whether the port is configured to use the fast-start feature. |
For network security, you can isolate parts of your network by limiting the scope and access of your users. To limit access, you can do the following:
There are two types of filters that you can configure for the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module: protocol filters and MAC address filters. MAC address filters, based on MAC address (source address or destination address), can be configured for only input ports. Protocol (Destination Service Access Point [DSAP]/Subnetwork Access Protocol [SNAP]), filters can be configured for both input and output ports. You can configure up to 16 MAC address or DSAP/SNAP filters for each port on the Token Ring module.
To filter data based on MAC address, you specify an address and indicate whether you want to block or allow frames that contain the address as a source or destination address. To filter data based on protocol, specify either a DSAP or SNAP and specify whether to permit or deny frames with that protocol.
When configuring a MAC address filter, you can enter the MAC address in canonical or non-canonical format. Frames received that contain the MAC address specified as a source or destination address are dropped or passed, depending on whether you have specified for the filter to permit or deny the frames.
To add a filter based on MAC addresses, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set port filter mod_num/port_num mac_addr {permit | deny}After entering the set port filter command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set port filter 3/2 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 permit Port 3/2 filter Mac Address 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 set to permit. Console> (enable)
For a list of possible Ethertypes that you can specify, see the "Ethertypes" section of the "Codes" section of this configuration note. You can specify up to 16 DSAPs (in hexadecimal format) separated by spaces. For a list of possible service access points (SAPs), refer to the "Service Access Points" section of the "Codes" section.
To add a filter based on protocols, issue the following command in privileged mode:
set port filter mod_num/port_num protocol_type {permit | deny}After entering the set port filter command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) set port filter 3/2 ip permit Port 3/2 filter Protocol ip set to permit. Console> (enable)
Using the clear port filter command, you can clear MAC address or protocol filters that have been configured on a specific port. You can also use the clear port filter command to clear all the filters configured for each of the ports on the Token Ring module.
To clear a MAC address filter or protocol filter, issue the following command in privileged mode:
clear port filter mod_num/port_num {mac_addr | protocol_type}To clear all configured filters, issue the following command in privileged mode:
clear port filter allAfter entering the clear port filter to clear a specific MAC address filter on a port command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) clear port filter 3/2 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 Port 3/2 filter Mac Address 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 cleared. Console> (enable)
After entering the clear port filter to clear all configured filters, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> (enable) clear port filter all All filter MAC addresses and Protocols cleared Console> (enable)
To verify the filters you have configured for the Token Ring module or for a specific port on the module, use the show port filter command.
To verify the filters configured on port 2 of module 3, issue the following command:
show port filter 3/2After entering the show port filter command, you see a display similar to the following:
Console> show port filter 3/2
Port Mac-Addr Type
----- ----------------- ------
3/2 00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
Port Protocol Type
----- ----------------- ------
3/2 0x8035(ip) deny
0xffff deny
0xfefe deny
0xffff deny
0xfefe deny
0xffff deny
0xfefe deny
0xffff deny
Table 12 describes the information returned by the show port filter command issued with a module and port number specified.
| Field | Description |
| Port | Module and port number. |
| MAC-Addr | MAC address contained in packets to be filtered. |
| Type | Type of MAC address filter configured. Possible types are deny (block any packet containing a specific MAC address) or permit (allow any packet containing a specific MAC address.) |
| Protocol | Types of protocols that you want to filter. |
| Type | Type of protocol filter configured. Possible types are deny (block any packet containing a specific protocol type) or permit (allow any packet containing a specific protocol type.) |
Use the following show commands to complete the listed tasks:
| Task | Command |
| View module configuration and status. | show module [mod_num] |
| View port configuration and status. | show port [mod_num[/port_num] |
| View Token Ring configuration | show tokenring |
| View MAC counters. | show mac [mod_num[/port_num]] |
| View RIF information. | show rif |
| View port filters. | show port filter [mod_num[/port_num] |
| Display the error log for the system or a specific module. | show log [mod_num] |
| View VLANs. | show vlan [vlan] |
| View Spanning-Tree Protocols for a VLAN. | show spantree vlan |
| Display the error log for the system or a specific module. | show log [mod_num] |
| Display MAC counters. | show mac |
| Display the results of diagnostic tests. | show test [mod_num] |
| Display the current state of a logical port. | show spantree portstate trcrf |
As enhancements are made to the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module, you may need to update the software or microcode that is contained in the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
This section includes procedures for updating the software on the Catalyst 5000 series switch. New software to implement enhancements and maintenance releases will be provided periodically.
Perform the following steps to download software from a console using TFTP:
Step 1 Make sure the workstation acting as the download server has the TFTP daemon.
Step 2 On Sun workstations, make sure the /etc/inetd.conf file contains the following line:
Make sure the /etc/services file contains the following line:
Step 3 Copy the new software from the floppy disks to the home directory specified for the TFTP daemon on the workstation (usually /tftpboot). If this directory does not exist, create it before continuing. The file you copy is epsmain.dot1_0_xxx.bin, where xxx is the software revision number.
Step 4 Log in to the Catalyst 5000 through the administrative interface or through a Telnet session.
Step 5 Use the download command. Specify the IP address or host name of the workstation acting as the download server. Also specify the file to download and the number of the Token Ring module. The following is the command syntax:
In the following example, the file is downloaded to module 3:
download 190.180.122.40 filename.bin 3
Step 6 When the following prompt appears, press y:
filename from IP address to Module 3? (y/n) [n]? y
Step 7 Use the show version command to check the file you have just downloaded. If the version number is the correct number for the new software, the download was successful. If the version number is not the correct number, the download failed, and you must repeat the download procedure. Refer to the troubleshooting procedures below if the download failed.
Follow the steps below for troubleshooting a failed serial download procedure:
Step 1 Make certain that the Catalyst 5000 has a route to the TFTP server, and use the ping command to test this connectivity.
Step 2 Make certain that the software image to be downloaded is in the correct directory.
The network portion of the Catalyst 5000 IP address must be the same as the network portion of the TFTP server address. If the network download procedure fails because the power was interrupted during the download procedure, or for some other reason, the Flash code can become corrupted and the boot> prompt appears on the administration port. In that case, you can use the network download procedure to download the Flash code again through an enabled port in VLAN 1. By default, only port 1/1 is enabled. You can use port 1/1 or enable another port.
This section contains the following information:
Because the number of stations that can be connected to any single ring is limited, large Token Ring LANs are divided into smaller rings. Furthermore, because stations must contend for the token with other stations on the same ring, attaching fewer stations to a ring gives each one a greater number of opportunities to transmit and receive information. This results in a larger number of rings, or segments.
The traditional method of connecting multiple Token Ring segments is to use a source-routing bridge. For example, bridges are often used to link workgroup rings to the backbone ring. However, the introduction of the bridge can significantly reduce performance at the user's workstation. Further problems may be introduced by aggregate traffic loading on the backbone ring.
To maintain performance and avoid overloading the backbone ring, you can locate servers on the same ring as the workgroup that needs to access the server. However, this makes the servers more difficult to back up, administer, and secure than if they are located on the backbone ring, and limits the number of servers that particular stations can access.
Collapsed backbone routers offer greater throughput than bridges, and can interconnect a larger number of rings without becoming overloaded. Routers provide both bridging and routing function between ring and have sophisticated broadcast control mechanisms. These mechanisms become increasingly important as the number of devices on the network increase.
The main drawback of using routers as the campus backbone is the relatively high price-per-port and the fact that the throughput typically does not increase as ports are added. A Token Ring switch is designed to provide wire speed throughput regardless of the number of ports in the switch. In addition, the switch can be configured to provide very low latency between Token Ring ports by using cut-through switching.
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module supports the following bridging modes:
SRB is the original method of bridging used to connect Token Ring segments. A source-route bridge makes all forwarding decisions based on data in the RIF. It does not learn or look up MAC addresses. Therefore, SRB frames without a RIF are not forwarded.
Clients or servers that support source routing typically send an explorer frame to determine the path to a given destination. There are two types of explorer frames: all-routes explorer and spanning-tree explorer. All SRB bridges copy all-routes explorer frames and add their own routing information. For frames that are received from or sent to ports that are in the spanning-tree forwarding state, bridges copy spanning-tree explorer frames and add their own routing information. Because all-routes explorer frames will traverse all paths between two devices, they are used in path determination. Spanning-tree explorer frames are used to send datagrams because the spanning tree will ensure that only one copy of an spanning-tree explorer frame is sent to each ring.
SRT bridging is an IEEE standard that combines source-route bridging and transparent bridging. An SRT bridge forwards frames that do not contain a RIF based on the destination MAC address. Frames that contain a RIF are forwarded based upon source-routing. The SRT bridge only runs the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol. It does not support the IBM Spanning Tree Protocol.
Similar to a transparent bridge, the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module can forward broadcast, multicast, and unicast frames based on MAC address. If, however, you have source-route bridges in your network, the Token Ring module can forward frames based on the RIF. This dual frame-forwarding technology is called source-route switching.
In source-route switching, the switch learns and forwards frames based on source-route descriptors for stations that are one or more source-route bridge hops away. A route descriptor is a portion of a RIF that indicates a single hop. It is defined as a ring number and a bridge number. When a source-routed frame enters the switch, the switch learns the route descriptor for the hop closest to the switch. Frames received from other ports with the same next-hop route descriptor as their destination will be forwarded to that port.
The key difference between SRB and source-route switching is that while a source-route switch looks at the RIF, it never updates the RIF. Therefore, all ports in a source-route switch group have the same ring number.
Source-route switching provides the following benefits:
Classic 4- and 16-Mbps Token Ring adapters must be connected to a port on a concentrator. These adapters are also limited to operating in half-duplex mode. In half-duplex mode, the adapter can only be sending or receiving a frame; it cannot do both simultaneously.
Dedicated Token Ring, developed by the IEEE, defines a method in which the switch port can emulate a concentrator port, thereby eliminating the need for an intermediate concentrator. In addition, dedicated Token Ring defines a new full-duplex data passing mode called Transmit Immediate, which eliminates the need for a token and allows the adapter to transmit and receive simultaneously.
Dedicated Token Ring is particularly useful for providing improved access to servers. A server can be attached directly to a switch. This allows the server to take advantage of the full 16 Mbps available for sending and receiving and results in an aggregate bandwidth of 32 Mbps.
Within a Token Ring VLAN, logical rings can be formed by defining groups of ports that have the same ring number. The IEEE calls such a port group a Token Ring Concentrator Relay Function (TrCRF). In general, a TrCRF is limited to the ports in a single Token Ring module on the Catalyst 5000 series switch. However, there is one exception to this rule that is discussed in the "Adding or Changing TrCRF Parameters" section of this configuration note.
Within the TrCRF, source-route switching is used for forwarding based on either MAC addresses or route descriptors. If desired, the entire VLAN can operate as a single ring. Frames can be switched between ports within a single TrCRF.
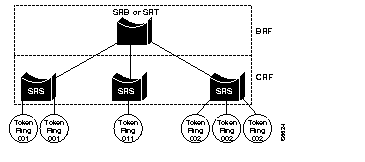
As shown in Figure 15, multiple TrCRFs can be interconnected using a single Token Ring Bridge Relay Function (TrBRF). For source routing, the switch appears as a single bridge between the logical rings. The TrBRF can function as an SRB or SRT bridge running either the IBM or IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol. If SRB is used, duplicate MAC addresses can be defined on different logical rings.
