Step 10 Exit privileged mode with the disable command.
Table 1 lists configuration commands by LocalDirector features:
Table 1 : Commands By Feature Summary
| ARP cache:
|
arp
clear arp-cache
|
Configuration
Privileged
|
| Failover cable (optional):
- Configure
- Force LocalDirector to active
- Force LocalDirector to standby
- Show status
|
failover
failover active
failover standby
show failover
|
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Unprivileged
|
| Fast Ethernet configuration
|
interface ethernet
|
Configuration
|
| Flash memory access:
- Clear
- Display configuration
- Reload from
- Write to
|
write erase
show configuration
reload
write memory
|
Privileged
Privileged
Privileged
Privileged
|
| Floppy disk access:
- Read from
- Save configuration to
|
configure floppy
write floppy
|
Privileged
Privileged
|
| IP address, set
|
ip address
|
Configuration
|
| Load balancing:
- Bindings, associate or disassociate
- Bindings, show
- Connection usage, show
- In-service marking
- Out-of-service marking
- Port mappings, add or remove
- Port mappings, show
- Real server entries, add or remove
- Real server entries, show
- Sticky timers
- Threshold counts, adjust
- Virtual server entries, add or remove
- Virtual server entries, show
|
bind
show bind
show conn
in-service
out-service
map
show map
real
show real
sticky
threshold
virtual
show virtual
|
Configuration
Unprivileged
Unprivileged
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Unprivileged
Configuration
Unprivileged
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Unprivileged
|
| MAC addresses:
- Display associated with ports
- Flush associated with a bridge
|
show bridge
clear bridge
|
Unprivileged
Privileged
|
| Processes, show thread information
|
show processes
|
Unprivileged
|
| Prompt hostname, change
|
hostname
|
Configuration
|
| RIP listening, enable or disable
|
rip
|
Configuration
|
| Routing table:
|
ip route
show ip route
|
Configuration
Unprivileged
|
| Syslog:
- Address, view
- Dump buffer to console
- Hosts, view current
- Messages, change facility and level
- Server, assign
|
show ip address
syslog console
show syslog
syslog output
syslog host
|
Unprivileged
Configuration
Unprivileged
Configuration
Configuration
|
Sample Configuration
A configuration example follows:
rotor> enable
Password:
rotor# config terminal
rotor(config)# ip address 192.168.13.40 255.255.255.0
rotor(config)# interface ethernet 0 10baseT
rotor(config)# interface ethernet 1 10baseT
rotor(config)# ^z
rotor# write memory
rotor# disable
rotor>
In this example, enable starts privileged mode. Then config terminal starts configuration mode. The ip address command specifies that the IP address for LocalDirector is 192.168.13.40 and that the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. The interface ethernet command enables the Ethernet cards for 10baseT connections. Finally, the ^z command exits configuration mode, write memory saves the new settings, and disable exits privileged mode.
Configuration Guidelines
Observe the following guidelines during configuration:
- Configure all virtual servers on the same network.
- Ensure any IP address you specify exists. Virtual server IP addresses must be unique on network. Real server IP addresses must be the NIC-registered IP addresses (if your network connects to the Internet).
- When you enter commands, you can erase characters with the Backspace and Del keys. You can erase the previous word with ^W, erase the previous line with ^U, and redisplay the line with ^R.
Command Reference
Configure LocalDirector using the commands that follow. You can enter commands from your console computer or terminal.
This section lists the commands in the following format:
command (syntax variable variable[-variable] [keyword]) mode
| variable
|
Required variable information
|
| [variable]
|
Optional variable information
|
| variable[-variable]
|
You can supply additional parameters separated by spaces or you can supply a range of values by using a dash as the separator. For example, you can specify three IP addresses with the out-of-service command as:
10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3
or as:
10.0.0.1-10.0.0.3
|
[keyword]
|
Optional keyword
|
Command description.
example
Help Information
Help information is available by entering a question mark by itself for a listing of all commands, or with a command for command syntax. For example:
rotor> show map ?
show map [ip]
Commands
: (
: comment
) All modes. Comment character. Must be the first command in a line. Use to improve configuration file readability or to make configuration file commands not executable.
arp (
[no] arp
ip en
[alias]
)
Configuration mode.
ip
|
IP address for the ARP table entry
|
en
|
Ethernet MAC address for the ARP table entry
|
[alias]
|
Causes LocalDirector to respond to ARP requests for this IP address
|
Adds an entry to the LocalDirector ARP table. Use no arp to delete an entry from the LocalDirector ARP table.
rotor(config)# arp 192.168.0.42 0000.0101.0202
rotor(config)# arp 192.168.0.43 0000.0101.0203 alias
rotor(config)# no arp 192.168.0.52
bind (
[no] bind
v_ip r_ip[-r_ip]
)
Configuration mode.
v_ip
|
IP address for the virtual server
|
r_ip[-r_ip]
|
One or more real server IP addresses
|
Associates a virtual server with one or more real servers. Use virtual or real to define the virtual and real server addresses before using bind. Use no bind to release an association between a real and virtual server.
