Since the release of Configuration Builder 1.1, several features have been added. Configuration Builder 2.0 allows you to configure Cisco hubs and access servers as well as routers.
Note For detailed information on all Configuration Builder features, see the context-sensitive online help system. The comprehensive online help system provides procedures, overview material, and links to related information.
Configuration Builder Files
Configuration Builder generates and stores these files in the \data directory:
- *.cdf --- configuration files (binary)
- *.cfg--- configuration files (text)
- *.cbk --- configuration backup files
- snmphost.chl--- SNMP host names file
- zones.apt--- AppleTalk zones file
Configuration Builder generates and stores these files in the \data\snapin directory:
- *.aal --- AppleTalk access lists
- *.ial --- IP access lists
- *.nal --- IPX access lists
- *.nsl --- IPX SAP filter lists
- *.pql--- Priority queuing lists
The \data\srb directory contains files with the extension *.srb. These files define remote source-route bridging (SRB) groups.
The \data\sdlc directory contains files with the extension *.s. These files define synchronous data-link control (SDLC) tunnel groups.
 Caution If you create additional Configuration Builder icons through the Windows Program Manager, be sure to include the directory name in which you installed Configuration Builder 2.0 and the ciscocb.exe command. The working directory must specify the \data subdirectory.
Caution If you create additional Configuration Builder icons through the Windows Program Manager, be sure to include the directory name in which you installed Configuration Builder 2.0 and the ciscocb.exe command. The working directory must specify the \data subdirectory.
Configuration Builder Main Window
The Configuration Builder main window is illustrated in Figure 2-1. The number and type of network icons displayed in the main window will vary according to your network configuration.
Figure 2-1 : Configuration Builder Main Window
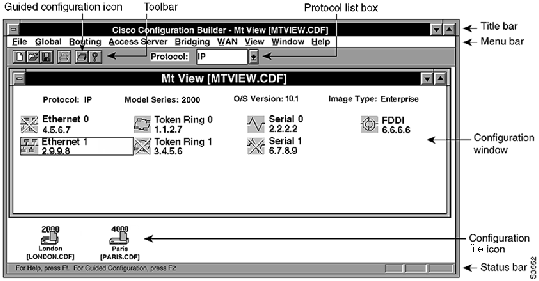
The main window consists of the following elements:
- Title bar---Displays the application name and the name of the currently active router configuration. The active configuration name includes the router host name, followed by the filename in brackets. In Figure 2-1, the host name is Mt View, and the filename is MTVIEW.CDF.
- Menu bar---Provides access to all Configuration Builder dialog boxes. Table 2-1 through Table 2-9 list and explain the options under each menu.
- Toolbar---Provides the Guided Configuration icon in addition to the standard create file, open file, save file, print file, and help icons. You can use the Guided Configuration icon or the F2 key to activate the guided configuration.
- Protocol list box---Used with configuration windows, it lets you select a routing protocol. The configuration window indicates whether interfaces are enabled for the specified routing protocol. In Figure 2-1, IP is the selected protocol. You can double-click on any interface icon to open the IP Routing Configuration window.
- Configuration windows---Appear within the main window and indicate the router model, Cisco software version and image type, and interface status information.
- In Figure 2-1, the Mt View configuration is for a Cisco 3000 router running Software Release 10.1. Ethernet 1, Token Ring 0, Serial 0, and FDDI 0 are IPenabled. Serial 1, Ethernet 0, and Token Ring 1 are not IP-enabled as indicated by the yellow cross-out over the interface icon. (A red cross-out over an interface icon would indicate that an interface has been administratively shut down.)
- Configuration file icons---Displayed for any open configuration window that is iconized. In Figure 2-1, the London and Paris configurations are iconized.
- Status bar---Provides a brief description of the currently selected menu item.
