|
|

This management function may be used to obtain, at any time, general information about the state and overall traffic load of the equipment. It has the special feature of including commands that may be used to modify:
In order to prevent a high statistics packets flow, there are 7 types of statistics:
Types 1 and 2 concern the activity of the equipment:
For type 1:
For type 2 (reserved MCX/FRX):
The users selects the type(s) desired, specifying additional optional information (ACO) in the call packet of the function. The ACO is in hexadecimal; the rules governing its information are the following:
In ASCII and binary modes, if the ACO number is missing, types 1 and 2 are distributed.
The ACO number has no meaning in clear language mode. If the call packet specifies an ACO and is in clear language mode, then the call is cleared.
The syntax of the access code is:
| IS No: | 05:
06: 14: | BINARY MODE
ASCII MODE CLEAR-LANGUAGE MODE |
| PASSWORD: | Exists if configured (SS by default). | |
| ACO: | See paragraph below. |
The call may be cleared by the statistics service for the following reasons:
The users selects the type(s) desired, specifying additional optional information (ACO) in the call packet of the function. The ACO is in hexadecimal; the rules governing its information are the following:
The management of the ACO is summarized in Table 6-1.
| Type of statistics | 1 and 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| ACO in hexadecimal | 01 and/or 02 | 04 | 08 | 10 | 20 | 40 |
Utilization example:
ACO No. = OC means distribution of type 3 and 4 statistics.
ACO No. = OB means distribution of type 1, 2 and 4 statistics.
The ACO number may be absent or may take on the value 00. If another values is specified in the DCO, then the call is cleared.
In ACO absent mode, the line status statistics are distributed periodically and commands S, P, I, J, H and D are available.
In ACO equal zero mode, no periodic distribution takes place and the commands of the ACO absent mode are available.
The number of statistics message blocks depends of the type of equipment.
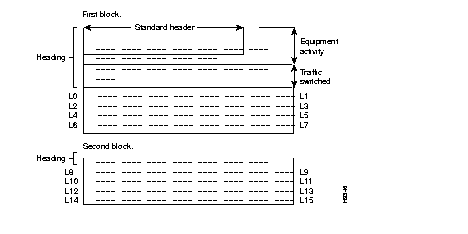
The statistics messages distributed by the FastPADmp consist of two blocks (type 1):
| First block | = information about lines 0 to 7. |
| Second block | = information about lines 8 to 15. |
Each information block contains three separate zones following the standard heading:
| · equipment activity, | |
| · traffic switched, | See Table 6-2 for description |
| · links. |
A statistics message transmitted by the FastPADmpr is composed of seven blocks.
| · first5 blocks | = | information related to lines (8 by 8 as for FastPADmp). |
| · 6th block | = | information relative to LIUs (Inter-Unit line):
same format as the preceding blocks. |
| · 7th block | = | type 2 block. |
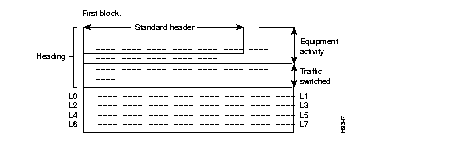
The statistics messages distributed by the FastPADmp 6 are made up of a type 1 block: information related to lines 0 to 7.