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.42
rotor(config)# real 192.168.0.3
rotor(config)# real 192.168.0.4
rotor(config)# bind 192.168.0.42 192.168.0.3
rotor(config)# no bind 192.168.0.42 192.168.0.4
clear arp-cache (
clear arp-cache
) Privileged mode. Clears the LocalDirector ARP table.
rotor# clear arp-cache
clear bridge (
clear bridge
) Privileged mode. Clears the LocalDirector bridge table.
rotor# clear bridge
configure floppy (
configure floppy
) Privileged mode. Replaces the current running configuration with the configuration stored on floppy disk. This command assumes that the floppy disk is in IBM format and was previously created by the write floppy command.
rotor# configure floppy
configure memory (
configure memory
) Privileged mode. Replaces the current running configuration with the configuration stored in flash memory.
rotor# configure memory
configure terminal (
configure terminal
) Privileged mode. Starts configuration mode. Exit configuration mode by entering exit or pressing ^Z. After exiting configuration mode, use write memory to store your changes in flash memory.
rotor# configure terminal
disable (
disable
) Privileged mode. Exits privileged mode and returns to unprivileged mode.
rotor# disable
rotor>
enable (
enable
) Unprivileged mode. Starts privileged mode. LocalDirector prompts you for your privileged mode password. Use disable to exit privileged mode. Use enable password to change the password.
rotor> enable
Password: ######
rotor# disable
rotor>
enable password (
enable password
newpassword
) Configuration mode.
Changes the privileged mode password, which appears after you enter the enable command.
failover (
[no] failover [active]
) Configuration mode.
active
|
Forces LocalDirector failover into the active mode.
|
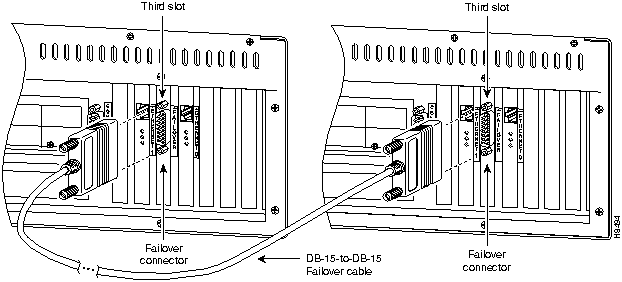
The failover command without an argument, indicates that you have connected the optional failover cable from your primary LocalDirector to a secondary LocalDirector. Failover works by passing control to the secondary unit should the primary unit fail. The switch between units occurs within 60 seconds of the failure event.
The primary LocalDirector does not maintain a copy of the connection state in the secondary unit. If the primary fails, the respective clients and servers must re-establish their own connections.
Put the failover command in the configuration files for both the primary and secondary units to enable failover.
If you want to force a LocalDirector to be active or go to standby you can use the failover active or no failover active command. Use this feature to force a LocalDirector offline for maintenance.
For configuration files, only use the failover command without the active argument.
Use the show failover command to verify the status of the connection.
rotor(config)# failover
hostname (
hostname
newname
) Configuration mode.
newname
|
New host name for the LocalDirector prompt
|
Changes the host name label on prompts. The default host name is "rotor."
rotor(config)# hostname spinner
spinner(config)# hostname rotor
rotor(config)#
in-service (
in-service [virtual|real]
ip[-ip]
) Configuration mode.
virtual
|
Mark one or more virtual servers as in service.
|
real
|
Mark one or more real servers as in service.
|
ip[-ip]
|
One or more server IP addresses; if you specify more than one IP address, only IP addresses previously configured in LocalDirector are marked as in service.
|
Marks one or more real or virtual servers as being in service (IS). When servers are in service, they can handle client requests received by LocalDirector.
