To aid in system management, the Catalyst 3900 allows you to obtain a variety of status, statistic, and diagnostic information. This chapter provides information on the following:
For information about setting up a console session, refer to the "Planning for Configuration and Management" chapter.
Note The Catalyst 3900 allows LAN Network Manager LLC frames to flow through the switch. Therefore, communication between LAN Network Manager and existing source-route bridges and controlled access units is maintained. However, some error reporting functions and ring map functions might be lost for the rings attached to the Catalyst 3900.
The Catalyst 3900 allows you to view status information and statistics for individual ports or for the Catalyst 3900 as a whole. This information is displayed on several panels that are accessible from the Statistics Menu.
To access the Statistics Menu, select Statistics on the Main Menu. The Statistics Menu (Figure 6-1) is displayed.
Figure 6-1: Statistics Menu Panel
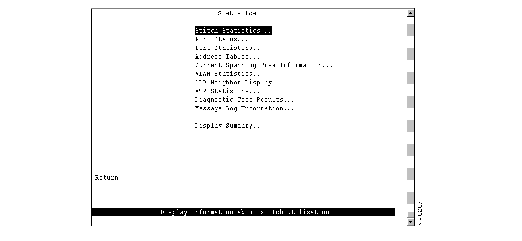
To view operating statistics for the Catalyst 3900, select Switch Statistics on the Statistics Menu. The Switch Statistics panel (Figure 6-2) is displayed. The information on the statistics panels is refreshed approximately every 5 seconds. To reset the information displayed on any of the statistics panels, select Reset.
Figure 6-2: Switch Statistics Panel
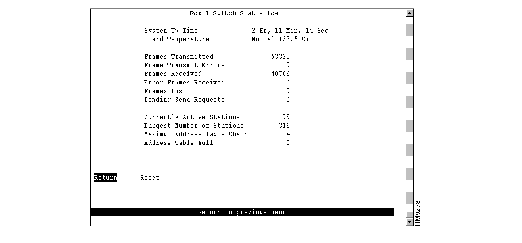
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- System Up Time--Length of time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) since the last reset or power cycle.
- Board Temperature--Indicates whether the board temperature is Normal or Unacceptably high (over 140°F or 60°C).
- Frames Transmitted--Number of frames transmitted from the Catalyst 3900 control processor.
- Frame Transmit Errors--Number of frames unable to be transmitted by the processor because of transmit errors.
- Frames Received--Number of frames received by the Catalyst 3900 control processor.
- Error Frames Received--Number of frames received that were too long or short.
- Frames Lost--Number of frames dropped because of errors.
- Pending Send Requests--Number of frames in the send queue.
- Currently Active Stations--Number of entries in the address table, that represent currently active stations, or nodes, on all ports of the Catalyst 3900.
- Largest Number of Stations--Largest number of addresses in the address table at any one time since the last reset or power cycle.
- Maximum Address Table Chain--Largest number of addresses that have hashed to the same location in look-up tables having the same index.
- Address Table Full--Number of times the address table has reached capacity.
To view status information for each port of the Catalyst 3900, select Port Status on the Statistics Menu. The Port Status panel (Figure 6-3) is displayed.
Figure 6-3: Port Status Panel

The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Port--Port number.
- TrCRF--Name of the TrCRF to which this port belongs. The panel shows only the first 16 characters of the name.
- TrBRF--Name of the TrBRF to which this port belongs. The panel shows only the first 16 characters of the name.
- Enabled--Indicates whether the port is enabled.
- Ins--Indicates whether the port is inserted into the ring.
- Spd--Speed of the port in Mbps.
- Oper Mode--Operating mode of the port. Possible values are:
- HDX port--Half-duplex mode in which only a dedicated connection to a station is supported. The Tx/Rx pinouts are the same as a concentrator's.
- HDX station--Half-duplex mode in which the port operates like a station. The connection may be dedicated or shared. The Tx/Rx pinouts are the same as an adapter's.
- FDX port--Full-duplex mode in which only a dedicated connection to a station is supported. The Tx/Rx pinouts are the same as a concentrator's.
- FDX station--Full-duplex mode in which the port operates like a station. The connection may be dedicated or shared. The Tx/Rx pinouts are the same as an adapter's.
- RI--Ring in mode.
- RO--Ring out mode.
- RI/RO--Ring-in/ring-out mode. Only displayed for ports 19 and 20.
- Passive--Port has been selected as a passive monitoring port. For information about port monitoring, refer to the "Monitoring Port Traffic" section in the "Configuring the Catalyst 3900" chapter.
- Fwd Mode--Forwarding mode of the port. Possible values are Cut-thru and Store & Forward. For ports with a speed of 4 Mbps, the only possible mode is Store & Forward.
You cannot change any information on this panel. To change the port parameters, refer to the "Configuring Port Parameters" section in the "Configuring the Catalyst 3900" chapter.
To view statistics for a specific port, select Port Statistics on the Statistics Menu and specify the port number. The Port Statistics panel (Figure 6-4) is displayed.
Figure 6-4: Port Statistics Panel

The following options are displayed on this panel:
To view general port statistics, select General Statistics on the Port Statistics panel. The Port x General Statistics panel (Figure 6-5) is displayed. The information on the statistics panels is refreshed approximately every 5 seconds. To reset the information displayed on any of the statistics panels, select Reset.