Each information block contains three separate zones following the standard heading:
| · equipment activity, | |
| · traffic switched, | See Table 6-2 for description |
| · links. |
| Number (hexadecimal) | Meaning |
| 00 to 0B | Standard heading |
|
0C and 0D 0E 0F
10 and 11 12 and 13 (2) 14 and 15 16 and 17 18 and 19 1A 1B | EQUIPMENT ACTIVITY ZONE
Cumulative duration (X 0.1 s): elapsed time since departure of previous packet. Type of packets. This field is made up of flags: 01 = flag indicating the presence of a packet to be followed 02 = flag indicating the presence of a series for the current information element. 80 = flag indicating whether or not the packet is significant. Number of virtual circuits established. CPU load (max. 64). Total number of buffers created during initialization. Number of free buffers, not counting recoverable buffers (charging ticket, observation and outstanding events buffers). Not used. Not used. Number of traffic generators. |
|
20,21 and 22 23, 24 and 25 26, 27 and 28 29, 2A and 2B 2C, 2D and 2E 2F, 30 and 31 32 33 34 | TRAFFIC SWITCHED ZONE
Total number of data packets received by internal switching function since start of period. Total number of data bytes received by internal switching function since start of period. Total number of interrupt packets received by internal switching function since start of period. Total number of reset packets received by internal switching function since start of period. Total number of call request packets received by internal switching function since start of period. Total number of call confirmation packets received and successfully processed by internal switching function since start of period. This value is therefore the number of virtual circuits established since the start of the period. Indicator of block to follow (0 = no, 1 = yes) Total gain in volume (bytes), generated by the compression/scrambling function and stated in tenths. Total gain in billing (in segements), generated by the compression/scrambling function and stated in tenths. |
|
40 + (n x 8)
41 + (n x 8) 42 + (n x 8) 43 + (n x 8) 44 + (n x 8) (1) 45 + (n x 8) (1) 46 + (n x 8) (1) 47 + (n x 8) (1) | LINK ZONE
Characteristics of link
Number of logical channels not free in link at start: infinite counter (least significant byte). Number of logical channels not free at start (most significant byte, bits 1 to 4). Number of resets of link since start of period (most significant byte, bits 5 to 8). Total number of line incidents since start of period. Total number of times 256 bytes were received on link since start of period. All bytes received are counted, whether or not the frames are correct (CRC not included in total). Adding up since the start of the period (CRC not included in the total):
|
Value of n = 0 up to 7.
The values taken into account in a multimodule unit to enter the offsets 12 and 13 are the CPU loads of the module which maximize the total of the loads of the two CPUs.
Example: consider the CPU load values of Table 6-3 (value in decimal):
| Module | CPU A load | CPU B load | CPU A + CPU B |
| 0
1 2 | 20 %
10 % 02 % | 15 %
60 % 62 % | 35 %
70 % 64 % |
Take the values of the CPU load of module 1 to enter the offsets 12 and 13: OA3C.
Like a type 1 block, the type 2 block is made up of three zones: equipment activity, switched traffic and links.
|
- | offset 20 21 | = | load CPU A and B module 0 |
| - | offset 22 23 | = | load CPU A and B module 1 |
| - | offset 24 25 | = | load CPU A and B module 2 |
| - | offset 26 27 | = | number of free buffers in module 0 |
| - | offset 28 29 | = | number of free buffers in module 1 |
| - | offset 2A 2B | = | number of free buffers in module 2. |
| - | offset 2C-2F | = | status of module 0 |
| - | offset 33-36 | = | status of module 1 |
| - | offset 3A-3D | = | status of module 2 |
Each of these zones of 4 bytes is entered as follows:
| · byte 1: | most significant quartet = status of module |
| (0 = out of service, 1 = in service, 2 = boot) | |
| least significant quartet = configuration of module | |
| (0 = unreachable, 1 = fault, 2 = operational, 3 = start card) | |
| · byte 2: | version number |
| · byte 3: | most significant quartet = stage |
| least significant quarter = revision | |
| · byte 4: | addition number |
· bytes 2, 3, 4 are set to 0 if the module cannot be reached. | |
The statistics on an LAN link are distributed on two packets.