Table 2-1 : Configuration Builder File Menu Items
| New
|
Create a new configuration file.
|
| Open
|
Open an existing file.
|
| Close
|
Close an existing file.
|
| Save
|
Save changes to a file.
|
| Save Backup
|
Create a backup of a configuration file.
|
| Save As Text
|
Save a configuration file as a text file so it can be edited with a word processor or stored on a network server.
|
| Delete
|
Delete a configuration file.
|
| Communication Timeouts
|
Specify the timeouts to be used for transfer of data from Configuration Builder to the router.
|
| Send
|
Send a configuration file to a local or remote router.
|
| Print
|
Print a configuration file.
|
| Print Setup
|
Set up printer parameters.
|
| Exit
|
Exit Configuration Builder.
|
Table 2-2 : Configuration Builder Global Menu Items
| Guided Configuration
|
Step through the guided configuration.
|
| Basic
|
Set basic system parameters, including host names, passwords, and banner.
|
| SNMP
|
Specify Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) parameters for network management data, set community strings, and restrict SNMP access to the router.
|
| Priority Queuing
|
Create new priority output queuing lists or import snap-in lists.
|
| Modify Interfaces
|
Add or delete router interfaces and specify router type, software version, and image type. Specify device interfaces and lines. Change the sequence of the guided configuration.
|
| Add Commands
|
Configure advanced features and features added in later Cisco IOS releases.
|
| Hub
|
Enable hub configuration features.
|
Table 2-3 : Configuration Builder Routing Menu Options
IP:
-Configuration -Routing Protocols
-Access Lists
|
-Configure primary and secondary IP addresses.
-Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), and/or Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
-Create new access lists or import snap-in lists.
|
DECnet:
-Configuration -Options
|
-Configure DECnet areas and nodes and assign costs to interfaces
-Determine minimum and maximum routing costs.
|
AppleTalk:
-Configuration -Distribute-Out Filters
|
-Configure AppleTalk addresses, cable ranges, and zones
-Create access lists for filtering AppleTalk packets.
|
IPX:
-Configuration
-Access Lists
-SAP Filters
|
-Configure IPX addresses.
-Create new access lists or import snap-in lists.
-Create new SAP filters or import snapin lists.
|
| XNS
|
Configure Xerox Network Systems (XNS) addresses.
|
| Banyan VINES
|
Configure Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES) addresses.
|
| ISO CLNS (OSI)
|
Configure International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Service (CLNS) addresses and areas.
|
Table 2-4 : Configuration Builder Access Server Menu Options
Line Characteristics:
-Chat Script Manager
-Line Configuration
|
-Configure modem or login chat scripts
-Configure line characteristics for TTY and auxiliary lines.
|
Remote Node:
-Extended BootP Manager
-ARA
-Line Configuration
|
-Configure an access server for BootP to allow SLIP and PPP requests from clients.
-Configure AppleTalk Remote Access (ARA).
-Configure remote nodes for TTY and auxiliary lines.
|
Terminal Services:
-LAT Manager
-XRemote Manager
-Line Configuration
|
-Configure Local Area Transport (LAT)
-Configure XRemote protocol.
-Configure terminal services for console, TTY, auxiliary, and virtual terminal lines.
|
Security:
-Local User Name Manager
-TACACS Manager
-Line Configuration
|
-Assign user names and passwords.
-Configure login method, line passwords, PPP authentication, and assign IP access lists.
-Configure security for console, TTY, auxiliary, and virtual terminal lines.
|
Dial-on-Demand:
-Dialer Rotary Group
-IP
-IPX
|
-Configure the dialer rotary group.
-Configure dial-on-demand routing (DDR) for IP.
-Configure DDR for IPX.
|
| Protocol Translation
|
Configuration protocol translation features.
|
Table 2-5 : Configuration Builder Bridging Menu Items
Transparent Bridging:
-Configuration
-Bridge Groups
|
-Configure transparent bridging.
-Create bridge groups and set spanning-tree and circuit options.
|
Source-Route:
-Simple
-Remote
|
- Configure simple source-route bridging (SRB) options.
