|
|
Upload Prerequisites Procedures and Setup
This chapter provides the following information to enable you to plan and upload Native Service Point software to your NetView or NetMaster:
Use an IBM PC or compatible to upload CiscoWorks Blue Native Service Point software from a PC running IBM OS/2 or DOS to either an MVS, VM, or VSE host. This section describes the software and hardware requirements for the PC used to upload the CiscoWorks Blue Native Service Point software and the mainframe host requirements.
You must have the following operating system and software on your PC to upload Native Service Point software to your mainframe host.
To upload Native Service Point software to your mainframe host, your PC must meet the following minimum hardware requirements:
To use Native Service Point in your network, your mainframe host computer and Cisco routers must meet the following requirements:
Before you upload Native Service Point software to your MVS, VM, or VSE host, the following prerequisites must be met:
If these prerequisites are not met, you can still upload the Native Service Point software to a host, but you will not be able to view, access, or edit any router configurations.
To access a Cisco router by using Native Service Point from your NetView console, the Cisco router must be connected to the VTAM host. The MVS, VSE, or VM programmer should define the service point name (SPname) for each Cisco router in the VTAM configuration.
For each router in your network, add the following lines to your VTAM configuration, making sure you substitute the router name, IDBLK, and IDNUM variables for each router:
SWDRTRS VBUILD TYPE=SWNET ROUTER_NAME PU ADDR=01 x PUTYPE=2 x IDBLK=idblock number, x IDNUM=id number, x DISCNT=(NO), x ISTATUS=ACTIVE, x IRETRY=YES, x MAXOUT=7, x PASSLIM=5, x MAXPATH=4 SERVICE_POINT_NAME LU LOCADDR=locaddr,ISTATUS=status
Following is the syntax description for the router name, IDBLK, and IDNUM variables:
| router name | The service point name for the router. |
| idblock number | The idblock number that will be sent to the host during connection establishment. The block number 05D is recommended for routers. The XID value is 8 hexadecimal digits that include both Block and ID numbers. For example, if the XID value is 05D00001, the Block number is 05D and the ID number is 00001. |
| id number | The ID number for the router. |
Following is an example of a VTAM configuration for a router called glendusk with a service point name glendusk.
SWDRTRS VBUILD TYPE=SWNET x GLENDUSK PU ADDR=01 X x PUTYPE=2 X x IDBLK=05D x IDNUM=BB000 x DISCNT=(NO) x ISTATUS=ACTIVE x IRETRY=YES x MAXOUT=7 x PASSLIM=5 x MAXPATH=4 x GLENDUSK LU LOCADDR=02, ISTATUS=INACTIVE x
Your Cisco routers must be configured and connected to your network according to the instructions provided in the Cisco documentation. For detailed information about configuring Cisco routers, refer to the documentation list in the About This Guide section in this manual.
To access your Cisco routers by using Native Service Point, the following requirements should be met.
Your router's configuration must have the following specified:
In addition, your router's configuration must contain the commands shown in the section Minimum Router Configuration for Using Native Service Point.
If your routers are attached remotely to another router and require RSRB definitions, also use the additional sna host commands for RSRB that are described later in this chapter.
You can use Native Service Point to access your routers if each router's configuration contains the following commands:
sna enable-host [lsap lsap-addr]
sna start [resource-name]
These commands are sufficient i f a router is directly connected to the host Token Ring and the router PU sends the XID directly to the Token Ring in a Source Route Bridging (SRB) frame. RSRB definitions are not used in this situation. See Figure 1-1 for an example.
Figure 1-1 Router Attached to a Host Token Ring
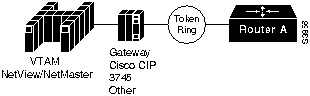
Following is the syntax description for the sna host command:
| host-name | The specified SNA host. |
| xid-snd xid | The XID that will be sent to the host during connection establishment. The XID value is 8 hexadecimal digits and include both Block and ID numbers. For example, if the XID value is 05D00001, the Block number is 05D and the ID number is 00001. |
| rmac mac | The MAC address of the remote gateway, for example CIP or 3745.. |
| rsap remote-sap | [Optional] Specifies the SAP address used by the SNA to establish connection with the remote host. |
| lsap local-sap | [Optional] Specifies the the local SAP address used by the SNA to establish connection with the remote host. |
| focalpoint | Specifies that the host link will be used for the focal point support. |
The following command defines a link to an SNA host:
sna host CNM01 xid-snd 05dbb000 rmac 4001.3745.1088 rsap 4 lsap 4 focalpoint
Following is the syntax description for the sna enable-host command:
| lsap | [Optional] Activate a local SAP as an upstream SAP, for both receiving connectIn attempts and for starting connectOut attempts. |
| local-sap | Local SAP. The default is 12. |
The following example enables SNA on the interface and specifies that the local SAP 4 will be used for the session to the host:
sna enable-host lsap 4
Following is the syntax description for the sna start command:
| resource-name | The name of a host defined in a sna host command. |
The following example initiates a connection to CNM01:
sna start CNM01
This section explains sna host commands you add to your router's configuration if the following situation exists:
Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3 show the physical and logical views of the router PUs attached to a remote Token Ring.