The packets have the following format:
|
| OC-D | 1 word | Time elapsing since last distribution. |
| OE | 1 byte | Type of packet. | |
| OF | 1 byte | This field is made up of flags: | |
| 01 = | Flag indicating the presence of a packet to follow. | ||
| 02 = | Flag indicating the presence of a series for the current information element. | ||
| 04 = | Flag indicating the first packet of a sub-type. | ||
| 80 = | Flag indicating whether or not the packet is significant. | ||
| 10 | 1 byte | Number of fields completed by this packet and the packets of the same type of follow. | |
| 11 | 1 byte | Number of elements completed by the packet. |
| 12 | 1 byte | Line number. | |
| 13 | 1 byte | Type of LAN (-1: Ethernet, -2: Cheapernet, -3: Ethernet Twisted Pair). | |
| 14 | 1 byte | Status of LAN | |
| -0: LAN interface out of service, | |||
| -1: LAN interface in service). | |||
| 15 | 1 byte | Module number. | |
| 16-1B | 6 bytes | Ethernet address of equipment on 6 bytes. | |
| 1C | 1 word | LAN interface status (this is the value of the status register of the LAN interface unit). | |
| 1E | 1 word | Counter Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR). | |
| This counter allows the location of a problem on the cable. | |||
| 20 | 1 long | Transputer CPU charge counter. | |
| 24 | 1 long | Counter accumulation time. This is the time elapsing since the last start-up of the LAN interface unit. | |
| 28 | 1 long | Mask of statistics counters having changed. | |
| 2C | 1 long | Transmitted byte counter. | |
| 30 | 1 long | Transmitted frame counter. | |
| 34 | 1 long | Counter of frames transmitted without error. | |
| 38 | 1 long | Counter of frames transmitted without error after collision. | |
| 3C | 1 long | Counter of frames transmitted without error after two collisions or more. | |
| 40 | 1 long | Counter of frames transmitted with "no heartbeat" error. | |
| The heartbeat function of the Ethernet transmitter is used to indicate to the LAN driver the status of its collision detector. Thus, if following a transmission, the transmitter does not send the SQE signal of the heartbeat function to the LMX, then the frame is considered to be sent with "no heartbeat" error. | |||
| 44 | 1 long | Counter of frames sent without error after waiting to clear the bus. | |
| 48 | 1 long | Counter of frames not transmitted with "late collision" error (detection of collision after the end of the time slot). | |
| 4C | 1 long | Counter of frames not transmitted following collision detection during authorized repetitions (16). | |
| 50 | 1 long | Counter of frames not transmitted because of a "no carrier sense" error (loss of carrier detection signal during transmission). | |
| 54 | 1 long | Counter of frames not sent with excessive lateness error (bus busy). | |
| 58 | 1 long | Counter of frames not sent because of "loss of CTS" (clear to send) error. | |
| 5C | 1 long | Counter of frames not sent because of "DMA underrun" (absence of reply when expected by the memory bus to a DMA cycle). |
| 12 | 1 byte | Line number. | |
| 13 | 1 byte | LAN type (same as packet 1). | |
| 14 | 1 byte | LAN status (same as packet 1). | |
| 15 | 1 byte | Module number. | |
| 16 | 1 long | Received byte counter. | |
| 1A | 1 long | Received frame counter. | |
| 1E | 1 long | Counter of frames received without error. | |
| 22 | 1 long | Counter of frames received with alignment error (with a CRC error and containing a number of bits not a multiple of 8). | |
| 26 | 1 long | Counter of frames received with CRC error only. | |
| 2A | 1 long | Counter of frames received with excessively long frame error (longer than the maximum authorized length). | |
| 2E | 1 long | Counter of frames received with excessively short frame error (number of frames received but lost because shorter than the minimum required length). | |
| 32 | 1 long | Counter of frames received with missing resource error (memory resource insufficient at controller level). | |
| 36 | 1 long | Counter of frames received with "DMA overrun" (absence of replies when expected from the memory bus to a DMA cycle). | |
| 3A | 1 long | Counter of frames received with "receive collision" error (frames received, but invalidated owing to a collision detection during reception). | |
| 3E | 1 long | Counter of received frames returned to the application (frames received without error which have been accepted by the filtering system and which are sent to the bridge function). | |
| 42 | 1 long | Counter of frames rejected on overflow of transmission queue with 68302. | |
| 46 | 1 long | Supervision counter OK. | |
| 4A | 1 long | Supervision counter not OK. | |
| 4E | 1 long | Receive reset counter. | |
| 52 | 1 long | Counter of frames accepted by bridge filtering system. | |
| 56 | 1 long | Counter of frames rejected by bridge filtering system. |
The type 4 packet describes the Bridge and IP Router functions and has the following format:
|
12 | 1 byte | Type of function |
| - 1: remote bridge, | ||
| - 2: IP router. | ||
