|
|
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 (shown in Figure 1-1) are Ethernet switches that provide high-speed configuration flexibility for workgroup applications. With 25 switched Ethernet ports for individual workstations and 10BaseT hubs and either 2 high-speed expansion slots or 2 fixed high-speed ports for servers and backbones, these switches provide Ethernet switching to 100BaseT, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), and future Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks.
Figure 1-1 : Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900
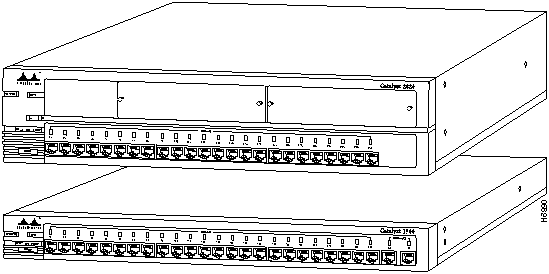
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 offer the following features:
See the "Concepts" chapter for more information about these features. To implement them via out-of-band management or Telnet, turn to the "Out-of-Band Management" chapter for more information. If you are using SNMP, the switch's inband capabilities are described in the "Standard MIBs and MIB Extensions" section in the "In-Band Management" chapter.
Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 Ports
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 have the following ports:
The 10BaseT ports shown in Figure 1-2 use RJ-45 connectors to connect to single workstations, 10BaseT hubs, or any 10BaseT compatible device. The attached devices use standard 10BaseT adapters and wiring. Port 25, located on the back panel, supports an alternative AUI connection for attachment to a thick coaxial, thin coaxial, or a fiber-optic media transceiver.
Figure 1-2 : Catalyst 1900 Ports
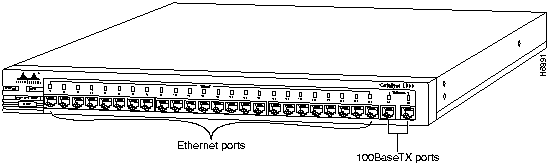
The Catalyst 1900 has two 100BaseTX ports for server or backbone connectivity. One or both of these can be set to CollisionFree full-duplex mode for full-duplex operation. Each 100BaseTX port is internally bridged to the other Catalyst 1900 ports.
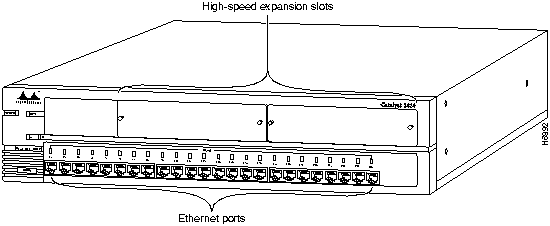
The Catalyst 2820 has two high-speed expansion slots that are compatible with Catalyst 2820 field-pluggable modules and provide high-bandwidth connections to backbones, servers, and other high-performance devices. Each expansion slot is internally switched to all other Catalyst 2820 ports. Figure 1-3 shows a Catalyst 2820.
Figure 1-3 : Catalyst 2820 Expansion Slots
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 have an extensive range of LEDs that enable you to easily monitor network activity and performance. Figure 1-4 and Figure 1-5 show the location of the LEDs.
Figure 1-4 : Catalyst 2820 LEDs
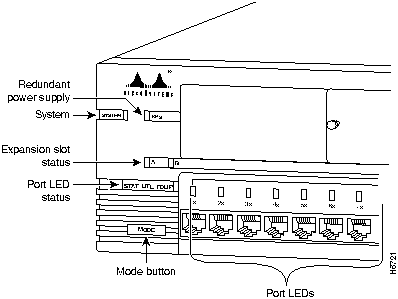
Figure 1-5 : Catalyst 1900 LEDs
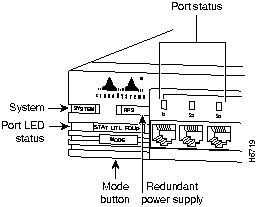
This LED reflects the overall well-being of the switch, as shown in Table 1-1.
| Visual Indication | System Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Normal operation. |
| Amber | Switch failed POST and is not forwarding packets. |
| Off | System not powered on. |
The redundant power supply (RPS) LED shows the RPS status, as shown in Table 1-2. When the RPS is in use, the local power supply should be turned off by unplugging the AC power cord.
| Visual Indication | RPS Status | Local Power Supply Status |
|---|---|---|
| Green | RPS operational | Not operational or unplugged |
| Amber | RPS installed but not operational | -- |
| Off | RPS not installed | -- |
| Alternating green/off | RPS operational | Operational, not unplugged |
These LEDs show the status of an inserted module. Check the LEDs on the module itself for the module port status, as shown in Table 1-3. The A and B LEDs correspond to the left and right expansion slots, respectively.
Table 1-3 : Expansion Slot LEDs
| Visual Indication | Expansion Slot Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Module is operational. |
| Alternating green-off | Module is running POST. |
| Amber | Module failed POST and is not operational. |
| Off | No module is in the slot. |
Port LEDs indicate one of the following, depending on the Mode button setting:
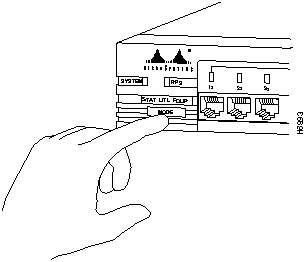
Changing the Mode of the Port LED
To change the mode being displayed by the port LEDs, press the Mode button, as shown in Figure 1-6, to highlight in sequence each of the possibilities: STAT (port status), UTL (bandwidth utilization), and FDUP (full-duplex status). When the correct mode is lit, release the button to make the change. As long as you hold the button down, the mode does not change.
