|
|
Installing LINF Cards in the Cisco HyperSwitch A100
This publication contains the following sections:
The following are common ATM terms and acronyms for your reference:
AAL---ATM Adaptation Layer. An AAL defines the conversion of user information into cells. AAL1 and AAL2 handle isochronous traffic, such as voice and video; AAL3/4 and AAL5 pertain to data communications through the segmentation and reassembly of packets.
ATM---Asynchronous transfer mode. A cell-switching and multiplexing technology combining the benefits of circuit switching (constant transmission delay, guaranteed capacity) with those of packet switching (flexibility, efficiency for intermittent traffic). ATM is defined by ITU-T standards.
Average-rate---The average rate, in Kbps, at which a given virtual circuit (VC) will transmit.
BISDN---Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network. A set of standards under development by the ITU-T for services based on ATM switching and SONET/SDH transmission.
CCITT---Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (This international standards body recently adopted the name International Telecommunication Union/Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T).
CLP---Cell loss priority.
DXI---Data exchange interface.
ILMI---Interim Local Management Interface---Described in the ATM Forum's UNI specification, ILMI allows end users to retrieve a basic set of information, such as status and configuration about virtual connections and addresses, for a particular UNI.
ITU-T---International Telecommunications Union Telecommunication Sector (formerly the Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT))
LINF card---Line interface card. The LINF card contains the interface to the ATM cable. (See the section "HyperSwitch A100 LINF Card Types.")
MIB---Management Information Base.
MIC---Media Interface Connector.
MID---Message identifier---In AAL3/4 encapsulation, the 2-byte MID field allows multiplexing of streams of cells on one virtual channel.
NSAP---Network Service Access Point.
OAM---Operation and Maintenance (cells).
PDU---Protocol data unit---An OSI term for a packet.
Peak-rate---The maximum rate, in Kbps, at which VC can transmit.
PMD---Physical medium dependent. The lower half of BISDN Layer 1.
PVC---Permanent virtual circuit.
QOS---Quality of service.
Rate queues---Rate queues define the speed at which the individual VCs will transmit data to the remote end. Every VC must be associated with one rate queue. After attachment to this rate queue, the VC is assumed to have its peak rate set to that of the rate queue. Each rate queue can be configured independently to a portion of the overall bandwidth available on the ATM link. The combined bandwidths of all rate queues should not exceed the total bandwidth available. For E3, rate queues greater than 34 Mbps are disallowed. For DS3, rate queues greater than 45 Mbps are disallowed.
SAR---Segmentation and reassembly.
SDH---Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. International standard for optical digital transmission at hierarchical rates from 155 Mbps to 2.5 Gbps and greater.
SDU---Service data unit.
SONET---Synchronous Optical Network. An ATM UNI specification and American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard (T1.1051988) for optical digital transmission at hierarchical rates from 51.840 Mbps (STS-N) to 2.5 Gbps and greater.
SONET OC3---Optical Carrier-3 specification.
SSCOP---Service Specific Connection Oriented Protocol---Resides in the service specific convergence sublayer of the ATM adaptation layer. SSCOP is used to transfer variable-length service data units between users of SSCOP. SSCOP provides for the recovery of lost or corrupted SDUs.
SSCS---Service specific convergence sublayer.
SVC---Switched virtual circuit.
UNI---User-to-Network Interface. An ATM interface defined by the ATM Forum for public and private ATM network access.
UTP---Unshielded twisted pair.
VC---Virtual circuit---Point-to-point connections to remote hosts/routers. Each ATM VC has the following characteristics associated with the VC: peak rate, average rate, burst rate, quality of service (QOS), AAL mode (AAL3/4 or AAL5), encapsulation type (LLC/SNAP, NLPID, SMDS, MUX, QSAAL). The VC characteristics are defined when the VC is created.
VCD---Virtual circuit descriptor.
VPI/VCI---Virtual path identifier/virtual channel identifier. ATM virtual connection information. A virtual path is a generic term for a bundle of virtual channels that have the same end point.
The line interface (LINF) card shipping container contents includes the LINF card set (set of LINF card and front panel with window).