| 13 | 1 byte | Number of LAN line attached to function. |
| 14 | 1 byte | Status of function |
| - 0: function out of service, | ||
| - 1: function in service. |
| 15 | 1 byte | Module number |
|
16 | 2 long | Number of bridge frames sent (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 1E | 2 long | Number of bridge frames received (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 26 | 2 long | Number of service messages sent (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 2E | 2 long | Number of service messages received (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 36 | 2 long | Number of data frame distributions (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 3E | 2 long | Number of service frame distributions (1st long = cumulative, 2nd long = delta). |
| 16 | 1 long | IP address of router. |
| 1A | 1 word | Number of LLCs out of service. |
| 1C | 1 word | Reserved. |
| 1E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on all interfaces. |
| 26 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on all interfaces and lost because of unknown protocol. |
| 2E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on all interfaces and lost because routing was not possible. |
| 36 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on all interfaces and lost because of a datagram error. |
| 3E | 2 long | Counters for routed IP datagrams. |
| 46 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams routed to LLC by default. |
| 4E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on all interfaces and lost because LLC is out of service or saturated. |
| 56 | 2 long | Counters for ICMP datagrams sent. |
| 5E | 2 long | Counters for ICMP datagrams received on all interfaces. |
| 66 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams sent on all interfaces. |
| 6E | 2 long | Counters for number of bytes received with IP protocol. |
| 76 | 2 long | Counter for number of bytes sent with IP protocol. |
| 16 | 1 long | Min. IP address or LAN interface network address. |
| 1A | 1 long | Max. IP address or LAN interface mask subnet. |
| 1E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams sent on LAN interface. |
| 26 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received on LAN interface. |
| 2E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams lost because routing was not possible. |
| 36 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received LAN interface and lost because of an error. |
| 3E | 2 long | Counter for number of bytes received on LAN interface with IP protocol. |
| 46 | 2 long | Counters for number of bytes sent on LAN interface with IP protocol. |
| 4 long | Reserved. | |
| 4E | 2 long | Counters for failed ARP resolutions. |
| 56 | 2 long | Counters for transmitted RIP datagrams. |
All counters of the IP Router statistics zone are broken down as follows:
A type 5 packet contains the description of an LLC and has the following format:
| 12 | 1 word | LLC identifier. |
| 14 | 1 byte | Line number. Number of the virtual line attached to the function (flag 80 positioned) |
| 15 | 1 byte | Status of LLC (- 0: LLC out of service, - 1: LLC in service). |
| 16 | 2 long | Counters for bridge frames transmitted. |
| 1E | 2 long | Counters for bridge frames received. |
| 26 | 2 long | Counters for service messages sent. |
| 2E | 2 long | Counters for service messages received. |
| 36 | 8 long | Reserved. |
| 56 | 1 word | DNIC of remote equipment. |
| 58 | 1 byte | ZO of remote equipment. |
| 59 | 1 byte | AB of remote equipment. |
| 5A | 1 byte | AB of local equipment. |
| 5B | 1 byte | Type of encapsulation. |
| 5C | 1 byte | Type of function using this LLC |
| - 1: bridge of remote type. | ||
| 5D | 1 byte | Reserved. |
If flag 80 is not positioned, offset 14 gives the module number
| 12 | 1 word | LLC identifier. |
| 14 | 1 byte | Number of the vertical line attached to the function flag 80 positioned). |
| 15 | 1 byte | Status of LLC (- 0: LLC out of service, - 1: LLC in service). |
| 16 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams sent. |
| 1E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received. |
| 26 | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received and lost because routing was impossible. |
| 2E | 2 long | Counters for IP datagrams received and lost because of a datagram error. |
| 36 | 2 long | Counters for number of bytes received on LLC with the IP protocol. |
| 3E | 2 long | Counters for number of bytes sent on the LLC with the IP protocol. |
| 46 | 4 long | Reserved. |
| 56 | 1 word | DNIC of remote equipment. |
| 58 | 1 byte | ZO of remote equipment. |
| 59 | 1 byte | AB of remote equipment. |
| 5A | 1 byte | AB of local equipment. |
| 5B | 1 byte | Type of encapsulation. |
| 5C | 1 byte | Type of function using this LLC |
| - 2: IP Router. | ||
| 5D | 1 byte | Reserved. |
Type 5 packets describe the LLCs in service or out of service if the number of LLCs does not exceed 10. For more than 10, only the active LLCs are described.
