|
|

This guide is a quick hardware installation and initial software configuration for your Catalyst 5000 series switch. Use your Catalyst 5000 Series Installation Guides and the Catalyst 5000 Series Advanced Software Configuration Guide for complete information. Use the Catalyst 5000 Series Module Installation Guide for module-specific information.
The Catalyst 5000 switches are a series of LAN switches that allow you to migrate from traditional shared-hub LANs to large-scale, fully integrated internetworks. Catalyst 5000 switches provide switched connections to individual workstations, servers, LAN segments, backbones, or other Catalyst 5000 series switches using shielded twisted-pair (STP) and unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable.
Before using this guide:
1. Ensure your safety. Lift the chassis safely, cooperate with the natural laws of electricity, and when cabling, ensure that the power service at your site is suitable for the chassis you are connecting.
2. Set up the site by configuring plant wiring using AC or DC power, preparing equipment racks, and setting up the site environment.
3. Prepare network connections.
4. Check the system contents and verify the following components: left and right L brackets, cable guide, six M4 Phillips screws, eight 12-24 x 3/4-inch Phillips binder-head screws, and eight 10-32 x 3/4-inch slotted binder-head mounting screws.
5. Obtain the following equipment: numbers 1 and 2 Phillips screwdrivers, 3/16-inch flat blade screwdriver, antistatic mat, ESD grounding strap, tape measure, and level.
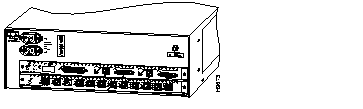
| 2-slot switch | Supports one Supervisor Engine I or II and one additional switching module (Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Copper Distributed Data Interface/fiber Distributed Data Interface [CDDI/FDDI], or ATM). Supports optional redundant AC-input power supply. |
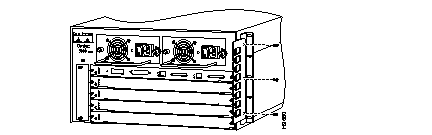
| 5-slot switch | Supports one Supervisor Engine I or II and four additional switching module (Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, CDDI/FDDI, or ATM). Supports optional redundant AC- or DC-input power supply. |
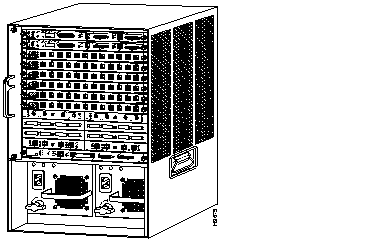
| 13-slot switch | Supports one Supervisor Engine II and up to 12 additional switching modules (Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, CDDI/FDDI, ATM, and LightStream 1010). Supports optional redundant Supervisor Engine II. Supports optional redundant AC- or DC-input power supply. |
This four-step installation summary is for experienced installers. For more complete installation instructions, see the "Quick Installation" procedures section of this guide. For detailed intructions, refer to the Catalyst 5000 Series Installation Guide that accompanied your switch.
1. Rack-mount the switch.
1 Attach the L brackets.
2 Align mounting holes.
3 Secure chassis in rack.

1 Attach the L brackets.
2 Align mounting holes.
3 Secure chassis in rack.

1 Attach the shelf bracket to the rack.
2 Attach the L brackets.
3 Place the chassis on the shelf bracket.
4 Align mounting holes.
5 Secure chassis in rack.
2. Connect the switch.
This section refers to all Catalyst 5000 series switch models.

1 Connect the network cables.
2 Connect the external cables.
3 Connect the modules.
3. Connect the power.

1 Check the security of all connections.
2 On one power supply, plug in the power cord.
3 Connect the power supply cord to a separate input line.
4 Connect the redundant power supply to a separate input line by plugging in the
power cord on the redundant power supply.

1 Check the security of all connections.
2 On one power supply, plug in the power cord.
3 Connect the power supply cord to a separate input line.
4 Connect the redundant power supply to a separate input line by plugging in the
power cord on the redundant power supply.
5 Connect the other end of the redundant power supply to an input line different
from the initial power supply.