The selected mode remains lit for 30 seconds before returning to the default mode of port status.
Figure 1-6 : Changing the LED Mode
This LED mode provides the status of switched ports, as shown in Table 1-4.
| Visual Indication | Port Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Link present. |
| Flashing green-off | Activity: port is transmitting or receiving data. |
| Alternating green-amber | Link fault. Error frames can affect connectivity and errors such as excessive collisions, CRC errors, and alignment and jabber errors are monitored for a link fault indication. |
| Amber | Port is not forwarding. For example, this could be because the port was disabled by management, suspended due to an address violation, or suspended by STP due to the presence of network loops. |
| Off | No link. |
A port configured for full-duplex operation must be connected to another full-duplex port. You can display the full-duplex status of a port, as shown in Table 1-5, by pressing the Mode button and releasing it when FDUP is highlighted.
Table 1-5 : Full-Duplex LED
| Visual Indication | Full-Duplex Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Full-duplex is operational. |
| Off | Half-duplex is operational. |
These LEDs show the current utilization of the switch (see Table 1-6). The peak utilization is also recorded in the current bandwidth capture interval. You can invoke the utilization mode LEDs by pressing the Mode button and releasing it when UTL is highlighted. Change the bandwidth-capture interval with the Bandwidth Usage Report described in the chapter "Out-of-Band Management."
The switch uses the port LEDs to establish a scale indicating the two utilizations in megabits per second (Mbps). This scale is shown in Table 1-7.
Table 1-6 : Utilization LEDs
| Visual Indication | Utilization |
|---|---|
| Alternating green-amber | Current utilization. |
| Farthest right amber LED | Peak utilization recorded in the current bandwidth capture interval. |
Table 1-7 : Utilization LEDs Scale
| Port LEDs | Mbps |
|---|---|
| 1--8 | 0.1--5 |
| 9--16 | 6--100 |
| 12--24 | 120--280 |
The rear panel, shown in Figure 1-7 and Figure 1-8, contains the following components:
Figure 1-7 : Catalyst 1900 Rear Panel
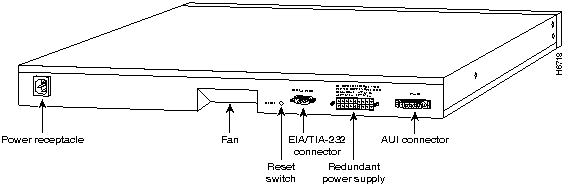
Figure 1-8 : Catalyst 2820 Rear Panel
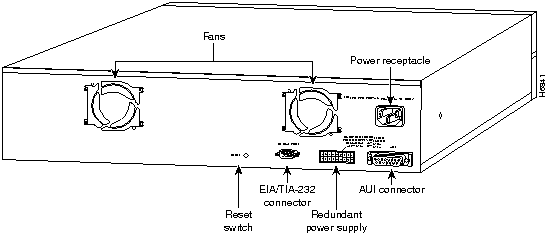
Use the reset switch only if the Catalyst 2820 or 1900 does not respond to network management or if packet forwarding has stopped. Resetting the switch has the same effect as turning it off and on. The reset switch is located on the rear panel, as shown in Figure 1-7 and Figure 1-8. Use a paper clip or pen to reach through the hole and reset the switch.
Configuring and Managing a Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900
You can configure and manage a Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 using any SNMPcompatible management station, or you can connect an ASCII terminal to the switch via the EIA/TIA-232 (RS-232) port and use the management console. The management console is also accessible via Telnet. SMT-compatible workstations can support installed Catalyst 2820 FDDI modules.
The management console provides a menu-driven interface for configuring and monitoring your network. The application is password-protected and locks out a user who fails to enter the password within a definable number of attempts. In such a case, the network administrator can be alerted via in-band management.
Most of the statistics and information generated by the switch are available through the management console. You can continue to use it even when the network is down.
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 are fully manageable by any SNMP-compatible management station.
The product supports all pertinent SNMP MIB II variables, the 802.1d bridge MIB, and a comprehensive set of MIB extensions designed for maximum support of the switch's hub and switching capabilities. The Catalyst 2820 also supports the FDDI MIB and the MIB supporting Catalyst 2820 modules.
Supported Network Management Platforms
The Catalyst 2820 and 1900 SNMP MIBs are supplied in ASCII format for compiling into any SNMP network management system using a general MIB browser. You can display switch information from the following network management platforms.
The Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 must be configured for SNMP management. To do this, you need to assign an IP address to the switch using the menu described in "IP Configuration" in the "Out-of-Band Management" chapter. Although the switch will immediately register the IP address the first time you assign it, if you change the IP address it does not take effect until after the switch is reset. You can also use the Bootstrap protocol (BOOTP) described in the "Configuring the Switch for SNMP Management with BOOTP" section in the "In-Band Management" chapter.
You can use the CiscoView graphical user interface to configure your Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches and to generate the same statistics available through the management console.
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.