To accommodate SNA traffic, you can use a combination of SRT and SRB modes. In a mixed mode the TrBRF considers some ports (logical ports connected to TrCRFs) to be operating in SRB mode while others are operating in SRT mode.
The TrBRF can be extended across a network of switches via high-speed uplinks between the switches. These links must have the ability to multiplex multiple VLANs and provide the necessary information to support logical rings.
The Spanning-Tree Protocol is a broadcast algorithm used by network bridge connections to dynamically discover a loop-free subset of the network topology while maintaining a path between every pair of LANs or VLANs in the network.
To accomplish this, the Spanning-Tree Protocol blocks ports that, if active, would create bridging loops. If the primary link fails, it activates one of the blocked bridge ports to provide a new path through the network.
In a traditional bridged network, there is one Spanning-Tree Protocol for each bridge connection. Each bridge maintains its own database of configuration information and transmits and receives only on those ports belonging to the bridge. The type of Spanning-Tree Protocol that runs on a bridge depends on the transmission mode of the bridge connection (whether the connection is transparent, SRB, source-source route switched, or SRT).
In a switched network, you can configure virtual networks. A switch can have ports that belong to different VLANs, some of which may span several switches.
As discussed in the "Virtual LAN Support" section, in a Token Ring switch, there are two levels of VLANs. The grouping of ports (TrCRFs) is connected by logical bridges (TrBRFs).
Therefore, in a Token Ring switched network, to ensure loops are removed from the topology you must configure a separate Spanning-Tree Protocol for each logical bridge (TrBRF) and for each of the port groupings (TrCRF) configured for a VLAN.
The following is a general summary of how the Spanning-Tree Protocol eliminates loops in the network:
The first 2 bytes are a priority field, and the last 6 bytes contain one of the bridge's MAC addresses. The bridge with the lowest bridge identifier among all bridges on all LAN segments is the root bridge. The network administrator can assign a lower bridge priority to a selected bridge to control which bridge becomes the root, or the administrator can use default bridge priorities and allow the Spanning-Tree Protocol to determine the root.
The path cost represents the cost of transmitting a frame to a bridged segment through that port. A network administrator typically configures a cost for each port based on the speed of link (for example, the cost of a port connected to a 16-Mbps LAN could be assigned a lower path cost than a port connected to a 4-Mbps LAN).
The root port is the port that represents the shortest path from itself to the root bridge. The root path cost is the total cost to the root.
All ports on the root bridge have a zero cost.
A designated bridge is the bridge on each LAN segment that provides the minimum root path cost. Only the designated bridge is allowed to forward frames to and from that LAN segment toward the root.
The selected ports will be the root port plus the designated ports for the designated bridge. Designated ports are those where the designated bridge has the best path to reach the root. In cases where two or more bridges have the same root path cost, the bridge with the lowest bridge identifier becomes the designated bridge.
The Spanning-Tree Protocol calculation requires that bridges communicate with other bridges in the network that are running the Spanning-Tree Protocol. Each bridge is responsible for sending and receiving configuration messages called bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).
BPDUs are exchanged between neighboring bridges at regular intervals (typically 1 to 4 seconds) and contain configuration information that identifies the:
If a bridge fails and stops sending BPDUs, the bridges detect the lack of configuration messages and initiate a spanning-tree recalculation.
Figure 16 shows the format of the fields inside a BPDU.
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Protocol Identifier | Version | Message Type | Flags | Root ID | Root Path Cost | Bridge ID | Port ID | Message Age | Max Age | Hello Time | Forward Delay |
| Protocol Identifier | Identifies the protocol. This field contains the value zero. |
| Version | Identifies the version. This field contains the value zero. |
| Message Type | Identifies the message type. This field contains the value zero. |
| Flags | 1-byte field, of which only the first two bits are used. The topology change (TC) bit signals a topology change. The topology change acknowledgment (TCA) bit is set to acknowledge receipt of a configuration message with the TC bit set. This field is not valid for IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDUs. |
| Root ID | Identifies the root bridge by listing its 2-byte priority followed by its 6-byte ID. |
| Root Path Cost | Cost of the path from the bridge sending the configuration message to the root bridge. |
| Bridge ID | Priority and ID of the bridge sending the message. |
| Port ID | Port number (IEEE or Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU) or the ring and bridge number (IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU) from which the configuration message was sent. This field allows loops created by multiple attached bridges to be detected and corrected. |
| Message Age | Indicates the amount of time that has elapsed since the root sent the configuration message on which the current configuration message is based. |
| Max Age | Indicates when the current configuration message should be deleted. |
| Hello Time | Indicates the time between root bridge configuration messages. |
| Forward Delay | Indicates the length of time that bridges should wait before transitioning to a new state after a topology change. If a bridge transitions too soon, it is possible that not all network links will be ready to change their state and loops can result. |
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module supports the following Spanning-Tree Protocols:
The Catalyst 5000 series switch uses the IEEE 802.1D and IBM Spanning-Tree Protocols on TrBRFs. The Spanning-Tree Protocol running on the TrCRF is either the Cisco or IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol, depending upon the Spanning-Tree Protocol being run on the TrBRF and the bridging mode configured for the TrCRF using the set vlan command. The default configuration has all Spanning-Tree Protocols enabled.
Table 14 lists the Spanning-Tree Protocol activity at the TrBRF and TrCRF levels depending upon the TrBRF Spanning-Tree Protocol and the TrCRF bridge mode configuration.
| TrBRF STP Setting | TrCRF Bridge Mode / ISL Port Setting | TrBRF STP | TrCRF STPF |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBM | SRB SRT ISL Ports | IBM None1 IBM | IEEE Cisco None |
| IEEE | SRB SRT ISL Ports | None1 IEEE IEEE | IEEE Cisco None |
The following sections briefly describe the type of transmission mode supported by each Spanning-Tree Protocol.
The IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol can be used at the TrCRF or the TrBRF level. This type of spanning tree supports bridge domains and allows the bridge to construct a loop-free topology across an extended LAN. Specifically, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning-Tree Protocol supports the following bridge modes:
The IEEE 802.1d Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU format is:
Destination Address | Source Address | SAP | BPDU |
Transparent Bridging
When a bridge connection is transparent mode:
Source-Route Switching
When a bridge connection is source-route switching:
Source-Route Transparent Bridging
When a bridge connection is source-route transparent:
The IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol can be used at the TrBRF level. This type of spanning tree was developed to maintain the path for source-route broadcast traffic.
Source-Route Bridging
When a bridge connection is source-route:
The IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU format is:
Destination Address | Source Address | SAP | BPDU |
The Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol was designed for use at the TrCRF level. This type of spanning tree was developed to address a looping problem that can be introduced when you use VLANs in a Token Ring environment.
One of the rules in processing source-route traffic is that a source-route frame should never be forwarded to a ring that it has previously traversed. If the RIF of a source-route frame already contains the ring number for the next hop, the bridge assumes that the frame has already been on that ring and drops the frame.
With Token Ring VLANs, however, this rule can cause a problem. With the existing Spanning-Tree Protocol, a frame that originated on one physical ring of a Token Ring VLAN and is processed by an external SRT bridge would not be forwarded to another physical ring of the same Token Ring VLAN. Therefore, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning-Tree Protocol was used as a basis to create the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol. The Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol ensures that traffic from one physical ring of a VLAN is not blocked from the other physical rings that comprise the VLAN.
Table 15 summarizes the activities occurring in the TrCRF and TrBRF when the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol is run.
| TrCRF Bridging Mode | TrCRF | TrBRF |
| SRB |
|
|
|
SRT |
|
|
The Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU format is:
Destination Address | Source Address | RIF | SAP | BPDU |
For each BPDU format:
For the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU format, the source address must have the "msp masked" on to indicate the presence of a RIF in the header. The information carried in the RIF for the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol BPDU is a 2-byte field and must be set to 0x0200.
This section lists and describes commands specific to the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module as well as existing Catalyst 5000 series switch commands that have been altered for the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module. For a complete description of all the Catalyst 5000 series switch commands and the switch command-line interface, refer to the Catalyst 5000 Series Command Reference.
Use the clear port filter privileged command to clear all MAC address or protocol filters that have been configured or those filters configured on a specific port.
clear port filter [mod_num/port_num] [mac_addr | protocol_type]| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| mac_address | MAC address contained in the packets to be filtered. This address can be entered in canonical format (00-11-33-44-55) or in non-canonical (00:11:22:33:44:55) format. |
| protocol_type | Type of protocol to be filtered. |
The command has no default setting.
Switch command
Privileged
Up to 16 MAC address filters or 16 protocol (eight SAP and eight DSAP) filters can be configured per port on the Token Ring module.
The following example shows configuring a port filter on port 2 MAC address 00:40:0b:01:65) of module 3:
Console> (enable) set port filter 3/2 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 permit Port 3/2 filter Mac Address 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 set to permit. Console> (enable)
set port filter
show port filter
Use the set help normal or privileged command to list the set commands with brief descriptions of their functions.
set helpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal and privileged
In normal mode, the set help command lists the set commands available in normal mode. In privileged mode, the set help command lists the set commands available in privileged mode.
The following example shows how to list the set commands available in normal mode:
Console> set help Commands: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ set help Show this message set length Set number of lines in display (0 to disable 'more') Console>
The following example shows how to list the set commands available in privileged mode:
Console> (enable) set help Set commands: ------------------------------------------------------------------------ set alias Set alias for command set arp Set ARP table entry set authentication Set TACACS authentication set banner Set message of the day banner set bridge Set bridge, use 'set bridge' for more info set cam Set CAM table entry set cdp Set cdp, use 'set cdp help' for more info set cgmp Set CGMP (enable/disable) set enablepass Set privilege mode password set fddi Set FDDI, use 'set fddi' for more info set help Show this message set interface Set network interface configuration set ip Set IP, use 'set ip help' for more info set length Set number of lines in display (0 to disable 'more') set logging Set system logging configuration information set logout Set number of minutes before automatic logout set module Set module, use 'set module help' for more info set multicast Set multicast router port set ntp Set NTP, use 'set ntp help' for more info set password Set console password set port Set port, use 'set port help' for more info set prompt Set prompt set snmp Set SNMP, use 'set snmp help' for more info set span Set switch port analyzer set spantree Set spantree, use 'set spantree help' for more info set summertime Set summertime set system Set system, use 'set system help' for more info set tacacs Set TACACS information set time Set time set timezone Set timezone set tokenring Set tokenring information set trunk Set trunk ports set vlan Set virtual LAN information set vmps Set VMPS information set vtp Set VLAN Trunk Information Console> (enable)
disable (Switch Command)
enable (Switch Command)
Use the set port filter privileged command to configure a MAC address filter or a protocol filter for ports on your Token Ring module.
set port filter mod_num/port_num {mac_addr | protocol_type} {permit | deny}| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| mac_address | MAC address contained in the packets to be filtered. This address can be entered in canonical format (00-11-33-44-55) or in non-canonical (00:11:22:33:44:55) format. |
| protocol_type | Protocol type that you want to filter. For a list of the protocol types that you can filter, see the "Codes" section. |
| permit | Keyword used to specify that the filter can permit packets with the specified MAC address or protocol type. |
| deny | Keyword used to specify that the filter can deny packets with the specified MAC address or protocol type. |
The command has no default setting.
Switch command
Privileged
Up to 16 MAC address filters or 16 protocol (eight SAP and eight DSAP) filters can be configured per port on the Token Ring module.