All HyperSwitch A100 LINF interfaces are full-duplex. You must use the appropriate ATM Physical Medium Dependent (PMD) interface cable to connect the HyperSwitch A100 with an external ATM network. The HyperSwitch A100 provides an interface to ATM switching fabrics for transmitting and receiving data at rates of up to 155 Mbps bidirectionally; the actual rate is determined by the PMD interface. The HyperSwitch A100 can support LINF cards that connect to the following physical layers:
For wide-area networking, ATM is currently being standardized for use in Broadband Integrated Services Digital Networks (BISDNs) by the International Telecommunications Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) (formerly the Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT)) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). BISDN supports rates from E3 (34 Mbps) to multiple gigabits per second (Gbps). The DS3 interface performs physical layer translation from the LINF card to a DS3 line interface in accordance with ATM Forum UNI Specification Version 3.1, ACCUNET T45 service specifications, and ANSI T1.107.
Figure 1 shows the Category 5 155 Mbps UTP LINF card.
Figure 1 Category 5 UTP LINF Card
Figure 2 shows the OC3 LINF card.
Figure 3 shows the E3 or DS3 LINF card and Table 1 lists the distinguishing features of the two types.
Figure 3 E3 and DS3 LINF Card---Representative of Both
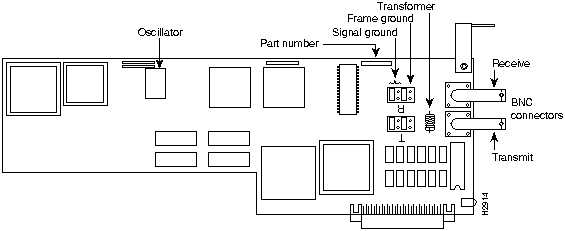
Table 1 Distinguishing Between the E3 and DS3 LINF Cards
| LINF Card | Oscillator | Part Number |
|---|---|---|
| E3 | 34 MHz | P-8X1K |
| DS3 | 44.736 MHz | P-8X1H |
The jumpers shown in Figure 3 are as they should be to tie signal ground to frame ground---best for EMI as within a building. For safety compliance in certain European public carrier networks, it is required that the transmitter be connected only to signal ground and not to frame ground. To connect to signal ground, but not to frame ground, remove the jumpers on the pins indicated as frame ground in Figure 3.
Figure 4 shows the single-mode fiber-optic OC-3 LINF card.
Figure 4 Single-Mode Fiber-Optic OC-3 LINF Card
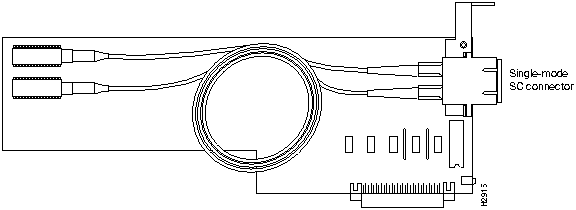
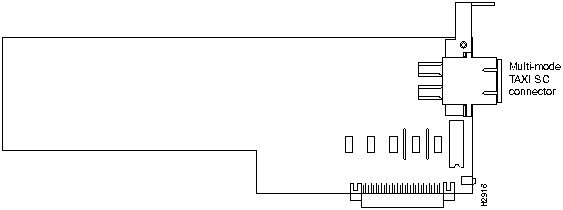
Figure 5 shows the multimode fiber-optic TAXI LINF card.
Figure 5 Multimode Fiber-Optic TAXI LINF Card
This section is derived from the ATM Forum Technical Committee ATM Physical Medium Dependent Interface Specification for 155 Mb/s over Twisted Pair Cable: AF-PHY-0015.000; September 1994. This section outlines methods of terminating the unshielded twisted pair cable for improved EMC performance including reduction of radiated emissions and increased immunity to electromagnetic noise.
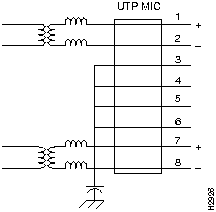
Figure 6 shows the RJ-45 connectors and Table 1 shows the UTP-5 pinout (contact assignment) for the RJ-45 receptacle. Refer to Figure 6 for pin (contact) reference locations.