Figure 6-5: Port x General Statistics Panel
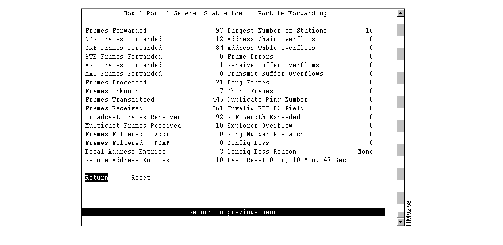
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Frames Forwarded--Number of frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- NSR Frames Forwarded--Number of non-source-routed frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- SRF Frames Forwarded--Number of source-routed frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- STE Frames Forwarded--Number of spanning-tree explorer frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- ARE Frames Forwarded--Number of all-routes explorer frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- MAC Frames Forwarded--Number of MAC frames received on this port and forwarded by the Catalyst 3900 hardware or processor.
- Frames Processed--Number of frames received on this port and delivered to the Catalyst 3900 system software for processing.
- Frames Unknown--Number of frames processed by the Catalyst 3900 system software that contained either an unknown source address or unknown destination address.
- Frames Transmitted--Number of frames transmitted by the port.
- Frames Received--Number of frames received by the port.
- Broadcast Frames Received--Number of broadcast frames received without errors.
- Multicast Frames Received--Number of multicast frames received without errors.
- Frames Filtered - Addr--Number of frames filtered by the MAC address filters.
- Frames Filtered - DSAP--Number of frames filtered by the protocol filters.
- Local Address Entries--Number of addresses on this port that belong to the local segment.
- Remote Address Entries--Number of addresses on this port that belong to another segment.
- Largest Number of Stations--Largest number of addresses active since the last reset of the Catalyst 3900.
- Address Chain Overflows--Number of times an address hash bin has reached the maximum number of entries.
- Address Table Overflows--Number of times the address table has reached the maximum number of entries.
- Frame Errors--Total number of frames received or transmitted by this port that contained errors.
- Receive Buffer Overflows--Number of frames received on this port that caused a buffer overflow.
- Transmit Buffer Overflows--Number of frames lost because of the inability of the transmit queue to accept a frame from another port.
- Long Frames--Number of frames received that exceed the maximum frame length limit of 4540 bytes.
- Short Frames--Number of frames received that were less than 18 bytes.
- Duplicate Ring Number--Number of frames received that contained a duplicate ring number.
- Invalid RIF RC Field--Number of frames received that contained an illegal Routing Control field.
- RIF Length Exceeded--Number of frames received that contained a RIF that was too long.
- Explorer Overflow--Number of explorer frames dropped because the maximum explorer-forwarding rate was exceeded (as specified on the Port Configuration panel described in the "Configuring Port Parameters" section of the "Configuring the Catalyst 3900" chapter).
- Ring Number Mismatch--Number of frames received that did not correctly include the port's ring number.
- Config Loss--Number of Token Ring configuration loss events after the port has completed the join process and then lost communication.
- Config Loss Reason--Error code of the latest configuration loss event. Possible values are None, Wire Fault, Lobe Test Fail, TKP Frame Error, Heart Beat Fail, TXI New Station, TXI Prot Error, Speed Error, Remove Received.
- Last Reset--Time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) since the port statistics were last reset.
To view 802.5 port statistics, select 802.5 Statistics on the Port Statistics panel. The Port x 802.5 Statistics panel (Figure 6-6) is displayed. This panel is automatically refreshed every 5 seconds.
Figure 6-6: Port x 802.5 Statistics Panel
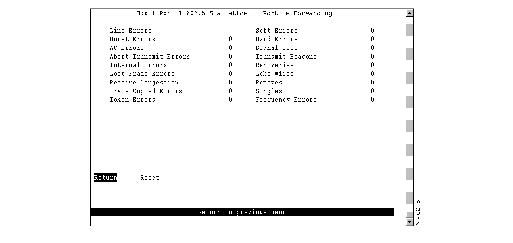
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Line Errors--Number of times a frame or token was copied or repeated by a station.
- Burst Errors--Number of times a station has detected the absence of transitions for five half-bit timers (burst-five error).
- AC Errors--Number of times a station received an Active Monitor Present (AMP) frame or a Standby Monitor Present (SMP) frame in which both the address recognized (A) bit and the frame copied (C) bit are set to 0, indicating that no station has recognized the destination address and copied the frame, and then receives another SMP frame in which both the address recognized bit and the frame copied bit are set to 0 without first receiving an AMP frame. This condition indicates a station that cannot set the address recognized and the frame copied bits properly.
- Abort Transmit Errors--Number of times a station transmitted an abort delimiter while transmitting.
- Internal Errors--Number of times a station recognized an internal error.
- Lost Frame Errors--Number of times a station was transmitting and its return-to-repeat timer expired. This condition indicates a condition where a transmitting station in strip mode does not receive the trailer of the frame before the return to repeat timer goes off.
- Receive Congestion--Number of times a station recognized a frame addressed to its specific address, but had no available buffer space, indicating that the station is congested.
- Frame Copied Errors--Number of times a station recognized a frame addressed to its specific address and detected that the frame status field A bits are set to 1, indicating a possible line hit or duplicate address.
- Token Errors--Number of times a station acting as the active monitor recognized an error condition that required a token to be transmitted.