The following example shows configuring a port filter on port 2 MAC address 00:40:0b:01:65) of module 3:
Console> (enable) set port filter 3/2 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 permit Port 3/2 filter Mac Address 00:40:0b:01:bc:65 set to permit. Console> (enable)
clear port filter
show port filter
Use the set port speed privileged command to configure the speed of a port interface. You can configure the speed of a Fast Ethernet interface and a Token Ring interface.
set port speed mod_num/port_num {4 | 10 | 16 | 100 | auto}| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| 4 | 10 | 16 | 100 | auto | Keyword used to set a port speed to 4, 10, 16, 100 Mbps, or auto speed detection mode. The default is auto. Port speeds 4 and 16 Mbps apply only to Token Ring ports. Port speeds 10 and 100 Mbps apply only to Ethernet ports. |
The default configuration has all Token Ring module ports set to auto.
Switch command
Privileged
Token Ring interfaces on the Token Ring module can be configured to either 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps. They can also be set to auto speed detection mode, allowing them to sense and distinguish between 4-Mbps and 16-Mbps port transmission speed. Set at auto speed detection mode, the interfaces automatically configure themselves to operate at the proper speed.
If you change the transmission speed of a port that is open to 4 or 16 Mbps, the port will close and reopen at the new transmission speed. If a port closes and reopens on an existing ring using a transmission speed different from that which the ring is operating, the ring will beacon.
If the ports on the Token Ring module are configured to automatically sense the speed of the ring, the first port inserted on the ring will not set the speed, for it will be unable to detect the speed.
The following example shows how to set ports 2, 3, and 4 on module 3 to 16 Mbps, 4 Mbps, and auto speed detection mode:
Console> (enable) set port speed Usage: set port speed<4|10|16|100|auto> Console> (enable) set port speed 3/4 16 Port(s) 3/4 speed set to 16Mbps. Console> (enable) set port speed 3/4 auto Port(s) 3/4 speed set to auto detect.
set port disable
set port enable
set port help
set port name
set port trap
set tokenring portmode
set tokenring priority
show port
Use the set spantree help privileged command to list the available set spantree commands.
set spantree helpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Privileged
The following example shows how to list the set spantree commands:
Console> (enable) set spantree Set spantree commands: ---------------------------------------------------------------------- set spantree disable Disable spanning tree set spantree enable Enable spanning tree set spantree fwddelay Set spantree forward delay set spantree hello Set spantree hello interval set spantree help Show this message set spantree maxage Set spantree max aging time set spantree multicast-address Set the spantree functional address set spantree portcost Set spantree port cost set spantree portfast Set spantree port fast start set spantree portpri Set spantree port priority set spantree portstate Set spantree logical port state set spantree portvlancost Set spantree port cost per vlan set spantree portvlanpri Set spantree port vlan priority set spantree priority Set spantree priority set spantree root Set switch as primary or secondary root set spantree uplinkfast Enable or disable uplinkfast groups Console> (enable)
Use the set spantree multicast-address command to specify to use the bridge functional address instead of the IEEE Spanning Tree Protocol address when a TrBRF is configured to use the IEEE Spanning Tree Protocol.
set spantree multicast-address vlan_num {ieee | ibm}| vlan_num | Number of the TrBRF for which you are setting the address. |
| ieee | Keyword used to specify for the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol address to be used. |
| ibm | Keyword used to specify for the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol address to be used. |
The default configuration has IEEE.
Switch command
Privileged
This command applies only to a TrBRF that is running IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol.
The following example shows specifying for the bridge functional address to be used:
Console> (enable) set spantree multicast-address ibm 100
Use the set spantree portcost privileged command to set the path cost for a physical port or logical port (the connection between a TrCRF and TrBRF).
set spantree portcost {mod_num/port_num | trcrf} cost| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| trcrf | Number of the TrCRF for which you are setting the path cost. |
| cost | Number from 1 to 65535 that indicates the cost of the path. 1 is a low cost and 65535 is a high cost. |
The default configuration is as follows:
Switch command
Privileged
The Spanning-Tree Protocol uses port path costs to determine which port to select as a forwarding port. Therefore, lower numbers should be assigned to ports attached to faster media (such as full duplex) and higher numbers should be assigned to ports attached to slower media. The possible range is 1 to 65535. The default for the Token Ring module ports is 62. The recommended path cost is 1000/LAN speed in Mbps.
The following example shows how to set the port cost for port 4 on module 3 to 16 Mbps:
Console> (enable) set port speed 3/4 16 Port(s) 3/4 speed set to 16Mbps. Console> (enable)
Use the set spantree portpri privileged command to set the bridge priority for a spanning-tree port or TrCRF.
set spantree portpri {mod_num/port_num | trcrf} priority| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| trcrf | Number identifying the TrCRF for which you are setting the bridge priority. |
| priority | Number that represents the cost of a link in a spanning-tree bridge. The priority level is from 0 (high) to 63 (low). |
The default configuration has all ports with bridge priority set to 32.
Switch command
Privileged
The specified bridge priority on an ATM port applies to all emulated LANs on that port.
The following example shows how to set the priority of port 1 on module 4 to 63:
Console> (enable) set spantree portpri 4/1 63 Bridge port 4/1 priority set to 63. Console> (enable)
Use the set spantree portstate privileged command to manually set the state of a logical port (the connection between a TrCRF and TrBRF).
set spantree portstate trcrf {block | forward | auto} [trbrf]| trcrf | Number of the TrCRF. |
| block | forward | auto | Keywords used to set the logical port to a blocked state (block), forwarding state (forward) or to have the correct state automatically determined by the Spanning-Tree Protocol (auto). |
| trbrf | Number of the parent TrBRF. |
There is no default configuration for this command.
Switch command
Privileged
This command can only be used to set the port state when the the TrCRF is in SRT mode and the TrBRF is running the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol, or, the TrCRF is in SRB mode and the TrBRF is running the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol.
When Spanning-Tree Protocol is enabled, every switch in the network goes through the blocking state and the transitory states at power up. The ports then stabilize to the forwarding or blocking state. With TrBRFs and TrCRFs, there are two exceptions to this rule that require you to manually set the state of the logical ports of a TrBRF. The two exceptions are if:
The following example shows the manual setting of TrCRF 900 to a forwarding state:
Console> (enable) set spantree portstate 900 forward Console> (enable)
Use the set tokenring acbits privileged command to specify whether AC bits shall be set unconditionally when a port forwards certain LLC frames.
set tokenring acbits mod_num/port_num {enable | disable}| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| enable | disable | Keyword used to unconditionally (enable) or conditionally (disable) set AC bits when a port forwards certain LLC frames. |
The default configuration is disable.
Switch command
Privileged
Using the set tokenring acbits command, you can specify whether the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit should be set unconditionally on repeated source-routed Logical Link Control (LLC) frames. These include source-routed frames with a RIF length greater than 2 and all spanning-tree explorer and all-routes explorer frames.
If this parameter is set to disable, the setting of these bits is based on whether the frame was actually forwarded.
The following examples show port 4 on module 4 being enabled to unconditionally set the AC bits when forwarding certain LLC frames and then being disabled.
Console> (enable) set tokenring acbits 4/4 enable Port 4/4 acbits enabled. Console> (enable) set tokenring acbits 4/4 disable Port 4/4 acbits disabled.
Use the set tokenring configloss privileged command to specify thresholds that, when exceeded during the user-specified interval, will cause the port to be administratively disabled.
set tokenring configloss mod_num/port_num [threshold thresh_num] [interval int_num]| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| threshold thresh_num | Keyword to set the threshold for configuration losses. Valid values are 1 to 100. The default is 8. |
| interval interval_num | Keyword to set the interval at which the configuration loss is measured. Valid values are 1 to 99 minutes. The default is 10. |
The default threshold configuration is 8. The default interval is 10.
Switch command
Privileged
Configuration loss occurs when a port completes a connection, allows data traffic to flow, and subsequently closes. The configuration loss threshold is used to control the number of configuration losses that can occur within a specified time. When the threshold is exceeded, the port is disabled and must be enabled using the set port enable command or an SNMP manager.
The following shows how to set a configuration loss threshold of 25 and an interval of 5 minutes for port 1 on module 4.
Console> (enable) set tokenring configloss 4/1 threshold 25 interval 5
Port 4/1 configloss threshold set to 25, interval set to 5.
Console> (enable)
Use the set tokenring etr privileged command to enable or disable a Token Ring port's use of the Early Token Release procedure when transmitting frames.
set tokenring etr mod_num/port_num {enable | disable}| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| enable | disable | Keyword used to specify that Early Token Release should be used (enable) or not used (disable) when transmitting frames. |
For 16 Mbps and auto speed-detection ports, the default configuration is enable Early Token Release.
Switch command
Privileged
Early Token Release cannot be enabled for 4 Mbps ports. Enabling or disabling Early Token Release on a port will cause the port to be closed and reopened.
The following example shows how to enable Early Token Release on port 2 on module 3:
Console> (enable) set tokenring etr 3/2 enable Port 3/2 Early Token Release enabled.
The following example shows how to disable Early Token Release on port 2 on module 3:
Console> (enable) set tokenring etr 3/2 disable Port 3/2 Early Token Release disabled.
Use the set tokenring help privileged command to list the Token Ring-specific set commands with brief descriptions of their functions.
set tokenring helpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Privileged
The set tokenring help command lists the Token Ring set commands that are available in privileged mode.
The following example shows how to list the Token Ring set commands that are available in privileged mode:
Console> (enable) set tokenring help Set tokenring commands: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- set tokenring acbits Set the AC bits set tokenring configloss Specify the behavior in case of lots of failures set tokenring etr Enable/disable Early Token Release set tokenring help Show this help message set tokenring portmode Set port mode set tokenring priority Set port priority Console> (enable)
set help
Use the set tokenring portmode privileged command to specify the connection type and access protocol being used by a port.
set tokenring portmode mod_num/port_num {auto | fdxcport | hdxcport | fdxstation || mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| auto | Keyword used to have the port detect the mode of connection. |
| fdxcport | Keyword used to set the port to operate as a concentrator port in full duplex mode. |
| hdxcport | Keyword used to set the port to operate as a concentrator port in half duplex mode. |
| fdxstation | Keyword used to set the port to operate as a station in full duplex mode. |
| hdxstation | Keyword used to set the port to operate as a station in half duplex mode. |
| riro | This parameter is applicable to fiber modules only. |
The default configuration is auto.
Switch command
Privileged
The following example shows how to set the port mode to autosensing on port 1 on module 4 and to set port 2 on module 4 to operate as a concentrator port in full-duplex mode:
Console> (enable)set tokenring portmode 4/1 autoPort 4/1 mode set to auto. Console> (enable)set tokenring portmode 4/2 fdxcportPort 4/2 mode set to fdxcport.
Use the set tokenring priority privileged command to specify the highest Token Ring frame priority that shall go to the low-priority transmit queue and the minimum Token Ring frame priority that will be used when requesting a token.
set tokenring priority mod_num/port_num {threshold thresh_num | minxmit min_num}| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port on the module. |
| threshold thresh_num | Keyword used to specify the priority queue threshold. Valid values are 0 to 7. The default is 3. |
| minxmit min_num | Keyword used to specify the minimum frame priority to be used. Valid values are 0 to 6. The default is 4. |
The default configuration for threshold is 3. The default configuration for minxmit is 4.
Switch command
Privileged
The following example shows how to set the priority threshold and minimum priority levels on port 2 on module 4:
Console> (enable)set tokenring priority 4/2 threshold 6Port 2 priority threshold set to 6. Console> (enable)set tokenring priority 4/2 minxmit 5Port 2 priority minxmit set to 5.