- Configure remote SRB options. Remote source-route bridging provides multiple router configuration capability. That is, equivalent statements in the configuration files of devices in the same virtual ring are automatically updated.
|
| SR/TLB
|
Configure source-route translational bridging (SR/TLB).
|
Table 2-6 : Configuration Builder WAN Menu Items
| Wide-Area Protocols
|
Configure wide-area network (WAN) protocols, including HighLevel Data Link Control (HDLC), Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), X.25, Frame Relay, and Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS).
|
| Dial-on-Demand
|
Configure dial-on-demand routing (DDR) destination subnet, subnet mask, telephone numbers, destination router IP address, and timers.
|
| Dial Backup
|
Configure dial backup interfaces and delay options.
|
| SDLC Transport
|
Configure devices for SDLC transport, a subset of serial tunneling (STUN). Provides multiple router configuration capability. That is, equivalent statements in the configuration files of other SDLC devices are automatically updated.
|
Table 2-7 : Configuration Builder View Menu Items
| By Protocol
|
Display configuration commands grouped by protocol type.
|
| By Interface
|
Display configuration commands grouped by interface.
|
| Configuration
|
Display the configuration as a text file.
|
| Toolbar
|
Display or hide the toolbar.
|
| Status Bar
|
Display or hide the status bar.
|
| Expert Mode
|
Select expert mode to enable an additional path for configuring global access server features.
|
Table 2-8 : Configuration Builder Window Menu Items
| Cascade
|
Resize and layer windows so that each title bar is visible.
|
| Tile
|
Resize and arrange windows side by side.
|
| Arrange Icons
|
Evenly arrange icons.
|
| file selection
|
Select a previously opened configuration file.
|
Table 2-9 : Configuration Builder Help Menu Items
| Contents
|
Open the Configuration Builder help system table of contents.
|
| Cisco Support Information
|
Find out how to contact Cisco Systems for product support and how to obtain additional documentation.
|
| Using Help
|
Learn how to use the online help system.
|
| About Configuration Builder
|
Display Configuration Builder software release and copyright information.
|
Show Commands
Show Commands allows you to quickly display detailed system and protocol information for Cisco devices without requiring you to remember complicated command-line language or syntax.
What's in this Release
You can display the following system information for Cisco devices:
- Software version
- Device configuration (running memory and nonvolatile random-access memory [NVRAM])
- Controller status
- Buffer status
- Device voltage and temperature status
- Flash memory status
You can display detailed information about Cisco device interfaces that are configured to support the following protocols:
- IP
- IPX
- AppleTalk
- DECnet
- CLNS
- Frame Relay
- X.25
- VINES
Note For detailed information on all Show Commands features, see the context-sensitive online help system. The comprehensive online help system provides procedures, overview material, and links to related information.
Show Commands Main Window
The Show Commands main window is illustrated in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 : Show Commands Main Window
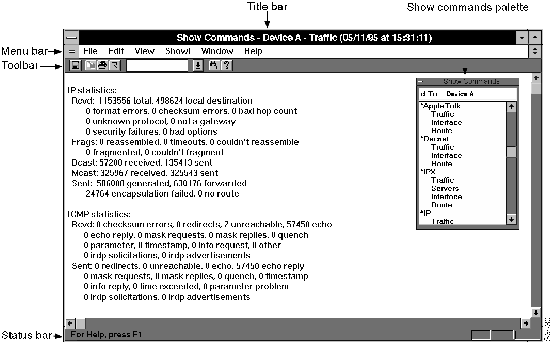
The Show Commands main window consists of the following elements:
- Title bar---Displays the Show Commands application name, the active device name, and the name of the current show command window.
- Menu bar---Provides access to all Show Commands dialog boxes. Table 2-10 through Table 2-15 list and explain the items under each menu.
- Toolbar---Provides save file, copy text, print file, window refresh, enter text for searching, find entered text, and help contents icons.
- Status bar---Provides a brief description of the currently selected menu item.
- Show Commands palette---Floating window from which you can access all Show Commands options.
Table 2-10 : Show Commands File Menu Items
| Close
|
Closes Show Commands window.
|
| Save
|
Save changes to a file.
|
| Save As
|
Save Show Commands output to a new filename.
|
| Connect
|
Connect to a specific device.
|
| Print
|
Send a Show Commands screen display to a printer.
|
| Print Preview
|
View the file before printing. Zoom in or out and scan pages.
|
| Print Setup
|
Set printing options.
|
| Exit
|
Exit the Show Commands application.
|
Table 2-11 : Show Commands Edit Menu Items
| Copy
|
Copy text from an active window.
|
| Select All
|
Select all text within an active window.
|
| Find
|
Find a keyword within an active window.
