Step 3 Verify that the connection has the proper polarity. Be sure the Tx connector on the ATM module is linked to the Rx connector on the other device, and that the Rx connector on the ATM module is linked to the Tx connector on the other device. (ATM Duplex SC connectors are "keyed" to indicate proper polarity, but the polarity of your connector cables may not be clearly marked.)
Checking the Installation
The following tables describe the connectors, LEDs, and switches on the WS-X3006A module.
Table 5 : ATM Expansion Module LEDs
| Name
|
Description
|
| LINK
|
Off = link not detected
Green = link detected
|
| DIAG
|
Running self-diagnostic or if ATM module fails
|
Table 6 : ATM Expansion Module Connector
| Name
|
Description
|
| Network Port
|
SC type multi-mode optical fiber connector
|
When the link is established, the LINK LED is on. The LED should be green. If the LED is not on, or if the LED is an amber color, try the following tests:
- Check the cable connections
- Try swapping the TX/RX fiber connectors at one end
- Verify that you are using the correct type of cable
- Test whether the cable is bad by trying a different one
- Check the power-up diagnostics to see if any problems were reported
If the above tests do not correct the problem, contact Cisco support.
If, after installation, there is poor system performance or the ATM module does not work at all, remove the module and check for any damage or bent connector pins. You may need a bright light to see inside the expansion module slot to check for bent pins. If you cannot find an immediate cause for the problem, contact Cisco support.
The WS-X3007 and WS-X3008 100VG Expansion Module
The 100VG module is an expansion module that can be added to a Catalyst switch to provide 100VG high speed connectivity. The 100VG module is compatible with the IEEE 802.12 standard.
The 100VG expansion module is available in the following two models. Each model has two high-speed 100VG ports.
- WS-X3007.
- The WS-X3007 is a 100VG module with two installed transceivers with fiber-optic connectors.
- WS-X3008.
- The WS-X3008 is a 100VG module with two installed transceivers with UTP (Unshielded Twisted-Pair) connectors.
The following topics for the 100VG expansion module are discussed in this section:
- Descriptions
- Installation Steps
- Transceiver specifications
- Transceiver installation and cabling
- Accessing the 100VG Configuration and Statistic Screens
Figure 11 : 100VG Expansion Module
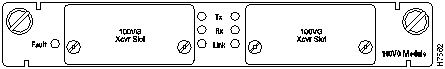
Descriptions
Physical
Dimensions
Width: 6.00 cm (6.30 in)
Depth: 1.89 cm (8.62 in)
Height: 2.36 cm (0.93 in)
Weight: 86.33 g (10.10 oz) (with no transceivers installed)
Environmental
Operating temperature: 0C to 40C (41F to 104F)
Nonoperating temperature: 40C to 70C (-40F to 158F)
Relative humidity: 5% to 80% at 40C (104F) non-condensing
Maximum operating altitude: 3.1 km (10,000 feet)
Electromagnetic
Emissions
FCC part 15 Class A
EN55022 / CISPR-22 Class A
VCCI Level 1
Immunity
Complies with Canadian EMC Class A requirements.
Declaration of Conformity for the 100VG Module complies with ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN 45014. The declaration identifies the product, the manufacturer's name and address, and the applicable specifications that are recognized in the European community.
Inserting the 100VG Module
Expansion modules are installed in the expansion slots on the front of the Catalyst switch. All front expansion modules are installed in a similar way. Use the previous section "Installing The WS-X3001 (100Base TX) Expansion Module" as an example for detailed installation instructions and precautions for the 100VG module.
Verifying the Installation
Connect the Catalyst switch to a power source and it will begin its power-on self-test diagnostics. The following lists the LED pattern that occurs during the diagnostics.
- At Power On, all LEDs turn on.
- The self-test diagnostics for the Catalyst switch and 100VG Module requires approximately 5 minutes. The Catalyst switch DIAG LED and all 100VG Module LEDs are on during this test.
- After diagnostics, All LEDs on the module are off.
When the self-tests of the Catalyst switch and the 100VG Module complete successfully, the Catalyst switch and its module(s) are now operational. Connect the appropriate cable to your transceiver.
See the transceiver section for the cable specifications and instructions.