- Soft Errors--Number of soft errors the port has detected. Soft errors are those that are recoverable by the MAC layer protocols. The soft error number directly corresponds to the number of report error MAC frames that this port has transmitted.
- Hard Errors--Number of times this port has detected an immediately recoverable fatal error. This denotes the number of times this port has either transmitted or received a beacon MAC frame.
- Signal Loss--Number of times this port has detected a loss of signal condition from the ring.
- Transmit Beacons--Number of times this port has transmitted a beacon frame.
- Recoveries--Number of claim token MAC frames received or transmitted after the port has received a ring purge MAC frame. This counter signifies the number of times the ring has been purged and had recovered back into a normal operating state.
- Lobe Wires--Number of times the port has detected an open or short circuit in the lobe data path. The adapter will be closed and ring state will signify this condition.
- Removes--Number of times the port has received a remove ring station MAC frame request. When this frame is received the port will enter the closed state.
- Singles--Number of times the port has sensed that it is the only station on the ring. This occurs if the port is the first one up on a ring, or if there is a hardware problem.
- Frequency Errors--Number of times the port has detected that the frequency of the incoming signal differs from the expected frequency by more than that specified by the IEEE 802.5 standard.
To view 802.5 port state information, select 802.5 State Information on the Port Statistics panel. The Port x 802.5 State Information panel (Figure 6-7) is displayed.
Figure 6-7: Port x 802.5 State Information Panel
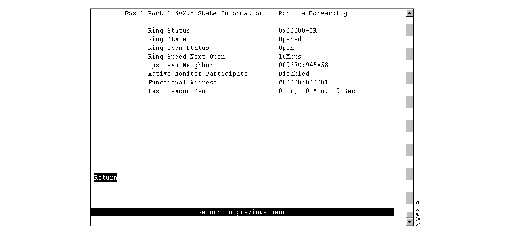
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Ring Status--Current port status on the ring. This field has the general format
0xnnnnn-text_string where nnnnn is a hexadecimal error code value, and text_string can be No Status, OK, or Error. Before an open is completed, the field has the value: 0x20000-No Status. If no problems are detected this field will display: 0x00000-OK. Other error conditions are indicated by: 0xnnnnn-Error.
- Ring State--Current port state with respect to the port entering or leaving the ring. Possible values are Opened, Closed, Opening, and Closing.
- Ring Open Status--Indicates whether the station successfully entered the ring in its most recent attempt, and, if not, the reason for failure. Possible values are Open, No Open, Lobe Failed, Signal Loss, Insertion Timeout, Ring Failed, Beaconing, Duplicate MAC Address, Request Failed, and Remove Received.
- Ring Speed Next Open--Ring speed, if known, that will be used the next time the port inserts into the ring. Possible values are Unknown, 4 Mbps, and 16 Mbps.
- Upstream Neighbor--MAC address of the nearest active upstream neighbor station on the ring.
- Active Monitor Participate--Indicates whether this port will participate in the active monitor selection process. Possible values are Enabled (yes) and Disable (no).
- Functional Address--Bit mask of all Token Ring functional addresses for which this port will accept frames.
- Last Beacon Sent--Elapsed time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) since a beacon frame was last sent on this port.
To view 802.5 port dedicated Token Ring MAC information, select 802.5 DTR MAC Information on the Port Statistics panel. The Port x 802.5 DTR MAC Information panel (Figure 6-8) is displayed.
Figure 6-8: Port x 802.5 DTR MAC Information Panel

The following options are displayed on this panel:
If you select TXI Information on the Port x 802.5 DTR MAC Information panel, the Port x 802.5 DTR MAC TXI Information panel (Figure 6-9) is displayed.
Figure 6-9: Port x 802.5 DTR MAC TXI Information Panel
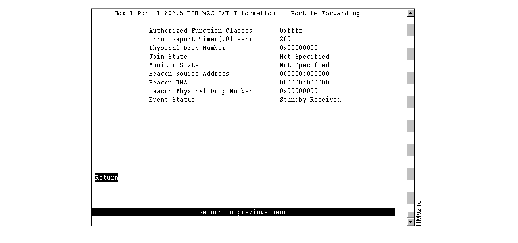
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Authorized Function Classes--Functional classes that a node is enabled to transmit. This value is set in the Enabled Function Class subvector (x'06') of the Change Parameters MAC frame. Possible values are 0x0000 through 0xFFFF. Each bit that is enabled corresponds to a function class that is enabled.
- Error Report Timer (.01 sec)--Timeout value (in milliseconds) of the ring stations soft error report timer. This value is set in the Error Timer Value subvector (x'05') of the Change Parameters MAC frame or the Initialize Station MAC frame.
- Physical Drop Number--Physical location of the sending ring station. This value is set in the Assign Physical Location subvector (x'04') of the Change Parameters MAC frame or the Initialize Station MAC frame. Possible values are 0x00000000 through 0xFFFFFFFF.
- Join State--Present state of the join finite state machine. Possible values are Not Specified, Bypass, Registration, Lobe Test, Dup Addr Check, Dup Addr Det, Join Complete, and Await Notify.
- Monitor State--Present state of the monitor finite state machine. Possible values are Not Specified, Operational, Transmit Beacon, Wire Fault Delay, and Int Test Wait.
