|
|
Read this chapter to learn how to use diagnostics and other methods to isolate faults in LightStream 2020 enterprise ATM switches.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Static electricity can damage or degrade electronic components. To avoid damage, observe the following precautions when you touch hardware.
Before you expose circuitry, make sure that your body, the rack, and the circuit boards are at the same ground potential to prevent damaging ESD. To connect yourself to ground, use a wrist strap connected to one of the system's grounding jacks, or to the bare metal surface of the system frame.
All spare cards are shipped in reusable antistatic shielding bags. When cards are not installed in the machine, keep them in antistatic bags. Do not remove cards from their bags unless you are grounded. Do not place these bags on exposed electrical contacts, where they can cause short circuits.
This chapter will help you isolate problems in a LightStream 2020 switch to a single field-replaceable unit (FRU), such as a line card, blower, or power supply. Once you've identified the faulty FRU, refer to the chapter "Replacing FRUs" for instructions on removing and replacing it.
This section briefly describes three methods of identifying problems in a LightStream 2020 switch:
POST diagnostics are described below, and instructions for general troubleshooting and running hardware diagnostics are provided later in this chapter.
Power-on self test (POST) diagnostics are the first line of defense for identifying hardware problems. POST runs automatically on each card whenever the system or the slot is powered up or when the card is reset; it takes about 90 seconds. There are POSTs for the following components:
The POST for each line card also checks the accompanying access card.
In the resulting display, look at the POST: line and the Application: line. If the Application: line says DISABLED, you may be able to correct the problem by enabling (activating) the card. See the LightStream 2020 Network Operations Guide for instructions.
If a card fails POST, review the portion of the section "Troubleshooting" for the card in question. In most cases, you should also run the hardware diagnostics to confirm that a problem exists. (Hardware diagnostics are described briefly below; the instructions for running them appear in the section "Using the Diagnostic Software".)
LightStream 2020 hardware diagnostics are used to discover the location of hardware faults. You can run diagnostics on a line card or a backup NP while the rest of the system continues to operate. Generally, only the card under test comes out of service during the diagnostics. (The exception is when you're testing the single NP in a non-redundant system; this requires taking the system off line.)
Note that certain tests should not be run while the system is operating, and other restrictions may apply as well. See the "Test Notes" section for details.
You can run diagnostics either remotely over a telnet or modem connection, or locally from a console connected to the console port. (The exceptional case is running diagnostics on the sole NP in a non-redundant system. This task requires a local console.)
The diagnostics reside on each NP's hard disk. Several parts of the system can be tested:
Procedures for running the diagnostics appear in the section "Using the Diagnostic Software."
General troubleshooting tasks can be performed before, after, instead of, or in addition to running the diagnostic software. These tasks provide additional ways of identifying faults in NPs, switch cards, and line cards. They are the only way to identify faults in subsystems that are not covered by POST or diagnostics, such as blowers and power supplies. The section that follows describes general troubleshooting tasks.
Use the information in this section to help isolate faults in a LightStream 2020 switch. This section is to be used in conjunction with the diagnostic software. Some of these procedures require you to be in the same room with the faulty system; others can be performed remotely.
When the Problem Won't Go Away
If your LightStream 2020 switch doesn't operate properly after you've tried the suggestions below, call your customer support representative.
Before resorting to the diagnostics or to complex troubleshooting, check simple things:
If you're bringing up a new LightStream 2020 node, a new card, or a new kind of port for the first time, a likely source of problems is configuration. The problem may exist at either the LightStream side or the remote side of the connection; be sure to check both configurations. Refer to the LightStream 2020 Configuration Guide for information on software configuration.
The symptoms listed below indicate problems that may require replacement of a switch card. Switch card replacement instructions appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs".
If the NP fails to power up, check its access card at the back of the chassis. An NP requires an NP access card (NPAC); it can't operate with any other kind of access card.
Replace the NP if any of the following applies. NP replacement instructions appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If the system fails to boot, it could indicate either a problem with the NP itself, a problem with the NP's hard disk drive, or a problem with the software on the hard drive.
Troubleshooting Interface Modules
This section provides information on how to isolate faults in interface modules. (An interface module consists of a line card and its access card.)
The following will help you distinguish between problems in a line card and problems in an access card.
If you're having trouble bringing up an interface module, check the following:
If you're having signal quality problems with a physical interface on an access card, check the following:
The following conditions may require replacement of either a line card or its access card. Replacement instructions appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
The following conditions indicate failure of a blower. See the chapter "Replacing FRUs" for replacement instructions.
Troubleshooting Bulk Power Trays
In a system with one power tray, no power will be present if the power tray is faulty. Suspect a problem with the power tray if cycling the system's power has no effect.
A system with two power trays can operate normally when only one is working; if you suspect a problem, use the CLI command show chassis powersupply. The display for a healthy dual-tray system is shown below. (In a system with only one power tray, both lines for the unused slot will read "Empty.")