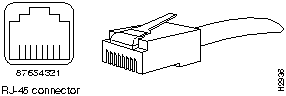
Table 2 Category 5 UTP Receptacle (Jack) Contact Assignment
| Pin Number(1) | ATM User Device | ATM Network Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transmit + | Receive + |
| 2 | Transmit -- | Receive -- |
| 3 | Unterminated | Unterminated |
| 4 | Unterminated | Unterminated |
| 5 | Unterminated | Unterminated |
| 6 | Unterminated | Unterminated |
| 7 | Receive + | Transmit + |
| 8 | Receive -- | Transmit -- |
The following are proposed techniques for terminating the unused pairs of of the UTP connectors for Category 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) 155 Mbps unshielded twisted pair .
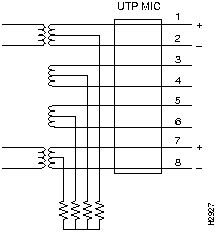
Terminate the common mode impedence of the cable pairs resistively at the UNI. (See Figure 7.)
Figure 7 Example of Common Mode Resistive Termination of Pairs
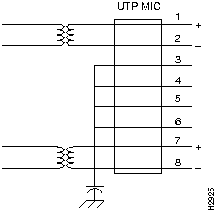
Terminate one or more the the unused cable pairs to the chassis reference of the equipment. (See Figure 8.)
Figure 8 Example of Common Mode Termination to Chassis Reference
Terminate one or more the the unused cable pairs to the chassis reference of the equipment with longitudinal chokes in the active pairs. (See Figure 9.)
Figure 9 Example of Mode Termination to Chassis Reference with Chokes
Follow these guidelines to ensure general safety:
![]()
Follow these guidelines when working on equipment powered by electricity:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic printed circuit cards are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures. Always follow ESD prevention procedures when removing and replacing cards. Ensure that the router chassis is electrically connected to earth ground. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted chassis frame surface to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis.
![]()
Proper installation requires the following equipment:
References throughout this publication refer to the HyperSwitch A100 front and rear panel layouts. Figure 10 shows the front panel layout and Figure 11 shows the rear panel layout.
Figure 10 HyperSwitch A100 Front Panel Layout
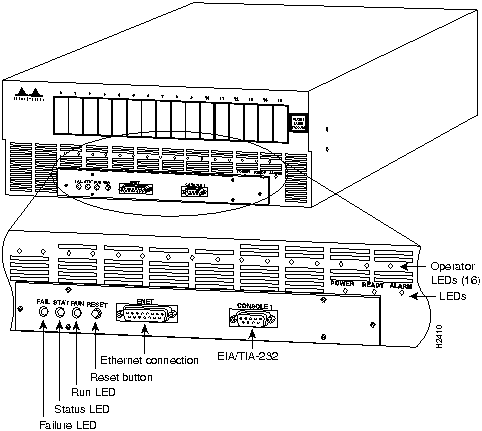
Figure 11 HyperSwitch A100 Rear Panel Layout
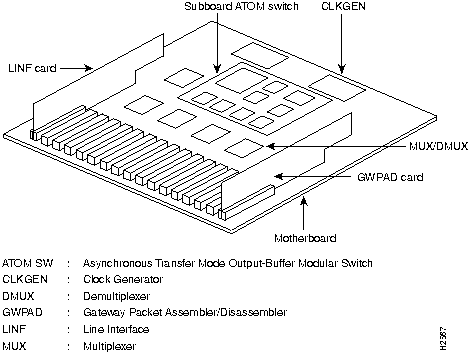
Figure 12 and Figure 13 show HyperSwitch A100 internal views.