1 Check the security of all connections.
2 Install the AC or DC power supply.
3 On one power supply, plug in the power cord.
4 Connect the power supply cord to a separate input line.
5 Connect the redundant power supply to a separate input line by plugging in the
power cord on the redundant power supply.
6 Connect the other end of the redundant power supply to an input line different
from the initial power supply.
4. Start the system.
This section refers to all Catalyst 5000 series switch models.

1 Verify the following:
2 Check the LEDs.
3 Verify the following:
4 Press Return at each of the password prompts on the console screen.

5002 Installation
Attach the left and right L brackets using the four M4 Phillips pan-head screws provided in the rack-mount kit.
No shelf is required with this assembly; the shelf brackets support the weight of the chassis in the rack.
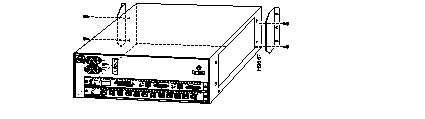
Attach the L Brackets
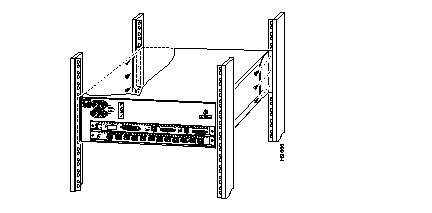
Install the Switch in the Rack

5000 Installation
Three people are required to install the switch in an open rack:
Install the Switch in the Rack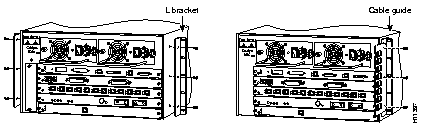

5500 Installation
No shelf is required with this assembly; the shelf brackets support the chassis in the rack.
Attach the L-Brackets and Cable Management Brackets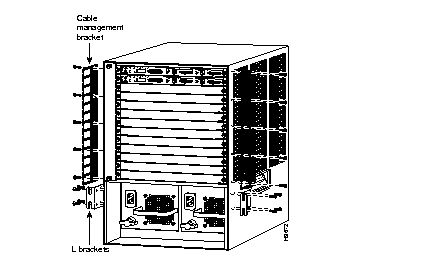
Install the Switch in the Rack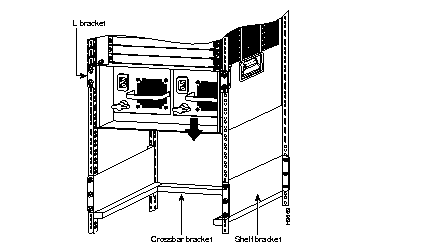
This section refers to all Catalyst 5000 series switch models.

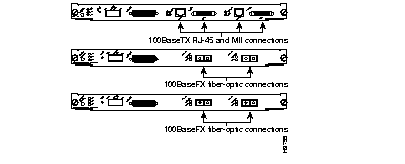
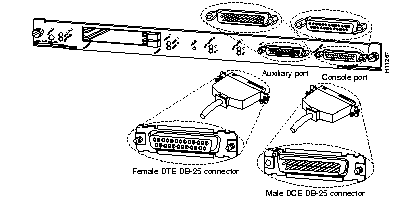
Dual RJ-45 and MII and MMF and SMF connections.
Supervisor Engine Connections 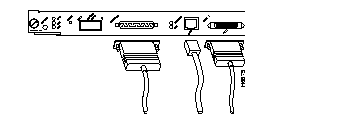
100BaseTX RJ-45 Connector Type
SC Fiber-Optic Connector Type
Attach all Ethernet, ATM, and FDDI/CDDI cable connectors and secure them in the appropriate ports.
When installing Ethernet modules, you need an Ethernet cable between the attacted device and the switch port.
Group Switching Ethernet Module (10BaseT 48 port)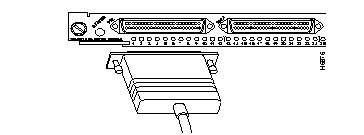
Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseT 24 port)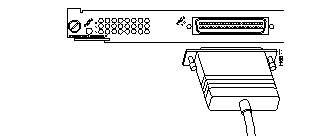
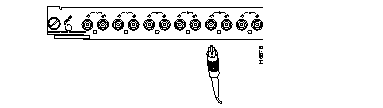
Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseFL 12 port)
10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Switching Module (10/100BaseTX 12 port)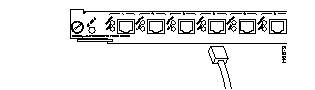
Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseTX 12 port)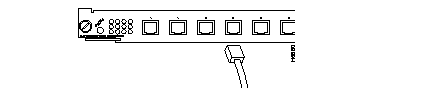
Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseFX 12 port)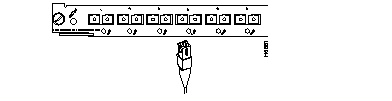