If a status line for an occupied slot says anything other than Good, check the faulty power tray to see that it's properly connected. (Power tray slot A is on top; slot B is on the bottom.) If the problem persists, replace the power tray as described in the section "Replacing a Power Tray" in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
Troubleshooting Disk Assemblies
Disk assembly problems are indicated by the following symptoms:
If a disk problem is indicated, check the disk assembly connector for bent or broken pins. To do so, remove the disk assembly as described in the section "Replacing a Disk Assembly" in the chapter "Replacing FRUs." Then examine the 64-pin male connector at the back of the slot. If any pins are bent or damaged, they are the likely source of the problem. Replace the disk assembly connector as described in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If the connector is in good condition, the problem may be in the disk assembly itself, or in the software on the disk. If you suspect a problem with the software, you should be able to correct it by reinstalling the software as described in the LightStream 2020 Network Operations Guide. If that doesn't solve the problem, or if you believe the problem lies in the hardware, see the section "Replacing a Disk Assembly" in the chapter "Replacing FRUs" for instructions on replacing the disk assembly.
Midplane problems are indicated by the following symptoms. Midplane replacement instructions appear in the section "Replacing the Midplane" of the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
This section tells you how to run diagnostics on specified cards in a LightStream 2020 switch. You can access the diagnostics in three ways:
The rest of this section is divided into the following subsections:
This section tells you how to use the test command in CLI to run field diagnostics on a line card in a specified slot or on a backup NP.
The first subsection below describes the switches you can use with the test command. The second subsection explains how to use the test command to test a line card, and the third tells you how to use the test command to test a backup NP.
The syntax of the CLI test command is as follows:
where
If you use the test command with multiple switches, you must enter each one with its own - (minus) character and separate the switches with spaces. For example:
If you run the test command with no switches, diagnostics are loaded and run on the specified card in the background, and your CLI prompt returns so you can perform other tasks. The diagnostics complete in a minimum of 5 minutes. To display their status, type test <slot#> -r.
Using the test Command on a Line Card
This procedure explains how to use the test command in CLI to run diagnostics on a line card. CLI must be running on the system you plan to test.
Using the test Command on a Backup NP
Follow the procedures in this section to use the test command in CLI to run diagnostics on a backup NP. (If you need to test a lone NP, see the procedure "Loading Manufacturing Diags into a Lone NP.") This task requires either a local console connected to the switch under test or a modem connection. You cannot use telnet.
The first procedure below explains how to force the active and backup NPs to switch roles; this is only necessary if the NP you want to test is currently active. The second procedure tells you how to run the diagnostics.
Forcing the Active NP to Become Backup
Testing the Backup NP
Start with step 1 of this procedure unless you just completed the previous procedure.
Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics
You must use manufacturing diagnostics to test the single NP in a nonredundant system. If you wish, you can also use them to test backup NPs and line cards.
This section contains the following procedures:
After loading the diagnostics, see the section "Running Manufacturing Diagnostics" for instructions on what to do next.
Loading Manufacturing Diags into a Lone NP
This procedure explains how to load the manufacturing diagnostics into the sole NP in a nonredundant system. Note that this procedure requires the system under test to stop passing traffic. It also requires you to have a local console connection or a modem connection to the switch whose NP you are testing. You cannot use telnet or rlogin.
The commands used in the procedure are listed below, followed by the procedure itself.
You'll see the following display:
Loading Manufacturing Diags into a Line Card or Backup NP
If you wish, you can use the manufacturing diagnostics to test backup NPs and line cards. Use the procedure in this section to load the manufacturing diagnostics, then go on the following section, "Running Manufacturing Diagnostics," for further instructions.
As you follow the procedure below, you'll use these commands:
Running Manufacturing Diagnostics
Read this section for information on running manufacturing diagnostics. The first subsection, "Running Sets of Tests," applies to all of the test procedures that follow it.
In each of the diagnostics packages, commands are provided to run preselected sets of tests:
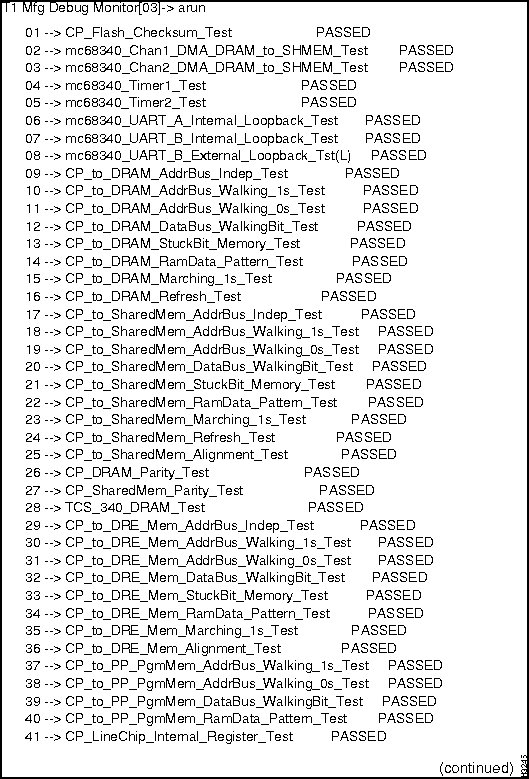
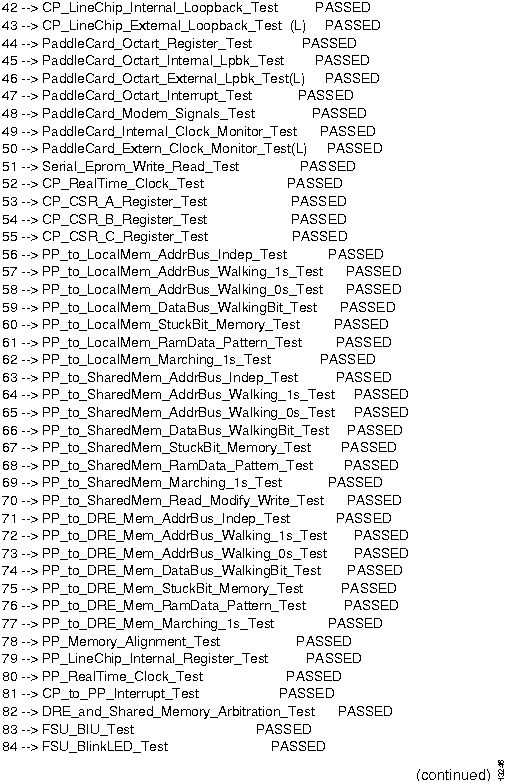
Use this procedure to run diagnostics on an NP card. It assumes that you have already loaded the diagnostics onto the card, as described in the section "Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics."
