|
|
Installing the IPeXchange Client Software
This chapter describes how to install the IPeXchange client software on a PC. This chapter contains the following sections:
To install the IPeXchange client software, you need the following:
In addition, to ensure smooth installation and startup on a Windows for Workgroups operating system, check the IPX/SPX version numbers and compatibility of configured frame types before installing the IPeXchange client software.
The IPeXchange client relies on the Novell IPX/SPX components and versions listed in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 : Required Versions of IPX/SPX Components
| Component | Version | Applicable Operating System | Where Located |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPXODI | 3.0 or later | Windows 3.1 | Typically installed in \nwclient |
| LSL | 2.12 or later | Windows 3.1 | Typically installed in \nwclient |
| NWIPXSPX.DLL | 4.10 or later | Windows 3.1
Windows 95 |
Typically installed in \windows or \windows\system |
| NWCALLS.DLL | 4.10 or later | Windows 3.1
Windows 95 |
Typically installed in \windows or \windows\system |
| VIPX.386 | 1.19 or later | Windows 3.1 | Windows installed in \windows or \windows\system |
To determine the version numbers of your files, you can download the Novell Technical Support (NTS) Windows Diagnostics tool, ntswd.exe. This tool is in a self-extracting file named windr3.exe that is located at Novell's FTP site, ftp.novell.com/pub/netwire/
novfiles/. You can also find it by searching http://support.novell.com/ with your web browser.
If your installed Novell files are outdated, you can download new files from NetWire, CompuServe, or ftp.novell.com. In addition, NWIPXSPX.DLL and NWCALLS.DLL are provided in the NETWARE.DLL subdirectory of the IPeXchange client diskette.
Checking Windows for Workgroups Frame Types
On Windows for Workgroups computers, the NWLINK component supplied by Microsoft must interoperate with the IPX/SPX component supplied by Novell. These components use different configuration files, but both configuration files must specify the same frame type. Mismatched frame types are a common source of problems.
To ensure that the IPX/SPX frame type and the NWLINK frame type are set to the same value, follow these steps:
Table 4-2 : NET.CFG and PROTOCOL.INI Frame Formats
Checking Windows 95 Frame Types
To ensure that the IPX/SPX-compatible protocol is set to the appropriate frame type, follow these steps:
From the Windows File Manager, start the installation of the IPeXchange client software:
The setup program asks you to select the setup program you want to use:
If you choose Express Setup, the Setup program takes the following actions:
If you choose Custom Setup, the Setup program takes the following actions:
Testing Connectivity to the Gateway
After your computer has rebooted, start the IPeXchange client by double-clicking its icon.
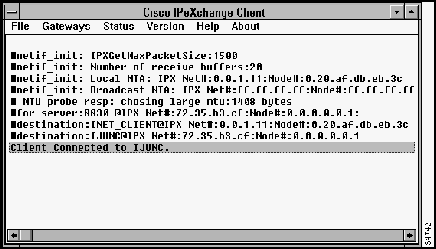
The window shown in Figure 4-1 appears, displaying diagnostic information.
Figure 4-1 : Client Status Window
When the client connects to the IPeXchange Internet gateway, a message is displayed identifying the gateway. For example, if the client connects to the gateway named, IPeX-gateway, the following message is displayed:
Once you have installed the IPeXchange client software and confirmed that the IPeXchange client and gateway work together successfully, you can install and run any of the applications listed in the appendix "Applications Certified for Use with the IPeXchange Gateway," or other WinSock 1.1--compliant applications.
Once the IPeXchange client software is running, you do not usually need to start or stop it explicitly. When any WinSock 1.1--compatible application starts, the IPeXchange client automatically starts and connects to an IPeXchange gateway on behalf of the application. When applications shut down and the client is idle, the IPeXchange client automatically exits.
The section "Performing Advanced Configuration Tasks" describes additional software features.
Performing Advanced Configuration Tasks
This section describes the following advanced configuration procedures for the IPeXchange client. You do not need to perform these procedures unless you have multiple gateways.
Changing the Preferred Gateway
If your site has multiple IPeXchange gateways, the IPeXchange client software performs load sharing by picking an IPeXchange gateway from among those available. However, you can specify a client's preferred gateway---the IPeXchange gateway to which the client tries to connect at startup. Specifying preferred gateways can be useful for dividing the user community---for example, for administrative or accounting purposes. If the preferred gateway is unavailable, the client connects to any available IPeXchange gateway.
To specify a preferred gateway, do one of the following:
To edit the WIN.INI file, perform the following steps:
Modifying the Command Line or Target Property
If a Windows icon represents an executable program, its Properties window includes information that tells Windows how to start the program. This information is called the command line property in Windows 3.1 and Windows for Workgroups and the target property in Windows 95.
The following command line or target property starts ipexclnt.exe:
gateway-name specifies the client's preferred IPeXchange gateway.
For example, the following property causes the client to try to connect with the gateway boojum:
If boojum is unavailable, the client connects to any available gateway.
To change the preferred gateway, edit the properties of the IPeXchange item. When the IPeXchange client starts, it writes gateway-name into the win.ini file as the new value for the preferred gateway.
Sometimes a client might want to disconnect from one IPeXchange gateway and connect to another. For instance, your network could be configured so that one IPeXchange gateway provides Internet access and another provides internal TCP/IP access, and a client might want to switch between the two.
The Gateways menu in the IPeXchange client window displays a list of known IPeXchange gateways. A check mark indicates the gateway to which the client is currently connected. The client software periodically refreshes the list, adding names as gateway SAP messages arrive, and removing the names of servers that stop sending SAP messages.
To change a client's current gateway, perform the following steps:
When a client changes the current gateway, the new gateway automatically becomes the preferred gateway. The client software writes the IPeXchange gateway name into the win.ini file and attempts to connect to that gateway the next time it starts.
Displaying the Status of an IPeXchange Client
The IPeXchange window for the IPeXchange client includes a Status menu item. This option provides information about the IPeXchange client or gateway software and its current connections.
When you first select the Status menu item, the display is static---status appears on the screen once and does not refresh itself.
Select the Status menu item again to start a low-level tracing program that shows the transmission of SAP messages and routing information packet (RIP) messages. Generating a trace can be helpful if you need to troubleshoot a problem.
To stop the trace program, select the Status menu item again. An updated static display appears.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
Frame Ethernet_802.3
Frame Ethernet_802.2
Frame Ethernet_II
Frame Ethernet_SNAP
Protocol IPX 0 Ethernet_802.3
Protocol IPX E0 Ethernet_802.2
Protocol IPX 8137 Ethernet_II
Protocol IPX 8137 Ethernet_SNAP
NET.CFG Format
PROTOCOL.INI Format
Protocol IPX 0 Ethernet_802.3
FRAME=ETHERNET_802.3
Protocol IPX E0 Ethernet_802.2
FRAME=ETHERNET_802.2
Protocol IPX 8137 Ethernet_II
FRAME=ETHERNET_II
Protocol IPX 8137 Ethernet_SNAP
FRAME=ETHERNET_SNAP
![]()
device=vipx.386
TimerCriticalSection=10000
[vipx]
VipxMappingPages=20
VipxFailOverSizedPackets=ON
[IPeXchange Client]
Preferred Gateway=Any
device=vipx.386
TimerCriticalSection=10000
[vipx]
VipxMappingPages=20
VipxFailOverSizedPackets=ON
[IPeXchange Client]
Preferred Gateway=gateway-name
Client Connected to IPeX-gateway
[IPeXchange Client]
Preferred Gateway = Any
ipexclnt -g boojum
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()