|
|

Supplement to DOC-CATALYSTUG5 (Document Number 78-1264-05)
Boot Firmware Version 1.1
Data Movement Processor (DMP) Flashcode Version 4.1
Network Management Processor (NMP) Flashcode Version 4.1
This release note describes the features and modifications of the Catalyst 1200 series switch for software release 4.1 and also contains applicable caveats and workarounds. Refer to previous release notes for information about previous releases. Refer to the Catalyst Series Workgroup Switch User Guide for detailed information about the Catalyst Series Workgroup Switch.
The Catalyst 1200 Series Switch User Guide and all related release notes are available for the Catalyst 1200 series switch in printed form and in electronic form on UniverCD.
The Catalyst Series Workgroup Switch is an Ethernet-to-Copper Distributed Data Interface/Fiber Distributed Data Interface (CDDI/FDDI) switch that provides high-speed transparent bridging between Ethernets, and high-speed translational bridging between Ethernet and CDDI/FDDI. The switch has eight 10-megabit-per-second (Mbps) Ethernet ports and two 100-Mbps CDDI or FDDI ports. Refer to the "Product Overview" chapter in the Catalyst 1200 Series Switch User Guide for details of product features and functions.
Use Table 1 as a guide to troubleshoot problems when downloading software to the Catalyst 1200 series switch.
| Error | Possible Cause | Possible Solution |
|---|---|---|
| File not found.
tftp_req_file failed, val=-1 | The command syntax is incorrect, or the file cannot be found on the TFTP server. | Enter download help for syntax information and retype the command. Make sure the file name is correct and that the file is located on the TFTP server. |
| No more processes.
tftp_reqfile failed, val=-1 | The Catalyst 1200 switch has no processes available (max. = 16) | Terminate unnecessary tasks, such as telnet sessions or pings. Then retry the download. |
| TFTP session in progress. Try again later. | There is already a download in progress. | Retry the download when the current download process is complete. |
| <LCP> not enough memory, use fragmented buffers.
<LCP> use fragmented buffers for download. | The Catalyst 1200 switch did not find an unfragmented memory chunk, as required for the download process. The Catalyst 1200 allocates the fragmented buffers to a chained list and continues. | None required. |
| <LCP> RMON task killed.1 | If after allocating the fragmented buffer to a chained list, the Catalyst 1200 switch still does not have enough memory, it terminates the RMON task. | None required. |
| <LCP> Router RIP killed.1
<LCP> SNMPDM killed.1 <LCP> THREAD killed.1
| If after allocating the fragmented buffer to a chained list and terminating the RMON task, the Catalyst 1200 switch still does not have enough memory, it terminates the RIP, SNMPDM, and THREAD tasks. | None required.
|
| No Response from host.
tftp_req_file_failed, val=-1 | The Catalyst 1200 attempted to connect to the TFTP server, but the connection failed. | Check the physical connectivity to the server. Then check that the IP address or alias for the TFTP server is correct and retry the download. |
| Can't allocate process state buffer. | The Catalyst 1200 switch does not have enough memory to start the TFTP process. | Other applications might be using too much memory. Retry the download when there is less traffic or terminate the unnecessary telnet sessions or pings. |
| TFTP failed. Too many retries. | The Catalyst 1200 was disconnected from the TFTP server while downloading the image file. | Check that the network is operational, then retry the download. |
| Downloaded NMP code length is bad.
tftp_req_file failed, val=-1 | The image was corrupted because of a TFTP problem. | Retry the download. |
| Downloaded NMP code checksum failed.
tftp_req_file failed, val=-1 | The image was corrupted because of a TFTP problem. | Retry the download.
|
| The NMP flash was damaged, must first download a valid image. | The user entered Ctrl-C while the Catalyst 1200 switch was clearing or erasing Flash memory. | Retry the download of the same Flash image. If this error occurs again, contact Cisco's Technical Assistance Center.
|
RMON domains can be archived so that if the Catalyst 1200 series switch reboots, the RMON domains can be retrieved. To save the installed RMON domains, follow these steps:
Step 1 After installing the RMON domains from a NetScout Manager on a server, change to the bin directory under the directory where NetScout Manager is installed. For example, if the NetScout Manager is installed in/usr/nsman, then change to the /usr/nsman/bin directory.
Step 2 Save the list of installed domains of an agent into a new file (agent-list) in the directory where the startup file is saved, for example, in /user/nshome/usr. To save the domains on a UNIX server, type the following:
Step 3 Change to the /usr/nshome/usr directory.
Step 4 Copy the startup file (startup) into a new file (agent-startup).
Step 5 Open the new file (agent-startup). Replace the dvinst.cfg parameter in both places with the name of the new agent list file (agent-list) created in Step 2. Save and exit this file.