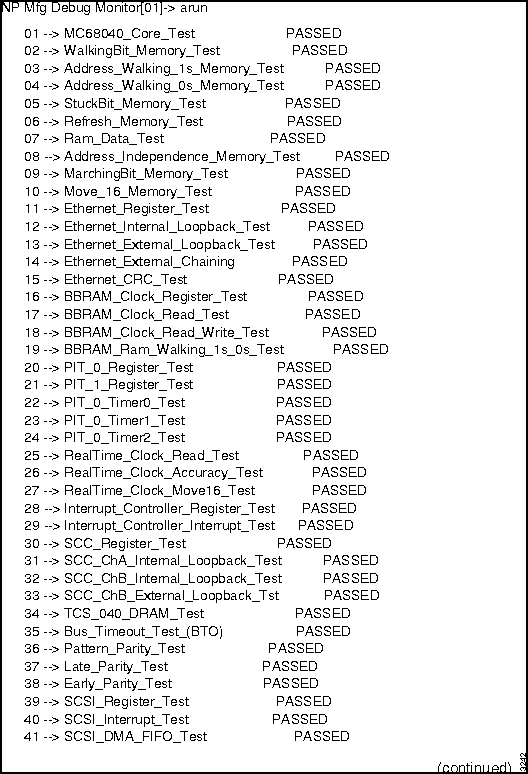
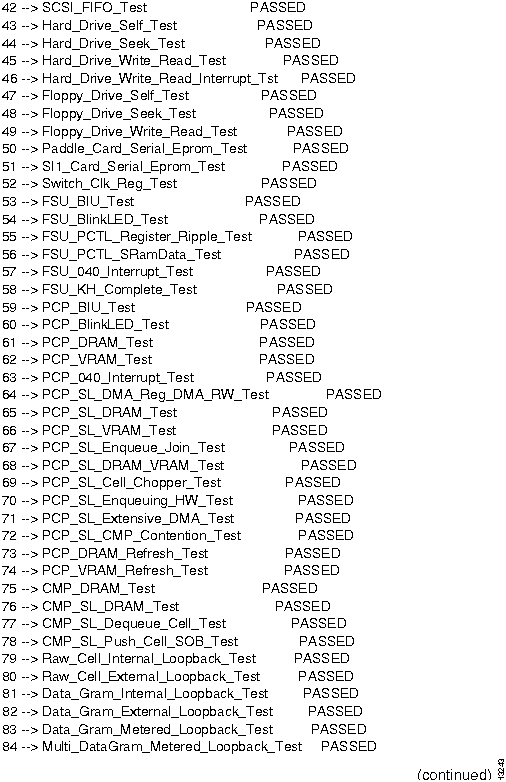
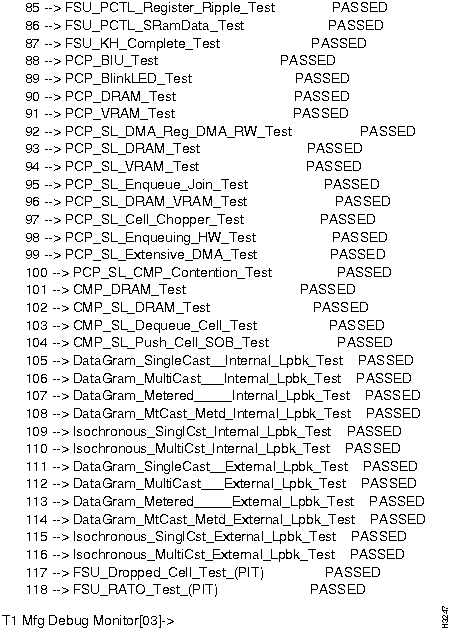
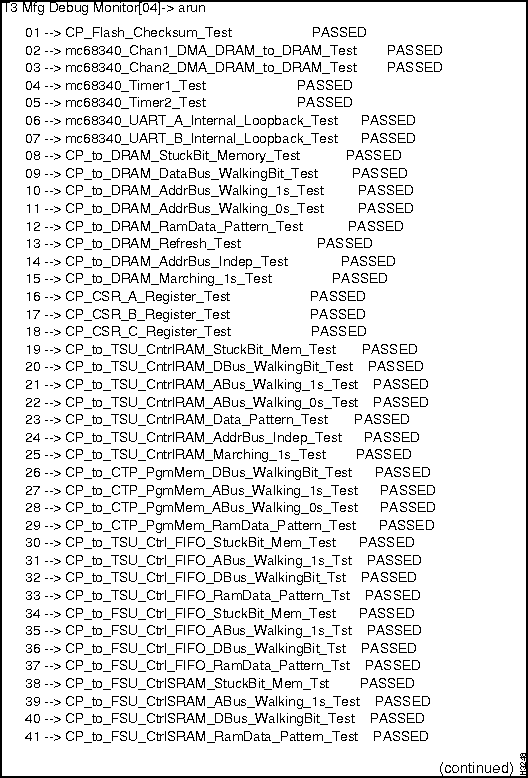
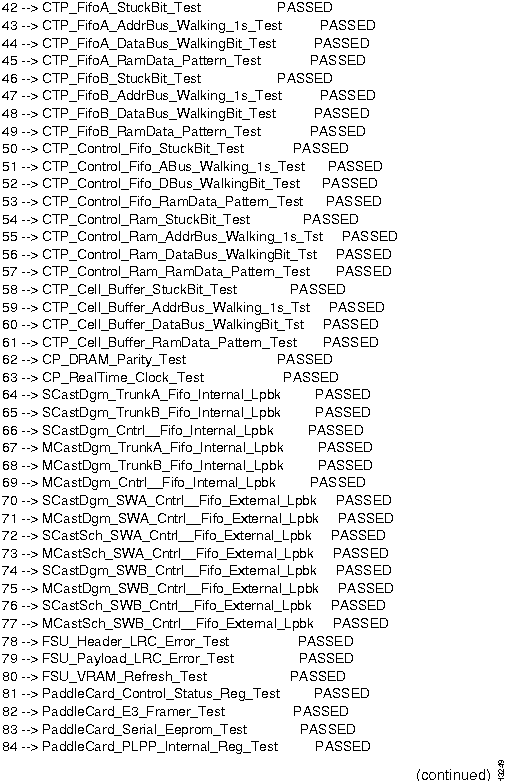
Figure 2-1 : NP diagnostics output. Figure 2-2 : NP diagnostics output, continued. Figure 2-3 : NP diagnostics output, concluded. How to Proceed
If any tests fail, replace the card being tested. Replacement procedures appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If all tests pass but you're still experiencing a problem, test the other cards in the chassis. Replace any cards that fail diagnostics. If the problem persists, investigate causes outside the LightStream hardware, including leased lines and edge devices.
Use this procedure to run diagnostics on a low-speed line card. It assumes that you have already loaded the diagnostics onto the card, as described in the section "Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics."
Figure 2-4 : Low-speed line card diagnostics output. Figure 2-5 : Low-speed line card diagnostics output, continued. Figure 2-6 : Low-speed line card diagnostics output, concluded. How to Proceed
If any tests fail you may need to replace either the line card being tested or its access card. (Replacement procedures appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs.") Look at the numbers of the tests that failed to determine which card to replace:
If all tests pass but you're still experiencing a problem, test the other cards in the chassis. Replace any cards that fail diagnostics. If the problem persists, investigate causes outside the LightStream hardware, including leased lines and edge devices.
Use this procedure to run diagnostics on a medium-speed line card. It assumes that you have already loaded the diagnostics onto the card, as described in the section "Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics."
Figure 2-7 : Medium-speed line card diagnostics output. Figure 2-8 : Medium-speed line card diagnostics output, continued. Figure 2-9 : Medium-speed line card diagnostics output, concluded. How to Proceed
If any tests fail you may need to replace either the line card being tested or its access card. (Replacement procedures appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs.") Look at the numbers of the tests that failed to determine which card to replace:
If all tests pass but you're still experiencing a problem, test the other cards in the chassis. Replace any cards that fail diagnostics. If the problem persists, investigate causes outside the LightStream 2020 hardware, including leased lines and edge devices.
Use this procedure to run diagnostics on a packet line card. It assumes that you have already loaded the diagnostics onto the card, as described in the section "Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics."
When they are loaded, the PLC diagnostics determine which type of access card is installed with the line card under test. Tests appropriate for the access card are enabled. You can use the access command, described in the section "Command Reference," to display the type of the access card.
How to Proceed
If test 55 (or any of its subtests, 55.01 through 55.15) fails, this indicates a failure in the access card. In this case replace the access card, as described in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If any other tests fail, replace the card being tested. Replacement procedures appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If all tests pass but you're still experiencing a problem, test the other cards in the chassis. Replace any cards that fail diagnostics. If the problem persists, investigate causes outside the LightStream hardware, including leased lines and edge devices.
Use this procedure to run diagnostics on a cell line card. It assumes that you have already loaded the diagnostics onto the card, as described in the section "Loading Manufacturing Diagnostics."
When they are loaded, the CLC diagnostics determine which type of access card is installed with the line card under test. Tests appropriate for the access card are enabled. You can use the access command, described in the section "Command Reference," to display the type of the access card.
How to Proceed
If test 51 (or any of its subtests) fails, this indicates a failure in the access card. In this case replace the access card, as described in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If any other tests fail, replace the card being tested. Replacement procedures appear in the chapter "Replacing FRUs."