rotor(config)# in-service real 192.168.0.2
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.80
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.81
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.85
rotor(config)# in-service virtual 192.168.0.80-192.168.0.85
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.84
rotor(config)# show virtual
virtual machines:
IP State Sticky
192.168.0.84 OOS 0
192.168.0.85 IS 0
192.168.0.81 IS 0
192.168.0.80 IS 0
interface ethernet (
interface ethernet
unit
[10baseT|100baseTX|auto]
) Configuration mode.
unit
|
Interface number starting from 0.
|
10baseT
|
10Mbit Ethernet
|
100baseTX
|
100Mbit Ethernet
|
auto
|
Automatically determine speed
|
Identifies the port bandwidth about a given Ethernet interface.
rotor(config)# interface ethernet 0 100baseTX
rotor(config)# interface ethernet 1 10baseT
ip address (
ip address
ip
[mask]
) Configuration mode.
ip
|
IP address
|
[mask]
|
Subnet mask
|
Assigns an IP address to the LocalDirector.
rotor(config)# ip address 130.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
ip route (
[no] ip route
network mask next-hop [metric]
) Configuration mode.
network
|
Destination IP network address; if default route, specify as all zeros (0.0.0.0)
|
mask
|
Subnet mask for the network; if default route, specify as all zeros (0.0.0.0)
|
next-hop
|
The adjacent gateway to reach network
|
[metric]
|
Optional distance metric (defaults to one)
|
Adds a static route to the IP routing table. Use no ip route to remove a static route from the IP routing table.
rotor(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1.1
rotor(config)# no ip route 192.168.88.0
map (
[no] map
v_ip, vport, r_ip, rport
) Configuration mode.
v_ip
|
Virtual server IP address
|
vport
|
Virtual server target port number
|
r_ip
|
Real server IP address bound to v_ip by previous use of the bind command
|
rport
|
Real server port number to map vport into. Connections bound for the virtual server that you assign to this real server also have the destination port number changed to rport.
|
Maps a virtual server IP address and port to a real server IP address and port. If you have multiple virtual servers pointing to a single real server, you need background programs (daemons) on the server with a unique address and port number to listen to. For example, if you have a number of home pages that all need to be invoked from daemons and each daemon requires a unique IP address and port on which to listen, you use map to point the virtual server IP address and port number to the real IP address and port.
When a real server is unbound from the virtual server, LocalDirector deletes all port mappings. Use no map to remove mappings. A virtual server IP address and port can be mapped to one or more real server IP addresses and ports. Use show map to display the current mappings.
rotor(config)# map 192.168.42.30 80 10.0.0.1 8001
rotor(config)# no map 192.168.42.99 20 10.42.42.0 8100
out-of-service (
out-of-service [virtual|real]
ip[-ip]) Configuration mode.
virtual
|
Mark one or more virtual servers as out of service.
|
real
|
Mark one or more real servers as out of service.
|
| ip[-ip]
|
One or more server IP addresses
|
Marks one or more virtual or real servers as being out of service (OOS). When you mark a real server as being out of service, LocalDirector does not assign new connections to it, but lets old connections continue to run until their translations complete. Any connection attempt or traffic on exiting connections causes LocalDirector to return a reset (RST) packet to the client. An out-of-service real server can still be accessed by clients specifying its actual IP address. Use show real to watch the status of open connections; when all connections appear as OOS, you can power-off the server or reconfigure it as required.
rotor(config)# out-of-service real 192.168.0.42
rotor(config)# out-of-service virtual 192.168.0.80-192.168.0.85
real (
[no] real
ip
[is|oos]
) Configuration mode.
| ip
|
IP address of an underling server.
|
is
|
Mark server as being in service.
|
oos
|
Mark server as being out of service (the default)
|
Define a real server. ip is the actual IP address of an underling server. Use no real to remove a real server from LocalDirector. Underling servers can always be accessed using their actual IP address.
rotor(config)# real 192.168.0.42
rotor(config)# real 192.168.0.7 is
reload (
reload
) Privileged mode. Reboots and reloads the system from flash memory. LocalDirector prompts for confirmation before starting.
rotor# reload
Proceed with reload?[confirm] y
Rebooting...
rip (
[no] rip
) Configuration mode. Enables IP routing table updates from received RIP broadcasts. Use no rip to disable LocalDirector IP routing table updates. The default is to enable IP routing table updates.
rotor(config)# rip
rotor(config)# no rip
show bind (
show bind
) Unprivileged mode. Displays how virtual servers are bound to real servers. The left column displays the virtual server's IP address and its service state in parentheses. The right column displays the real servers that underlie the virtual server and its service state.