Group Switching Ethernet Module (100BaseT 24 Port)
Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseT 24 Port)

10/100 Fast Ethernet Switching Module (10/100BaseTX 12 Port)
All ATM interfaces are full-duplex interfaces. Use the appropriate interface cable to connect the ATM multimode or UTP switching module to the external ATM network.
FDDI uses two types of fiber-optic cable: single-mode and multimode fiber.
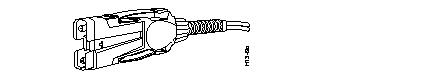
Multimode FDDI Network Interface Connector (MIC Type)
FDDI Network Interface Connector (ST Type)
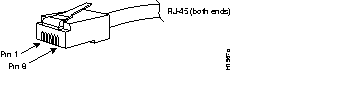
CDDI Interface RJ-45 Connector

Connect the Power on the 5002
The 155W, AC-input power supply of the Catalyst 5002 uses a universal input circuit that allows it to operate on input voltage and current within the ranges of 100 to 240 VAC and 47 to 63 Hz. To see translated versions of these warnings, refer to the Catalyst 5002 Installation Guide.
 | Caution Care must be given to connecting units to the supply circuit so that wiring is not overloaded. |
 | Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use. |
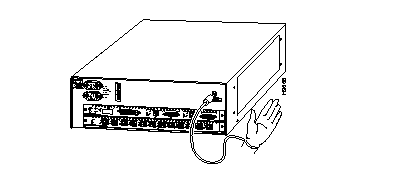
Catalyst 5002 ESD Grounding
When all interfaces are connected, perform a final check of all connections, then follow these steps to check the components and power up the system:
(a) Each switching module is inserted securely.
(b) All interface cable connections are secured.
(c) All power supply cables are securely connected to the power supply.
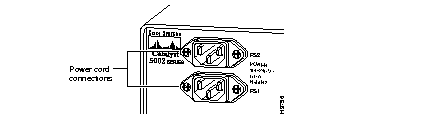
Catalyst 5002 Power Cord Connections
(a) At the power source end of the power cable, make sure the connector is securely installed in a grounded outlet and that the source power is within the range labeled on the back of the switch.
(b) When two power supplies are present, make sure that the second cord is connected to a separate line from the first, if possible.

Connect the Power on the 5000
To see the following warnings in multiple languages, refer to Appendix C, "Translated Safety Warnings" in the Catalyst 5000 Installation Guide.

Catalyst 5000 ESD Grounding
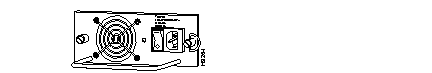
Catalyst 5000 AC Power Supply
 | Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use. |
Catalyst 5000 48-VDC Power Supply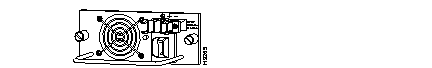
 | Warning The illustration shows the DC power supply terminal block. Wire the DC power supply using the appropriate lugs at the wiring end, as illustrated. The proper wiring sequence is ground to ground, positive to positive (line to L), and negative to negative (neutral to N). Note that the ground wire should always be connected first and disconnected last. |
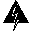 | Warning After wiring the DC power supply, remove the tape from the circuit breaker switch handle and reinstate power by moving the handle of the circuit breaker to the ON position. |