If the diagnostics fail or if the FAULT LED is on or blinking, refer to the Troubleshooting section at the end of this document.
100VG Recessed Transceivers
The following sections describe the 100VG Recessed Transceivers. Use this section to cable a compatible network device to a specific 100VG Module transceiver.
Each 100VG Module has preinstalled transceivers, but if a transceiver must be replaced, refer to this section for removal or installation instructions. If there is a problem with a transceiver, use the following sections to verify the installation or to troubleshoot the problem.
Introduction
The 100VG Recessed Transceivers provide connection to various network media for the 100VG Module. The transceivers are installed into the Xcvr Slots of the 100VG Module.
Figure 12 shows the Unshielded Twisted-Pair Recessed Transceiver for the WS-X3007 model of the 100VG Expansion Module.
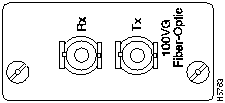
Figure 13 shows the Fiber-Optic Multimode ST Recessed Transceiver for the WS-X3008 model.
Figure 12 : Unshielded Twisted-Pair Recessed Transceiver
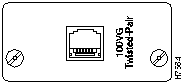
Figure 13 : Recessed 100VG Fiber-Optic Multimode ST Transceiver
Descriptions
Physical
Dimensions
All Transceivers
Width: 4.14 cm (1.63 in)
Depth: 9.22 cm (3.63 in)
Height: 2.36 cm (.93 in)
Weight: 50 g
Environmental
Operating temperature: 0C to 55C (32F to 131F)
Nonoperating temperature: 40C to 70C (-40F to 158F)
Relative humidity: 5% to 95% at 40C (104F) non-condensing
Maximum operating altitude: 4.6 km (15,000 feet)
Electromagnetic
Emissions
FCC part 15 Class A
EN55022 / CISPR-22 Class A
VCCI Level 1
Immunity
Complies with Canadian EMC Class A requirements.
Declaration of Conformity for the 100VG Module complies with ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN 45014. The declaration identifies the product, the manufacturer's name and address, and the applicable specifications that are recognized in the European community.
Installation Steps
 Caution Disconnect the power to the device in which the transceiver is to be removed or installed.
Caution Disconnect the power to the device in which the transceiver is to be removed or installed.
Use the following steps to install a 100VG Recessed Transceivers. Reverse the installation procedure to remove a transceiver.
Step 1 Disconnect AC power from the networking device or device module; then, using a flat-bladed or Torx T-10 screwdriver, unscrew the two retaining screws on the 100VG Xcvr cover plate, or existing transceiver, and remove it from the networking device or device module.
Step 2 Touch a grounded, metal object (such as a powered-on hub) to discharge any static electricity on your body, then carefully remove the transceiver from its protective anti-static packaging. Hold the transceiver by its edges, taking care not touch any of its metal connectors.
Step 3 Slide the transceiver firmly into the 100VG Xcvr slot as far as it will go. The transceiver's faceplate should touch the face of the device.
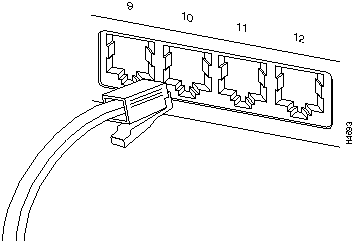
The following illustration shows two twisted-pair transceivers sliding into a 100VG Module.
Figure 14 : 100VG Expansion Module Transceiver Insertion
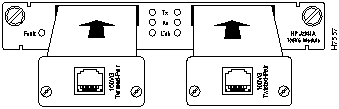
Step 4 Using the flat-bladed or Torx T-10 screwdriver, tighten the spring-loaded retaining screws on the transceiver until they are snug. Be careful that you do not overtighten the screws.
Step 5 Connect network cables to the transceiver or port.
Step 6 Return power to the unit.
Cabling the 100VG Module
The cabling instructions for each transceiver are different and are described in following sections of this guide. For cabling details, find the section that corresponds to your transceiver.
Recessed 100VG Twisted-Pair Transceiver
The Recessed 100VG Twisted-Pair Transceiver connects a networking device to an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) network.
This transceiver is compatible with IEEE 802.12 standard.
Twisted-Pair Cable Installation
Use the following information for cabling a UTP Transceiver.