Figure 12 HyperSwitch A100 Internal View
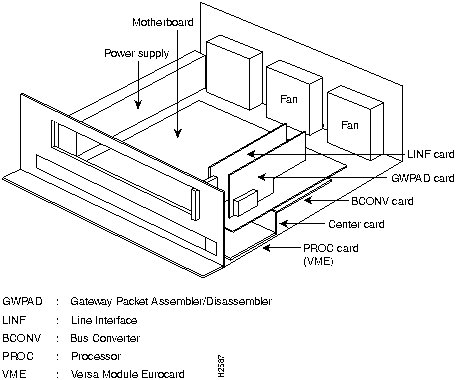
Figure 13 Expanded Internal View (Motherboard)
Do the following to open the HyperSwitch A100 cover:
Figure 14 PROC Card Panel Layout
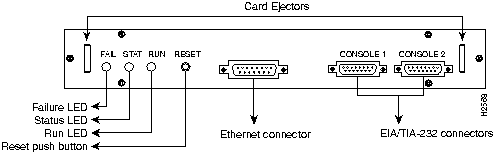
Figure 15 HyperSwitch A100 Bottom View
![]()
Figure 16 Sliding the HyperSwitch A100 Cover
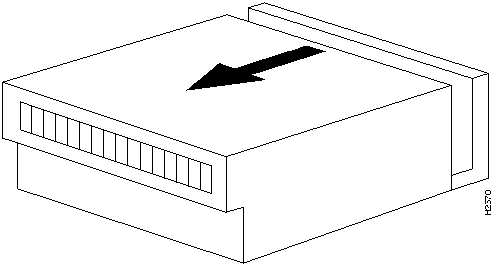
Figure 17 Lifting the HyperSwitch A100 Cover
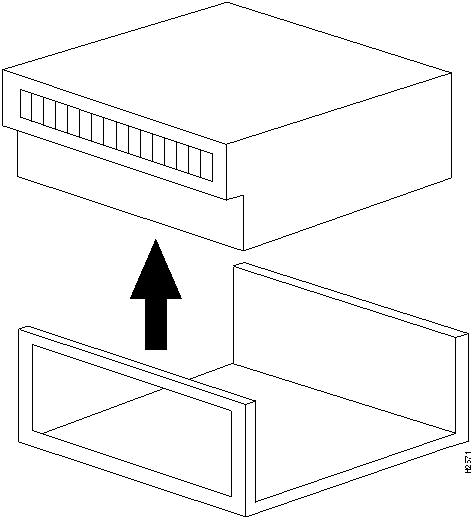
This section describes the initial installation method for the two LINF card types: OC3 (155 Mbps) and Transparent Asynchronous Transmitter/Receiver Interface (TAXI) (100 Mbps). All LINF card types install the same way. Before installing LINF cards, ensure the power switch on the back of the HyperSwitch A100 is OFF.
Table 3 provides recommended mounting positions in the slots where LINF cards are installed, depending on the number of cards installed. If designating the HyperSwitch A100 as a slave switch, always install OC3 LINF card in Slot 0.
Table 3 LINF Card Mounting Positions
| Number of Interface Cards | Suggested Slot Mounting Locations |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0,2 |
| 3 | 0,2,4 |
| 4 | 0,2,4,6 |
| 5 | 0,2,4,6,8 |
| 6 | 0,2,4,6,8,10 |
| 7 | 0,2,4,6,8,10,12 |
| 8 | 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14 |
| 9 | 0-2,4,6,8,10,12,14 |
| 10 | 0-...4,6,8,10,12,14 |
| 11 | 0-......6,8,10,12,14 |
| 12 | 0-........8,10,12,14 |
| 13 | 0-...........10,12,14 |
| 14 | 0-...............12,14 |
| 15 | 0-...................14 |
| 16 | 0-......................15 |
Perform the following procedure to install a LINF card:
Figure 18 Installing a LINF Card
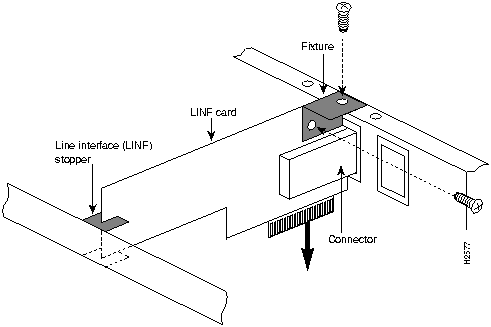
Perform the following procedure to replace the front panel (without window) of the slot where the LINF card is installed with a front panel (with window) packed with the LINF card.
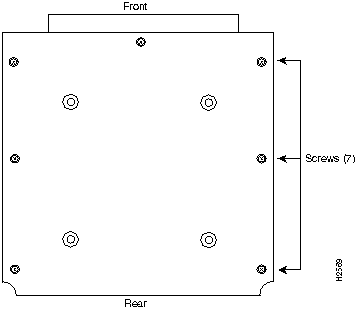
Do the following to close the HyperSwitch A100 cover.