Install the Power on the 5500
To see the warnings in multiple languages, refer to the Catalyst 5500 Installation Guide
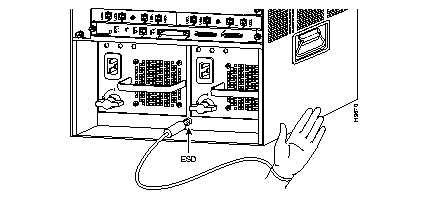
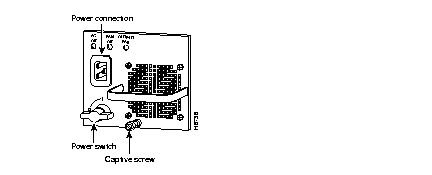
Catalyst 5500 AC Power Supply
(a) Verify that the green LEDs on the front panel are on. This indicates that the power supply is on and is receiving AC power.
(b) Verify that the appropriate Supervisor Engine II PS1 or PS2 LED is on and green.
(c) Use the show system command to display the power supply and the system status.
 | Warning Do not touch the power supply when the power cord is connected. For systems with a power switch, note that line voltages are present within the power supply even when the power switch is off and the power cord is connected. For systems without a power switch, note that line voltages are present within the power supply when the power cord is connected. |
Catalyst 5500 DC Power Supply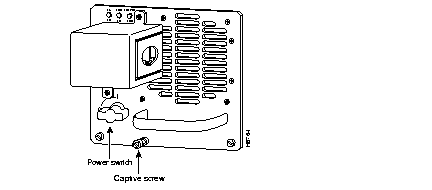
(a) If this is a new installation, remove the adhesive strip covering the CO ground connector on the switch.
(b) Use a copper ground-wire lug, and attach it to the switch.
(c) Use an 8 AWG ground wire.
 | Caution Connect the ground wire first. |
This section refers to all Catalyst 5000 series switch models.