If all tests pass but you're still experiencing a problem, test the other cards in the chassis. Replace any cards that fail diagnostics. If the problem persists, investigate causes outside the LightStream hardware, including leased lines and edge devices.
This section lists special requirements for tests in each diagnostic package.
NP Tests with Special Requirements
Tests that Write to the Hard Disk
The NP tests listed below write data to the hard disk. These tests are disabled by default; you must explicitly enable them in order to run them. Unless you are testing a new disk drive or have reason to suspect a fault in your hard disk, it's recommended that you avoid running these tests:
Tests that Send Data to the Switch Card
The NP tests listed below send data through the switch card. Take the LightStream 2020 node off line before running these tests, as described in the procedure following the list of tests. Do not run them on a system that's passing traffic. (If the node is running, these tests may fail when they would otherwise pass. In addition, the "bad" data passed to the switch by the tests may cause traps.)
If you wish to run these tests, use the procedure below to disable the system and all the other cards in the chassis. This prevents the other cards from sending packets to the card under test that cause these tests to fail even when no problem exists.
Tests that Require Looping Plugs
The NP tests listed below will fail if they are run on a system that does not have looping plugs installed on the NP Ethernet port and Diag2 port. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -l switch.) If you do not have looping plugs installed, it's recommended that you avoid running these tests:
Tests that Require a Scratch Diskette
The NP tests listed below will fail if they are run on a system that does not have writable diskettes in its floppy disk drives. If you do not have a scratch diskette in each floppy drive, it's recommended that you avoid running these tests:
Long-Running Memory Tests
The NP memory tests listed below take longer than one minute to run. (Some take many minutes.) Avoiding these tests saves time. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -x switch.)
BB-RAM Clock Test
The NP diagnostics include tests for the battery-backed RAM clock that keeps time for the whole system. If the tests fail, you will be prompted to reset the clock; you must supply the current time and date. If the system under test has two NPs, make certain that their clocks agree to within one minute. (If the clocks don't agree, file consistency problems between the two NPs may result.)
LSC Tests with Special Requirements
Tests that Send Data to the Switch Card
The low-speed line card tests listed below send data through the switch card. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -s switch.) Take the LightStream 2020 node off line before running these tests. Do not run them on a system that's passing traffic. (If the node is running, these tests may fail when they would otherwise pass. In addition, the "bad" data passed to the switch by the tests may cause traps.)
If you wish to run these tests, use the procedure below to disable the system and all the other cards in the chassis, and then to load the diagnostics into the card you wish to test. This procedure prevents the other cards from sending packets to the card under test that cause these tests to fail even when no problem exists.
Tests that Require Looping Plugs
The LSC tests listed below will fail if they are run on a system that does not have looping plugs installed on the I/O ports. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -l switch.) If you do not have looping plugs installed, it's recommended that you avoid running these tests:
Long-Running Memory Tests
The low-speed line card memory tests listed below take longer than one minute to run. (Some take many minutes.) Avoiding these tests saves time. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -x switch.)
MSC Tests with Special Requirements
Tests that Send Data to the Switch Card
The medium-speed line card tests listed below send data through the switch card. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -s switch.) Take the LightStream node off line before running these tests. Do not run them on a system that's passing traffic. (If the node is running, these tests may fail when they would otherwise pass. In addition, the "bad" data passed to the switch by the tests may cause traps.)
If you wish to run these tests, use the procedure below to disable the system and all the other cards in the chassis, and then to load the diagnostics into the card you wish to test. This procedure prevents the other cards from sending packets to the card under test that cause these tests to fail even when no problem exists.
Tests that Require Looping Plugs
The MSC tests listed below will fail if they are run on a system that does not have looping plugs installed on the I/O ports. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -l switch.) If you do not have looping plugs installed, it's recommended that you avoid running these tests:
Long-Running Memory Tests
The medium-speed line card memory tests listed below take longer than one minute to run. (Some take many minutes.) Avoiding these tests saves time. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -x switch.)
PLC Tests with Special Requirements
Tests that Send Data to the Switch Card
The packet line card tests listed below send data through the switch card. (In field diagnostics, these tests are invoked when you use the test command's -s switch.) Take the LightStream 2020 node off line before running these tests. Do not run them on a system that's passing traffic. (If the node is running, these tests may fail when they would otherwise pass. In addition, the "bad" data passed to the switch by the tests may cause traps.)
If you wish to run these tests, use the procedure below to disable the system and all the other cards in the chassis, and then to load the diagnostics into the card you wish to test. This procedure prevents the other cards from sending packets to the card under test that cause these tests to fail even when no problem exists.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
cli>
show chassis powersupply
Power Supply A:
Power Supply A Type:
Power Supply B:
Power Supply B Type:
cli>
Good
1200W AC Power Supply
Good
1200W AC Power Supply
cli> show tcs 1 voltage
Slot 1 Voltage:
TCS VCC Voltage: 5.053 (Normal Range: 4.614 / 5.371)
VCC Voltage: 5.029 (Normal Range: 4.370 / 5.615)
SCSI Voltage: 4.833 (Normal Range: 4.614 / 5.371)
VPP Voltage*: 0.000 (Normal Range: 11.067 / 12.858)
*VPP Voltage Is Valid Only During FLASH Initialization
cli>
test <slot#> [-l -p -s -x -r -m] [-F<filename>]
diag_np1.aout :
NP diagnostics
diag_clc1.aout:
Cell line card diagnostics
diag_plc1.aout :
Packet line card diagnostics
diag_ls1.aout :
Low-speed line card diagnostics
diag_ms1.aout :
Medium-speed line card diagnostics
test 4 -p -x
test 4 -px
cli>
protected
*cli>
set snmp community <write-community>
*cli>
test 4
*cli>
test 4 -r
Diagnostics are running, test 73, heartbeat = 18673
*cli>
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
*cli>
set snmp community <read-community>
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
TCS hub<<A>>
connect 1
`.
to return to the TCS hub.