|
Table 2-12 : Show Commands View Menu Items
| Toolbar
|
Display or hide the toolbar.
|
| Status Bar
|
Display or hide the status bar.
|
| Show Command Palette
|
Display the Show Commands Palette floating window.
|
Table 2-13 : Show Commands Show! Menu Items
| Show!
|
Use the Show! command to display the Show Commands window. From the Show Commands window, execute and display output from a specific show command.
|
Table 2-14 : Show Commands Window Menu Items
| Cascade
|
Resize and layer windows so that each title bar is visible.
|
| Tile
|
Resize and arrange windows side by side.
|
| Arrange Icons
|
Evenly arrange icons.
|
| Close All
|
Close all open Show Commands windows.
|
| Refresh
|
Refresh the active Show Commands window. The time and date are updated.
|
| window selection
|
Select a previously opened Show Commands window.
|
Table 2-15 : Show Commands Help Menu Items
| Contents
|
Open the Show Commands help system table of contents.
|
| Help for Current Show Command
|
Open the help window specific to the active show command window.
|
| Cisco Support Information
|
Find out how to contact Cisco Systems for product support and how to obtain additional documentation.
|
| Using Help
|
Learn how to use the online help system.
|
| About Show Commands
|
Display Show Commands software release and copyright information.
|
Health Monitor
Health Monitor is a dynamic fault and performance management tool that provides real-time statistics on device characteristics, interface status and utilization, and protocol utilization.
Health Monitor allows you to customize feedback on device and interface status via settings in the Preferences dialog box:
- Choose fatal and warning thresholds for CPU load and interface types.
- Fatal and warning indications are provided by color changes. Color indications include:
- Green (up)
- Yellow (warning)
- Red (fatal)
- Color indications are provided within the IfErrors, IfUtilization, IfStatus, and Environment tabs. And, for the overall health of a device, color indication is provided within the Health Monitor application icon.
- Select polling frequency value to control when you receive device and interface feedback.
- Set the no-response timeout value to control the duration of time Health Monitor will wait for a reply from a monitored device.
- Sort interfaces by status or media type.
What's in this Release
Health Monitor provides the following device and interface information:
- Provides device name, type, Cisco IOS version, location, and device contact information. Lists total and available random access memory (RAM), flash memory, and nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM). Also provides a reason for the last restart of the device.
- Graphs interface error rates and provides warning and fatal threshold color indications for interface error rates.
- Graphs interface utilization and provides warning and fatal threshold color indications for interface utilization.
- Graphs number of bytes per protocol that an interface has sent or received. Provides interface status by color indication: up (green), test (magenta), dormant (cyan)---waiting for an external event, administratively down (brown), and operational failure (red).
- Graphs number of packets per protocol that the device has forwarded.
- Graphs device CPU utilization in 5-second, 1-minute, and 5-minute intervals.
- Environmental card status (Cisco 7000 series and AGS+ only)
- Depicts air temperature and power supply voltage readings for a device. Provides warning and fatal threshold color indications for these readings.
Note For detailed information on all Health Monitor features, see the context-sensitive online help system. The comprehensive online help system provides procedures, overview material, and links to related information.
Health Monitor Main Window
The Health Monitor main window is illustrated in Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3 : Health Monitor Main Window
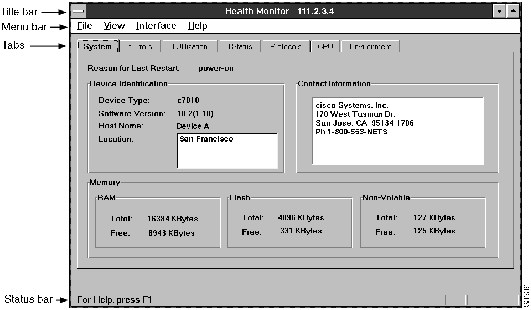
The Health Monitor main window consists of the following elements:
- Title bar---Provides the Health Monitor application name and the name of the current connected device.
- Menu bar---Provides access to all Health Monitor dialog boxes. Table 2-16 through Table 2-19 list and explain the items under each menu.
- Tabs---Provide access to all Health Monitor tabs. See Table 2-20.