- Beacon Source Address--Source address used in the last beacon MAC frame transmitted or received.
- Beacon UNA--Individual MAC address of the sending ring station's nearest active upstream neighbor (NAUN). This value is set in the NAUN subvector x'02' used in the last beacon MAC frame transmitted or received. Possible values are either a valid individual MAC address or Unknown.
- Beacon Physical Drop Number--Physical location of the sending ring station. This value is set in the Physical Location subvector (x'0B') of the last beacon MAC frame transmitted or received. Possible values are 0x00000000 through 0xFFFFFFFF.
- Event Status--Latest event status of the TXI interface. Possible values are Insert REQ Rec, Insert RPS Rec, Report Error, Heart Beat Lost, Signal Loss, Beacon Received, Remove, Internal Error, Station/CPort Err, Wire Fault, Claim Received, Purge Received, Standby Received, Invalid SA, Act Mon Recvd, Phantom Loss, and Dup Addr Det.
If you select Station-CPort, the Port x 802.5 DTR MAC Station-CPort Information panel (Figure 6-10) is displayed.
Figure 6-10: Port x 802.5 DTR MAC Station-CPort Information Panel
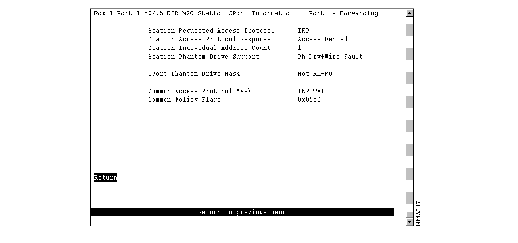
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Station Requested Access Protocol--Protocol requested for station access. This value is set in the Access Protocol Request subvector (x'0E') of the registration request MAC frame. Possible values are TXI and TKP.
- Station Access Protocol Response--Response to protocol request. This value is set in the Access Protocol Response subvector (x'0F') of the registration response MAC frame. Possible values are Access Denied and TXI+Wire Fault.
- Station Individual Address Count--Number of individual addresses supported by the MAC and used in the Individual Address Count subvector (x'21'). This field will always display the value 1.
- Station Phantom Drive Support--MAC's support of phantom drive and wire fault detection. It indicates the value of the Station Phantom Vector (Phantom Drive) [SPV(PD)] variable and the value of the phantom subvector X'0C' used in the registration request MAC frame. This field will always display Ph Drv+Wire Fault for phantom drive and wire fault support.
- CPort Phantom Drive Mask--Value of the C-Port policy variable Port Phantom Vector (Phantom Drive Mask [PPV(PD_MASK)]. This variable indicates the phantom drive and wire fault detection methods supported by the C-Port. Possible values are RI-RO and Not RI-RO.
- Common Access Protocol Mask--Access protocols can be supported by the PMAC. It displays the value of the PPV(AP_MASK). Possible values for this field are TKP, TXI, and TKP+TXI.
- Common Policy Flags--Station policy flags as a hexadecimal value of the form 0xnnnn.
You can view the address and route descriptor tables, which are used in forwarding frames, for the following:
- Catalyst 3900
- Individual VLANS
To view address and route descriptor tables, select Address Tables on the Statistics Menu. The Address Tables panel (Figure 6-11) is displayed.
Figure 6-11: Address Tables Panel

The following options are displayed on this panel:
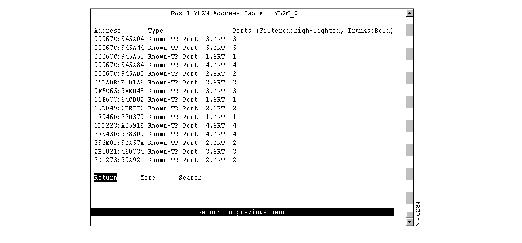
To view all entries in the master address table, select Master Address Table on the Address Table panel. The Master Address Table panel (Figure 6-12) is displayed. The master address table can contain up to 10,000 entries.
Figure 6-12: Master Address Table Panel
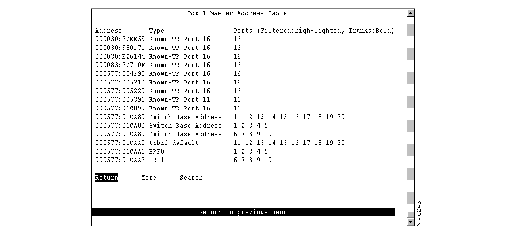
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Address--MAC address.
- Type--Type of address. Possible values are:
- Switch Base Address for the address assigned to the Catalyst 3900.
- VLAN Name for an address assigned to a VLAN domain. Only the first 16 characters of the name are displayed.
- STP Port x for the switch port's MAC address that is used by the Spanning-Tree Protocol.
- Known-port_type Port x for a known address. Possible values of port_type are TR (Token Ring port) and STK (stack port).
- Unknown for a MAC address with an unknown location.
- STP Multicast for a BPDU multicast address reserved for the port (hello packet).
- Multicast for a multicast address.
- Multicast-Cisco for a Cisco multicast address.
- STP Multicast-IBM for the IBM bridge functional address.
- STP Multicast-Cisco for the Cisco spanning-tree address.
- Broadcast for a broadcast address.
- Ports--Ports of the switch or a feature card whose address tables include this MAC address.