Figure 19 Screw Locations Seen from the Reverse Side of the Cover
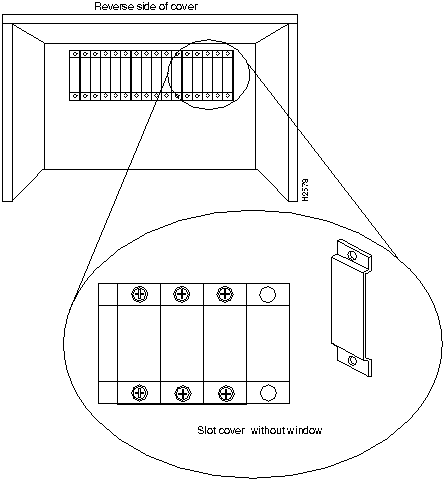
This section provides the procedure for connecting optical cables to the LINF cards installed in the HyperSwitch A100. The upper optical connector on LINF cards is for receive and the lower optical connector is for transmit. Use a single-core or two-core optical cable to connect the LINF cards installed on the HyperSwitch A100. Figure 20 shows the single-core and two-core cables.
Figure 20 Single-Core and Two-Core Cable
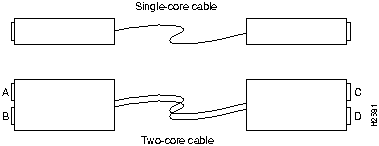
When using a single-core optical cable, ensure the transmission end connects to the reception connector of one device and that the reception end connects to the transmission connector of the other device. Use the appropriate two-core cable, straight (A-C, B-D connections) or cross (A-D, B-C connections). When connecting two or more HyperSwitch A100 units with two-core cable, use cross-cable connection.
To connect optical cables, perform the following procedure:
This section provides the procedure for connecting an EIA/TIA-232 cable to the HyperSwitch A100. To connect the cable, do the following:
Figure 21 EIA/TIA-232 Cable Connectors
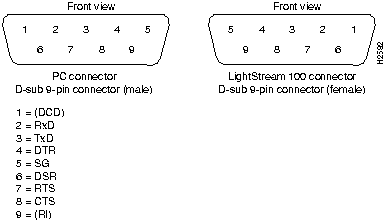
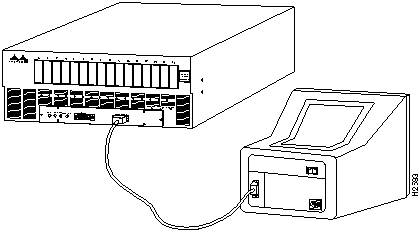
Figure 22 Console Terminal to HyperSwitch A100 Connection
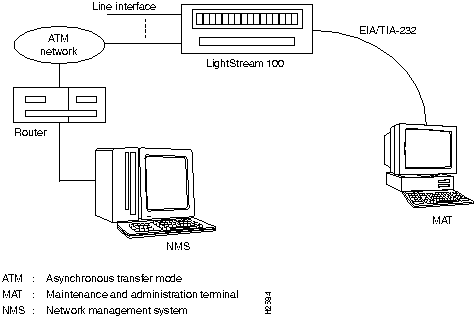
Using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) over User Datagram Protocol (UDP)/Internet Protocol (IP)/ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5), the HyperSwitch A100 communicates with the NMS manager via an ATM line. Figure 23 shows the connection of the HyperSwitch A100 to the console terminal and the NMS. Refer to the NMS configuration documentation to configure the interface between the HyperSwitch A100 and the NMS.
Figure 23 HyperSwitch A100 to Console Terminal and NMS Connection
Complete the tasks described in the preceding sections before connecting the power cable to the HyperSwitch A100 and turning the power ON.
![]()
To connect the power cable, do the following:
To connect the console terminal power supply, plug the console terminal power cord into a power outlet. Refer to the documentation provided with the console terminal for additional information.
A self-diagnostic test runs when the HyperSwitch A100 is powered ON or reset. The results display on the console terminal. The following example shows self-diagnostic test output:
Cisco Systems, Inc. ATM HyperSwitch
Software Version 1.2(0)
Boot ROM Version K07 10 Sep 94
ATMSIG Version 1.2(0)
Hardware Configuration:
CPU Board : OK;
Bus Convertor : OK;
Switch Core : OK;
Gateway PAD : OK;
Slot 0: OC-3C(MMF) OK;
Slot 1: OC-3C(MMF) OK;Slot 2: 100M-TAXI OK;
Slot 3: 100M-TAXI OK;
Slot 4: Not Installed;
Slot 5: Not Installed;
Slot 6: Not Installed;
Slot 7: Not Installed;
Slot 8: Not Installed;
Slot 9: Not Installed;
Slot10: Not Installed;
Slot11: Not Installed;
Slot12: Not Installed;
Slot13: Not Installed;
Slot14: Not Installed;
Slot15: Not Installed;
System Initialization finished.