Use the set tokenring reduction privileged command to reduce broadcast storms in an externally looped network.
set tokenring reduction {enable | disable}| enable | disable | Keywords used to turn broadcast reduction on (enable) or off (disable). |
The default configuration is enabled.
Switch command
Privileged
The following example shows how to enable and disable All-Routes Explorer Reduction:
Console> (enable)set tokenring reduction enableConsole> (enable)set tokenring reduction disable
Use the set vlan privileged command to group ports into a virtual LAN.
set vlan vlan_num mod/portsset vlan vlan_num [name name] [type {ethernet | fddi | fddinet | trcrf | trbrf}]
Syntax Description
| vlan_num | Number identifying the VLAN. |
| mod | Number of the module. This parameter is not valid when defining or configuring TrBRFs. |
| ports... | Numbers of the port on the module belonging to the VLAN. This parameter does not apply to TrBRFs. |
| name name | (Optional) Keyword that defines a text string used as the name of the VLAN (1 to 32 characters). |
| type {ethernet | fddi | fddinet | trcrf | trbrf} | (Optional) Keyword used to identify the VLAN type. |
| state {active | suspend} | (Optional) Keyword used to specify whether the state of the VLAN is active or suspended. VLANs in suspended state do not pass packets. The default is active. |
| said said | (Optional) Keyword that specifies the security association identifier. Possible values are 1 to 4294967294. This parameter does not apply to TrCRFs or TrBRFs. |
| mtu mtu | (Optional) Keyword that specifies the maximum transmission unit (packet size, in bytes) that the VLAN can use. Possible values are 1500 to 18190. Valid MTU values for Token Ring VLANs are 1500 or 4472. For Token Ring VLANs, the default is 4472. |
| ring ring_number | (Optional) Keyword that specifies the logical ring number for Token Ring VLANs. Possible values are hexadecimal numbers 01 to FFF. For Token Ring VLANs, this parameter is valid and required only when defining a TrCRF. |
| bridge bridge_number | (Optional) Keyword that specifies the identification number of the bridge. Possible values are hexadecimal numbers 01 to 0F. For Token Ring VLANs, the default is 0F. This parameter is not valid for TrCRFs. |
| parent vlan_num | (Optional) Keyword used to set a parent VLAN. The range for vlan_num is 1to 1005. This parameter identifies the TrBRF to which a TrCRF belongs and is required when defining a TrCRF. |
| mode {srt | srb} | Bridging mode of a TrCRF. Valid values for this parameter are srt and srb. |
| stp {ieee | ibm} | (Optional) Keyword that specifies which version of the Spanning-Tree Protocol for a TrBRF to use; source routing transparent (ieee) or source route bridging (ibm). |
| translation vlan_num | (Optional) Keyword that specifies a translational VLAN used to translate FDDI or Token Ring to Ethernet. Possible values are 1 to 1005. |
| backupcrf {off | on} | Whether the TrCRF is a backup path for traffic. |
| aremaxhop hopcount | Maximum number of hops for all-routes explorer frames. Possible values are 1 to 14. The default is 7. This parameter is only valid when defining or configuring TrCRFs. |
| stemaxhop hopcount | Maximum number of hops for spanning-tree explorer frames. Possible values are 1 to 14. The default is 7. This parameter is only valid when defining or configuring TrCRFs. |
Default
The default configuration has all switched Ethernet ports and Ethernet repeater ports in VLAN 1. The default SAID is 100001 for VLAN 1, 100002 for VLAN 2, 100003 for VLAN 3, and so on. The default type is ethernet. The default mtu is 1500 bytes. The default state is active.
The default TrBRF is 1005 and the default TrCRF is 1003. The default mtu for TrBRFs and TrCRFs is 4472. The default state is active.
Switch command
Privileged
Valid MTU values for Token Ring VLANs are 1500 or 4472. While a user can enter any value for the MTU value, the value they enter will default to the next lowest valid value.
You cannot set multiple VLANs for ISL ports using this command. The VLAN name can be from 1 to 32 characters in length. If adding a new VLAN, the VLAN number must be within the range 2 to 1001. When modifying a VLAN, the valid range for the VLAN number is 2 to 1005.
In the case of a new Token Ring VLAN, if the parent parameter is not specified for a TrCRF, the default TrBRF (1005) is used.
The following example shows how to set VLAN 850 to include ports 3 through 7 on module 3. Ports 3 through seven were assigned to TrCRF 1003, therefore, the message reflects the modification of VLAN 1003:
Console> (enable) set vlan 850 3/4-7 VLAN 850 modified. VLAN 1003 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 850 3/4-7
clear vlan
show vlan
Use the show counters privileged command to display hardware counters for a port.
show counters mod_num/port_num| mod_num | Number of the module. |
| port_num | Number of the port. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the counters for port 1 on module 3:
Console> show counters 3/1
32 bit counters
0 dot5StatsLineErrors = 0
1 dot5StatsBurstErrors = 0
2 dot5StatsACErrors = 0
3 dot5StatsAbortTransErrors = 0
4 dot5StatsInternalErrors = 0
5 dot5StatsLostFrameErrors = 0
6 dot5StatsReceiveCongestions = 0
7 dot5StatsFrameCopiedErrors = 0
8 dot5StatsTokenErrors = 0
9 dot5StatsSoftErrors = 0
10 dot5StatsHardErrors = 0
11 dot5StatsSignalLoss = 0
12 dot5StatsTransmitBeacons = 0
13 dot5StatsRecoverys = 0
14 dot5StatsLobeWires = 0
15 dot5StatsRemoves = 0
16 dot5StatsSingles = 0
17 dot5StatsFreqErrors = 0
18 dot1dSrPortSpecInFrames = 0
19 dot1dSrPortSpecOutFrames = 0
20 dot1dSrPortApeInFrames = 0
21 dot1dSrPortApeOutFrames = 0
22 dot1dSrPortSteInFrames = 0
23 dot1dSrPortSteOutFrames = 0
24 dot1dSrPortSegmentMismatchDiscards = 0
25 dot1dSrPortDuplicateSegmentDiscards = 0
26 dot1dSrPortHopCountExceededDiscards = 0
27 dot1dSrPortDupLanIdOrTreeErrors = 0
28 dot1dSrPortLanIdMismatches = 0
29 tokenRingMLStatsDropEvents = 0
30 tokenRingMLStatsMacOctets = 0
31 tokenRingMLStatsMacPkts = 0
32 tokenRingMLStatsRingPurgeEvents = 0
33 tokenRingMLStatsRingPurgePkts = 0
34 tokenRingMLStatsBeaconEvents = 0
35 tokenRingMLStatsBeaconPkts = 0
36 tokenRingMLStatsBeaconTime = 0
37 tokenRingMLStatsClaimTokenEvents = 0
38 tokenRingMLStatsClaimTokenPkts = 0
39 tokenRingMLStatsNAUNChanges = 0
40 tokenRingMLStatsLineErrors = 0
41 tokenRingMLStatsInternalErrors = 0
42 tokenRingMLStatsBurstErrors = 0
43 tokenRingMLStatsACErrors = 0
44 tokenRingMLStatsAbortErrors = 0
45 tokenRingMLStatsLostFrameErrors = 0
46 tokenRingMLStatsCongestionErrors = 0
47 tokenRingMLStatsFramesCopiedErrors = 0
48 tokenRingMLStatsFrequencyErrors = 0
49 tokenRingMLStatsTokenErrors = 0
50 tokenRingMLStatsSoftErrorReports = 0
51 tokenRingMLStatsRingPollEvents = 0
52 tokenRingMLStatsHistoryActiveStations = 0
53 tokenRingPStatsDropEvents = 0
54 tokenRingPStatsDataOctets = 0
55 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts = 0
56 tokenRingPStatsDataBroadcastPkts = 0
57 tokenRingPStatsDataMulticastPkts = 0
58 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts18to63Octets = 0
59 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts64to127Octets = 0
60 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts128to255Octets = 0
61 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts256to511Octets = 0
62 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts512to1023Octets = 0
63 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts1024to2047Octets = 0
64 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts2048to4095Octets = 0
65 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts4096to8191Octets = 0
66 tokenRingPStatsDataPkts8192to18000Octets = 0
67 tokenRingPStatsDataPktsGreaterThan18000Octets(null) = 0
68 dot1dTpPortInFrames = 0
69 dot1dTpPortOutFrames = 0
70 dot1dTpPortInDiscards = 0
Console>
Table 16 describes the fields shown in the show counters command output when the command has been issued against a Token Ring module port.
