
Table of Contents
Workgroup Director User Guide Errata for Release 4.1
Workgroup Director User Guide Errata for Release 4.1
December 22, 1994
This document provides corrections and additional information for the 4.1 version of the Cisco Workgroup Director User Guide publication.
The contents of this errata document are as follows:
- General Issues, page 1
- Corrections to Chapter 2, Installing Workgroup Director on a SPARCstation, page 1
- Corrections to Chapter 3, Installing Workgroup Director on the IBM RS/6000, page 2
- Corrections to Chapter 4, Installing Workgroup Director on HP Workstations, page 4
- Corrections to Chapter 5, Using Workgroup Director, page 4
- Corrections to Appendix B, Hub and Module Windows, page 4
- Corrections to Appendix C, SNMP Windows, page 5
Workgroup Director 4.1 supports all WSC1000, WSC1100, Catalyst, and WSC1400 series hubs. It also supports all Cisco Systems' FDDI/CDDI adapters.
On page 2-1 in the section "Installation Requirements," the amount of disk space required for loading Workgroup Director is incorrect. Change the values to the following:
| SunOS 4.x OPEN LOOK |
2200 kilobytes (KB) |
| SunOS 4.x Motif |
1100 KB |
| Solaris 2.x OPEN LOOK |
2200 KB |
| Solaris 2.x Motif |
2200 KB |
On page 2-2 in the section "Installing Workgroup Director on SunOS 4.x (Solaris 1.x)," change Steps 3 and 4 to read as follows:
- Step 3 Choose the SunOS 4.x Motif or OPEN LOOK installation disk(s) and insert the disk(s) into the SPARCstation floppy disk drive.
- Step 4 Enter tar xvf/dev/rfd0 to copy files from the installation disk(s) to your hard disk. All files are stored in the WGD subdirectory.
On page 2-3, replace the entire text in the section "Installing Workgroup Director on Solaris 2.x (SunOS 5.x)," with the following:
To install the Workgroup Director on your Solaris 2.x, perform the following steps (after you remove any old versions of Workgroup Director):
- Step 1 Choose the Solaris 2 Motif or OPEN LOOK installation disk and insert it into the SPARCstation floppy disk drive.
- Step 2 Enter pkgadd -d /dev/rdiskette.
- Step 3 Enter go.
- The program lists the packages available on the floppy disk and asks which package you want to install.
- Step 4 Enter WGD.
- The program indicates that the package contains scripts that will be executed during the installation process and asks if you want to continue installing the software.
- Step 5 To continue, enter y.
- The installation program lists the files as they are installed and verified. When installation is complete, the message "Installation of Workgroup Director was successful" appears.
- Step 6 Enter e to eject the floppy disk. If the disk does not eject, enter eject /dev/rdiskette.
- Step 7 If you terminated the vold process as part of the Workgroup Director removal procedure, enter /usr/sbin/vold & to restart a new vold process.
- Step 8 Continue with the section "Starting Workgroup Director as a Standalone Application" or "Starting Workgroup Director from a Network Management System."
On page 2-9, replace the entire text in the section "Removing Workgroup Director from Solaris 2.x," with the following:
To remove Workgroup Director from Solaris 2.x, perform the following steps:
- Step 1 Log in to your system as root.
- Step 2 Enter ps to check for the vold process in your system. If you find the vold process, use the kill command to terminate the vold process.
- Step 3 Enter pkginfo WGD to check if Workgroup Director is already installed on your system. If you find a copy of Workgroup Director, enter pkgrm WGD to delete the installed copy.
- The program asks if you want to remove this package.
- Step 4 Enter y.
- The program indicates that the package contains scripts that will be executed during the removal process and asks if you want to continue installing the software.
- Step 5 Enter y to continue.
- The removal program lists the files as they are removed. When the process is finished, the message "Removal of Workgroup Director was successful" appears.
On page 3-1 change the introductory paragraph to read as follows:
This chapter explains how to install Workgroup Director in your IBM RS/6000 and start it as a standalone application or from AIX (3.2.x) NetView/6000 (V2). Included is a step-by-step procedure for removing Workgroup Director from your IBM RS/6000.
On page 3-1 in the section "Installation Requirements," add the following bullet at the end of the bulleted list:
- Have 3300 KB of disk space to load Workgroup Director. Use the df command to check your available disk space.
On page 3-1, replace the entire text in the section "Installing Workgroup Director," with the following:
To install the Workgroup Director software on your IBM RS/6000, perform the following steps:
- Step 1 Log in to your system as root.
- Step 2 Insert the installation disk into the IBM RS/6000 floppy disk drive.
- Step 3 Enter smit to run the SMIT utility.
- Step 4 Select Software Installation & Maintenance.
- Step 5 Select Install/Update Software.
- Step 6 Select Install/Update Selectable Software (Custom Install).