1 Verify the following before you begin:
2 Turn the power supplies ON.
3 Check the LEDs:
During Startup:4 Press Return at each of the password prompts on the console screen.
You will need the following information:
This section contains default configurations for each module and quick configuration tables for each module and features.
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the port name. | set port name mod_num/port_num [name_string] |
| Set the port priority level. | set port level mod_num/port_num {normal | high} |
| Set the port speed. | set port speed mod_num/port_num {10 | 100 | auto} |
| Set the port transmission type. | set port duplex mod_num/port_num {full | half} |
| Check connectivity.
Step 1 Send an echo request from the Catalyst 5000 series switch to the host. Step 2 If the host is unresponsive, check the configuration for the IP address and default IP route. |
ping host show interface show ip route |
Configure Spanning-Tree Protocol.
|
enable |
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Configure from the terminal:
Step 1 Enter the configuration mode, selecting the terminal option. Step 2 Enter the necessary configuration commands. Step 3 Quit the configuration mode. Step 4 Save the configuration file modifications to NVRAM. | configure terminal
Ctrl-Z write memory
|
| Configure from nonvolatile memory: |
configure memory |
| Implement LANE by performing these tasks: | |
|
show lane default-atm-addresses | |
Step 1 Change the preferred PHY to the one not currently in use. Step 2 Display the default ATM addresses. Step 3 Determine the active PHY. |
show interface |
|
Step 1 Enter the configuration mode. Step 2 Enter the address of the LEC. Step 3 Verify the address entered. |
atm lecs-address atm_address show atm ilmi-configuration |
Step 1 Enter the configuration mode. Step 2 Specify the subinterface for the first ELAN. Step 3 Enable the LES/BUS on the subinterface. Step 4 Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for all other ELANs on this card.configure terminal interface atm 0. subinterface_num
| |
|
Step 1 Create a named database for the LANE configuration LECS. Step 2 In the configuration database, bind the name of the ELAN to the ATM address of the LES. Step 3 In the configuration database, provide a default name for the ELAN. Step 4 Exit from database configuration mode and return to global configuration mode. |
name elan_name server-atm-address default-name elan_name exit |
Step 1 Create a named database for the LANE configuration LECS. Step 2 In the configuration database, bind the name of the first ELAN to the ATM address of the LES for that ELAN. Step 3 In the configuration database, bind the name of the second ELAN to the ATM address of the LES. Repeat this step, providing a different ELAN name and ATM address for each additional ELAN in this switch cloud. Step 4 (Optional) Specify a default ELAN for LECs not explicitly bound to an ELAN. Step 5 Exit from database configuration mode and return to global configuration mode. |
name elan_name1 server-atm-address |
Step 1 Create a named database for the LECS. Step 2 In the configuration database, bind the name of the first ELAN to the ATM address of the LES for that ELAN. Step 3 In the configuration database, bind the name of the second ELAN to the ATM address of the LES. Repeat this step, providing a different name and a different ATM address for each additional ELAN. Step 4 (Optional) Specify a default ELAN for LECs not explicitly bound to an ELAN. Step 5 Add a database entry associating a specific LEC ATM address with a specific restricted-membership ELAN. Repeat this step for each of the LECs of each of the restricted-membership ELANs on this switch cloud, in each case specifying the LEC ATM address and the name of the ELAN with which it is linked. Step 6 Exit from database configuration mode and return to global configuration mode. |
name elan_name1 server-atm-address name elan_name2 server-atm-address |
Step 1 Enter the configuration mode. Step 2 Select the ATM interface. Step 3 Specify the name of the LECS. Step 4 Specify the address of the LECS. Step 5 Bind the interface. Step 6 Exit the configuration mode. |
configure terminal interface atm0 lane config test lane config auto-config-atm-address lane config database database_name end |
Step 1 Specify the subinterface for a VLAN on this switch. Step 2 Enable a LANE client for the first ELAN. |
interface atm 0. subinterface_num |
| Monitor and maintain LANE components.
Step 1 Display the global and per-VCC LANE information for all the LANE components and ELANs configured on an interface or any of its subinterfaces. Step 2 Display the global and per-VC LANE information for the BUS configured on any subinterface or ELAN. Step 3 Display the global and per-VC LANE information for all LECs configured on any subinterface or ELAN. Step 4 Display the global and per-VC LANE information for the LECS configured on any interface. Step 5 Display the LANE LECS database. Step 6 Display the LANE ARP table of the LECs configured on the specified subinterface or ELAN. Step 7 Display the global and per-VC LANE information for the LES configured on a specified subinterface or ELAN. |