- A 100VG LAN supports Categories 3, 4, and 5 four-pair, 100-ohm UTP cables. Category 3 UTP cable is standard, voice-grade, telephone cable. If you have a twisted-pair cable that complies with Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 Type 10BaseT specifications and it is four-pair, you can use the same cable for this transceiver.
- For Category 3 and Category 4, the maximum cable length is 100 meters. For Category 5, you can use up to 500 meters of cable.
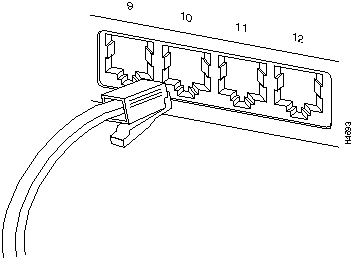
- Push the cable's 8-pin RJ-45 plug into the transceiver's jack until it clicks into place.
Figure 15 : UTP Cable Connection
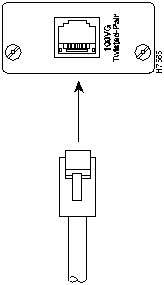
- When power has been supplied to the networking device or device module into which the transceiver is installed, check the Link or port LED that pertains to the transceiver on the device. If the transceiver is receiving a signal properly, the Link or port LED should be ON. If the Link or port LED is OFF, see the Troubleshooting section.
Recessed Fiber-Optic Multimode ST Transceiver
The Recessed Fiber-Optic Multimode ST Transceiver connects a networking device to a fiber-optic network. This transceiver is compatible with the IEEE 802.12 and its wavelength is 1300nm. Optical fibers conforming to the ISO/IEC DIS 11801 standard will work with this transceiver.
Fiber-Optic Cable Installation
Use the following steps to cable a Fiber-Optic Transceiver:
Observe the following warnings and notes when cabling a Dual Port Fast Ethernet expansion module with fiber-optic cable.
 Warning Laser radiation is present when the system is open.
Warning Laser radiation is present when the system is open.
Warning Do not stare into the laser beam.
The ports on the module, and the fiber-optic network to which it is connected, use laser light. Do not stare into a fiber-optic port or into the end of a cable that is connected to a fiber-optic port.
Step 1 Remove the plastic dust covers from the cable connectors and the transceiver jacks.
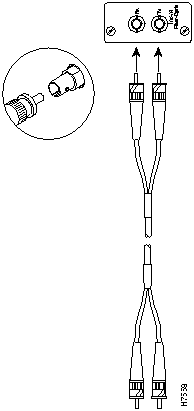
Step 2 Check the polarity of each side of the fiber-optic cable. Use one side of the fiber-optic cable to connect from the transmit (Tx) side of a 100VG Module to the receive (Rx) side of another device. Use the other side of the cable to connect the receive side of the 100VG Module to the transmit side of the other device.
Note Fiber-optic cables have two separate fibers for delivery of data to and from the transceiver. The two fibers are identical, but for polarity purposes there are several different conventions to enable you to tell the fibers apart. There may be a difference in color, or on some fiber-optic cables, only one of the fibers has lettering imprinted on its insulating sheath. Use the markings as polarity indicators.
Step 3 Match the "key" on the connector of one of the fibers to the slot in the transceiver's jack. See Figure 16.
Step 4 Press and twist the connector onto the jack so that the pins on the jack slide into the diagonal slots on the connector and the connector snaps securely into place.
Step 5 Repeat the previous steps for the other fiber. Connect it to the other jack on the transceiver.
Step 6 When power is applied to this transceiver in its module, the Link or port LED should be ON. If the LED is off, see the Troubleshooting section.
Figure 16 : Fiber-Optic Cable Connection
Troubleshooting
If the 100VG module is not working properly, the following problems may exist:
- Check all cabling and connections (including patch panels) to see if the connections to the transceiver are broken or faulty.
- Check for proper cable polarity.
- Check if a connected device is not transmitting the signal.
- Check that the connection is to a 100VG device such as a 10/100VG PCI LAN Adapter (see the networking device's manual for more information).
Accessing the 100VG Console Screens
By default, the 100VG ports are enabled and do not need configuring. The default Mode setting for the 100VG ports is Auto Detect (Auto). If a 100VG port needs a specific configuration other than the default, use the following information to configure that port.