Note Filtered ports are displayed as highlighted entries. Trunk ports are displayed as bold entries.
| To
| Select
| Then
|
|---|
| Search for a specific MAC address...
| Search
| Specify the address.
|
To view all the route descriptors (and their associated ports) that have been learned by the Catalyst 3900, select Master Route Descriptor Table on the Address Tables panel. The Master Route Descriptor Table panel (Figure 6-13) is displayed. These descriptors are contained within the 10,000 entries allowed for the master address table.
Figure 6-13: Master Route Descriptor Table Panel
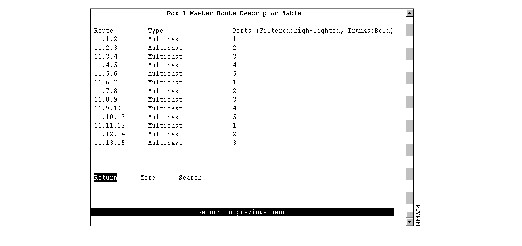
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Route--Route descriptor associated with a port in the format:
local_segment_number.bridge_number.remote_segment_number
- The local segment number is displayed in hexadecimal and is the same for all ports within a single domain. Possible ring numbers are 01 through FFF. Possible bridge numbers are 00 through 0F.
- Type--Type of route descriptor. Possible values are:
- Known-port_type Port x for a known source-route descriptor. Possible values of port_type are TR and STK.
- Unknown if the source route location is unknown.
- Ports--Ports of the switch or a feature card whose address tables include this route descriptor.
|
To
| Select
| Then
|
|---|
| Search for a specific route descriptor...
| Search
| Specify the route descriptor.
|
To view the entries in the address table for each VLAN, select VLAN Address Table on the Address Tables panel and select the desired TrCRF. The VLAN Address Table panel (Figure 6-14) is displayed. The entries are listed in the order in which they were learned.
Figure 6-14: VLAN Address Table Panel
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Address--MAC address.
- Type--Type of address. Highlighted entries indicate filtered ports. Possible values are:
- Switch Base Address for the address assigned to the Catalyst 3900.
- VLAN Name for an address assigned to a VLAN domain. Only the first 16 characters of the name are displayed.
- STP Port x for an address reserved for a Spanning-Tree Protocol port.
- Known-port_type Port x for a known address. Possible values of port_type are TR and STK.
- Unknown for a MAC address with an unknown location.
- STP Multicast for a BPDU multicast address reserved for the port (hello packet).
- Multicast for a multicast address.
- STP Multicast-Cisco for the Cisco spanning-tree address.
- STP Multicast-IBM for the IBM bridge functional address.
- Broadcast for a broadcast address.
- Ports--Ports of the switch or a feature card whose address tables include this MAC address.
Note Highlighted entries indicate filtered ports. Bold entries indicate trunk ports.
| To
| Select
| Then
|
|---|
| Search for a specific MAC address...
| Search
| Specify the address.
|
To view the entries in the route descriptor table for each VLAN, select VLAN Route Descriptor Table on the Address Table panel and specify the desired TrCRF. The VLAN Route Descriptor Table panel (Figure 6-15) is displayed.
Figure 6-15: VLAN Route Descriptor Table Panel
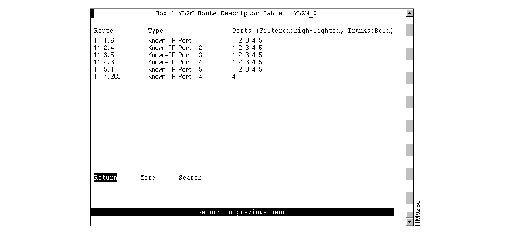
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Route--Route descriptor associated with a port in the format:
local_segment_number.bridge_number.remote_segment_number
- The local segment number is displayed in hexadecimal and is the same for all ports within a single domain. Possible ring numbers are 01 through FFF. Possible bridge numbers are 00 through 0F.
- Type--Type of route descriptor. Possible values are:
- Known-port_type Port x for a known source-route descriptor. Possible values of port_type are TR and STK.
- Unknown if the source route location is unknown.
- Ports--Ports of the switch or a feature card whose address tables include this route descriptor.
| To
| Select
| Then
|
|---|
| Search for a specific route descriptor...
| Search
| Specify the route descriptor.
|
To display the spanning-tree parameters for a TrBRF, select Current Spanning Tree Information on the Statistics Menu and specify the desired TrBRF. The Current Spanning Tree Information panel (Figure 6-16) is displayed.
Figure 6-16: Current Spanning Tree Information Panel
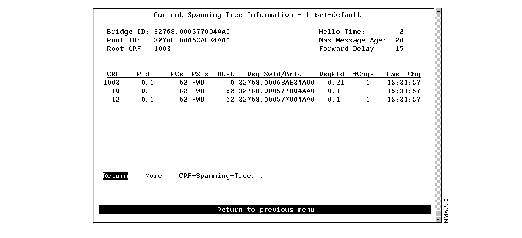
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Bridge ID--Priority and MAC address of this bridge.
- Root ID--Priority and MAC address of the root bridge.
- Root CRF--Number of the VLAN ID of the TrCRF that is closest to the root. This Catalyst 3900 communicates with the root through this TrCRF.