| Field | Description |
| dot5StatsLineErrors | Number of times a frame or token was copied or repeated by a station. |
| dot5StatsBurstErrors | Number of times a station has detected the absence of transitions for five half-bit timers (burst-five error). |
| dot5StatsACErrors | Number of times a station received an Active Monitor Present (AMP) frame or a Standby Monitor Present (SMP) frame in which both the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit are set to 0, indicating that no station has recognized the destination address and copied the frame, and then receives another SMP frame in which both the address recognized bit and the frame copied bit are set to 0 without first receiving an AMP frame. This condition indicates a station that cannot set the A bit and the C bit properly. |
| dot5StatsAbortTransErrors | Number of times a station transmitted an abort delimiter while transmitting. |
| dot5StatsInternalErrors | Number of times a station recognized an internal error. |
| dot5StatsLostFrameErrors | Number of times a station was transmitting and its return-to-repeat timer expired. This condition indicates a condition where a transmitting station in strip mode does not receive the trailer of the frame before the return-to-repeat timer goes off. |
| dot5StatsReceiveCongestions | Number of times a station recognized a frame addressed to its specific address, but had no available buffer space, indicating that the station is congested. |
| dot5StatsFrameCopiedErrors | Number of times a station recognized a frame addressed to its specific address and detected that the frame status field A bits are set to 1, indicating a possible line hit or duplicate address. |
| dot5StatsTokenErrors | Number of times a station acting as the active monitor recognized an error condition that required a token to be transmitted. |
| dot5StatsSoftErrors | Number of soft errors the port has detected. Soft errors are those that are recoverable by the MAC-layer protocols. The soft error number directly corresponds to the number of report error MAC frames that this port has transmitted. |
| dot5StatsHardErrors | Number of times this port has detected an immediately recoverable fatal error. This denotes the number of times this port has either transmitted or received a beacon MAC frame. |
| dot5StatsSignalLoss | Number of times this port has detected a loss of signal condition from the ring. |
| dot5StatsTransmitBeacons | Number of times this port has transmitted a beacon frame. |
| dot5StatsRecoverys | Number of claim token MAC frames received or transmitted after the port has received a ring purge MAC frame. This counter signifies the number of times the ring has been purged and had recovered back into a normal operating state. |
| dot5StatsLobeWires | Number of times the port has detected an open or short circuit in the lobe data path. The adapter will be closed and ring state will signify this condition. |
| dot5StatsRemoves | Number of times the port has received a remove ring station MAC frame request. When this frame is received the port will enter the closed state. |
| dot5StatsSingles | Number of times the port has sensed that it is the only station on the ring. This occurs if the port is the first one up on a ring, or if there is a hardware problem. |
| dot5StatsFreqErrors | Number of times the port has detected that the frequency of the incoming signal differs from the expected frequency by more than that specified by the IEEE 802.5 standard. |
| dot1dSrPortSpecInFrames | Number of Specifically-Routed frames received. |
| dot1dSrPortSpecOutFrames | Number of Specifically-Routed frames transmitted. |
| dot1dSrPortApeInFrames | Number of All-Paths (All-Routes) explorer frames received. |
| dot1dSrPortApeOutFrames | Number of All-Paths (All-Routes) explore frames transmitted. |
| dot1dSrPortSteInFrames | Number of Spanning-Tree explorer frames received. |
| dot1dSrPortSteOutFrames | Number of Spanning-Tree explorer frames transmitted. |
| dot1dSrPortSegmentMismatchDiscards | Number of explorer frames discarded by this port because the route descriptors field contained an invalid adjacent segment value. |
| dot1dSrPortDuplicateSegmentDiscards | Number of explorer frames discarded by this port because the routing descriptor filed contained a duplicate segment value. |
| dot1dSrPortHopCountExceededDiscards | Number of explorer frames discarded because the number of routing descriptors in the RIF exceeded the specified maximum hop count. |
| dot1dSrPortDupLanIdOrTreeErrors | Number of duplicate LAN IDs or Tree errors. This assists in detection of problems in networks containing older IBM Source Routing Bridges. |
| dot1dSrPortLanIdMismatches | Number of all-routes explorer and spanning-tree explorer frames that were discarded because the last LAN ID in the routing information field did not equal the LAN-in ID. This error can occur in implementations which do only a LAN-in ID and Bridge Number check instead of a LAN-in ID, Bridge Number, and LAN-out ID check before forwarding broadcast frames. |
| tokenRingMLStatsDropEvents | Number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe due to lack of resources. This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped; it is just the number of times this condition has been detected. This value is the same as the corresponding tokenRingPStatsDropEvents. |
| tokenRingMLStatsMacOctets | Number of octets of data in MAC packets (excluding those that were not good frames) received on the network. This excludes framing bits but includes FCS octets. |
| tokenRingMLStatsMacPkts | Number of MAC packets (excluding packets that were not good frames) received. |
| tokenRingMLStatsRingPurgeEvents | Number of times that the ring enters the ring purge state from a normal ring state. The ring purge state that comes in response to the claim token or beacon state is not counted. |
| tokenRingMLStatsRingPurgePkts | Number of ring purge MAC packets detected by probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsBeaconEvents | Number of times that the ring enters a beaconing state (beaconFrameStreamingState, beaconBitStreamingState, beaconSetRecoveryModeState, or beaconRingSignalLossState) from a non-beaconing state. A change of the source address of the beacon packet does not constitute a new beacon event. |
| tokenRingMLStatsBeaconPkts | Number of beacon MAC packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsBeaconTime | Amount of time that the ring has been in the beaconing state. |
| tokenRingMLStatsClaimTokenEvents | Number of times that the ring enters the claim token state from normal ring state or ring purge state. The claim token state that comes in response to a beacon state is not counted. |
| tokenRingMLStatsClaimTokenPkts | Number of claim token MAC packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsNAUNChanges | Number of NAUN changes detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsLineErrors | Number of line errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsInternalErrors | Number of adapter internal errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsBurstErrors | Number of burst errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsACErrors | Number of AC (Address Copied) errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsAbortErrors | Number of abort delimiters reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsLostFrameErrors | Number of lost frame errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsCongestionErrors | Number of receive congestion errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsFramesCopiedErrors | Number of frame copied errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsDropEvents | Number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe due to lack of resources. This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped; it is just the number of times this condition has been detected. This value is the same as the corresponding tokenRingPStatsDropEvents. |
| tokenRingMLStatsFrequencyErrors | Number of frequency errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsTokenErrors | Number of token errors reported in error reporting packets detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsSoftErrorReports | Number of soft error report frames detected by the probe. |
| tokenRingMLStatsRingPollEvents | Number of ring poll events detected by the probe. For example, the number of ring polls initiated by the active monitor that were detected. |
| tokenRingMLStatsHistoryActiveStations | Maximum number of active stations on the ring detected by the probe during this sampling interval. |
| tokenRingPStatsDropEvents | Number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe due to lack of resources. This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped; it is the number of times this condition has been detected. This value is the same as the corresponding tokenRingMLStatsDropEvents. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataOctets | Number of octets of data in good frames received on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets) in non-MAC packets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts | Number of non-MAC packets in good frames received. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataBroadcastPkts | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were directed to an LLC broadcast address (0xFFFFFFFFFFFF or 0xC000FFFFFFFF). |
| tokenRingPStatsDataMulticastPkts | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were directed to a local or global multicast or functional address. Note that this number does not include packets directed to the broadcast address. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts18to63Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 18 and 63 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts64to127Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 64 and 127 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts128to255Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts256to511Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts512to1023Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts1024to2047Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 1024 and 2047 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts2048to4095Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 2048 and 4095 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts4096to8191Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 4096 and 8191 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPkts8192to18000Octets | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were between 8192 and 18000 octets in length inclusive, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| tokenRingPStatsDataPktsGreaterThan18000Octets(null) | Number of good non-MAC frames received that were greater than 18000 octets in length, excluding framing bits but including FCS octets. |
| dot1dTpPortInFrames | Number of frames that have been received by this port from its segment. Frames received on the interface corresponding to this port are only counted by this object if, and only if, they are for a protocol being processed by the local bridging function, including bridge management frames. |
| dot1dTpPortOutFrames | Number of frames that have been transmitted by this port to its segment. Frames transmitted on the interface corresponding to this port are only counted by this object if, and only if, they are for a protocol being processed by the local bridging function, including bridge management frames. |
| dot1dTpPortInDiscards | Number of valid frames received which were discarded (for example, filtered) by the forwarding process. |
clear counters
Use the show mac normal command to display MAC counters.
show mac [mod_num[/port_num]]| mod_num | (Optional) Number of the module. If a number is not specified, all modules are shown. |
| /port_num | (Optional) Number of the port on the module. If a number is not specified, all ports are shown. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display MAC information for port 3 on module 4:
Console> (enable) show mac 3/4
MAC Rcv-Frms Xmit-Frms Rcv-Multi Xmit-Multi Rcv-Broad Xmit-Broad
-------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
3/4 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAC Dely-Exced MTU-Exced In-Discard Lrn-Discrd In-Lost Out-Lost
-------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
3/4 0 0 0 0 0 0
Port InUnicast InMulticast InBroadcast
-------- -------------------- -------------------- --------------------
3/4 0 0 0
Port OutUnicast OutMulticast OutBroadcast
-------- -------------------- -------------------- --------------------
3/4 0 0 0
Port InOctet OutOctet
-------- -------------------- --------------------
3/4 0 0
Last-Time-Cleared
--------------------------
Wed Sep 17 1997, 08:31:20
Console> (enable)
Table 17 describes the fields in the show mac command output when the command is issued against a Token Ring module and port.
| Field | Description |
| MAC | Module and port. |
| Rcv-Frms | Number of frames received on the port. |
| Xmit-Frms | Number of frames transmitted on the port. |
| Rcv-Multi | Number of multicast frames received on the port. |
| Xmit-Multi | Number of multicast frames transmitted on the port. This field is not valid for Token Ring ports. |
| Rcv-Broad | Number of broadcast frames received on the port. |
| Xmit-Broad | Number of broadcast frames transmitted on the port. This field is not valid for Token Ring ports. |
| Dely-Exced | Total transmit frames aborted due to excessive deferral. |
| MTU-Exced | Number of frames for which the MTU1 size was exceeded. |
| In-Discard | Number of incoming frames that were discarded because the frame did not need to be switched. |
| Lrn-Discard | Number of content-addressable memory entries discarded because of a page full in EARL. |
| In-Lost | Number of incoming frames that were lost before being forwarded (because of insufficient buffer space). |
| Out-Lost | Number of outgoing frames that were lost before being forwarded (because of insufficient buffer space). |
| InUnicast | Number of packets received on this interface that were sent to a single (unicast) address. |
| InMulticast | Number of packets received on this interface that were sent to a multicast address. |
| InBroadcast | Number of packets received on this interface that were sent to a broadcast address. |
| OutUnicast | Number of packets sent on this interface that used a unicast address. |
| OutMulticast | Number of packets sent on this interface that used a multicast address. |
| OutBroadcast | Number of packets sent on this interface that used a broadcast address. |
| InOctet | Number of octets received at this interface. |
| OutOctet | Number of octets transmitted at this interface. |
Use the show module normal command to display module status and information.
show module [mod_num]| mod_num | (Optional) Number of the module. If a number is not specified, all modules are shown. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display status and information for module 3:
Console> (enable) show module 3
Mod Module-Name Ports Module-Type Model Serial-Num Status
--- ------------------- ----- --------------------- --------- --------- -------
3 16 Token Ring ws-x5030 900000002 ok
Mod MAC-Address(es) Hw Fw Sw
--- ---------------------------------------- ------ ------- ----------------
3 00:40:0b:01:bc:64 thru 00:40:0b:01:bc:74 3.0 1.0(108 1.0(110)
Console> (enable)
Table 18 describes the fields shown in the show module command output.
| Field | Description |
| Mod | Module number. |
| Module-Name | Name, if configured, of the module. |
| Ports | Number of ports on the module. |
| Module-Type | Module type (such as 10BaseT Ethernet or Token Ring). |
| Model | Model number of the module. |
| Serial-Num | Serial number of the module. |
| Status | Status of the module. Possible status strings are: ok, disable, faulty, other, standby, error. |
| MAC-Address(es) | Module MAC address (or range). Token Ring module addresses are non-canonical. |
| Hw | Hardware version of the module. |
| Fw | Firmware version of the module. |
| Sw | Software version on the module. |
Use the show port normal command to display port status and counters.
show port [mod_num[/port_num]]| mod_num | (Optional) Number of the module. If a number is not specified, the ports on all modules are shown. |
| /port_num | (Optional) Number of the port on the module. If a number is not specified, all the ports on the module are shown. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the status and counters for port 4 on module 3:
Console> (enable) show port 3/4
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------
3/4 inactive 1003 normal auto auto TokenRing
Last-Time-Cleared
--------------------------
Wed Sep 17 1997, 08:31:20
Console> (enable)
Table 19 describes the fields shown in the show port command output.
| Field | Description |
| Port | Module and port number. |
| Name | Name (if configured) of the port. |
| Status | Status of the port (connected, notconnect, connecting, standby, faulty, inactive, shutdown, disabled, or monitor). |
| Vlan | VLANs to which the port belongs. |
| Level | Shows the level setting for the port (normal or high). |
| Duplex | Duplex setting for the port (auto, full, fdx, half, hdx, a-half, a-hdx, a-full, a-fdx). |
| Speed | Speed setting for the port (auto, 10, 100, 155, a-10, a-100, 4, 16, a-4, a-16). |
| Type | Port type (10BaseT, 10BaseFL MM, 100BaseTX, 100BaseT4, 100BaseFX MM, 100BaseFX SM, 10/100BaseTX, TokenRing, FDDI, CDDI, MLT3 CDDI, SDDI, SMF-FDDI, PreStd CDDI, SCF FDDI, OC3 MMF ATM, OC3 SMF ATM, OC3 UTP ATM, Route Switch). |
Use the show port filter normal command to view MAC address and protocol filters that have been configured on the ports on your Token Ring module or configured on a specific port on the Token Ring module.
show port filter [mod_num[/port_num]
Syntax Description
| mod_num | (Optional) Number of the module. |
| /port_num | (Optional) Number of the port on the module. If a number is not specified, filters configured on all the ports on the module are shown. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the filters configured for a port on the Token Ring module:
Console> (enable) show port filter 3/1
Port Mac-Addr Type
----- ----------------- ------
3/1 00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
00:00:00:00:00:00 deny
Port Protocol Type
----- ----------------- ------
3/1 0x8038 deny
0xf0f0 deny
Table 20 describes the fields shown in the show port filter command output.