Note A 100VG port cannot be connected to any 100VG port labeled "Uplink."
Configuration and Statistic Console Screens
The following sections describe the Catalyst switch console menus that are used to configure ports and to show the statistics for the 100VG Module.
100VG Port Configuration
The 100VG Port Configuration screen and a 100 VG Port Configuration table are shown below. The 100VG Port Configuration screen is accessed from the Configuration screen.
Figure 17 : 100VG Port Configuration Screen
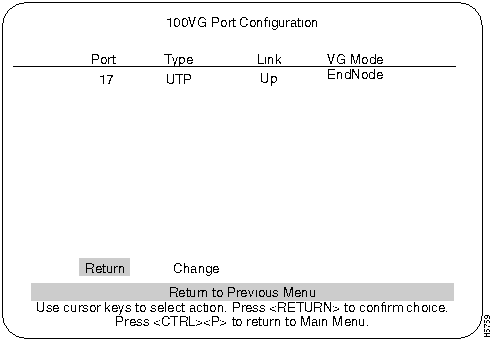
Use the following list in Table 7 for configuration information for a 100VG port.
Table 7 : 100VG Port Configuration
| Port
|
The port on the 100VG Module or modules. Possible values: (17, 19, 21, or 23)
|
| Type
|
The type of transceiver installed in the 100VG Module:
UTP is the abbreviation for unshielded twisted-pair.
STP is the abbreviation for shielded twisted-pair.
F27 is the abbreviation for the Recessed 100VG Fiber-Optic Multimode ST Transceiver.
VG-Empty indicates no transceiver is installed.
VG-New indicates a new transceiver was released after the software was created.
|
| Link
|
Specifies whether this port has trained or not.
|
| VG Mode
|
Either:
EndNode. Select EndNode if you will connect this port to a hub downlink port.
Master. Select Master if you are connecting this port to an end node PC or another Catalyst switch.
For a Catalyst switch to a Catalyst switch connection, one module should be set to Master mode and the other should be set to EndNode.
Auto. Auto tests the cable to see if the port should be a Master or EndNode mode and automatically selects the correct mode. After the software selects Master or End Node, either A-Master or A-EndNode appears in this column. Always connect the cable from the module to a downlink port on a hub. Do not connect the cable to an uplink port on the hub.
|
IEEE 802.12 Statistics
This screen is accessed from the Statistics screen. The following table lists and describes the terms used in the IEEE 802.12 screen.
Table 8 : IEEE 802.12 Statistics
| All Transmitted Frames
|
Total frames transmitted from this port.
|
| Transmitted High Priority Frames
|
Total high priority rather than normal priority frames transmitted from this port.
|
| All Transmitted Octets
|
Total octets transmitted from this port.
|
| All Received Frames
|
Total frames received by this port.
|
| Forwarded Frames
|
Total frames sent from this port to another port.
|
| Received Local Frames
|
Total frames received that had a destination on that local segment. The frames are not routed through the Catalyst switch but are dropped from the receive queue.
|
| Received Broadcast Frames
|
Total number of broadcast frames received by this port.
|
| Received Multicast Frames
|
Total number of multicast frames received by this port.
|
| Received Error Frames
|
Total received frames that contained errors.
|
| Dropped Frames
|
Total frames that were never sent out of this port because the buffer overflowed.
|
| Reset Statistics
|
Change all counters back to zero for this screen.
|
The WS-X3009 and WS-X3010 Dual-Port Fast Ethernet with ISL Module
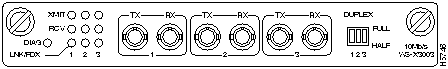
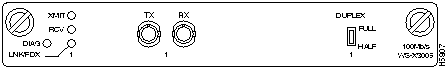
The Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) expansion module is a dual-port interface that is used to establish a connection between Catalyst 3000 series switches and high-speed devices, such as servers or routers. Each of the dual-ports can be configured as Fast Ethernet or ISL mode. 100Mbps Fast Ethernet is described in the Catalyst Stack Installation and Configuration Guide. For an explanation of ISL configurations see the section "ISL Functional Overview and Specifications" later in this document. For configuring ISL trunk ports from a console connection, see the "Console Configuration" chapter in the Catalyst Stack Installation and Configuration Guide. The dual-port Fast Ethernet expansion module with ISL is available in two models:
- WS-X3009 (shown in Figure 18) has dual-port SC fiber-optic connectors.