- Hello Time--Time (in seconds) that the root waits between sending configuration messages. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- Max Message Age--Time at which the configuration message used by the spanning-tree algorithm should be discarded. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- Forward Delay--Time the root waits between transitions from listening to learning and from learning to forwarding. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- CRF--VLAN ID of a TrCRF belonging to this TrBRF.
- PId--Port ID that is used to determine the role of the logical port in the spanning tree. The port ID is expressed in the form port priority.port number.
- PCst--Cost associated with each logical port. Lower numbers are generally assigned to ports attached to faster media (such as FDX or TokenChannel), and higher numbers are generally assigned to ports attached to slower media (such as 2400-baud modem links).
- PSts--Current status of this logical port within the spanning tree. Possible values are:
- DSB (disabled)
- BLK (blocked)
- LSN (listening)
- LRN (learning)
- FWD (forwarding)
- The rules that define the state of the logical port are as follows:
- A port on a network segment that contains no other switch or bridge is always forwarding.
- If two ports of the Catalyst 3900 are connected to the same network segment and there is no other bridge or switch, the port with the lower ID is forwarding and the other is blocked.
- When the switch is booted, all ports are blocked initially, and then some of them change to a different state: listening, learning, and forwarding, in that order. To see the change in states you must repeatedly exit from this menu, and then select it again. All ports that are going to change states from blocking to forwarding will have done so after two to three times the value of:
- Switch Maximum Message Age + (2 x Switch Forward Delay)
- DCst--Cost for a packet to travel from this port to the root in the current spanning-tree configuration. The slower the media, the higher the cost.
- Dsg SwId/BrId--Priority and MAC address of the device through which this port has determined it must communicate with the root of the spanning tree.
- DsgPId--Port on the designated bridge through which this Catalyst 3900 will communicate with the root of the spanning tree. This information is useful if the Catalyst 3900 is the designated bridge on one or more network segments.
- #Chgs--Number of topology changes, that is, the number of times the port has entered the forwarding state plus the number of times the port has made the transition from forwarding to blocking. The counter is reset when the switch is reset or the spanning tree is turned on.
- Last Chg--Time since the port last entered the forwarding state or made the transition from forwarding to blocking.
You cannot change any information on this panel. To change the spanning-tree parameters, refer to the section "Configuring Spanning-Tree Parameters" in the "Configuring the Catalyst 3900" chapter.
To display the spanning-tree parameters for a TrCRF that belongs to the currently displayed TrBRF, select CRF-Spanning-Tree on the Current Spanning Tree Information panel for a TrBRF and specify the desired TrCRF. The Current Spanning Tree Information panel (Figure 6-17) is displayed.
Figure 6-17: Current Spanning Tree Information for a TrCRF Panel
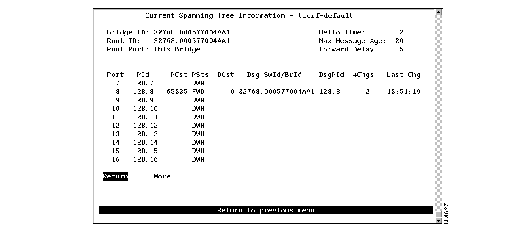
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Bridge ID--Priority and MAC address of this bridge.
- Root ID--Priority and MAC address of the root bridge.
- Root Port--Number of the port on this Catalyst 3900 that is closest to the root. This Catalyst 3900 communicates with the root through this port. If this Catalyst 3900 has been accepted as the root of the spanning-tree network, this field displays "This Bridge."
- Hello Time--Time (in seconds) that the root waits between sending configuration messages. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- Max Message Age--Time at which the configuration message used by the spanning-tree algorithm should be discarded. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- Forward Delay--Time the root waits between transitions from listening to learning and from learning to forwarding. This time is advertised by the root and used by all devices and switches in the active topology of the spanning-tree network.
- Port--Port number.
- PId--Port ID that is used to determine the role of the port in the spanning tree. The port ID is expressed in the form port priority.port number.
- PCst--Cost associated with each port. Lower numbers are generally assigned to ports attached to faster media (such as FDX or TokenChannel), and higher numbers are generally assigned to ports attached to slower media (such as 2400-baud modem links).
- PSts--Current status of this port within the spanning tree. Possible values are:
- DSB (disabled)
- BLK (blocked)
- LSN (listening)
- LRN (learning)
- FWD (forwarding)
- The rules that define the state of the port are as follows:
- A port on a network segment that contains no other switch or bridge is always forwarding.
- If two ports of the Catalyst 3900 are connected to the same network segment and there is no other bridge or switch, the port with the lower ID is forwarding and the other is blocked.
- When the switch is booted, all ports are blocked initially, and then some of them change to a different state: listening, learning, and forwarding, in that order. To see the change in states you must repeatedly exit from this menu, and then select it again. All ports that are going to change states from blocking to forwarding will have done so after two to three times the value of:
- Switch Maximum Message Age + (2 x Switch Forward Delay)
- DCst--Cost for a packet to travel from this port to the root in the current spanning-tree configuration. The slower the media, the higher the cost.
- Dsg SwId/BrId--Priority and MAC address of the device through which this port has determined it must communicate with the root of the spanning tree.
- DsgPId--Port on the designated bridge through which this Catalyst 3900 will communicate with the root of the spanning tree. This information is useful if the Catalyst 3900 is the designated bridge on one or more network segments.