A100>
To power OFF the HyperSwitch A100, set the power switch to the OFF position. The Power LED goes OFF.
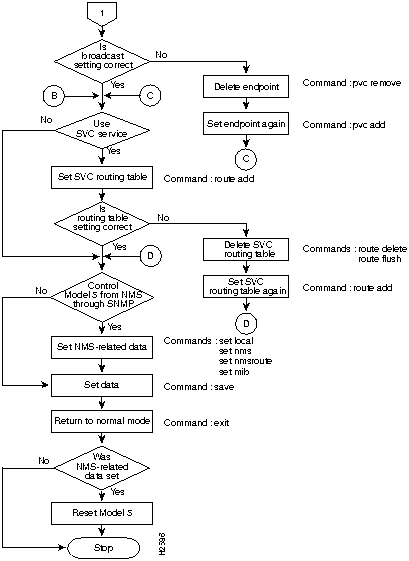
Figure 24 and Figure 25 show two parts of a flowchart of the configuration data setting procedure. The following sections provide command input information that corresponds to the commands indicated in the flowchart.
Input commands entered at the console terminal provide instructions to the HyperSwitch A100. Commands for the HyperSwitch A100 comprise user commands, which show configuration data, and privileged commands, which show and configure system data.
Figure 24 Initial Installation Data Setting Procedure (Part 1)
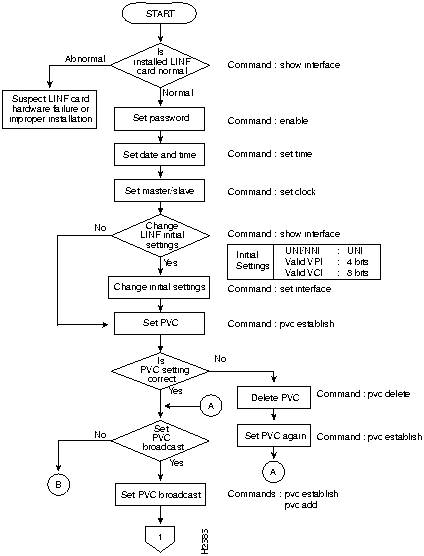
Figure 25 Initial Installation Data Setting Procedure (Part 2)
The following example shows basic command input format:
prompt command subcommand P1 P2 ...
The system shows two prompt types: > and #. The > prompt indicates operation in user mode, and the # prompt indicates operation in privileged mode.
If the host name (for example, A100) is registered for the system, it shows before the prompt.
Following are mode examples.
User mode example:
A100>
Privileged mode example:
A100#
Enter a space between the command, subcommand, and each parameter. Parameters are indicated as P1, P2, and so on.
The system does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase characters except in setting or reading the password.
The following list gives command information to display LINF data for cards installed in the HyperSwitch A100. Data does not display for a line without a LINF card installed or for a line whose information cannot be read because of a failure.
Command mode: user
Format:
A100> show interface
Output:
Line Number UNI/NNI Physical Layer Forum/ITU Valid VPI Valid VCI
0 0 2 0 4 8
1 0 2 0 4 8
·
·
·
15 0 2 0 4 8
Confirm that the line numbers of the installed LINF cards display. When a specific line number does not display, the corresponding LINF card is not installed, the LINF card is improperly installed, or a LINF hardware error exists. Turn OFF the HyperSwitch A100 and check the LINF card.
The numbers displayed in fields to the right of the line number are line configuration parameters. The following list gives initial settings of these parameters:
Following are possible error messages.
The following list gives command information to enter the privileged command mode and to set a password that allows entry to the privileged command mode.
Command mode: user
Format:
Enter the enable command.
When the command name is wrong, the following messages display:
The following list gives command information to set the clock synchronization mode. When a HyperSwitch A100 unit connects to another HyperSwitch A100 unit or to a different type of device, this function designates this HyperSwitch A100 as master or slave.
Command mode: privileged
Format:
Explanation:
Before setting the slave mode, ensure an OC3 LINF card is installed in Slot 0 of the HyperSwitch A100.