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
TCS hub<<A>>
connect 2
cli>
protected
*cli>
set snmp community <write-community>
*cli>
test 1
*cli>
test 1 -r
Diagnostics are running, test 73, heartbeat = 18673
*cli>
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
*cli>
set snmp community <read-community>
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
TCS hub<<A>>
connect 1
**** LynxOS [rebooted by /bin/reboot] is down ****
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
1-Boot ATM switch application
2-Begin full installation with boot from floppy disk
3-List contents of hard disk root directory
4-List contents of floppy disk root directory
5-Boot system single-user
6-Escape to full set of bootstrap options
7-Extended help
Option>
Option>
6
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
Enter "help" for documentation on extended bootstrap options
Default: (sd0a)lynx.os
Boot:
Boot:
(sd0b)diag/diag_np1.aout
booting: drive:0, partition:1, kernel:"diag/diag_np1.aout", flags:0x4201
Resetting SCSI bus
Diagnostic linked for 0x0
LOAD AT 0x0
442980+0+0
START AT 0x5000
RMeg Bit value = 0
Configuring Main Memory for 32 Megabytes
*****************************************
* Network Processor Debug Monitor *
* RELEASE 1.00 *
* Revision 1.371 (Sep 1 1993) *
* Type 'help' or '?' for help *
*****************************************
NP Mfg Debug Monitor[01]->
`.
to return to the TCS hub. Then use the command reset <slot#> to reset the NP.
cli> protected
*cli>
set snmp community <write-community>
*cli>
test <slot#> -m
fcload: (ls2_1) compiled Aug 04 1995 @ 06:07:15 [version 1.79.2.1]
fcload: slot 7: taking per-slot synchronization lock
fcload: slot 7: initialization of VCIs complete
fcload: slot 7: disabling switch interface...
fcload: slot 7: resetting card...
fcload: slot 7: waiting for initialization...........initialization sequence complete
fcload: slot 7: (clc1 card oc3 accesscard) starting SWACC loader
fcload: slot 7: waiting for initialization.initialization sequence complete
fcload: slot 7: waiting for remote SWACC loader to initialize:.Ready
Loading "/usr/diag/diag_clc1.aout" into clc1 card oc3 accesscard in slot 7 via SWITCH (409 6 bytes per dot)
Loading 467728 (0x72310) bytes starting at 0x10000000..................................... ...........................
...................................................Done
Loading 452064 (0x6e5e0) bytes starting at 0x10072310.............
................................................................
..................................Done
NOT clearing 63360 (0xf780) bytes of bss starting at 0x100e08f0!
fcload: slot 7: (clc1 card oc3 accesscard) starting SRAM image
fcload: slot 7: setting start address to 0x10000408
fcload: slot 7: releasing per-slot synchronization lock
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>-----CONNECT----->>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
User 'root' (localhost) connected at Fri Sep 1 17:35:44 1995
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>-----CONNECT----->>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
connected
******************************************
* CLC1 Diag Monitor *
* Revision 1.410 (Jul 27 1995) *
* Type 'help' or '?' for help *
******************************************
CLC1 Diag Monitor[07]->
run executes a set of tests that have been designed to run quickly and safely on a system that is operating. The tests omitted by run are as follows:

diags>
run 5-15
diags>
help 10
diags>
exit
`.
, then reset <slot#> to reset the NP, then connect <slot#> to reconnect to the NP. Replace <slot#> with the slot number of the card you were testing.