show lane [interface atm 0 show lane le-arp [interface atm 0
|
| Configure specialized LANE features as follows: | |
Step 1 On the ATM switch, enter all the multiple LECS addresses. Step 2 On the ATM module, specify redundant LES/BUSs. Enter the command for each LES address on the ELAN. |
set configserver index_address_mask (for the atm lecs-address address (for the Cisco name elan_name server-atm-address |
|
|
| Step 1 Set up an LEC using VTP:
a. Enable VTP. b. From the Supervisor module, create an LEC on each ATM module of all Catalyst 5000 switches on a specified VTP domain. |
session mod_num set vlan vlan_num default |
| Step 2 Set Up VTP
a. Session to the ATM module. b. Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. c. Enter the configuration mode. d. Enable VTP. e. Exit the configuration mode. f. Write the current configuration to NVRAM. Step 3 Return to the Supervisor console. |
session mod_num enable vtp enable Ctrl-Z write memory |
Step 1 Activate the privileged mode on the Supervisor module. Step 2 Enter your password. Step 3 Assign an Ethernet port to the specified VLAN. Step 4 Session to the ATM module. Step 5 Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. Step 6 Enter the configuration mode. Step 7 Select the ATM interface. Step 8 Set up the PVCs. Step 9 Bind the PVCs to the VLAN. Step 10 Set up other PVCs for the same VLAN if needed by repeating Steps 8 and 9. Step 11 Exit configuration mode. Step 12 Verify the setup. Step 13 Write the configuration to NVRAM. |
enable set vlan vlan_num enable interface atm0 atm pvc vcd vpi vci aal5snap atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlan_num
show atm vlan write memory |
|
Step 1 Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. Step 2 Enter the configuration mode. Step 3 Select the ATM interface. Step 4 Remove the PVC from the VLAN. Step 5 End the session. |
interface atm0 no atm pvc vcd Ctrl-Z |
Step 1 Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. Step 2 Enter the configuration mode. Step 3 Select the ATM interface. Step 4 Unbind the PVC from the VLAN. Step 5 End the session. |
interface atm0 no atm bind pvc vlan vcd vlan_num Ctrl-Z |
|
To throttle the output of the entire interface: Step 1 Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. Step 2 Select the ATM interface. Step 3 Apply output throttling. Step 4 End the session. To place the output-rate to the default of 155 Mbps: Step 1 Activate the privileged mode on the ATM module. Step 2 Select the ATM interface. Step 3 Disable output throttling. Step 4 End the session. |
enable atm traffic-shape rate Ctrl-Z enable no atm traffic-shape rate Ctrl-Z |
Specify the UNI Version |
[no] atm uni-version {3.0 | 3.1} |
The features you can customize have default values that will most likely suit your environment and need not be changed. The default values of these features are set as follows:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the default IPX protocol translations. | |
|
Step 1 Configure the appropriate translation protocol. Step 2 Verify that the correct translation protocol was configured. |
|
|
Step 1 Configure the appropriate protocol translation. Step 2 Verify that the correct protocol translation was configured. |
|
Step 1 Configure the appropriate protocol translation. Step 2 Verify that the correct translation protocol was configured. |
show bridge
|
Set the minimum time to transfer the FDDI PHY line state.
|
set fddi tlmin mod_num/port_num time |
Set the interval between neighbor notification frames.
|
|
Set the timer for negotiating Token Ring timer.
|
|
Specify the user-data string.
|
set fddi userdata mod_num userdata_string |
Disable IP fragmentation.
|
|
Disable ICMP-unreachable messages.
|
|
Set the link error rate alarm.
|
set fddi alarm mod_num/port_num value |
Set the link error rate cutoff.
|
set fddi cutoff mod_num/port_num value |
Setting the port name.
|
set port name mod_num/port_num |
Set the port priority level.
|
set port level mod_num/port_num |
Set up a native VLAN on FDDI.
|
set vlan vlan_num mod_num/port_num
|
| Set up an FDDI 802.10 configuration.
Step 1 Provide a VLAN number and activate a VLAN in the management domain. Step 2 Create a VLAN with the type FDDI. Step 3 Map the Ethernet VLAN translation to an FDDI VLAN. Step 4 Turn the trunking on for the FDDI port. |
set vlan vlan_num set vlan vlan_num type fddi set vlan ether_vlan_num translation set vlan fddi_vlan_num translation set trunk mod_num/port_num on |
Reject MAC address learning.
|
set bridge fddicheck enable |