| Field | Description |
| Port | Module and port number. |
| MAC-Addr | MAC address contained in packets to be filtered. |
| Type | Type of MAC address filter configured. Possible types are deny (block any packet containing a specific MAC address) or permit (allow any packet containing a specific MAC address). |
| Protocol | Types of protocols that you want to filter. |
| Type | Type of protocol filter configured. Possible types are deny (block any packet containing a specific protocol type) or permit (allow any packet containing a specific protocol type). |
clear port filter
set port filter
Use the show rif normal command to display RIF information.
show rif [vlan]
Syntax Description
| vlan | (Optional) Number of the VLAN for which you want to view RIF information. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display RIF information for the system and for a VLAN:
Console>show rifMAC VLAN RIF -------------------- -------- -------------------- 00:00:30:e2:cf:00 on 401 via 0610.001a.0020 00:05:77:01:bc:4a on 1020 via 0690.00d1.00e2 00:05:77:01:bc:4b on 1020 via 0690.00d1.00e2 00:05:77:01:bc:48 on 1020 via 0690.00d1.00e2 Console>show rif 401MAC VLAN RIF -------------------- -------- -------------------- 00:00:30:e2:cf:00 on 401 via 0610.001a.0020 Console>
Use the show spantree normal command to display spanning-tree information for a VLAN.
show spantree [vlan | mod_num/port_num]
| vlan | (Optional) Number of the VLAN. If the VLAN number is not specified, the default is VLAN 1. |
| mod_num | (Optional) Number of the module. |
| port_num | (Optional) Number of the port on the module. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the spanning tree configuration for VLAN 1005:
Console> (enable) show spantree 1005
VLAN 1005
Spanning tree enabled
Designated Root 00-40-0b-8f-8b-ec
Designated Root Priority 32768
Designated Root Cost 0
Designated Root Port 1/0
Root Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec
Bridge ID MAC ADDR 00-40-0b-8f-8b-ec
Bridge ID Priority 32768
Bridge Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec
Port,Vlan Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Fast-Start Group-method
--------- ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ------------
1003 1005 inactive 80 32 disabled
Console> (enable)
Table 21 describes the fields shown in the show spantree command output when issued against a TrBRF.
| Field | Description |
| VLAN | VLAN for which spanning tree information is shown. |
| Spanning tree | Indicates whether Spanning-Tree Protocol is enabled or disabled. |
| Designated Root | MAC address of the designated spanning-tree root bridge. |
| Designated Root Priority | Priority of the designated root bridge. |
| Designated Root Cost | Total path cost to reach the root. |
| Designated Root Port | Port through which the root bridge can be reached (shown only on non-root bridges). |
| Root Max Age | Amount of time a BPDU1 packet should be considered valid. |
| Hello Time | How often the root bridge sends BPDUs. |
| Forward Delay | How much time the port spends in listening or learning mode. |
| Bridge ID MAC ADDR | Bridge MAC address. |
| Bridge ID Priority | Bridge priority. |
| Bridge Max Age | Bridge maximum age. |
| Hello Time | Indicates how often the bridge sends BPDUs. |
| Forward Delay | Indicates how much time the bridge spends in listening or learning mode. |
| Port | Port number. |
| Vlan | VLAN to which the port belongs. |
| Port-State | Indicates spanning tree port state (disabled, inactive, not-connected, blocking, listening, learning [this state does not apply to the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol], forwarding, bridging). |
| Cost | Cost associated with the port. |
| Priority | Priority associated with the port. |
| Fast-Start | Indicates whether the port is configured to use the fast-start feature. |
Use the show spantree portstate normal command to view the Spanning-Tree Protocol state of a logical port (the connection between a TrBRF and a TrCRF).
show spantree portstate trcrf| trcrf | Number of the TrCRF for which you want to view the spanning-tree port state of the the logical port. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the spanning tree configuration for VLAN 1005:
Console> (enable) show spantree portstate 1003
Port,Vlan Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Fast-Start Group-method
--------- ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ------------
1003 1005 forwarding 80 32 disabled
* = portstate set by user configuration
Console> (enable)
Table 22 describes the fields shown in the show spantree portstate command output.
| Field | Description |
| Port, Vlan | TrCRF for which the port state is shown. |
| Vlan | TrBRF to which the TrCRF is associated. |
| Port-State | Indicates spanning tree port state (disabled, inactive, not-connected, blocking, listening, learning [this state does not apply to the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol], forwarding, bridging). |
| Cost | Cost associated with the port. |
| Priority | Priority associated with the port. |
| Fast-Start | Indicates whether the port is configured to use the fast-start feature. |
Use the show tokenring normal command to display the current values of various Token Ring specific configuration parameters.
show tokenringThis command has no arguments or keywords.
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display the Token Ring settings for port 4 on module 3:
Console> (enable) show tokenring 3/4
Ports Crf/Brf Ring# Port-Mode Early-Token AC-bits
----- --------- ----- ------------- ----------- --------
3/4 1003/0 3276 auto enabled disabled
Ports Prior-Thresh Min-Xmit MAC-Address
----- ------------ -------- -----------------
3/4 3 4 00:05:77:01:bb:11
Ports Cfg-Loss-Thresh Cfg-Loss-Intvl Cfg-Loss-Count Cfg-Loss-Reason
----- --------------- -------------- -------------- ---------------
3/4 8 1 0 none
Table 23 describes the fields shown in the show tokenring command output.
| Field | Description |
| Ports | Module and port number. |
| Crf/Brf | TrCRF to which a port is assigned and the parent BRF associated with the CRF. |
| Ring | Logical ring number (in hexadecimal format) assigned to the TrCRF. Possible values are 01 through FFF. |
| Port-Mode | Operation mode of the port. Possible values are auto, fdxcport, fdxstation, hdxcport, hdxstation, passive, and riro. Only FDX and HDX modes can be automatically detected. The operation mode of riro applies to fiber ports only. |
| Early-Token | Indicates whether the port is enabled for Early Token Release. Possible values are Yes and No. The default is Yes. Early Token Release is valid for 16 Mbps media only. If the Early Token Release is enabled and the media speed is 4 Mbps, the switch will force Early Token Release to be disabled. |
| AC-bits | Indicates whether the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit should be set unconditionally on repeated source-routed LLC frames. These include source-routed frames with RIF length greater than 2 and all spanning-tree explorer and all-routes explorer frames. The default is no. If this parameter is set to no, the setting of these bits is based on whether the frame was actually forwarded. |
| Prior-Thresh | Highest Token Ring frame priority in the Frame Control field of the frame that the switch should place in the low-priority transmit queue. Possible values are 0 through 7. The default is 3. |
| Min-Xmit | Minimum reservation priority used when requesting a token on a busy ring. Possible values are 0 through 6. The default is 4. |
| MAC-Address | MAC address of the port. |
| Cfg-Loss-Thresh | Value used to control the number of configuration losses that can occur within the configuration loss sampling interval. Configuration loss occurs when a port completes a connection, allows data traffic to flow, and subsequently closes. When the threshold is exceeded, the port is disabled and must be enabled via this panel or an SNMP manager. Possible values are 1 through 100. The default is 8 |
| Cft-Loss-Intvl | Sampling period (in minutes) used when measuring the number of configuration losses occurring. Possible values are 1 through 60. The default is 1. |
| Cfg-Loss-Count | Number of Token Ring configuration loss events after the port has completed the join process and then lost communication. |
| Cfg-Loss-Reason | Error code of the latest configuration loss event. Possible values are None, Wire Fault, Lobe Test Fail, TKP Frame Error, Heart Beat Fail, TXI New Station, TXI Prot Error, Speed Error, Remove Received. |
Use the show vlan normal command to display VLAN information.
show vlan [vlan]| vlan | (Optional) Number of the VLAN. If the VLAN number is not specified, all VLANs are displayed. |
This command has no default setting.
Switch command
Normal
The following example shows how to display information for all VLANs:
Console> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/2
2/1-48
10 ether-test suspend
901 ether-test2 suspend
999 brf-999 suspend
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active 3/7-8,3/10-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
10 enet 100010 1500 - - - - - 0 0
901 enet 100901 1500 - - - - - 0 0
999 trbrf 100999 4472 - - 0xe ieee - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - 0x0 - - - 0 0
1003 trcrf 101003 1500 0 0x0 - - - 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 0x0 ieee - 0 0
1005 trbrf 101005 1500 - - 0x0 ibm - 0 0
VLAN AREHops STEHops Backup CRF
---- ------- ------- ----------
1003 7 7 off
Table 24 describes the fields shown in the show vlan command output.
| Field | Description |
| VLAN | VLAN number. |
| Name | Name, if configured, of the VLAN. |
| Status | Status of the VLAN (active or suspend). |
| Mod/Ports, VLANs | Ports that belong to the VLAN. |
| Type | Media type of the VLAN. |
| SAID | Security association ID value for the VLAN. |
| MTU | Maximum transmission unit size for the VLAN. |
| Parent | Parent VLAN, if a parent VLAN exists. |
| RingNo | Ring number for the VLAN, if applicable. |
| BrdgNo | Bridge number for the VLAN, if applicable. |
| Stp | Spanning-Tree Protocol type used on the VLAN. |
| BrdgMode | Bridging mode for this VLAN. Possible values are SRB and SRT. The default is SRB. |
| Trans1 | First translational VLAN used to translate FDDI or Token Ring to Ethernet. |
| Trans2 | Second translational VLAN used to translate FDDI or Token Ring to Ethernet. |
| AREHops | Maximum number of hops for all-routes explorer frames. Possible values are 1 through 13. The default is 7. |
| STEHops | Maximum number of hops for spanning-tree explorer frames. Possible values are 1 through 13. The default is 7. |
| Backup CRF | Whether the TrCRF is a backup path for traffic. |
The Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module comes with a default configuration that allows you to use the switch without modification in many small networks. By default, the module is configured as a single VLAN. All ports are assigned to the default TrCRF (trcrf-default) and the default TrCRF is assigned to the default TrBRF (trbrf-default).
To assist users in understanding how to configure VLANs, this section provides an example of configuring two additional VLANs for a Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module.
Figure 17 illustrates the initial VLAN configuration of the Catalyst 5000 series Token Ring module. We want to add a new VLAN that includes ports 1 and 2 to for some of our accounting department and another VLAN that includes ports 3 and 4 for some of our marketing department. Our Token Ring module is inserted in slot 3 of our Catalyst 5000.
Only the default TrCRF can be assigned to the default TrBRF. You cannot assign new TrCRFs to the default TrBRF. Therefore, we must first define a new TrBRF, then we can define our TrCRFs and assign ports to them.
To define a TrBRF, do the following:
Step 1 At the Catalyst 5000 command prompt, enter enable.
Step 2 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 100 name brf100a type trbrf bridge 1.
Step 3 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 18, indicates that brf100a has been added but that it does not have any TrCRFs assigned to it yet.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
100 brf100a active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
To define the TrCRF for the NetBIOS users, do the following:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 110 name crf110a type trcrf ring 1 parent 100 mode srb.