Output:
The console terminal displays the set mode: Master or Slave.
The following list gives command information to register a line. This function can change the following initial settings of a line:
To confirm the initial settings, enter the show interface command.
Command mode: privileged
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
The initial setting of line number specified in P1 changed.
The following list gives command information to set a point-to-point permanent virtual circuit (PVC). This command becomes effective immediately after it is set.
Command mode: privileged
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
The entered values for line number, VPI, VCI, UPVP, and COOP display.
If a PVC is set incorrectly, first delete the PVC using the pvc delete command; then, reenter the pvc establish command. Use the pvc delete command as follows:
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
Line number, VPI, VCI, UPVP, and COOP data for the deleted line display. UPVP and COOP values were registered with the pvc establish command.
To set a multicast (point-to-multipoint) connection, use the pvc establish command, which establishes a connection, and the pvc add command, which adds a PVC endpoint for multicast.
The system accepts only multicast connection when the connection is added or when an endpoint is deleted. When deleting the multicast connection, delete the endpoints one by one. (The deletion order need not be the same as the setup order.)
Use the pvc establish command to set the connection type to multicast; then, use the pvc add command to add the endpoint. Enter the same source parameters (line number, VPI, and VCI) as those specified in the pvc establish command.
Command mode: privileged
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
Line number, VPI, VCI, UPVP, and COOP data display for added endpoints. UPVP and COOP were registered with the pvc establish command. Output continues to display up to the last endpoint.
Use the pvc remove command as follows. This command deletes one endpoint at a time.
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
Line number, VPI, VCI, UPVP, and COOP data display for the removed endpoint. UPVP and COOP values were registered with the pvc establish command. Output continues to display up to the last endpoint.
The following are commands to set switched virtual circuits (SVC).
Command mode: privileged
Format:
Explanation:
Output:
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal
Number of parameter is illegal
Enter Privileged Command Mode
A100> enable
Command name is illegal
Sub command name is illegal
Number of parameter is illegal
Set Clock Synchronization Mode
A100# set clock p1
Operational Mode: xxxxxx
Set Clock Synchronization Mode Error Messages
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal.
Number of parameter is illegal.
Specified parameter is out of range.
Register Line
A100# set interface p1 p2 p3 p4 p5
Line interface P1 has been registered.
Register Line Error Messages
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal.
Number of parameter is illegal.
Specified line is invalid.
Specified UNI/NNI is out of range.
Specified Forum/ITU parameter is out of range.
Specified VALID VPI is out of range.
Specified VALID VCI is out of range.
Specified VALID VPI+VALID VCI is out of range.
Connection is already established on this line.
Set Permanent Virtual Circuit
A100# pvc establish p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 p8 p9 p10 p11 p12 p13
Uni/Bi/Multicast direction Guaranteed/Best Effort Connection has been established.
Low: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxx, x
High: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxx, x
Set Permanent Virtual Circuit Error Messages
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal.
Number of parameter is illegal.
Specified line is invalid.
Specified VPI is out of range.
Specified VCI is out of range.
Specified UPVP parameter is out of range.
Specified COOP parameter is out of range.
Specified VPI+VCI is out of range.
Deleting a PVC
A100# pvc delete p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 p8
Uni/Bi/Multicast direction Best Effort/Guaranteed Connection has been deleted.
Low: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxxx, x
High: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxxx, x
Error Message
No such connection
Setting Multicast Command
A100# pvc add p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6
Connection endpoint has been added.
Modified Connection:
Low: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxxx, x
High: xx, xxxx, xxxxx
·
·
·
Setting Multicast Command Error Messages
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal.
Number of parameter is illegal.
Specified line is invalid.
Specified VPI is out of range.
Specified VCI is out of range.
Specified VPI+VCI is out of range.
Specified connection is uni/bi-direction
ICI Hunt Error.
BCI Hunt Error
A100# pvc remove p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6
Connection endpoint has been removed.
Modified Connection:
Low:: xx, xxxx, xxxxx, xxxx, x
High: : xx, xxxx, xxxxx
·
·
·
PVC Remove Error Message
No such connection
Setting Switched Virtual Circuits
A100# route add P1 P2 P3 P4
SVC route has been added.
Setting Switched Virtual Circuits Error Messages
Command name is illegal.
Sub command name is illegal.