- #Chgs--Number of topology changes, that is, the number of times the port has entered the forwarding state plus the number of times the port has made the transition from forwarding to blocking. The counter is reset when the switch is reset or the spanning tree is turned on.
- Last Chg--Time since the port last entered the forwarding state or made the transition from forwarding to blocking.
You cannot change any information on this panel. To change the spanning-tree parameters, refer to the section "Configuring Spanning-Tree Parameters" in the "Configuring the Catalyst 3900" chapter.
The Catalyst 3900 provides statistical information for both TrCRFs and TrBRFs. To access statistics for VLANs, select VLAN Statistics on the Statistics Menu.
To view statistics for a TrCRF, select VLAN Statistics on the Statistics Menu, select TrCRF, and then select the desired TrCRF. The VLAN Statistics panel (Figure 6-18) is displayed.
Figure 6-18: VLAN Statistics Panel (for a TrCRF)

The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Parent VLAN--Name of the parent TrBRF.
- Currently Active Stations--Number of addresses currently in the master address table that are recognized by ports belonging to this domain.
- Largest Number of Stations--Largest number of addresses in the master address table since the last reset or power cycle that are recognized by ports belonging to this domain.
- Ports--List of ports that belong to this TrCRF.
To view statistics for a TrBRF, select VLAN Statistics on the Statistics Menu, select TrBRF, and then select the desired TrBRF. The VLAN Statistics panel (Figure 6-19) is displayed.
Figure 6-19: VLAN Statistics Panel (for a TrBRF)
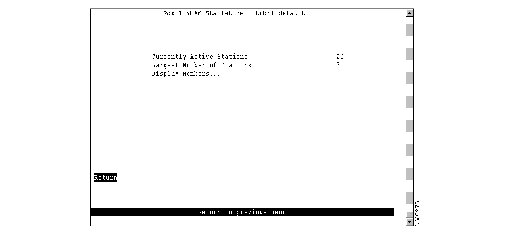
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Currently Active Stations--Number of addresses currently in the master address table that are recognized by ports belonging to this domain.
- Largest Number of Stations--Largest number of addresses in the master address table since the last reset or power cycle that are recognized by ports belonging to this domain.
To display the TrCRFs associated with a TrBRF, select Display Members on the VLAN Statistics panel. The VLAN Statistics panel (Figure 6-20) is displayed.
Figure 6-20: VLAN Statistics Panel (for a TrCRF)

This panel lists VLAN names of all the TrCRFs associated with the parent TrBRF.
To view information about other Cisco devices with which the Catalyst 3900 is communicating via CDP, select CDP Neighbor Display on the Statistics Menu. The CDP Neighbor Display panel (Figure 6-21) is displayed.
Figure 6-21: CDP Neighbor Display Panel
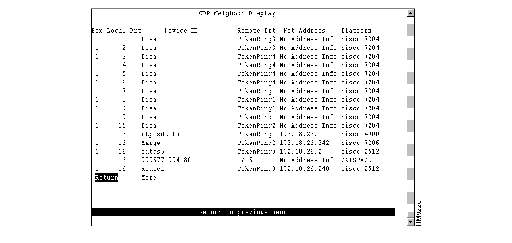
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Box Local Prt--Port on the Catalyst 3900 that is enabled for CDP.
- Device ID--Host name or hardware serial number (in ASCII) of the remote device.
- Remote Prt--Port on the remote device that is enabled for CDP.
- Net Address--IP address of the remote device.
- Platform--Type of device (often indicated by the device name or part number).
You can view statistics about the VTP, including message counters. There are three types of VTP messages for which counters are maintained:
- Summary Advertisements--Contains the management domain name, the configuration revision number, the update timestamp and identity, the authentication checksum, and the number of Subset Advertisement messages which follow it.
- Subset Advertisements--Contains all information for one or more (but always an integral number of) VLANs, and indicates its own sequence number within those which follow the Summary Advertisement.
- Advertisement Requests--Requests information about VLANs.
If the switch is operating in Server mode, an advertisement is sent across the trunk port when the following events occur:
- Immediately upon a change in the configuration of VLAN information.
- When no other Summary Advertisement with the current configuration revision number has been received within the timeout period.
Each advertisement consists of one Summary Advertisement immediately followed by zero or more Subset Advertisements. The number of Subset Advertisement messages that follow a Summary Advertisement depends on the reason for sending the advertisement.
- If the advertisement is sent because neither this device nor any other device has recently sent an advertisement, then the Summary Advertisement is followed by zero Subset Advertisement messages.
- If the advertisement is sent because a configuration change has been made, then the Summary Advertisement is followed by the minimum number of Subset Advertisement messages required to contain all information on all VLANs and ordered in ascending order of ISL VLAN ID.
- If the advertisement is sent because an Advertisement Request for information on all VLANs was received, then the Summary Advertisement is followed by the minimum number of Subset Advertisement messages required to contain all information on all VLANs. The messages are sent in ascending order of ISL VLAN ID.
- If the advertisement is sent because an Advertisement Request for information on a subset of VLANs was received, the Summary Advertisement is followed by the minimum number of Subset Advertisement messages required to contain all information on all VLANs. The messages are sent in ascending order of ISL VLAN ID, however, the transmission of Subset Advertisements that only contain information on unrequested VLANs is suppressed.
An Advertisement Request is sent after a reboot. Also, if any of the following occurs then a timer is started.