Step 2 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 19, indicates that crf110b has been added but that it does not have any ports assigned to it yet. It also shows that brf100a is the parent of the VLAN with the ID of 110.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
100 brf100a active 110
110 crf110a active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 trbrf 100100 4472 - - 0x1 ibm - 0 0
110 trcrf 100110 4472 100 0x1 - - srb 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - 0x0 - - - 0 0
1003 trcrf 101003 4472 1005 0xccc - - srb 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 0x0 ieee - 0 0
1005 trbrf 101005 4472 - - 0xf ibm - 0 0
To define the TrCRF for the IPX users, do the following:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 120 name crf120a type trcrf ring 4 parent 100 mode srt.
Step 2 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 19, indicates that crf120b has been added but that it does not have any ports assigned to it yet. It also shows that brf100a is the parent of the VLAN with the ID of 120.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
100 brf100a active 110, 120
110 crf110a active
120 crf120a active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
100 trbrf 100100 4472 - - 0x1 ibm - 0 0
110 trcrf 100110 4472 100 0x1 - - srb 0 0
120 trcrf 100120 4472 100 0x4 - - srt 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - 0x0 - - - 0 0
1003 trcrf 101003 4472 1005 0xccc - - srb 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 0x0 ieee - 0 0
1005 trbrf 101005 4472 - - 0xf ibm - 0 0
To assign the ports to the TrCRFs, do the following:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 110 3/1-2.
Step 2 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 120 3/3-4.
The output, shown in Figure 21, shows that ports 1 and 2 on module 3 are assigned to crf110a and that ports 3 and 4 on module 3 are assigned to crf120a.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
100 brf100a active 110, 120
110 crf110a active 3/1-2
120 crf120a active 3/3-4
991 trcrf1 suspend
992 trcrf2 suspend
999 trbrf1 suspend 991, 992
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/5-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
Figure 22 illustrates the resulting VLAN configuration for the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module.
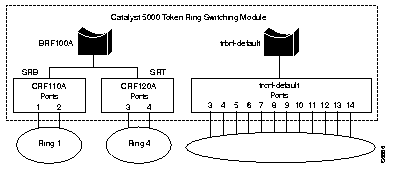
By default, the TrBRF runs the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol. The Spanning-Tree Protocol run on the TrCRFs is determined by the specified bridging mode. TrCRFs with a bridge mode of SRB will run the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol and TrCRFs with a bridge mode of SRT will run the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol.
The Catalyst 5000 Token Ring module considers the combination of the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol at the TrBRF and the bridge mode of SRT to be incompatible. As a result, it automatically blocks the logical port of the TrCRF that is configured for SRT. You can use the show spantree command to view the state of the logical ports. (See Figure 23.) You can then use the set spantree portstate command to change the forwarding mode of the logical port.
VLAN 100 Spanning tree enabled Spanning tree type ibm Designated Root 00-e0-1e-2f-6c-63 Designated Root Priority 32768 Designated Root Cost 0 Designated Root Port 1/0 Root Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec Bridge ID MAC ADDR 00-e0-1e-2f-6c-63 Bridge ID Priority 32768 Bridge Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec Port,Vlan Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Fast-Start Group-method --------- ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ------------ 1/2 100 forwarding 19 32 disabled 110 100 forwarding 80 32 disabled 120 100 blocking 80 32 disabled * = portstate set by user configuration
This section includes information about the codes for Service Access Points and Ethertypes that you can use when defining protocol filters. For information on configuring filters, see the "Configuring Filters" section.
Table 25 and Table 26 list the SAPs that may be used in defining protocol classes.
| Hexadecimal Value | Description |
|---|---|
| X'02' | LLC Sublayer Management |
| X'06' | DoD Internet |
| X'x6' | National Standards Bodies |
| X'0E' | Proway Network Management |
| X'4E' | Manufacturing Message Service |
| X'7E' | ISO 8208 |
| X'8E' | Proway Active Station List Maintenance |
| X'FE' | OSI Network Layer Protocols |
| X'42' | Bridge Spanning-Tree Protocol |
| Hexadecimal Value | Description |
|---|---|
| X'04' | SNA Path Control Individual |
| X'F0' | NetBIOS |
| X'F4' | LAN Management Individual |
| X'F8' | IMPL |
| X'FC' | Discovery |
| X'DC' | Dynamic Address Resolution |
| X'D4' | Resource Management |
Table 27 lists the possible Ethertypes that you can use in defining protocol filters.
| Hexadecimal Value | Description |
|---|---|
| X'0000' through X'05DC' | IEEE 802.3 |
| X'0600' | Xerox XNS IDP |
| X'0800' | DoD IP |
| X'0801' | X.75 Internet |
| X'0802' | NBS Internet |
| X'0803' | ECMA Internet |
| X'0804' | CHAOSnet |
| X'0805' | X.25 Level 3 |
| X'0806' | ARP (for IP and CHAOS) |
| X'6001' | DEC MOP Dump/Load Assistance |
| X'6002' | DEC MOP Remote Console |
| X'6003' | DEC DECnet Phase IV |
| X'6004' | DEC LAT |
| X'6005' | DEC DECnet Diagnostics |
| X'6010' through X'6014' | 3Com Corporation |
| X'7000' through X'7002' | Ungermann-Base download |
| X'7030' | Proteon |
| X'7034' | Cabletron |
| X'8035' | Reverse ARP |
| X'8046' through X'8047' | AT&T |
| X'8088' through X'808A' | Xyplex |
| X'809B' | Kinetics Ethertalk (Appletalk over Ethernet) |
| X'80C0' through X'80C3' | Digital Communications Associates |
| X'80D5' | IBM SNA Services over Ethernet |
| X'80F2' | Retix |
| X'80F3' through X'80F5' | Kinetics |
| X'80F7' | Apollo Computer |
| X'80FF' through X'8103' | Wellfleet Communications |
| X'8137' through X'8138' | Novell |
This section repeats in multiple languages the warnings in this guide.These translated warnings can be used with other documents related to this guide.
 | Warning This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. The warning symbol also means that you can see the warning in multiple languages in "Translated Safety Warnings." |
Waarschuwing Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. Het waarschuwingssymbool betekent ook dat u de waarschuwing in meerdere talen in "Translated Safety Warnings" kunt vinden.
Varoitus Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. Varoitusmerkki tarkoittaa myös sitä, että varoitus esiintyy useilla kielillä osassa "Translated Safety Warnings".
Attention Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées pour éviter les accidents. Le symbole d'avertissement signifie également que cet avis se trouve traduit dans plusieurs langues dans la section «Translated Safety Warnings».
Warnung Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. Das Warnsymbol bedeutet auch, daß Sie die Warnung in verschiedenen Sprachen unter "Translated Safety Warnings" lesen können.
Avvertenza Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. Il simbolo di avvertenza indica inoltre che l'avvertenza viene presentata in diverse lingue in "Translated Safety Warnings".
Advarsel Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Dette varselsymbolet betyr også at du kan lese advarselen på flere språk i «Translated Safety Warnings».
Aviso Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis acidentes. Este símbolo serve também para indicar que poderá ler este tipo de aviso em várias línguas na secção: "Translated Safety Warnings."
¡Atención! Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. Este símbolo de aviso también significa que la misma advertencia aparece en varios idiomas bajo el título "Translated Safety Warnings."
Varning! Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. Denna varningssymbol innebär också att du kan se varningsmeddelandet på flera språk i "Translated Safety Warnings."
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
Waarschuwing Tijdens onweer dat gepaard gaat met bliksem, dient u niet aan het systeem te werken of kabels aan te sluiten of te ontkoppelen.
Varoitus Älä työskentele järjestelmän parissa äläkä yhdistä tai irrota kaapeleita ukkosilmalla.
Attention Ne pas travailler sur le système ni brancher ou débrancher les câbles pendant un orage.
Warnung Arbeiten Sie nicht am System und schließen Sie keine Kabel an bzw. trennen Sie keine ab, wenn es gewittert.
Avvertenza Non lavorare sul sistema o collegare oppure scollegare i cavi durante un temporale con fulmini.
Advarsel Utfør aldri arbeid på systemet, eller koble kabler til eller fra systemet når det tordner eller lyner.
Aviso Não trabalhe no sistema ou ligue e desligue cabos durante períodos de mau tempo (trovoada).
¡Atención! No operar el sistema ni conectar o desconectar cables durante el transcurso de descargas eléctricas en la atmósfera.
Varning! Vid åska skall du aldrig utföra arbete på systemet eller ansluta eller koppla loss kablar.
 | Warning Do not touch the power supply when the power cord is connected. For systems with a power switch, line voltages are present within the power supply even when the power switch is off and the power cord is connected. For systems without a power switch, line voltages are present within the power supply when the power cord is connected. |
Waarschuwing U dient de voeding niet aan te raken zolang het netsnoer aangesloten is. Bij systemen met een stroomschakelaar zijn er lijnspanningen aanwezig in de voeding, zelfs wanneer de stroomschakelaar uitgeschakeld is en het netsnoer aangesloten is. Bij systemen zonder een stroomschakelaar zijn er lijnspanningen aanwezig in de voeding wanneer het netsnoer aangesloten is.
Varoitus Älä kosketa virtalähdettä virtajohdon ollessa kytkettynä. Virrankatkaisimella varustetuissa järjestelmissä on virtalähteen sisällä jäljellä verkkojännite, vaikka virrankatkaisin on katkaistu-asennossa virtajohdon ollessa kytkettynä. Järjestelmissä, joissa ei ole virrankatkaisinta, on virtalähteen sisällä verkkojännite, kun virtajohto on kytkettynä.
Attention Ne pas toucher le bloc d'alimentation quand le cordon d'alimentation est branché. Avec les systèmes munis d'un commutateur marche-arrêt, des tensions de ligne sont présentes dans l'alimentation quand le cordon est branché, même si le commutateur est à l'arrêt. Avec les systèmes sans commutateur marche-arrêt, l'alimentation est sous tension quand le cordon d'alimentation est branché.
Warnung Berühren Sie das Netzgerät nicht, wenn das Netzkabel angeschlossen ist. Bei Systemen mit Netzschalter liegen Leitungsspannungen im Netzgerät vor, wenn das Netzkabel angeschlossen ist, auch wenn das System ausgeschaltet ist. Bei Systemen ohne Netzschalter liegen Leitungsspannungen im Netzgerät vor, wenn das Netzkabel angeschlossen ist.
Avvertenza Non toccare l'alimentatore se il cavo dell'alimentazione ècollegato. Per i sistemi con un interruttore di alimentazione, tensioni di linea sono presenti all'interno dell'alimentatore anche quando l'interruttore di alimentazione è en posizione di disattivazione (off), se il cavo dell'alimentazione è collegato. Per i sistemi senza un interruttore, tensioni di linea sono presenti all'interno dell'alimentatore quando il cavo di alimentazione è collegato.
Advarsel Berør ikke strømforsyningsenheten når strømledningen er tilkoblet. I systemer som har en strømbryter, er det spenning i strømforsyningsenheten selv om strømbryteren er slått av og strømledningen er tilkoblet. Når det gjelder systemer uten en strømbryter, er det spenning i strømforsyningsenheten når strømledingen er tilkoblet.
Aviso Não toque na unidade abastecedora de energia quando o cabo de alimentação estiver ligado. Em sistemas com interruptor, a corrente eléctrica estará presente na unidade abatecedora, sempre que o cabo de alimentação de energia estiver ligado, mesmo quando o interruptor se encontrar desligado. Para sistemas sem interruptor, a tensão eléctrica dentro da unidade abatecedora só estará presente quando o cabo de alimentação estiver ligado.
