Step 4 After setting up the domains, add trunks between the junction nodes in the domains.
Summary of Commands
Table 13-1 shows the full name and starting page for the description of each command that is specific to structured networks.
Table 13-1 :
| cnfdmn
|
Configure domain
|
13-3
|
| cnfjct
|
Configure junction node
|
13-4
|
| dspdmns
|
Display domain alarm status
|
13-5
|
| dspjctnw
|
Display junction network
|
13-7
|
| dspnds
|
Display all nodes
|
13-9
|
| dspnwrt
|
Display network route
|
13-11
|
| prtjctnw
|
Print junction network
|
13-13
|
cnfdmn
Assigns a domain number to a node. Enter the cnfdmn command at any node in the domain. This command is used before packet lines are added to the other nodes in the domain. The domain name includes the domain number and appears as D1, D2, D3, etc. The domain name precedes the node name and is separated by a period when packet lines are eventually added to other junction nodes. The following command sequence is typical for configuring a junction node:
- cnfjct y
- cnfname alpha
- cnfdmn 1
The first command configures the node as a junction node. The second command is optional: it names the junction node if it is different from the existing name. The third command assigns a number to the domain. The display screen shows the domain name and node names after the trunks are added from the junction node to the other nodes in the domain. In the current example, the junction node name "alpha" subsequently appears as "D1.alpha."
Full Name
Configure a domain number
Syntax
cnfdmn <domain number>
Related Commands
cnfjct, cnfname
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1 Description
cnfdmn 1
Assign domain number 1 to a node.
Table 13-2 : cnfdmn -- Parameters
| domain number
|
Specifies a number for a domain. The range is 1--8.
|
cnfjct
Specifies a node as a junction node. This command can also delete junction node specification.
Full Name
Configure junction node
Syntax
cnfjct <Y/N>
Related Commands
cnfdmn, cnfname
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1 Description
cnfjct y
Create a junction node.
Example 2 Description
cnfjct n
Delete a junction node.
Table 13-3 : cnfjct -- Parameters
| Y/N
|
Specifies whether junction node status is added to or deleted from a node. "Y" indicates that the node is a junction node. "N" indicates that the node is not a junction node.
|
dspdmns
Displays the alarm state of all domains in a structured network. Execute dspdmns at any node in a structured network. The display shows only whether the alarm is major or minor. The dspnds command indicates nodes with alarms. To investigate alarm conditions on a remote node, use the vt command to start a virtual terminal session on the node. Use the dspalms command to get information on the alarm conditions at the node. The screen display is dynamic, so clearing an alarm after this command is entered changes the screen display.
Full Name
Display domain alarm status
Syntax
dspdmns
Related Commands
dspnds, dspalms, dspcons
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1 Description
dspdmns
Display the alarm status of domains in a structured network.
System Response
D3.delta TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:55 PST
Domain Alarm Junction Nodes
1 alpha zeta
2 beta phaser
3 Minor delta jammer
4 gamma telsa
5
6
7
8
Last Command: dspdmns
Next Command:
dspjctnw
Displays the interconnection of junction nodes. The dspjctnw command can execute at only a junction node. The information consists of the trunk numbers that connect all the junction nodes. For each trunk, the two entries that appear are "from-to" and "to-from."
Full Name
Display junction network
Syntax
dspjctnw [+b | -b] [+z | -z]
Related Commands
dspnw, prtjctnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1 Description
dspjctnw
Display junction network information. The system response in this example is an over-simplified, two-junction network with only one trunk.
System Response
D1.alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:55 PST
Junction Alarm Trunk Trunk Trunk
D2.beta 10-9/D1.alpha
alpha 9-10/D2.beta
Last Command: dspjctnw
Next Command:
Table 13-4 :
| +b
|
Specifies that only lines that support bursty data are displayed.
|
| -b
|
Specifies that only lines that do not support bursty data are displayed.
|
| +z
|
Specifies that only lines that use ZCS encoding are displayed.
|
| -z
|
Specifies that only lines that do not use ZCS encoding are displayed.
|
dspnds
Displays the name, type, and alarm status of all nodes within the domain of the node executing the command. The nodes are grouped by domain, with one domain per display. The remote node alarm status is provided on a per-domain basis. Therefore, a virtual terminal session (vt) on the remote node is necessary to obtain specific alarm information. If a node is in alarm, its name is highlighted, and the alarm type (major/minor) is displayed. A junction node is identified by the word "Yes" printed under the Jct column.
Full Name
Display all nodes
Syntax
dspnds [+n | -p | -d | domain]
Related Commands
dspnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1 Description
dspnds
Display the alarm status of all nodes within the domain
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:42 PST
NodeName Alarm
alpha MAJOR
beta MAJOR
gamma MAJOR
Last Command: dspnds
Next Command:
Table 13-5 : dspnds -- Optional Parameters
| domain number
|
Specifies the domain number (1--8). Only the nodes within the specified domain are displayed.
|
dspnwrt
Displays the end-to-end network route for a connection or group of connections. Enter the dspnwrt command at an end point of the connection. The display screen shows a snapshot of the present route for the connection. If a re-route occurs soon after the information appear, the new route does not appear until dspnwrt is again entered.
Full Name
Display network route
Syntax
dspnwrt <connection number>
Related Commands
dspnw, addcongrp, grpcon
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1 Description
dspnwrt 6.1
Display a network route. The example response illustrates a simplified structured network with a single connection.
System Response
D1.alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:55 PST
Network Route for 6.1 Snapshot
Domain
Local=alpha 10-- 7beta
Junction: D1.beta 9--10D2.gamma
Remote: gamma 9-- 8delta
Last Command: dspnwrt 6.1
Next Command:
The system response is based on the following network topology:
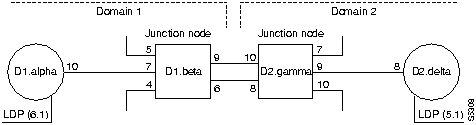
The dspnwrt command must be entered at node D1.alpha or D2.delta (the end points of the connection).
Table 13-6 : dspnwrt -- Optional Parameters
| connection number
|
Specifies the connection end point.
|
prtjctnw
Prints the interconnection of junction nodes. Enter the prtjctnw command at only a junction node. The information consists of the trunk numbers interconnecting all junction nodes. For each trunk, the two entries have the form "from-to" and "to-from." The prtjctnw command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as the dspjctnw command.
Full Name
Print junction network
Syntax
prtjctnw [+b | -b] [+z | -z]
Related Commands
dspnw, dspjctnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Table 13-7 : prtjctnw -- Optional Parameters
| +b
|
Specifies that only lines that support bursty data are displayed.
|
| -b
|
Specifies that only lines that do not support bursty data are displayed.
|
| +z
|
Specifies that only lines that use ZCS encoding are displayed.
|
| -z
|
Specifies that only lines that do not use ZCS encoding are displayed.
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()