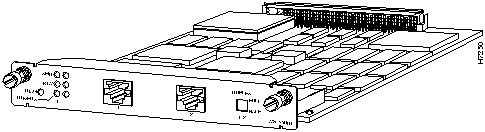
- WS-X3010 (shown in Figure 19) has dual-port UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) connectors.
The following topics are discussed in this section:
Figure 18 : WS-X3009 ISL Expansion Module
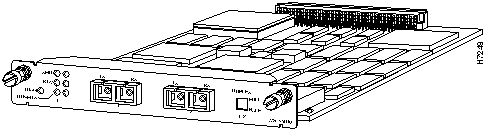
Figure 19 : WS-X3010 ISL Expansion Module
ISL Functional Overview and Specifications
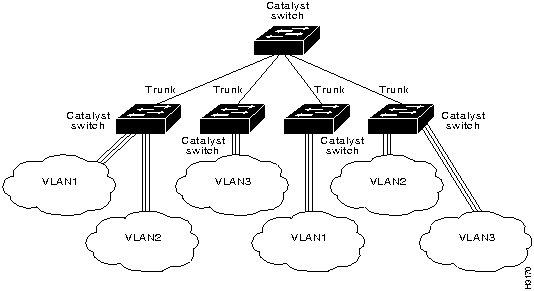
ISL is used to interconnect VLAN-capable Fast Ethernet devices like Catalyst 3000 and Catalyst 5000 switches and Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7500 routers to network servers, or to high-performance backbone devices such as Fast Ethernet hubs, switches, and routers. The ISL protocol tags a standard Ethernet frame with the VLAN information associated with that frame. VLAN packet tagging allows networks to contain VLAN trunks.
VLAN Trunks
A trunk is a physical link between two Catalyst switches, or between Catalyst switches and routers, that carries the traffic of multiple VLANs. Trunks allow you to extend VLANs from one Catalyst switch to another. Users usually connect switches to each other and to routers using high-speed interfaces, such as Fast Ethernet, FDDI, and ATM.
The Catalyst series switch provides a means of multiplexing VLANs between switches and routers by using ISL on Fast Ethernet or LAN emulation on ATM protocols:
You can use any combination of these trunk technologies to form enterprise-wide VLANs. You can choose between low-cost copper and long-distance fiber connections for your trunks. An ISL trunk is like a continuation of the switching backbone. It provides a means for the Catalyst to multiplex VLANs between switches and routers.
Figure 20 and Figure 21 are examples of a Fast Ethernet ISL configuration.
Figure 20 : Fast Ethernet ISL Configuration Example
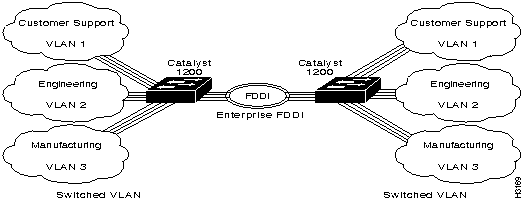
Figure 21 : Fast Ethernet ISL Configuration Example
Features
- ISL supports the construction and management of large scale virtual LANs (VLANS) across internetworks
- Support for 64 VLANs (see the VTP section for how these 64 VLANS are chosen from the
1024 VLANS that can be defined)
- Also supports
- Ethernet MIB
- IEEE 802.1d (spanning tree) (per VLAN)
- RMON (per port)
- Two Fast Ethernet or ISL ports per module
- Maximum of 4 Trunk ports (any combination of ATM and ISL, up to 4) per Catalyst switch
- Line speed forwarding
- Filtering (non-ISL ports)
- 1700 address memory per port
- Programmable demand address aging feature
- Selectable half/full duplex operation for up to 200Mbps collision-free point-to-point connections
- 256K input and output buffers per port
Specifications
The following tables display the specifications for the Dual-port Fast Ethernet with ISL module.