rotor> show bind
Virtual Real
10.1.1.101 (OOS)
192.168.200.3 (OOS)
192.168.200.1 (OOS)
10.1.1.100 (OOS)
192.168.200.3 (OOS)
192.168.200.2 (OOS)
192.168.200.1 (OOS)
show bridge (
show bridge
) Unprivileged mode. Displays the table that the LocalDirector bridge uses to determine how data packets are forwarded. The table consists of MAC addresses, actions to take when the MAC address is seen, the interface the MAC address is associated with, the time in seconds since the last time the MAC address was observed, the number of times a MAC address has been sent on an interface, and the number of times a packet from the MAC address has been forwarded.
rotor> show bridge
Address Action Interface Age RXcnt TXcnt
0000.243d.53f1 forward Ethernet185197 0
0000.243d.53ef forwardEthernet1 114 202 2
0000.243d.53f2 forward Ethernet0166 169 1
show config (
show config
) Privileged mode. Displays the configuration saved in flash memory.
rotor# show config
:Saved
... config commands ...
:End
show connections (
show connections
) Unprivileged mode. Displays a summary of the current and maximum number of operating system connection objects utilized. This information represents the current and maximum number of simultaneous TCP connections made to virtual servers.
rotor> show connections
conns = 1 max = 2
show failover (
show failover
) Unprivileged mode. Displays the current failover status.
rotor> show failover
Failover On
interface 0
this host: active 0 225
other host: standby 0 0
interface 1
this host: active 0 225
other host: standby 0 0
show ip address (
show ip address
) Unprivileged mode. Displays the IP address of the LocalDirector. You can ping this address to display the address of the syslog output.
rotor> show ip address
System IP 10.1.1.1, system subnet 255.255.255.0
show ip route (
show ip route
) Unprivileged mode. Displays the IP routing table. All virtual servers on the LocalDirector share this single IP routing table. The routing table display contains the destination network number and mask, along with the next hop IP address, the distance metric, and, if the route was manually entered, a static keyword.
rotor> show ip route
network=0.0.0.0 Address=192.168.0.1 Distance=1 static
show map (
show map
v_ip) Unprivileged mode.
| v_ip
|
Virtual server IP address
|
Displays the LocalDirector TCP port mappings for one or all of the virtual servers.
rotor> show map 192.168.0.42
Port mappings for 192.168.0.42
192.168.0.4280 maps to 192.168.0.28002
rotor> show map
Port mappings for all machines
192.168.0.42 80 maps to 192.168.0.28002
192.168.0.7780 maps to 192.168.0.28001
show memory (
show memory
) Privileged mode. Displays a summary of the maximum physical memory and current free memory available to the LocalDirector operating system. Everything in LocalDirector is preallocated and the amount of free memory should never change.
rotor> show memory
32505856 bytes total, 402860 bytes free
show processes (
show processes
) Unprivileged mode.Displays a summary listing of running processes. Processes are lightweight threads requiring only few instructions to switch. In the listing, PC is the program counter, SP is the stack pointer, STATE is the address of a thread queue, Runtime is the number of milliseconds that the thread has been running, SBASE is the stack base address, Stack is the current number of bytes used and the total size of the stack, and Process lists the thread's function.
rotor> show processes
PC SP STATE Runtime SBASE StackProcess
8000139e 8024ad00 80005354 940 80249d1c 36/4096 arp_timer
...
show real (
show real
[ip]) Unprivileged mode.
| [ip]
|
Real server IP address
|
Lists real server information. If you specify an IP address, LocalDirector displays a summary for all virtual servers using the real server. The listing contains the service state of each real server, its failure threshold value, and a reassigned count of the current number of failures (timeouts) that occurred while trying to reach the real server.
rotor> show real
real machines:
IPConnectRatioLoadStateThresh re-assigned
192.168.0.42 0 5120 2213 IS 8 0
rotor> show real 192.168.0.42
real 192.168.0.42 referenced by:
IPStateSticky
192.168.0.42 IS 0
192.168.0.77 IS 0
show syslog (
show syslog
) Unprivileged mode. Displays information about the current SYSLOG hosts.
show virtual (
show virtual
[ip]) Unprivileged mode.
| [ip]
|
Virtual server IP address
|
Lists virtual server information. The listing includes the service state of each virtual server and its sticky value. You can specify the IP address for a server to view more information.