All counters for the statistic zones per LLC are broken down as follows:
There is one buffer per module.
| Rox | Meaning |
| 0O to 0B | Standard management header |
| 0C to OF | Reduced statistics header (4 first bytes of |
| 10 to 1F | 16 bytes reserved for future use |
| 20 to 80 | Additional link zone |
Each information entity for a line is 8 bytes. The meaning of the fields of each information entity is described below:
| 20+n*8 | Number of line to which the additional information refers | |
| 21+n*8 | Bit map of ISO INS/status under test | |
If at 0 then line OOS | ||
| Bit 0,1 | ISO level | |
| bit 1 = 1, bit 0 = 1 | level 3 | |
| bit 1 = 1, bit 0 = 0 | level 2 | |
| bit 1 = 0, bit 0 = 1 | level 1 | |
| bit 1 = 0, bit 0 = 0 | line OOS | |
| Bit 7,6 | test status | |
| bit 7 = 1, bit 6 = 1 | under test | |
| bit 7 = 0, bit 6 = 0 | not under test | |
| 22+n*8 | type of line (same as C1R1) | |
| 23+n*8 | MLP trunk information | |
If bit 7 is at 1 then the line is the main line of an MLP trunk; | ||
If bit 6 is at 1, the line is in service seen from the MCX/FRX (this information is significant only when bit 7 is at 1); | ||
Bit 0-6: 0F in hex. if the line does not belong to a trunk, equal to the recurrence number of the trunk in class 25 otherwise; | ||
| 24+n*8 to 27+n*8 | Reserved | |
The number of messages sent depends on the number of FR lines configured as well as the number of DLCIs on each line.
A type 7 message describes a FR line and/or 12 DLCIs maximum.
It has the following format:
|
0C-0D | 1 word | Time elapsing since last |
| 0E | 1 byte | Type of packet |
| 0F | 1 byte | Packet to follow information. This field is composed of flags: |
| - | 01H = Flag indicating the presence of a packet to follow | |
| - | 02H = Flag indicating the presence of a series for the current. Information element. i.e blocks describing the DLCIs of the same physical FR line | |
| - | 04H = Flag indicating the first packet of a sub-type (a sub-type = all blocks describing the same physical FR line) | |
| - | 08H = Flag indicating whether or not the packet is significant. | |
| 10 | 1 byte total number of DLCIs on the physical FR line described | |
| 11 | 1 byte number of DLCIs entered in this packet | |
| - | Physical Frame Relay line statistics zone | |
| 12 | 1 byte FR line number | |
| 13 | 1 byte LMI status + line status | |
This field is composed of flags ( 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1)
| -02 and 01 | LMI status | |
| 00 LMI NC | ||
01 LMI available | ||
11 LMI not available | ||
| -08 | Physical line status | |
| 1 line In Service | 0 line Out of Service | |
| 14-15 | 1 word | Total number of buffers created during initialization |
| 16-17 | 1 word | Number of buffers free |
| 18-1F | Not used | |
| -DLCI statistics zone | ||
| 20+(n*8) and 21(n*8) | 1 word | DLCI number |
| 22+(n*8) | 1 byte | DLCI status |
This field is composed of flags (8-1)
23+(n*8) to 27+(n*8) reserved.