- A Subset Advertisement message is received that contains a configuration revision number that is higher than the device's currently known value.
- A Summary Advertisement is received that contains a configuration revision number that is greater than the device's currently known value and that is not followed by any Subset Advertisements.
- The expected number of Subset Advertisement messages is not received within a short period after receiving a Summary Advertisement message having a configuration revision number that is greater than the device's currently known value.
- A Summary Advertisement is received that contains a configuration revision number that is more than one greater than the device's currently known value.
If the timer expires before either an Advertisement Request or Summary Request is received, then an Advertisement Request is sent.
When an Advertisement Request is sent because some Subset Advertisement messages were missed, the Advertisement Request is set to request only those VLANs that were missed.
To view VTP message counters, select VTP Statistics on the Statistics Menu. The VTP Statistics panel (Figure 6-22) is displayed.
Figure 6-22: VTP Statistics Panel
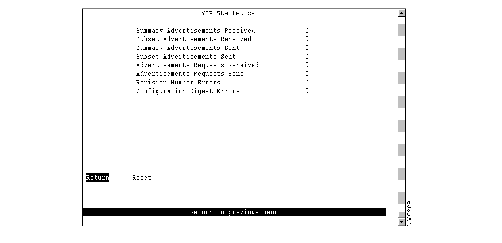
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Summary Advertisements Received--Total number of VTP Summary Advertisements received for this management domain.
- Subset Advertisements Received--Total number of VTP Subset Advertisements received for this management domain.
- Summary Advertisements Sent--Total number of VTP Summary Advertisements sent for this management domain.
- Subset Advertisements Sent--Total number of VTP Subset Advertisements sent for this management domain.
- Advertisements Requests Received--Total number of VTP Advertisement Requests received for this management domain.
- Advertisements Requests Sent--Total number of VTP Advertisement Requests sent for this management domain.
- Revision Number Errors--Number of occurrences of configuration revision number errors for this management domain. A configuration revision number error occurs when a device receives a VTP advertisement for which:
- The advertisement's Configuration Revision Number is the same as the current locally held value.
- The advertisement's digest value is different from the current locally held value.
- Configuration Digest Errors--Number of occurrences of configuration digest errors for this management domain. A configuration digest error occurs when a device receives a VTP advertisement for which:
- The advertisement's Configuration Revision Number is greater than the current locally held value.
- The advertisement's digest value does not match the VLAN information assumed by the receiver of the advertisement, where the information assumed is the combination of the information explicitly contained in the advertisement plus any omitted information as currently known by the receiving device.
To view the results of the most recent power-on diagnostics, select Diagnostic Test Results on the Statistics Menu. The Diagnostic Test Results panel (Figure 6-23) is displayed.
Figure 6-23: Diagnostic Test Results Panel
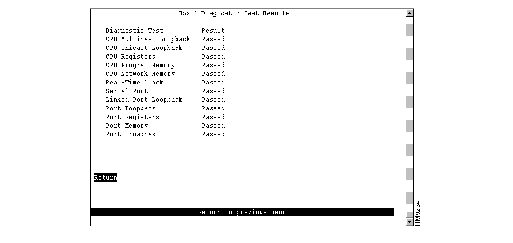
This panel displays a list of the self-diagnostic tests that the Catalyst 3900 performs and the result of each. For information about running the diagnostic tests, refer to the "Resetting the Catalyst 3900" chapter.
To view the message log, select Message Log on the Statistics Menu. The Message Log Information panel (Figure 6-24) is displayed. The data on this panel is useful to technical experts when they are solving complex problems.
Figure 6-24: Message Log Panel
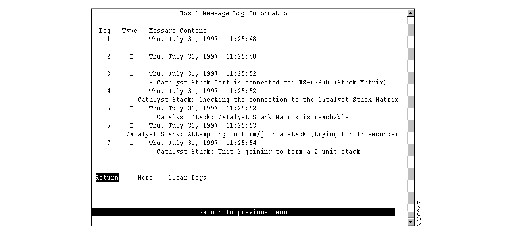
The following information is displayed on this panel:
- Log--Index number identifying the log file.
- Type--Message type. Possible values are:
- W--Warning
- I--Informational
- Message Content--Full text of the message
.
| To
| Select
|
|---|
| Delete the contents of the message log...
| Clear Logs
|
To display a summary of the configuration of your Catalyst 3900, select Display Summary on the Statistics Menu. The summary information is displayed on the console panel (Figure 6-25).
Figure 6-25: Configuration Summary
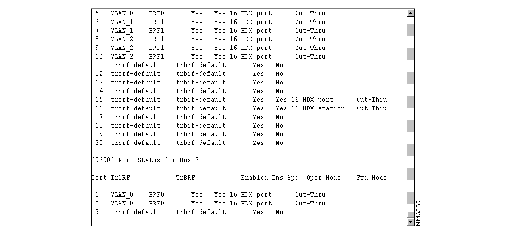
You can scroll through the information to view your current configuration parameter settings. The summary includes:
- Switch and stack information
- VLAN configuration information
- SNMP configuration information
- Spanning tree configuration information
- Port status
- CDP configuration information
- Module configuration information
- Message log
To exit from the configuration summary and return to the Statistics menu, wait until the configuration summary dump is complete and then press any key.

























