|
|
Catalyst 1700 Connector Pinouts
This appendix describes the connectors for Catalyst 1700 including:
Each of these connectors is described in the following sections.
There are 25 10Base-T connectors on the front panel of the Catalyst 1700. The first 24 are for the Personal Ethernet ports and the 25th is for the General Ethernet port.
Figure B-1 : 10Base-T Connector
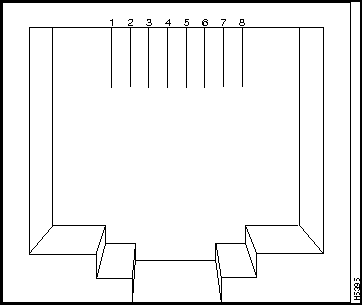
The arrangement of the pins is shown in Figure B-1 and the pinouts are shown in Table B-1.
Table B-1 : 10Base-T Connector Pinouts
| Pin | 1x through 24x, and Pin 25A when Uplink Switch is set to x | Pin | 25A when Uplink Switch is set to Uplink |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD+ | 1 | TD+ |
| 2 | RD- | 2 | TD- |
| 3 | TD+ | 3 | RD+ |
| 4 | NC | 4 | NC |
| 5 | NC | 5 | NC |
| 6 | TD- | 6 | RD- |
| 7 | NC | 7 | NC |
| 8 | NC | 8 | NC |
The Personal Ethernet ports have their transmit (TD) and Receive (RD) signals internally crossed (designated by the x) for attachment to an adapter using a straight-through cable. The General Ethernet port, 25A, has its TD and RD signals crossed when the Uplink switch is set to the x position for attachment to an adapter or bridge using a straight-through cable. Connection to a hub when set in the x position requires a crossover cable.
To connect to a hub using a straight-through cable using port 25A, the Uplink switch must be set in the Uplink position. This will uncross the TD and RD signals.
The AUI connector is a 15-pin female receptacle as shown in Figure B-2.
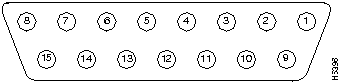
The pinouts are shown in Table B-2.
Table B-2 : AUI Connector Pinouts
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | CI+ | Positive AUI differential collision data input |
| 3 | Tx+ | Positive AUI differential transmit data input |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
| 5 | Rx+ | Positive AUI differential receive data output |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | ||
| 8 | GND | Ground |
| 9 | CI- | Negative AUI differential collision data input |
| 10 | TX- | Negative AUI differential transmit data input |
| 11 | GND | Ground |
| 12 | RX- | Negative AUI differential receive data output |
| 13 | +12V | 12 Volt supply for external MAU |
| 14 | GND | Ground |
| 15 |
A standard Ethernet 10Base2 BNC connector is used. The pin-outs are shown in Figure B-3.
The serial connector is a male nine-pin D subminiature connector as shown in Figure B-4.
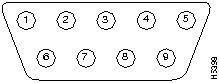
The pinouts are shown in Table B-3.
Table B-3 : Serial Connector Pinouts
| 1 | DCD |
| 2 | RD |
| 3 | TD |
| 4 | DTR |
| 5 | GND |
| 6 | DSR |
| 7 | RTS |
| 8 | CTS |
| 9 | RI |
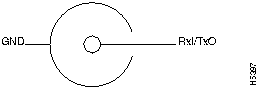
The shell is connected to the chassis ground. Use a standard modem cable to connect to a modem. Use a null modem cable to connect to a terminal.
Connection to another hub with internally crossed TD and RD pairs requires a crossover cable. The Modem Cable Schematic and the Null-Modem Cable Schematic are shown in Figure B-5 and Figure B-6.
Figure B-5 : Modem Cable Schematic
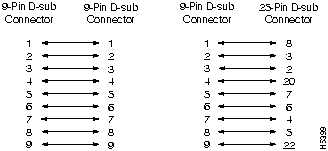
Figure B-6 : Null-Modem Cable Schematic
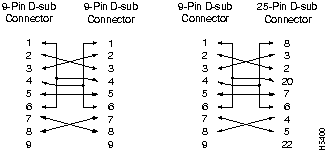
The two Fast Ethernet connectors use standard RJ-45 connectors. The arrangement of the pins is shown in Figure B-7.
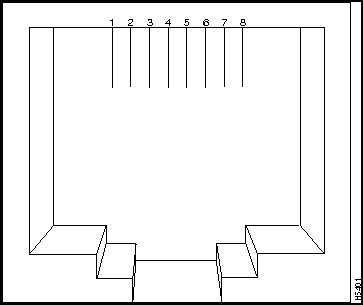
The pinout is shown in Table B-4.
Table B-4 : F1x and F2x Connector Pinouts
| Pin | |
|---|---|
| 1 | RD+ |
| 2 | RD- |
| 3 | TD+ |
| 4 | NC |
| 5 | NC |
| 6 | TD- |
| 7 | NC |
| 8 | NC |
The shell for both connectors is connected to the chassis ground. The Fast Ethernet Ports have their transmit (TD) and receive (RD) pairs internally crossed (designated by the x) for attachment to an adapter using a straight-through cable.
The Straight-through and Crossover Cable schematics are shown in Figure B-8 and Figure B-9.
Figure B-8 : Straight-through Cable Schematic
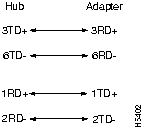
Figure B-9 : Crossover Cable Schematic
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.