Figure 1-2 Physical View of Router PU Attached to a Remote Token Ring
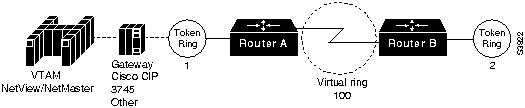
Figure 1-3 Logical View of Router Attached to a Remote Token Ring
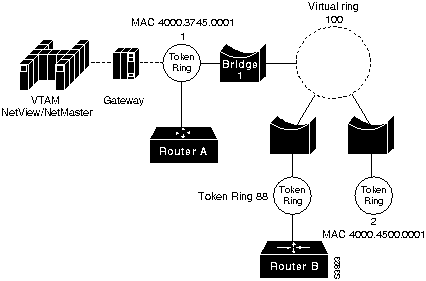
Router A's configuration contains the following router commands:
sna enable-host [lsap lsap-addr]
sna start [resource-name]
Router B's configuration contains the following router commands:
sna rsrb enable-pu [lsap local-sap]
The following example shows the defintion for a SNA host with CMP? and a connection to be established across an RSRB link:
sna rsrb 88 1 100 4000.4500.0001 sna rsrb enable-host lsap 10 sna host ibm3745 xid-snd 06500001 rmac 40 00.3745.0001 lsap 10
Following is the syntax description for the sna host command:
| host-name | The specified SNA host. |
| xid-snd xid | The XID that will be sent to the host during connection establishment. The XID value is 8 hexadecimal digits that include both Block and ID numbers. For example, if the XID value is 05D00001, the Block number is 05D and the ID number is 00001. |
| rmac remote mac | The MAC address of the remote host gateway. |
| rsap rsap-addr | [Optional] Specifies the SAP address used by the SNA to establish connection with the remote host. The default is 4. |
| lsap local-sap | [Optional] Specifies the the local SAP address used by the SNA to establish connection with the remote host. |
| focalpoint | Specifies the host link that will be used for the focal point support. |
Verify that routers in your network can be viewed from NetView. Use the following command at any command input prompt:
The router's status should display as ACTIV.
Verify that the routers in your network can be viewed from NetMaster. Use the following command at any command input prompt:
The router's status should display as ACTIV.
This section provides instructions on uploading Native Service Point for NetView and NetMaster:
Follow these instructions to upload Native Service Point CLISTs, panels, and .SEQ files for NetView to an MVS host.
C:\ a:
mvsuload drive host_session_identifier
mvsuload a a
SEND A:CISCOSCL.SEQ x:CISCOSCL.SEQ LRECL(80) RECFM(F) SEND A:CISCOSPL.SEQ x:CISCOSPL.SEQ LRECL(80) RECFM(F)
prefix.cisco*
Dataset Contents prefix CISCOSCL.SEQ CLISTS/ROUTINES prefix CISCOSPL.SEQ Panels
receive inds(/)
=
Dataset Contents prefix.CISCO.CLISTS CLISTS/ROUTINES prefix.CISCO.PANELS Panels prefix.CISCOSCL.SEQ Sequential Dataset prefix.CISCOSPL.SEQ Sequential Dataset
You are now ready to build a list of routers for accessibility through NetView and set up the automatic update of routers' status. After those steps are completed, the NetView operator is now ready to use Native Service Point to access, view, edit and manage the routers and their configurations from within NetView.
Follow these instructions to upload Native Service Point CLISTs, panels, and .SEQ files for NetView to a VM host.
a:
mvuload drive host_session_identifier
mvuload a a
You are now ready to build a list of routers for accessibility through NetView and set up the automatic update of routers' status. After those steps are completed, the NetView operator is now ready to use Native Service Point to access, view, edit and manage the routers and their configurations from within NetView.
Follow these instructions to upload Native Service Point CLISTs and panels for NetView to a VM host.
vseuload drive host_session_identifier
You are now ready to build a list of routers for accessibility through NetView and set up the automatic update of routers' status. After those steps are completed, the NetView operator is now ready to use Native Service Point to access, view, edit and manage the routers and their configurations from within NetView.