Step 6 Enter the NetScout Manager application. In the Start Up File field for the agent that needs to be saved, enter the name of the new agent startup file (agent-startup).
For each agent that uses this protocol and these groups in their domains, enter the name of the new agent startup file in the corresponding Start Up File field.
Step 7 Repeat Steps 4 through 6 for each agent that has different protocols and groups in its domain.
DMP Version 4.1 is an upgrade to the previously released DMP Version 3.27.
NMP Version 4.1 is an upgrade to the previously released NMP Version 3.27.
The following features have been added:
This section describes possible, unexpected behavior by software release 4.1. The caveats listed here describe only serious problems.
Workaround:
Disable the modem using the set modem disable command.
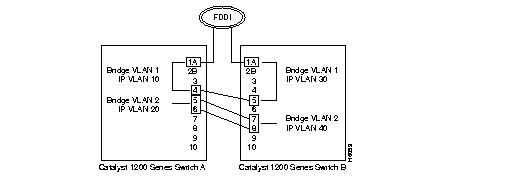
Refer to Figure 1 and the following example:
Catalyst 1200 series switch A has ports 1 and 4 in bridge VLAN 1 and ports 5 and 6 in bridge VLAN 2. This same switch has ports 1 and 4 in IP VLAN 10 and ports 5 and 6 in IP VLAN 20. This switch is connected in a looped configuration to Catalyst 1200 series switch B.
Catalyst 1200 series switch B has ports 1 and 5 in bridge VLAN 1 and ports 7 and 8 in bridge VLAN 2. This same switch has ports 1 and 5 in IP VLAN 30 and ports 7 and 8 in IP VLAN 40.
Workaround:
For IP connectivity, configure a default route on the Catalyst 1200 series switch instead of allowing it to learn RIPs.
Workaround:
Clear the ARP entry for the Catalyst's IP address from the originating IP station's ARP table, or clear the ARP table on the Catalyst you are trying to reach.
Workaround:
Do not abort a serial download. Let the serial download complete. If you do abort a serial download, reset the switch and reinitiate the serial download.
Workaround:
When you enter new route groups using the Brouter Table menu form in Workgroup Director, make sure to correctly enter all the IP information, including the IP address, subnet mask, and broadcast address. Click the SET button to add the new route group configuration.
Workaround:
Setup default routes in the Catalyst 1200 series switch's routing table and limit the number of broadcast frames that the switch receives by using set filter broadcast command throttling mechanism.
Workaround:
Do not abort a serial download. Let the serial download complete. If you do abort a serial download, reset the switch and reinitiate the serial download.
Workaround:
If you remove an IP network from your routing group, delete the corresponding default route using the clear route default command.
CAT5> (enable) Automatic logout... Enter password: no more free CAM entries, mac_addr = 0 0 d477 no more free CAM entries, mac_addr = 0 0 d4f7 no more free CAM entries, mac_addr = 0 0 d40f
However, entries can still be added manually. The Catalyst 1200 series switch discards the oldest dynamic entry and adds the new entry.
The following caveats were experienced in previous Catalyst 1200 series switch releases and have been corrected in Release 4.1.
Also, this situation might have caused the non-root bridge to send duplicate ping responses on a blocked spanning-tree port. The switch could not respond to pings on a blocked spanning-tree port.
The situations described above no longer occur.
The console no longer gets locked.
Reassembly of large packets has been disabled; therefore, the Catalyst 1200 series switch now drops any large packets.
The Catalyst 1200 series switch automatically detects the correct status of the port.
The following caveats to the NetScout RMON have been identified and workarounds provided:
All submenu actions items must be completed before other Main menu items may be activated.
Workaround:
Reduce the frozen screen(s) to icons to find the active submenu screen hidden behind. The active submenu screen must be closed to allow another Main menu selection.
The Catalyst Switch will attempt to install all possible resources using the available memory. If the switch is not successful installing all of the enabled groups for the chosen domain, it will install as many as possible and display the following error messages:
no resources... could not install
Workaround:
Use the Domain Management menu to confirm completion of the RMON configuration or use the Domain Manager submenu from the Main menu screen to install logical agents.
-- Error accessing agent < agent name > While retrieving Domains Error: cannot communicate with agent
This error message does not indicate the Catalyst switch is down. This error message may be caused by one or more of the following conditions:
Workaround:
To verify the Catalyst state, ping the switch or refer to the console window to determine the exact nature of the problem.
 | Caution If the sample configuration files become corrupted the RMON must be completely reinstalled to create new sample configuration files. |
Workaround:
Correct the mistakes by editing the configuration file associated with that agent and then reinstalling the file.


|
|