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
diags>
run 5-15
diags>
help 10
diags>
exit
*cli>
set card <slot#> active

diags>
run 5-15
diags>
help 10
diags>
exit
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
PLC1 Diag Monitor[08]-> run
01 CP_Flash_Checksum_Test PASSED
02 EEPROM_Checksum_Tests PASSED
03 CP_DRAM_Tests PASSED
04 CP_Parity_Test PASSED
05 CP_Parity_Buffer_Test PASSED
06 CP_Parity_DRAM_Test PASSED
07 CP_PDBL_SRAM_Tests PASSED
08 TSU_NQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
09 TSU_DQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
10 TSU_Internal_Timer_SRAM_Tests PASSED
11 TSU_Internal_CellFifo_SRAM_Tests PASSED
12 FSU_OSMC_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
13 FSU_ISMC_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
14 TLU_TLP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
15 TLU_RP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
16 FLU_FLP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
17 FLU_ALF_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
18 TSU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
19 FSU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
20 TLU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
21 FLU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
22 TSU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
23 FSU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
24 TLU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
25 FLU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
26 FSU_RealTimeClock_Test PASSED
27 FSU_IntervalTimer_Test PASSED
28 TLU_HoldoffTimer_Test PASSED
29 TCS_NMI_Test PASSED
30 TSU_Internal_ScratchPad_SRAM_Tests PASSED
31 TSU_External_CellBuffer_DRAM_Tests PASSED
32 TSU_External_Control_DRAM_Tests PASSED
33 FSU_Internal_SRAM_Tests PASSED
34 FSU_External_LRIC_SRAM_Tests PASSED
35 FSU_External_CRIC_DRAM_Tests PASSED
36 TLU_External_DRAM_Tests PASSED
37 FLU_External_ParseGraph_SRAM_Tests PASSED
38 FLU_External_Protocol_DRAM_Tests PASSED
39 TSU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
40 FSU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
41 TLU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
42 FLU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
43 TSU_FSU_SWA_External_Lpbk_Test PASSED
44 TSU_FSU_SWA_Internal_Lpbk_A_Test PASSED
45 TSU_FSU_SWA_Internal_Lpbk_B_Test PASSED
46 TSU_FSU_SWB_External_Lpbk_Test PASSED
47 TSU_FSU_SWB_Internal_Lpbk_B_Test PASSED
48 TSU_FSU_SWB_Internal_Lpbk_A_Test PASSED
49 TSU_FSU_MultiCast_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
50 TSU_FSU_Smoothing_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
51 TSU_FSU_RATO_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
52 TSU_TLU_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
53 FLU_FSU_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
54 FLU_TLU_Internal_Lpbk_Test PASSED
55 FDDI_Access_Card_Tests PASSED
55 Ethernet_Access_Card_Tests PASSED
55 Cemac_Tests PASSED
PLC1 Diag Monitor[08]->
diags>
run 5-15
diags>
help 10
diags>
exit
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
CLC1 Diag Monitor[07]-> run
01 CP_Flash_Checksum_Test PASSED
02 EEPROM_Checksum_Tests PASSED
03 CP_DRAM_Tests PASSED
04 CP_Parity_Test PASSED
05 CP_Parity_Buffer_Test PASSED
06 CP_Parity_DRAM_Test PASSED
07 TSU_NQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
08 TSU_DQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
09 TSU_Internal_Timer_SRAM_Tests PASSED
10 TSU_Internal_CellFifo_SRAM_Tests PASSED
11 TSU_B_NQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
12 TSU_B_DQP_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
13 TSU_B_Internal_Timer_SRAM_Tests PASSED
14 TSU_B_Internal_CellFifo_SRAM_Tests PASSED
15 FSU_OSMC_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
16 FSU_ISMC_uStore_Memory_Tests PASSED
17 TSU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
18 TSU_B_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
19 FSU_Register_Walking_1s_and_0s_Test PASSED
20 TSU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
21 TSU_B_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
22 FSU_uDiagnostic_Tests PASSED
23 FSU_RealTimeClock_Test PASSED
24 FSU_IntervalTimer_Test PASSED
25 TCS_NMI_Test PASSED
26 TSU_Internal_ScratchPad_SRAM_Tests PASSED
27 TSU_External_CellBuffer_DRAM_Tests PASSED
28 TSU_External_Control_DRAM_Tests PASSED
29 TSU_B_Internal_ScratchPad_SRAM_Tests PASSED
30 TSU_B_External_CellBuffer_DRAM_Tests PASSED
31 FSU_Internal_SRAM_Tests PASSED
32 FSU_External_LRIC_SRAM_Tests PASSED
33 FSU_External_CRIC_DRAM_Tests PASSED
34 TSU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
35 TSU_B_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
36 FSU_Functional_Register_Tests PASSED
37 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Ext_SWA_Test PASSED
38 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Ext_SWB_Test PASSED
39 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_B_Ext_SWA_Test PASSED
40 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_B_Ext_SWB_Test PASSED
41 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Int_SWA_Test PASSED
42 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Int_SWB_Test PASSED
43 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_B_Int_SWA_Test PASSED
44 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_B_Int_SWB_Test PASSED