Disable automatic packet recognition and translation.
|
|
| Check connectivity.
Step 1 Send an echo request from the Catalyst 5000 series switch to the host. Step 2 If the host is unresponsive, check the configuration for the IP address of the Catalyst 5000 series switch and default IP route, if appropriate. |
ping host show interface show ip route
|
Virtual LAN Configuration and Quick Reference
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Creating a VLAN across a domain
Step 1 Define the VLAN management domain.
Step 2 Define the VLAN.
|
set vtp [domain name] [mode mode] [interval interval] set vlan vlan_num [name name] [type type] [mtu mtu] [said said] [state state] [ring ring_number] [bridge bridge_number] [parent vlan_num] [stp stp_type] [translation vlan_num] |
Grouping Switch Ports to VLANs
|
set vlan vlan_num mod/ports |
| Configuring VLAN trunks
Step 1 Establish trunks on specific ports. Step 2 Verify that the trunk configuration is correct. |
set trunk mod_num/port_num [ on | off | desirable | auto ][ vlans ] show trunk |
Configuring VLAN trunk protocol
|
set vtp [domain domain name] [mode mode] [interval interval] passwd passwd] |
| Configuring VTP pruning
Step 1 Enable the VTP pruning option. Step 2 Disable the VLAN pruning eligibility. Step 3 Enable VTP pruning eligibility. Step 4 Disable the VTP pruning option. |
set vtp [domain_name [domain_name]] [mode <mode_type>] [password <password_string>] pruning enable clear vtp pruneeligible <vlan_range> set vtp pruneeligible <vlan_range> set vtp [domain_name [domain_name]] [mode <mode_type>] [password <password_string>] pruning disable |
| Configuring Dynamic Port VLAN Membership
Step 1 Configure the IP address of the TFTP server on which the ASCII file resides. Step 2 Enable VMPS. |
set vmps storage <ip_addr> [filename] set vmps state <enable | disable> |
| Configuring Dynamic Ports on Clients
Step 1 Configure the VMPS IP address to be queried on the client. Step 2 Configure the VLAN membership assignment to a port. |
set vmps server <ipaddress> [primary] set port membership < mod_num / port_num..> <dynamic | static > |
Multicast and Multimedia Configuration and Quick Reference
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
Cisco Group Multicast Protocol
Configuring CGMP: Step 1 Enable CGMP on a device. Step 2 Configure multicast router ports. |
set cgmp enable set multicast router mod_num/port_num |
Broadcast/Multicast suppression
Configuring Broadcast/Multicast suppression:
|
set port broadcast mod_num/port_num threshold [%] |
Network Management and Control Configuration Quick Reference
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
Simple Network Management Protocol (SMNP)
Configuring SNMP: Step 1 Configure the SNMP community strings.
Step 2 Assign a trap receiver address and community. If you enter incorrect information, use the clear snmp trap command to delete the entry. Then reenter the set snmp trap command again. Step 3 If desired, configure the switch so that it issues an authentication trap. |
set snmp community read-only | read-write | set snmp trap rcvr_address rcvr_community set snmp trap enable
|
Remote Monitoring (RMON)
Configuring RMON:
|
set snmp rmon enable |
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
Configuring NTP: Step 1 Enable the NTP broadcast client mode. Step 2 Configure the address of the NTP server to be queried. Step 3 Enable the NTP broadcast client mode. Step 4 Set the NTP broadcast packet delay. Step 5 Set the time zone. |
set ntp broadcastclient enable set ntp server <ip-address> set ntp broadcast delay <microseconds> set timezone <zone> <hours> [minutes] |
Domain Name System
Configuring DNS: Step 1 Set the address of the DNS server. Step 2 Set the domain name. Step 3 Enable DNS. |
set ip dns server <ip-addr> [primary] set ip dns domain <name> set ip dns <enable | disable> |
Login banner
Configuring Login banner: Step 1 Enter privileged mode. Step 2 Enter the message of the day. |
enable set banner motd |
Multiple Module Download
Configuring Multiple Module Download:
|
enable |
Network Security Configuration Quick Reference
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
MAC Address Security
Configuring MAC Address Security:
|
set port security mod_num/port_num(s) enable [mac_addr] |
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+)
Configuring TACACS+: Step 1 Enable TACACS+ authentication for login Step 2 Enable TACACS+ authentication for enable. Step 3 Configure the key used to encrypt packets. Step 4 Configure the server on which the TACACS+ server daemon resides. Step 5 Configure the number of login attempts allowed to the TACACS+ server. Step 6 Set the timeout interval in which the server daemon must respond. |
set authentication login tacacs enable set authentication enable tacacs enable set tacacs key key set tacacs server ip_addr set tacacs timeout N |
|
|