- Status bar---Provides a brief description of the currently selected menu item.
Table 2-16 : Health Monitor File Menu Items
| Connect
|
Connect to a specific device.
|
| Preferences
|
Set threshold value, interface sorting, polling frequency, and timeout preferences.
|
| Exit
|
Exit the Health Monitor application.
|
Table 2-17 : Health Monitor View Menu Items
| Status Bar
|
Display or hide the status bar.
|
Table 2-18 : Health Monitor Interface Menu Items
| Utilization
|
View interface utilization.
|
| Protocols
|
Determine interface protocol usage.
|
| Errors
|
View interface error rates.
|
| Show
|
View show interface command statistics for an interface.
|
Table 2-19 : Health Monitor Help Menu Items
| Contents
|
Open the Health Monitor help system table of contents.
|
| Help on Current Tab
|
Open the help window specific to the active Health Monitor tab.
|
| Cisco Support Information
|
Find out how to contact Cisco Systems for product support and how to obtain additional documentation.
|
| Using Help
|
Learn how to use the online help system.
|
| About Health Monitor
|
Display Health Monitor software release and copyright information.
|
Table 2-20 : Health Monitor Tabs
| System
|
View information on restarts, device identification, contact information, and memory usage.
|
| IfErrors
|
View interface error rates.
|
| IfUtilization
|
View interface utilization.
|
| IfStatus
|
Determine interface status (up, down, dormant, failure, test). Determine interface protocol usage.
|
| Protocols
|
View traffic forwarded per protocol for a device.
|
| CPU
|
Measure the device CPU load.
|
| Environment
|
Check device temperature and power supply voltage.
|
CiscoView
CiscoView provides a physical view of a device's back panel with real-time status indicated through message feedback in the status bar area and through changes in port colors. See the section "CiscoView Main Window" later in this chapter for more details.
You can select cards and ports and instantly obtain system information, device characteristics, interface statistics, configuration settings, and real-time operational statistics.
What's in this Release
CiscoView provides the following features:
- View of device back panel providing:
- Device type and operational status
- System information (Cisco IOS version and CPU utilization)
- Card types, number, and status
- Port types, number, and status
- Port reset capability
- Launch points from selected CiscoView devices, interfaces, and ports to the main window of these CiscoWorks for Windows applications:
- Show Commands
- Health Monitor
- Configuration Builder
Note For detailed information on all CiscoView features, see the context-sensitive online help system. The comprehensive online help system provides procedures, overview material, and links to related information.
CiscoView Main Window
The CiscoView main window is illustrated in Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4 : CiscoView Main Window
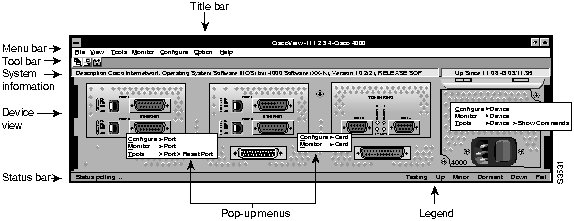
The main window consists of the following elements:
- Title bar---provides the CiscoView application name and the name of the currently connected device.
- Menu bar---Provides access to all CiscoView dialog boxes. Table 2-21 through Table 2-27 list and explain the items under each menu.
Note Menu items may vary slightly depending upon device type and interface/port configuration.
- Toolbar---Provides launch points for Health Monitor, Configuration Builder, and Show Commands applications.
- Device view---provides a view of the device's back panel.
- System information---Provides a brief description of the device type and the Cisco IOS version.
- Status bar---Provides a brief description of the currently selected device, interface, or port and provides ongoing operational status, including polling and error message information.
- Legend---Provides port status as follows: up (green), testing (magenta), minor alarm (yellow), dormant (cyan)---the port is waiting for an external event (such as having packets to transmit or dialing a remote site), administratively down (brown), and operational failure (red).
- Pop-up menus---launch Configuration Builder, Health Monitor, and Show Commands and open the main windows for these applications. To access the pop-up menus, press the right mouse button over devices, cards, or ports. From the device back panel, you can launch Configuration Builder, Health Monitor, and Show Commands applications. From specified interface cards and their ports, you can launch Configuration Builder and Health Monitor. From auxiliary and console ports, you can launch Configuration Builder.