¡Atención! No tocar la fuente de alimentación mientras el cable esté enchufado. En sistemas con interruptor de alimentación, hay voltajes de línea dentro de la fuente, incluso cuando el interruptor esté en Apagado (OFF) y el cable de alimentación enchufado. En sistemas sin interruptor de alimentación, hay voltajes de línea en la fuente cuando el cable está enchufado.
Varning! Vidrör inte strömförsörjningsenheten när nätsladden är ansluten. För system med strömbrytare finns det nätspänning i strömförsörjningsenheten även när strömmen har slagits av men nätsladden är ansluten. För system utan strömbrytare finns det nätspänning i strömförsörjningsenheten när nätsladden är ansluten.
 | Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment. |
Waarschuwing Installatie en reparaties mogen uitsluitend door getraind en bevoegd personeel uitgevoerd worden.
Varoitus Ainoastaan koulutettu ja pätevä henkilökunta saa asentaa tai vaihtaa tämän laitteen.
Avertissement Tout installation ou remplacement de l'appareil doit être réalisé par du personnel qualifié et compétent.
Achtung Gerät nur von geschultem, qualifiziertem Personal installieren oder auswechseln lassen.
Avvertenza Solo personale addestrato e qualificato deve essere autorizzato ad installare o sostituire questo apparecchio.
Advarsel Kun kvalifisert personell med riktig opplæring bør montere eller bytte ut dette utstyret.
Aviso Este equipamento deverá ser instalado ou substituído apenas por pessoal devidamente treinado e qualificado.
¡Atención! Estos equipos deben ser instalados y reemplazados exclusivamente por personal técnico adecuadamente preparado y capacitado.
Varning Denna utrustning ska endast installeras och bytas ut av utbildad och kvalificerad personal..
 | Warning Metal objects heat up when connected to power and ground, and can cause serious burns. |
Waarschuwing Metalen voorwerpen worden heet als ze met een voedingsbron en aarde verbonden zijn; in deze gevallen kunnen dergelijke voorwerpen ernstige brandwonden veroorzaken.
Varoitus Virtalähteeseen yhdistetyt ja maadoitetut metalliesineet kuumentuvat ja voivat aiheuttaa vakavia palovammoja.Seuraavassa on vielä yksi lauseen n:o 22 (SELV-piiriä koskeva varoitus) muunnos:
Avertissement Les objets métalliques s'échauffent lorsqu'ils sont sous tension et connectés à la terre. Ils risquent alors de provoquer de graves brûlures.
Achtung Metallteile erwärmen sich, wenn sie an Strom und Erde angeschlossen werden, und können schwere Verbrennungen verursachen.
Avvertenza Gli oggetti metallici collegati alle fasi e alla terra raggiungono temperature elevate e possono causare ustioni gravi.
Advarsel Metallgjenstander blir varme når de kobles til strøm og jord, og kan forårsake alvorlige brannskader.
Aviso Os objectos de metal aquecem quando ligados à corrente e à terra, e poderão causar queimaduras graves.
¡Atención! Los objetos de metal se calientan al estar conectados entre alimentación y tierra, con lo que pueden producir quemaduras graves.
Varning Metallföremål värms upp när de ansluts till spänning och jord och kan orsaka allvarliga brännskador.
 | Warning Unplug the power cord before you work on a system that does not have an on/off switch. |
Waarschuwing Voordat u aan een systeem werkt dat geen aan/uit schakelaar heeft, dient u de stekker van het netsnoer uit het stopcontact te halen.
Varoitus Ennen kuin teet mitään sellaiselle järjestelmälle, jossa ei ole kaksiasentokytkintä, kytke irti virtajohto.
Attention Avant de travailler sur un système non équipé d'un commutateur marche-arrêt, débrancher le cordon d'alimentation.
Warnung Bevor Sie an einem System ohne Ein/Aus-Schalter arbeiten, ziehen Sie das Netzkabel heraus.
Avvertenza Prima di lavorare su un sistema che non è dotato di un interruttore on/off, scollegare il cavo di alimentazione.
Advarsel Før det skal utføres arbeid på et system som ikke har en av/på-bryter, skal strømledningen trekkes ut.
Aviso Antes de começar a trabalhar num sistema que não possua um interruptor ON/OFF, desligue o cabo de alimentação.
¡Advertencia! Antes de trabajar sobre cualquier sistema que carezca de interruptor de Encendido/Apagado (ON/OFF), desenchufar el cable de alimentación.
Varning! Dra ur nätsladden innan du utför arbete på ett system utan strömbrytare.
 | Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use. |
Waarschuwing Deze apparatuur hoort geaard te worden Zorg dat de host-computer tijdens normaal gebruik met aarde is verbonden.
Varoitus Tämä laitteisto on tarkoitettu maadoitettavaksi. Varmista, että isäntälaite on yhdistetty maahan normaalikäytön aikana.
Attention Cet équipement doit être relié à la terre. S'assurer que l'appareil hôte est relié à la terre lors de l'utilisation normale.
Warnung Dieses Gerät muß geerdet werden. Stellen Sie sicher, daß das Host-Gerät während des normalen Betriebs an Erde gelegt ist.
Avvertenza Questa apparecchiatura deve essere collegata a massa. Accertarsi che il dispositivo host sia collegato alla massa di terra durante il normale utilizzo.
Advarsel Dette utstyret skal jordes. Forviss deg om vertsterminalen er jordet ved normalt bruk.
Aviso Este equipamento deverá estar ligado à terra. Certifique-se que o host se encontra ligado à terra durante a sua utilização normal.
¡Advertencia! Este equipo debe conectarse a tierra. Asegurarse de que el equipo principal esté conectado a tierra durante el uso normal.
Varning! Denna utrustning är avsedd att jordas. Se till att värdenheten är jordad vid normal användning.
 | Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
Waarschuwing Dit produkt dient volgens alle landelijke wetten en voorschriften te worden afgedankt.
Varoitus Tämän tuotteen lopullisesta hävittämisestä tulee huolehtia kaikkia valtakunnallisia lakeja ja säännöksiä noudattaen.
Attention La mise au rebut définitive de ce produit doit être effectuée conformément à toutes les lois et réglementations en vigueur.
Warnung Dieses Produkt muß den geltenden Gesetzen und Vorschriften entsprechend entsorgt werden.
Avvertenza L'eliminazione finale di questo prodotto deve essere eseguita osservando le normative italiane vigenti in materia.
Advarsel Endelig disponering av dette produktet må skje i henhold til nasjonale lover og forskrifter.
Aviso A descartagem final deste produto deverá ser efectuada de acordo com os regulamentos e a legislação nacional.
¡Advertencia! El desecho final de este producto debe realizarse según todas las leyes y regulaciones nacionales.
Varning! Slutlig kassering av denna produkt bör skötas i enlighet med landets alla lagar och föreskrifter.
 | Warning Apparatet skal kobles til en jordet stikkontakt. |
 | Warning Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat nätuttag. |
 | Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
Waarschuwing Alvorens aan apparatuur te werken die met elektrische leidingen is verbonden, sieraden (inclusief ringen, kettingen en horloges) verwijderen. Metalen voorwerpen worden warm wanneer ze met stroom en aarde zijn verbonden, en kunnen ernstige brandwonden veroorzaken of het metalen voorwerp aan de aansluitklemmen lassen.
Varoitus Ennen kuin työskentelet voimavirtajohtoihin kytkettyjen laitteiden parissa, ota pois kaikki korut (sormukset, kaulakorut ja kellot mukaan lukien). Metalliesineet kuumenevat, kun ne ovat yhteydessä sähkövirran ja maan kanssa, ja ne voivat aiheuttaa vakavia palovammoja tai hitsata metalliesineet kiinni liitäntänapoihin.
Attention Avant d'accéder à cet équipement connecté aux lignes électriques, ôter tout bijou (anneaux, colliers et montres compris). Lorsqu'ils sont branchés à l'alimentation et reliés à la terre, les objets métalliques chauffent, ce qui peut provoquer des blessures graves ou souder l'objet métallique aux bornes.
Warnung Vor der Arbeit an Geräten, die an das Netz angeschlossen sind, jeglichen Schmuck (einschließlich Ringe, Ketten und Uhren) abnehmen. Metallgegenstände erhitzen sich, wenn sie an das Netz und die Erde angeschlossen werden, und können schwere Verbrennungen verursachen oder an die Anschlußklemmen angeschweißt werden.
Avvertenza Prima di intervenire su apparecchiature collegate alle linee di alimentazione, togliersi qualsiasi monile (inclusi anelli, collane, braccialetti ed orologi). Gli oggetti metallici si riscaldano quando sono collegati tra punti di alimentazione e massa: possono causare ustioni gravi oppure il metallo può saldarsi ai terminali.
Advarsel Fjern alle smykker (inkludert ringer, halskjeder og klokker) før du skal arbeide på utstyr som er koblet til kraftledninger. Metallgjenstander som er koblet til kraftledninger og jord blir svært varme og kan forårsake alvorlige brannskader eller smelte fast til polene.
Aviso Antes de trabalhar em equipamento que esteja ligado a linhas de corrente, retire todas as jóias que estiver a usar (incluindo anéis, fios e relógios). Os objectos metálicos aquecerão em contacto com a corrente e em contacto com a ligação à terra, podendo causar queimaduras graves ou ficarem soldados aos terminais.
¡Advertencia! Antes de operar sobre equipos conectados a líneas de alimentación, quitarse las joyas (incluidos anillos, collares y relojes). Los objetos de metal se calientan cuando se conectan a la alimentación y a tierra, lo que puede ocasionar quemaduras graves o que los objetos metálicos queden soldados a los bornes.
Varning! Tag av alla smycken (inklusive ringar, halsband och armbandsur) innan du arbetar på utrustning som är kopplad till kraftledningar. Metallobjekt hettas upp när de kopplas ihop med ström och jord och kan förorsaka allvarliga brännskador; metallobjekt kan också sammansvetsas med kontakterna.
Properly shielded and grounded cables and connectors must be used in order to meet FCC emission limits. This company is not responsible for any radio or television interference caused by using other than recommended cables and connectors or by unauthorized changes or modifications to this equipment. Unauthorized changes or modifications could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This Class A digital apparatus meets the requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numerique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Reglement sur le materiel brouilleur du Canada.
This product is in conformity with the protection requirements of EU Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility. This company cannot accept responsibility for any failure to satisfy the protection requirements resulting from a non-recommended modification of the product, including the fitting of non-IBM option cards.
This product has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class B Information Technology Equipment according to CISPR 22 / European Standard EN 55022. The limits for Class B equipment were derived for typical residential environments to provide reasonable protection against interference with licensed communication devices.
Dieses Geraet ist berechtigt in Uebereinstimmung mit dem deutschen EMVG vom 9.Nov.92 das EG-Konformitaetszeichen zu fuehren. Der AuToken Ring WorkGroup Switchteller der Konformitaetserklaerung ist die IBM United Kingdom Laboratories Limited, Mail Point 147, Hursley Park Winchester, Hampshire S021 2JN, England.
Dieses Geraet erfuellt die Bedingungen der EN 55022 Klasse B.
This equipment is in the 1st Class category (information equipment to be used in commercial and/or industrial areas) and conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Information Technology Equipment aimed at preventing radio interference in commercial and industrial areas.
Consequently, when used in a residential area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio interference may be caused to radios and TV receivers, etc.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Documentation for Cisco products is available in three forms: in a CD-ROM package, printed books, and on the World Wide Web. You have the option of subscribing to the CD ROM package through an update service. Or you can order printed documentation at an additional cost. Refer to the information packet included with the router for detailed ordering information. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web URL http://www.cisco.com.

|
|