Table 9 : ISL Specifications
| Dimensions (w x d x h)
|
6.2 x 9 x 0.9 in.
|
| Packet Buffers
|
256K in each direction per port
|
| Operating Temperature
|
10 to 50 degrees Centigrade
|
| Non-operating Temperature
|
-25 to 75 degrees Centigrade
|
| Relative Humidity: operating
|
8 to 80%, non-condensing
|
| Non-operating Altitude
|
40,000 feet
|
| Safety
|
UL 1950, UL-C, EN 60950
|
| EMI Certifications
|
FCC Class A (Part 15), VCCI Class 2
EN 55022 A (CE Mark), CISPR-22B
|
Connectors, LEDs, and Switches
The following tables describe the connector, LEDs, and switches on the Dual Port Fast Ethernet module.
Table 10 : Connector
| Name
|
Description
|
| Network Ports (2)
|
RJ-45; UTP Category 5 Ethernet cable
SC type; multimode fiber optic cable
|
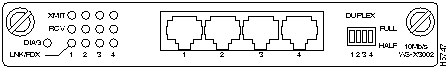
Table 11 : LEDs
| Name
|
Color
|
Description
|
| XMIT (Transmit)
|
Green
|
Transmitting data
|
| RCV (Receive)
|
Green
|
Receiving data
|
| LINK
|
Off
Green
Amber
|
Link not detected
Half-duplex link detected
Full-duplex link detected
|
| DIAG
|
Amber
|
Running self-diagnostic
|
Table 12 : Switches
| Name
|
Position
|
Description
|
| Duplex
|
Up
Down
|
Full
Half
|
Inserting the Dual Port Fast Ethernet With ISL Module
Expansion modules are installed in the expansion slots on the front of the Catalyst switch. All front expansion modules are installed in a similar way. Use the previous section "Installing The WS-X3001 (100Base TX) Expansion Module" as an example for detailed installation instructions and precautions for the Dual Port Fast Ethernet module.
Cabling Dual Port Fast Ethernet With ISL Modules
The Dual Port Fast Ethernet module's network port is either a RJ-45 or SC style connector, depending upon the model type. The RJ-45 connector uses UTP Ethernet Category 5 cable. The SC connector uses 1300 nm multimode fiber optic cable. (See the Catalyst Stack Installation and Configuration Guide for details on cables, connectors, and connections.)
Observe the following warnings and notes when cabling a dual-port Fast Ethernet expansion module with fiber-optic cable.
 Warning Laser radiation is present when the system is open.
Warning Laser radiation is present when the system is open.
Warning Do not stare into the laser beam.
The ports on the module, and the fiber-optic network that it is connected to, use laser light. Do not stare into a fiber-optic port or into the end of a cable that is connected to a fiber-optic port.
When cabling the Dual Port Fast Ethernet modules, the polarity of the fiber cable connectors must be "crossed-over." The TX (transmit) connector of one device goes to the RX (receive) connector of the other device. Check the polarity of each side of the fiber-optic cable. Use one side of the fiber-optic cable to connect from the transmit (Tx) side of a dual-port Fast Ethernet module to the receive (Rx) side of another device. Use the other side of the cable to connect the receive side of the dual-port Fast Ethernet module to the transmit side of the other device.
Note Fiber-optic cables have two separate fibers for delivery of data to and from the transceiver. The two fibers are identical, but for determining polarity there are several different conventions to enable you to tell the fibers apart. There may be a difference in color, or on some fiber-optic cables, only one of the fibers has lettering imprinted on its insulating sheath. Use the markings as polarity indicators.
Checking the Installation/Troubleshooting
When the link is established, the LINK LED is on. If the LED is not on, try the following tests:
- Check the cable connections.
- Try swapping the TX/RX fiber connectors at one end.
- Verify that you are using the correct type of cable
- Test whether the cable is bad by trying a different one.
- Check the power-up diagnostics to see if any problems were reported.
If the above tests do not correct the problem, contact Cisco support.
If, after installation, there is poor system performance or the Dual Port Fast Ethernet module does not work at all, remove the module and check for any damage or bent connector pins. You may need a bright light to see inside the expansion module slot to check for bent pins. If you cannot find an immediate cause for the problem, contact Cisco support.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()


![]()






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()