45 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Int_SWA_FSU_B_Test PASSED
46 Cell_lpbk_Tsu_A_Int_SWB_FSU_A_Test PASSED
47 RATO_lpbk_Tsu_A_Int_SWA_Test PASSED
48 Metering__Tsu_A_Int_SWA_Test PASSED
49 OC3_Access_Card_Tests PASSED
49 T3_Access_Card_Tests PASSED
49 E3_Access_Card_Tests PASSED
CLC1 Diag Monitor[07]->
diags>
run 5-15
diags>
help 10
diags>
exit
*cli>
set card <slot#> active
43 --> Hard_Drive_Self_Test
44 --> Hard_Drive_Seek_Test
45 --> Hard_Drive_Write_Read_Test
46 --> Hard_Drive_Write_Read_Interrupt_Tst
78 --> CMP_SL_Push_Cell_SOB_Test
80 --> Raw_Cell_External_Loopback_Test
82 --> Data_Gram_External_Loopback_Test
83 --> Data_Gram_Metered_Loopback_Test
84 --> Multi_DataGram_Metered_Loopback_Test
85 --> Chained_Data_Gram_Loopback_Test
86 --> Iso_Sngle_Cast_Loopback_Test
87 --> Multi_Cast_Data_Gram_Loopback_Test
88 --> Comp_Data_Gram_Loopback_Test
89 --> Multi_Cast_IsoLoopback_Test
90 --> FSU_RATO_Test
91 --> FSU_fast_dropper_Test
92 --> FSU_VRAM_mem_Test
93 --> FSU_VRAM_refresh_Test
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
1 - Boot ATM switch application
2 - Begin full installation with boot from floppy disk
3 - List contents of hard disk root directory
4 - List contents of floppy disk root directory
5 - Boot system single-user
6 - Escape to full set of bootstrap options
7 - Extended help
Option>
6
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
Enter "help" for documentation on extended bootstrap options
Default: (sd0a)lynx.os
Boot:
(sd0b)diag/diag_np1.aout
13 --> Ethernet_External_Loopback_Test
14 --> Ethernet_External_Chaining
33 --> SCC_ChB_External_Loopback_Tst
47 --> FLoppy_Drive_Self_Test
48 --> Floppy_Drive_Seek_Test
49 --> Floppy_Drive_Write_Read_Test
08 --> Address_Independence_Memory_Test
09 --> MarchingBit_Memory_Test
93 --> FSU_VRAM_refresh_Test
111 --> DataGram_SingleCast__External_Lpbk_Test
112 --> DataGram_MultiCast___External_Lpbk_Test
113 --> DataGram_Metered_____External_Lpbk_Test
114 --> DataGram_MtCast_Metd_External_Lpbk_Test
115 --> Isochronous_SinglCst_External_Lpbk_Test
116 --> Isochronous_MultiCst_External_Lpbk_Test
117 --> FSU_Dropped_Cell_Test_(PIT)
118 --> FSU_RATO_Test_(PIT)
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
1 - Boot ATM switch application
2 - Begin full installation with boot from floppy disk
3 - List contents of hard disk root directory
4 - List contents of floppy disk root directory
5 - Boot system single-user
6 - Escape to full set of bootstrap options
7 - Extended help
Option>
6
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
Enter "help" for documentation on extended bootstrap options
Default: (sd0a)lynx.os
Boot:
(sd0b)diag/sys_np1.aout
******************************************
* System Diagnostic Debug Monitor *
* Revision 1.258 (Jun 15 1994) *
* Type 'help' or '?' for help *
******************************************
System Monitor->
load <slot#> (sd0b)diag/diag_ls1.aout
`.
to return to the TCS hub.
08 --> mc68340_UART_B_External_Loopback_Tst(L)
43 --> CP_LineChip_External_Loopback_Test (L)
46 --> PaddleCard_Octart_External_Lpbk_Test(L)
50 --> PaddleCard_Extern_Clock_Monitor_Test(L)
09 --> CP_to_DRAM_AddrBus_Indep_Test
15 --> CP_to_DRAM_Marching_1s_Test
17 --> CP_to_SharedMem_AddrBus_Indep_Test
23 --> CP_to_SharedMem_Marching_1s_Test
66 --> PP_to_SharedMem_DataBus_WalkingBit_Test
69 --> PP_to_SharedMem_Marching_1s_Test
70 --> SCastDgm_SWA_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
71 --> MCastDgm_SWA_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
72 --> SCastSch_SWA_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
73 --> MCastSch_SWA_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
74 --> SCastDgm_SWB_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
75 --> MCastDgm_SWB_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
76 --> SCastSch_SWB_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
77 --> MCastSch_SWB_Cntrl__Fifo_External_Lpbk
79 --> FSU_Payload_LRC_Error_Test
78 --> FSU_Header_LRC_Error_Test
80 --> FSU_VRAM_Refresh_Test
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
1 - Boot ATM switch application
2 - Begin full installation with boot from floppy disk
3 - List contents of hard disk root directory
4 - List contents of floppy disk root directory
5 - Boot system single-user
6 - Escape to full set of bootstrap options
7 - Extended help
Option>
6
Network Processor bootstrap (version 1.3: Sep 13 1993)
Enter "help" for documentation on extended bootstrap options
Default: (sd0a)lynx.os
Boot:
(sd0b)diag/sys_np1.aout
******************************************
* System Diagnostic Debug Monitor *
* Revision 1.258 (Jun 15 1994) *
* Type 'help' or '?' for help *
******************************************
System Monitor->
load <slot#> (sd0b)diag/diag_ms1.aout
`.
to return to the TCS hub.
93 --> T3/E3_PLPP_TrunkA_Fifo_External_Lpbk
94 --> T3/E3_PLPP_TrunkB_Fifo_External_Lpbk
14 --> CP_to_DRAM_AddrBus_Indep_Test
15 --> CP_to_DRAM_Marching_1s_Test
24 --> CP_to_TSU_CntrlRAM_AddrBus_Indep_Test
25 --> CP_to_TSU_CntrlRAM_Marching_1s_Test
54 --> CTP_Control_Ram_StuckBit_Test
56 --> CTP_Control_Ram_DataBus_WalkingBit_Tst
57 --> CTP_Control_Ram_RamData_Pattern_Test
61 --> CTP_Cell_Buffer_RamData_Pattern_Test
80 --> FSU_VRAM_Rrefresh_Test
43 TSU_FSU_SWA_External_Lpbk_Test
46 TSU_FSU_SWB_External_Lpbk_Test
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.
`.
to get a TCS hub prompt.