n: order number (from 0 to 11) and not DLCI number
This is an example of a FastPAD with less than 12 PVC on line 0. PVC using DLCI 0500 is active and is running full duplex traffic.
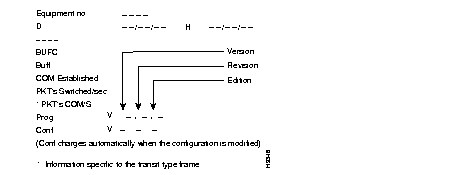
EQT No : 900000
D: 06/14/00 H: 12/42/54
BUFC:10246
BUFF:9527
FR SWITCHED : 0000
PROG:V 12.2.2.01
CONF:V 31
Line Number 00 / In Service / LMI available
0000 P X X 00000 00000 0200 P I O 00000 00000 0300 P I O 00000 00000
0400 P I O 00000 00000 0500 P A O 00040 00040 0600 P I O 00000 00000
0850 P I O 00000 00000
Line Number 01 / Out of Order / LMI NC
Line Number 06 / In Service / LMI NC
0160 P X X 00000 00000
Line Number 20 / In Service / LMI available
0000 P X X 00000 00000 0022 P I O 00000 00000
Line Number 33 / In Service / LMI NC
0500 P X X 00023 00023
*CLR
CLR CONF
CALL CLEARED
*90000099D06SS40
COM
CALL CONNECTED
I
9000 000C 6585 1D2F C21F 0706 0000 0785 0707 0081 2806 2536 0100 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 00C8 0500 0000 0000 012C 0500 0000 0000 0190 0500 0000 0000
01F4 0D00 0028 0028 0258 0500 0000 0000 0352 0500 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 000C 6585 1D2F C21F 0706 0000 0785 FF00 0100 2806 2535 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 000C 6585 1D2F C21F 0706 0000 0785 0101 0680 2806 2534 0000 0000 0000 0000
00A0 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 0008 3400 2E49 C21F 0706 0000 0785 0202 1481 2806 2544 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0016 0500 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 0008 504D 2E49 C21F 0706 0000 0784 0101 2180 2806 2537 0000 0000 0000 0000
01F4 0000 0047 0047 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
This is an example of a FastPAD with more than 12 pvc on line 0. PVC using DLCI 0500 is active and running full duplex traffic(ping).
EQT No : 900000
D: 06/14/00 H: 13/59/49
BUFC:10246
BUFF:9524
FR SWITCHED : 0000
PROG:V 12.2.2.01
CONF:V 33
Line Number 00 / In Service / LMI available
0000 P X X 00005 00008 0200 P I O 00000 00000 0300 P I O 00000 00000
0400 P I O 00000 00000 0500 P A O 00203 00203 0600 P I O 00000 00000
0850 P I O 00000 00000 0900 P I X 00000 00000 0910 P I X 00000 00000
0920 P I X 00000 00000 0930 P I X 00000 00000 0940 P I X 00000 00000
0950 P I X 00000 00000
Line Number 01 / Out of Order / LMI NC
Line Number 06 / In Service / LMI NC
0160 P X X 00000 00000
Line Number 20 / In Service / LMI available
0000 P X X 00006 00005 0022 P I O 00000 00000
Line Number 33 / In Service / LMI NC
0500 P X X 00000 00000
*90000099D06SS40
COM
CALL CONNECTED
I
9000 000D 8C94 1D2F C221 0706 0000 0787 0D0C 0081 2806 2537 0100 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0005 0008 00C8 0500 0000 0000 012C 0500 0000 0000 0190 0500 0000 0000
01F4 0D00 00CB 00CB 0258 0500 0000 0000 0352 0500 0000 0000 0384 0400 0000 0000
038E 0400 0000 0000 0398 0400 0000 0000 03A2 0400 0000 0000 03AC 0400 0000 0000
9000 000D 8C94 1D2F C221 0706 0000 0781 0D01 0081 2806 2537 0000 0000 0000 0000
03B6 0400 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 000D 8C94 1D2F C221 0706 0000 0785 FF00 0100 2806 2537 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 000D 8C94 1D2F C221 0706 0000 0785 0101 0680 2806 2537 0000 0000 0000 0000
00A0 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 0009 5AF1 2E49 C221 0706 0000 0785 0202 1481 2806 254D 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0006 0005 0016 0500 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
9000 0009 7744 2E49 C221 0706 0000 0784 0101 2180 2806 2539 0000 0000 0000 0000
01F4 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
The user-friendly mode does not support the distribution of statistics for LAN links and bridge functions.