Table 2-21 : CiscoView File Menu Items
| Open Device
|
Display the back panel of a new device.
|
| Print
|
Print the back panel display.
|
| Printer Setup
|
Set printer options.
|
| device selection
|
Select a previously opened device.
|
| Exit
|
Exit CiscoView
|
Table 2-22 : CiscoView View Menu Items
| Refresh
|
Refresh the current display.
|
| Rear View
|
Display the back panel of a device.
|
Table 2-23 : CiscoView Tools Menu Items
Device
-Show Commands
|
Launch Show Commands application for this device.
|
Port:
--Reset Port
|
Reset this port.
|
Table 2-24 : CIscoView Monitor Menu Items
| Device
|
Open the Health Monitor application for a specific device.
|
| Card
|
Open the Health Monitor application for a specific interface card.
|
| Port
|
Open the Health Monitor application for a specific port.
|
Table 2-25 : CiscoView Configure Menu Items
| Device
|
Open an existing or new Configuration Builder file for a specific device.
|
| Card
|
Open an existing or new Configuration Builder file for a specific interface card.
|
| Port
|
Open an existing or new Configuration Builder file for a specific port.
|
Table 2-26 : CiscoView Option Menu Items
| Show Toolbar
|
Display or hide the toolbar.
|
| Show System Information
|
Display or hide system information.
|
| Show Legend
|
Display or hide the legend.
|
| Device Property
|
Set the read-write community string and polling interval.
|
Table 2-27 : CiscoView Help Menu Items
| Contents
|
Open the CiscoView help system table of contents.
|
| Cisco Support Information
|
Find out how to contact Cisco Systems for product support and how to obtain additional documentation.
|
| Using Help
|
Learn how to use the online help system.
|
| About CiscoView
|
Display CiscoView software release and copyright information.
|
Online Help
Context-sensitive online help provides you with step-by-step instructions on how to use CiscoWorks for Windows applications. The online help system also provides a glossary and keyword search capability.
Dialog Box Help Button
Each dialog box has a Help button. Select the Help button to open a help window describing the purpose of the dialog box and the procedures to complete tasks specific to the dialog box. Links to overview material and related information may also be available, depending on the dialog box information requirements.
F1 Key and Context-Sensitive Help
Select a data-entry field within a Configuration Builder dialog box and then press the F1 key to open a context-sensitive help window with information about the selected field. The Health Monitor and Show Commands applications provide F1 key functionality for general dialog box or tab information only. In CiscoView, press the F1 key while the mouse is positioned over a device to view information about that device type.
Help Window Menu and Button Bars
Each help window has a menu bar and a button bar. The menu bar provides standard MS Windows help functions for printing help topics, copying and pasting text from help topics, making online notes about particular help topics, and placing bookmarks.
The button bar provides the following buttons:
- Contents---Opens the help table of contents. Help topics are highlighted and underlined. Select a help topic to open a help screen specific to the underlined topic. Some topics open popup windows which contain a list of subtopics. Select a help subtopic to open a help screen specific to the underlined subtopic.
- Search---Allows you to open a window in which you can enter keywords to find topics and go directly to help screens on those topics.
- Back---Allows you to move back sequentially to previously opened help screens.
- History---Allows you to see the sequence of help windows you have opened and to jump to any of them.
- Browse---Allows you to browse through sets of related help screens, providing quick access to overviews of particular Configuration Builder help topics.
- Main---Opens a help window that provides a top-level list of help contents with links to help on all applications, including Configuration Builder, Show Commands, Health Monitor and CiscoView. You can keep the top-level help contents open while you are navigating through other help windows.
- Glossary---Opens a help window that provides a list of terms that are arranged in alphabetical order. Select a term to open a pop-up window that gives an explanation of the term. You can keep the glossary window open while you are navigating through other help windows. Popup definitions are also available within most help screens.
Overview and See Also Buttons
Many help windows have Overview and See Also buttons in the help window topic caption area. You can select the Overview button to obtain background information for the procedure described in the current help window. Select See Also to view a list of related topics and to go directly to those topics from the current help window.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()




![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()