|
|
There are several ways to troubleshoot problems associated with a Catalyst 2820 or 1900 installation and performance. The LEDs on the front panel are the quickest way to evaluate the operation of the switch; statistics provided by the management console or SNMP management station can provide more details about the cause of connectivity and performance problems; the power-on self-test (POST) ensures that the switch is functioning properly at installation and when subsequently powered on.
Potential problems can be grouped into the following categories:
When the Catalyst 2820 or 1900 is first turned on and the switch begins its POST, the system and port LEDs are green. As each of the thirteen tests is run, the port LEDs, starting with number sixteen, turn off. (Because there are only thirteen tests, LEDs fifteen, fourteen, and thirteen are unaffected.)
After the POST completes successfully, the port LEDs turn green, indicating that the switch is operational. If a test fails, the associated port LED stays off, and the system LED turns amber.
All POST failures except the real-time clock test (number 5) are fatal. If the real-time clock fails POST, the switch begins forwarding packets, but the system LED turns amber, and a POST-failure message appears on the console screen. Certain switch features, such as the bandwidth utilization meter, are lost if the real-time-clock test fails.
Use Table 7-1 to identify your problem and resolve it. Note that those problems that refer to high-speed expansion slots and their inserted modules apply only to the Catalyst 2820.
Table 7-1 : Common Problems and Their Solutions
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Performance or Excessive Errors | Incorrect Full-Duplex Settings for 100BaseT Connections The full-duplex setting for modules is indicated by the full duplex LED on the module front panel. Fixed 100BaseTX full-duplex port status is shown with the Mode button and the FDUP LED. Check the port's statistics: |
|
|
Configure port for half-duplex. | |
|
Configure the port for full-duplex. | |
| Cabling Distance Exceeded Port statistics show excessive FCS, late-collision, or alignment errors. For 100BaseTX connections: |
||
|
Reduce the cable length to within the recommended distances. | |
|
See your 100BaseT repeater documentation for cabling guidelines. | |
| For 10BaseT connections: The distance between the port and the attached device exceeds 100 meters. | Reduce the cable length to within the recommended distances. | |
| Poor Performance or Excessive Errors | Bad Adapter in Attached Device Excessive errors found in port statistics. |
Run adapter card diagnostic utility. |
| No Connectivity | Incorrect or Bad Cable The following are indicated by no link at both ends:
|
See the "Connector Pinouts" section in the Appendix A for the correct pinouts and the proper application of cross-over vs. straight-through cables. |
|
Replace with a tested good cable. | |
| NetWare Network Numbers Misconstrued If NetWare is used, the following message can appear on the server screen: |
All the nodes connected to ports in a single VLAN should all be assigned the same network number. |
|
| No Connectivity | VLANs Misconfigured | |
|
Ensure the two nodes are connected to ports on the same VLAN. See the "VLAN Configuration" section in the "Out-of-Band Management" chapter to list ports of a VLAN. If you're using SNMP, see the "Catalyst 2820 and 1900 Enterprise-Specific MIB" section in the "In-Band Management" chapter for the MIB objects to use. | |
|
If there is a router, check the router configuration. Eliminate one of the two connections between the two VLANs. |
|
| Expansion Slot A or B LEDs Do Not Come On | Catalyst 2820 Module Not Properly Installed | See the Troubleshooting section of the Catalyst 2820 Modules User Guide. |
| System LED is amber and all port LEDs are off. | Switch is not responding due to corrupted firmware. | Attach a monitor to the serial port to display the diagnostic console. See the "Diagnostic Console Menu" section of this chapter for firmware upgrade instructions. |
| Unable to access the management console. |
|
Use the diagnostic console described in the "Diagnostic Console Menu" section of this chapter to reset the switch. Reset the modem parameters to their factory defaults with the diagnostic console. |
The diagnostic console is for those instances when the switch firmware has been corrupted or the present switch configuration prevents the firmware from executing properly. The Diagnostic Console Logon screen shown in Figure 7-1 is displayed when the firmware has been corrupted.
Figure 7-1 : Diagnostic Console Logon
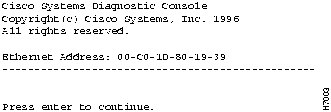
If you have defined a password for the switch, you are prompted for the password. If you have forgotten the password, you can obtain a factory-installed password by calling Cisco Systems and providing the Ethernet address displayed on the screen.
If no password has been defined, press Return to display the diagnostic console.
Displaying the Diagnostic Console
There can be times when you need the diagnostic console even though the firmware is valid. This could happen, for example, if the switch's configuration prevents the firmware from executing properly and you cannot display the normal console.
Use the following procedure to override the normal firmware startup and immediately display the diagnostic console.
Use this menu, shown in Figure 7-2, to troubleshoot firmware problems and then bring up the firmware as usual.
Figure 7-2 : Diagnostic Console
[C] Continue with system startup. Select this option after you have resolved the firmware problems with options [U] or [S]. It brings up the firmware as usual.
[U] Upgrade Operation Firmware. Select this option to initiate a firmware upgrade. This option works only with XMODEM and only uses the default RS-232 parameters:
Use the following procedure to upgrade the firmware with the XMODEM.
[S] System Debug Interface. Select this option to display the System Debug Interface menu shown in Figure 7-3. You can use this menu to reset the management console's RS-232 interface or the entire switch to its factory defaults.
Use this menu, shown in Figure 7-3, to reset the management console's RS-232 interface or the entire switch to their factory defaults. You can also use the management console to perform these functions.
Figure 7-3 : System Debug Interface [G] Generic I/O. For Cisco personnel only.
[M] Memory CPU (I/O). For Cisco personnel only.
[R] Return system to factory defaults. Use this option to return the switch to its factory settings. All static and dynamic addresses are removed, as is the IP address and all other configurations. Enter Y or N and press Return. The changes take effect the next time the switch is reset.
[R] Reset main console RS232 interface to 9600, 8, 1, N. Select this option if you have lost the management console connection because of an improper modem configuration. The next time the switch is reset, the default RS-232 configuration is used.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.

Operation firmware version: Status:
Validity of the current firmware. If the current image is not valid, option C on the diagnostic console is not displayed.
Boot firmware version:
Write-protected part of the firmware that supports the diagnostic console.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()