Follow these instructions to upload Native Service Point NCLs, panels, and .SEQ files for NetMaster to an MVS host. You will need the assistance of your MVS programmer to complete this procedure by moving the panels to the user's PANEL (CNMPNL1) library and renaming the $NWRUNCM NCL procedure as $NWRUNCX.
a:
mvslodn drive host_session_identifier
mvslodn a a
SEND A:CISCONCL.SEQ x:CISCONCL.SEQ LRECL(80) RECFM(F) SEND A:CISCONPL.SEQ x:CISCONPL.SEQ LRECL(80) RECFM(F)
prefix.cisco*
Dataset Contents prefix CISCONCL.SEQ prefix CISCONPL.SEQ
receive inds(/)
=
Dataset Contents prefix.CISCO.NCLPROCS prefix.CISCO.PNLBCKUP prefix.CISCONCL.SEQ prefix.CISCONPL.SEQ
//PNLS DD DSN=NETMASTR.V3101.PANLUSR, DISP=SHR //PNLSIN DD DSN=xxxxx.CISCO.PNLBCKUP, DISP=OLD
>>CHANGE 00010000
-* NAME : $NWRUNCM EWR0XX *00100000
>>TO 00100100
-* NAME : $NWRUNCX EWR0XX *00101000
-* *00110000
>>ADD 00120000
-* Modify DATE : 29-JUN-1995 *00231000
-* SHRVARS=(RTRHCOPY,SV32TXT,SYSMSG) *00232000
*00233000
>>ADD 01161000
-* JUL 95 Modified. Add RTRHCOPY to suppress output
H.Liberty*01170000
>>BEFORE 01170100
-* JUN 92 CREATION. B.YUNG *01171000
01210000
>>CHANGE (REQUIRED) 01220000
&CONTROL UCASE NOSHRVARS 01280000
>>TO 01280100
&CONTROL NOUCASE NOSHRVARS (Need lower case for router)
01280200
01280300
>>ADD 01300000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 03920000
>>BEFORE 03921000
&WRITE DATA=EW0019 &WK1 03930000
>>ADD 03940000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 04190000
>>BEFORE 04191000
&WRITE DATA=EW0020 &WK -* WRITE THE HIERARCHY 04200000
04201000
>>ADD 04210000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 04300000
>>BEFORE 04301000
&WRITE DATA=EW0020 &WK -* WRITE THE HIERARCHY 04310000
>>ADD 04320000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 04540000
>>BEFORE 04541000
&WRITE LOG=YES DATA=EWR003 MESSAGE TEXT 04550000
04560000
>>ADD 04570000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 04800000
>>BEFORE 04801000
&WRITE LOG=YES DATA=EWR004 &WK4 04810000
04811000
>>ADD 04820000
&IF .&RTRHCOPY NE .NO &THEN + -* Modified by HJL 05111000
>>BEFORE 05111100
&WRITE LOG=YES DATA=EW0018 *END* -* DISPLAY TERMINATION MSG
05112000
?
You are now ready to build a list of routers for accessibility through NetMaster and set up the automatic update of routers' status. After those steps are completed, the NetMaster operator is now ready to use Native Service Point to access, view, edit and manage the routers and their configurations from within NetMaster.
To view, access, and manage all of the routers in your network from NetView or NetMaster, build a list of accessible routers by editing the RTRSINIT CLIST (NetView) or RTRSINIT procedure (NetMaster).
Follow this procedure to build a list of routers for the NetView version of Native Service Point.
&RTRLSTn = 'SPname [domain] [host name]'
&MAXNUM = number_of_routers
&MAXMUM = 55
Follow this procedure to build a list of routers for the NetMaster version of Native Service Point.
&RTRLSTn = &STR SPname [domain] [host name]
&MAXNUM = number_of_routers
&MAXNUM = 55
To enable Native Service Point to automatically obtain and provide an updated status of your routers, the domains where they are located, and information of any operators that are logged in to the routers, your programmer needs to add certain commands to the NetView automation table or the NetMaster MSGPROC procedure.
If you use NetView, your programmer should complete this procedure to ensure that the latest status about your routers is available to you in Native Service Point.
IF MSGID='IST5901' & TEXT=MESSAGE THEN EXEC (CMD(`RTR590E' MESSAGE)) DISPLAY(Y) NETLOG(Y);
IF MSGID='IST5901' & TEXT=MESSAGE THEN EXEC (CMD(`RTR590E' MESSAGE)) DISPLAY(Y) NETLOG(Y) CONTINUE(Y);$
If you use NetMaster, your programmer should complete this procedure to ensure that the latest status about your routers is available to you in Native Service Point.
.M#IST590I .M#5D90I &NODE = &STR &5 -* SAVE THE NODE Name &NODECONN = &STR &2 -* GET THE NODE Status RTR590E &NODE &NODECONN -* Call Update status &GOTO .LOOP -* NEXT MESSAGE
&NODE = &STR &5 -* SAVE THE NODE Name &NODECONN = &STR &2 -* GET THE NODE Status RTR590E &NODE &NODECONN -* Call Update status
|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.