- Step 7 Select Install From All Available Software Packages.
- Step 8 Select List to display a list of available devices.
- Step 9 Select the disk drive from this list to automatically fill in the proper device name in the INPUT device/directory for software field.
- Step 10 Click Do at the bottom left of the window to continue the installation.
- SMIT displays the SMIT screen. You do not need to modify any entries on this screen.
- Step 11 Click Do in the SMIT screen.
- You are prompted to confirm installation of the software.
- Step 12 Click OK.
- A status screen displays copying of the software from the floppy disk. When the installation is completed, the status screen displays "SUCCESS" in the Result column.
- Step 13 Select Exit from the top of the screen.
You have completed installing the Workgroup Director software.
On page 3-5, replace the entire text in the section "Removing Workgroup Director from the IBM RS/6000," with the following:
To remove the Workgroup Director software from your IBM RS/6000, perform the following steps:
- Step 1 Log in to your system as root.
- Step 2 Enter smit to run the SMIT utility.
- Step 3 Select Software Installation & Maintenance.
- Step 4 Select Manage Applied Software (List, Commit, Reject, Remove).
- Step 5 Select Remove Applied Software Products.
- Step 6 Enter WGD.obj in the SOFTWARE name field.
- Step 7 Click Do.
The Workgroup Director software is removed from your IBM RS/6000.
On page 4-1 in the section "Installation Requirements," change the third bullet at the end of the bulleted list to the following text:
- Have 2300 KB of disk space to load Workgroup Director. Use the df command to check your available disk space.
On page 5-2, add the following display of the WSC1400 concentrator to Figure 5-2:
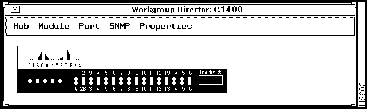
On page 5-3 in the section "LED Displays," change the first bullet to read as follows:
- Click on the ST or Status LED to view the Module (or Adapter) window.
On page 5-4, the information in the section "WSC1000 and WSC1100," applies to WSC1400 also.
On page 5-5, the information in the section "Traffic Meter LEDs (WSC1000 and WSC1100)," applies to WSC1400 also.
On page 5-6, the information in Table 5-5 applies to WSC1400 also.
On page B-2, change the second, third, and fourth bullets to read as follows:
- Power Supply---Displays the rating of the hub primary power supply.
- Power Supply Status---Displays the status of the hub primary power supply.
- Power Supply Errors---Displays the number of errors of the hub primary power supply.
After the fourth bullet, add the following bulleted items:
- Power Supply 2---Displays the rating of the hub secondary power supply.
- Power Supply 2 Status---Displays the status of the hub secondary power supply.
- Power Supply 2 Errors---Displays the number of errors of the hub secondary power supply.
On page B-3 in the section "Module Window," add the following note before Figure B-2:
Note There are three modules in a fully configured WSC1400. Module 1 represents line card 1 located in the lower slot of the chassis. Module 2 represents line card 2 located in the upper slot of the chassis. Module 3 is the motherboard in the chassis.
All three module windows can be accessed from the main Module menu. However, the motherboard module window can also be activated by clicking on the ST or STATUS LED.
On page B-5, change the last bullet to read as follows:
- Reset Module---resets the module, causing it to leave the FDDI ring and reconnect once the module is up. It also resets counters and sends an SNMP trap message to an SNMP trap receiver.
- In the WSC1400 concentrator, the Reset Module field is replaced with an Action field. The Action field has a pull-down menu with the following choices:
- Reset---works the same as Reset Module above.
- Enable---activates the module and connects it to the main module.
- Disable---deactivates the module and disconnects it from the main module.
On page C-11, under the bullet Type, delete the following item:
On page C-33, the FDDI Mac Window displayed in Figure C-15 is an SMT 6.x example. It is not an SMT 7.x example.
On page C-36 the FDDI Mac Window displayed in Figure C-16 is an SMT 6.x example. It is not an SMT 7.x example.
On page C-38, change the first item T Req to read as follows:
- T Req (read/write)---Displays the average token rotation time that the MAC element requests during the Claim Token process. Any change to this parameter causes the ring to go down and up.
- In SMT 7.x, this parameter is read only.
On page C-42, the FDDI Port window in Figure C-18 has two additional fields:
- Module Index
- SMT Port Index
On Page C-42, delete the first two bullets (SMT Index and Port Index), and add the following text to replace them:
- Module Index (R/W)---Displays a unique value for the module where this port is located.
- Port Index(R/W)---Displays a unique value for this port within a module.
- SMT Index(R/O)---Displays a corresponding SMT index for this FDDI port.
- SMT Port Index(R/O)---Displays a corresponding SMT port index for this FDDI port.

Copyright 1988-1995
©
Cisco Systems Inc.