This mode describes only statistics blocks of types 1 and 2.
The format of the display is the following:

Three digits when the number of VC's < 999
Four digits when the number of VC's > 999
The field mm is the status of the module, ES (in service) or HS (out of service) or BT (boot). If the module is in service, the status of its configuration is indicated as:
Mode reserved.
Plain text-statistics:new Frame Relay plain-text screen
EQT No: ------
D: --/--/-- H: --/--/--
BUFC: ----
BUFF: ----
TR RELAY./S: ----
PROG: V i,j,kk
CONF: V y
Physical line No --/In service/LMI available
| nnnn | a x y zzzz tttt | nnnn | a x y zzzz tttt | nnnn | a x y zzzz tttt | nnnn |
Physical line No. --/Out of service/LMI not available
or: nnnn = DLCI number
| a | P (PVC) |
| x | A (Active) or I (Inactive) or X (undetermined) |
| y | O (Old) or N (New) or X (undetermined) |
| zzzz | number of times 256 bytes have been transmitted |
| tttt | number of times 256 bytes have been received |
| Command Syntax | Command Processing |
|---|---|
| S
P(n) (a) I(n) (a) I99999 Jn (CR)
Hn (CR)
Dn (CR) | Immediate sending of statistics packet without resetting of counters.
Application of new sending period (n) for statistics packets after current period with resetting of counters. Instantaneous application of new sending period (n) for statistics packets with resetting of counters. Addition of statistics data without sending any packet (use the command I for sending a statistics packet). Change of date. n is the number of days from 1 january 1980 n = 3654 on 1 january 1990 1<n>7000 Change of hour n is between 0 and 23. Change of minutes and seconds in tenths of a second. n = number of tenths of a second. n is between 0 and 35999 |
a) The P(n) and I(n) command do not reset the counters of the type 3 statistics (LAN).
If an erroneous command is given, the call is reset and the operator must type the correct command.
The statistics messages displayed succeed one another at the rate of the period configured (n time 10 s, where n is the value configured). This period can be modified for the duration of a call, using the statistics function.
The commands P(n), I(n) and I99999 allow these modifications:
The statistics distribution period is calculated as follows:
A date and hour counter in the standard management message heading serves to date the management messages transmitted by the FastPADmp/FastPADmpr.
The equipment manages the date and hour, but adjustments for changes of legal time and for leap years must be made by the user.
For the FastPADmp6 equipment, the time-keeper constantly saves the date and hour.
User-Friendly stat:
To obtain the Frame Relay plain-text screen, call: 90000099D14SS40 or 90000099D14SS and then enter the command F.
The command X alllows you to return to the stat standard screen.
ASCIl stat:
To obtain type 7 messages, call: 90000099D06SS40 or 90000099D06SS and then enter the command F.
The command X enables you to display type 1 and 2 messages.
|
|