rotor> show virtual
virtual machines:
IPConnectRatioLoadStateThresh re-assigned
192.168.0.40 0 3840 0 IS 8 0
rotor> show virtual 192.168.0.40
virtual 192.168.0.40 consists of:
IP State Sticky
192.168.0.40 IS 0
192.168.0.77 IS0
sticky (
sticky
ip minutes) Configuration mode.
| ip
|
Virtual server IP address
|
| minutes
|
The time after which a connection from the same client can be reassigned to a different real server. The default is 0 minutes.
|
Sets the number of minutes during which a repeat request from a client should be passed to the same real server as the first request. Use this command if the real servers are caching information about their clients or their requests. Use show virtual to display the sticky value.
rotor(config)# sticky 192.168.0.42 5
syslog console (
[no] syslog console
) Configuration mode. Displays syslog messages on the console port. Use no syslog console to stop the display.
rotor(config)# syslog console
rotor(config)# no syslog console
syslog host (
[no] syslog host
i
p
) Configuration mode. Configures one or more host systems to receive syslog messages. Use no syslog host to remove a host from the receiving list. Use show syslog to view the current hosts.
rotor(config)# syslog host 192.168.0.99
rotor(config)# no syslog host 192.168.0.99
syslog output (
[no] syslog output
facility.level) Configuration mode.
| facility
|
Eight facilities LOCAL0(16) through LOCAL7(23); the default is LOCAL4(20). Hosts file the messages based on the facility number in the message.
|
| level
|
Message type; sets the level above which LocalDirector suppresses messages to the SYSLOG hosts. Setting the level to 3, for example, allows messages with levels 0, 1, 2, and 3 to display. Default is 3.
|
The levels are as follows:
| 0
|
System unusable
|
| 1
|
Take immediate action
|
| 2
|
Critical condition
|
| 3
|
Error message
|
| 4
|
Warning message
|
| 5
|
Normal but significant condition
|
| 6
|
Informational message
|
| 7
|
Debug-level messages
|
Configures the facility and level of SYSLOG messages. Because network devices share the eight facilities, syslog output lets you set the facility marked on all messages.
rotor(config)# syslog output 23.4
threshold (
threshold
ip reassigns) Configuration mode.
| ip
|
Real server IP address
|
| reassigns
|
The number of consecutive connection reassignments to tolerate; the default is 8. Zero is the same as one and the maximum number of reassigns is limited only by the size of an integer in memory.
|
Configures the number of consecutive TCP connection reassignments that a real server can exhibit before LocalDirector marks the real server as failed. Use show real to display real threshold values and to see which real servers have failed. Failed real servers are not utilized by virtual servers while in the failed state; however, LocalDirector retests each failed server periodically with a single TCP connection attempt to see if the server has returned to normal behavior. If so, LocalDirector marks the server in service which makes it available to handle virtual server requests.
rotor(config)# threshold 192.168.0.60 4
virtual (
[no] virtual
ip
[is|oos]
) Configuration mode.
| ip
|
IP address of a virtual server; the address must be unique to the network.
|
is
|
Mark server as being in service.
|
oos
|
Mark server as being out of service (the default)
|
Creates a virtual server to accept a connection from the network. LocalDirector assigns connections arriving at a virtual address to a real server. The network component of a virtual server's IP address must match the network component of the IP address assigned to LocalDirector using the ip address command. Specify ip address before specifying the virtual command. If no real servers are bound to the virtual server, use no virtual to remove the virtual server from LocalDirector.
rotor(config)# virtual 192.168.0.42
rotor(config)# no virtual 192.168.0.42
write erase
(write eras
e) Privileged mode. Clears the flash memory configuration. To clear the current running configuration, use write erase and then reload.
rotor# write erase
rotor# reload
write floppy (
write floppy
) Privileged mode. Saves the current running configuration to floppy disk. Use configure floppy to merge the configuration into the currently running box. The write floppy command assumes that the floppy disk is formatted for an IBM computer.
rotor# write floppy
write memory (
write memory
) Privileged mode. Saves the current running configuration to flash memory. Use configure memory to merge the configuration into the currently running box.
rotor# write memory
write terminal (
write terminal
) Privileged mode. Saves the current running configuration to the console computer. Use configure terminal to merge the configuration into the currently running box and then to paste the configuration back into the terminal. You can also use configure terminal to display the current configuration.
rotor# write terminal
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()