|
|

This appendix provides instructions for converting and loading NetCentral 1.3 map files into SunNet Manager (SNM) 2.0. If you do not have NetCentral 1.3 installed on your system, or you are not interested in preserving your existing NetCentral 1.3 map files, skip this appendix.
There are three ways you can build a database in SNM.
You can use any of these methods to build an SNM database. Generally, use the Discover program to make sure that all devices in a specific network are added to your network map. If you add a new device to your network, you could manually specify the device information instead of running the Discover program. The ncs2snm map conversion utility enables you to translate existing NetCentral 1.2 maps into an SNM database; however, you should be aware of the limitations of this program.
There are two ways you can create a Sybase database for CiscoWorks if an SNM database already exists as a result of following any one of the previous three steps.
If you are a NetCentral 1.3 user and have not decided whether you wish to use the ncs2snm map conversion utility to translate your NetCentral 1.3 map files and load them into SNM, refer to "Limitations of Map Translation."
The ncs2snm utility program is used translate NetCentral 1.3 maps when upgrading from NetCentral 1.3 to CiscoWorks. It enables you to use your existing NetCentral 1.3 maps by loading them into SNM and editing the map.
SNM must be running on your system in order to run the ncs2snm utility. The ncs2snm utility performs the following tasks:
You can run ncs2snm utility multiple times, but you need to remove unwanted database files each time.
If you wish to merge your original SNM database with a new translated map file, you can load the original SNM database file using Load from the SNM File menu. To load the previous database without the translated map, exit SNM. Use the following command at the UNIX prompt where filename is the name of the original database:
hostname%snm -ifilename&
The ncs2snm utility translates managed objects, not graphical objects. A graphical object is a drawing. Initially, all objects in NetCentral 1.3 maps are graphical objects until they are designated as networks or routers. CiscoWorks interacts with managed objects or devices in the SNM map.
SNM does not allow you to draw maps; therefore, the ncs2snm utility attempts to translate the managed information in a NetCentral 1.3 map file and present the managed objects in a map loaded into SNM. The ncs2snm utility does not translate unmanaged graphic elements in a NetCentral 1.3 map, even though they may look like network devices.
This section explains how the following areas are affected by map translation:
Designated networks are translated as the SNM "bus.ethernet" object. This is graphically represented in SNM as a line with two small squares on the ends. Token Ring and FDDI ellipses in NetCentral 1.3 map files are also translated as "bus.ethernet" because SNM does not provide any equivalent.
Figure B-1 illustrates different types of SNM and Cisco graphic elements including a network icon, router icons, and a connection between a router and a network.
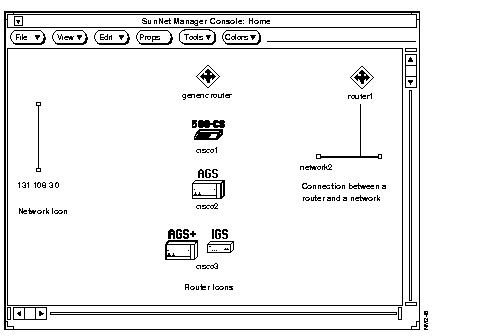
All routers are translated as a generic SNM "component.router" unless SNMP queries are enabled by using the -q option with the ncs2snm command line. If queries are enabled, the router will be classified as a generic router, AGS, IGS, or communication server. Workstations and servers that do routing are displayed as generic routers. You can use the SNM Change Type tool to display a device with a different icon.
Links or graphical elements associated with networks and routers in NetCentral 1.3 are mapped as connections in the SNM map.
Each managed item has one or more graphical elements associated with it; the items that were selected when you designated them as a network or a router. These graphical objects have coordinates representing their location in your map. To preserve the overall layout of your map, these coordinates are translated as SNM coordinates.
The objects selected determine the graphical objects' coordinates. When several graphical objects are associated with a managed object (network or router), the coordinates of the first associated graphical object are used. It is not possible to determine which of the graphical objects is most important in the map file.
With routers, the coordinates of the first rectangle associated with a router are used in preference to any other graphic objects associated with that router. With networks, if the coordinates are obtained from a rectangle, polygon, or ellipse, the long axis of the bounding rectangle (rectangle surrounding the drawing) is used for the coordinates of the network endpoints.
All mapping transformations (scaling, rotation) applied within the nmdraw are also tracked and applied as part of the translation process. Foreground colors are preserved unless you choose otherwise.
The ncs2snm utility translates object names and addresses. For networks, CiscoWorks does not store a name so the address is used. For routers, the address stored is that of the first interface in the map file. For routers stored in SNM as type "component.router," the address of the second interface (when present) is also entered as a property in the SNM database.
All routers in a NetCentral 1.3 map are displayed as generic SNM router icons. After translating a map, you need to manually convert each router icon into an appropriate Cisco router icon.
A router can have a number of interfaces. As the router is added to the view, it is also added to a network (represented by a cloud icon in SNM Console), and one for each router interface (with subnet mask applied). These networks are created in the current view as needed. If you choose to manage these subnets, you can use the SunNet Manger Discover tool to identify the devices in the subnet.
SNMP community information is preserved. CiscoWorks does not distinguish read and write community, so the same community string is stored in both the SNM RdCommunity and WrCommunity fields.
All routers are translated as having agents Cisco and snmp-mibII available. The Cisco agent may not be applicable to generic routers, but you can attempt to query and get a "No data" response.
SNM 2.0 must be running before you can run the ncs2snm utility. Start SNM with the following command:
hostname% snm &
The utility saves any existing SNM database that might be loaded.
If SNM is not running, you will get an error message similar to the following:
Saving the current SNM database to file /tmp/snm_current.db.
ERROR: SNM file save error (0, 0, 1)
ARE YOU RUNNING SNM?
To run the ncs2snm utility, enter the following command at the UNIX prompt:
hostname%$NMSROOT/contrib/ncs2snmoptionsmapfile
To avoid specifying the directory path for ncs2snm, include $NMSROOT/contrib as part of your PATH environment variable or change to the $NMSROOT/contrib directory.
For a synopsis of the available options, enter the following at the UNIX prompt:
hostname% $NMSROOT/contrib/ncs2snm -help
A listing of options and an example of usage is displayed:
ncs2snm -help
USAGE: ncs2snm [options] map_file1 map_file2 ...
NetCentral 1.3 to SNM 2.0 map conversion utility. Version 1.0.
SNM 2.0 must be running or ncs2snm won't work !!!
Options:
-h help: get this information
-v print version information
-p do NOT purge SNM database before loading map file
-u do NOT save loaded database in ASCII form
-q use SNMP queries to ask routers their type (default: no queries)
-t time SNMP query timeout (in seconds, default: 10)
-l viewname load map file(s) into SNM view <viewname> (default: "Home")
-c curfile store current SNM database in <curfile>
(default: /tmp/snm_current.db)
-n newfile store translated map SNM database in <newfile>
(default: /tmp/snm_new.db)
-k force default color values
-s factor scale coordinates by specified scaling factor (default 1.0)
-r rotkey specify a rotation / reflection (default: 0)
0: no rotation
1: 90 degree counterclockwise rotation
2: 180 degree rotation
3: 90 degree clockwise rotation
4: reflect vertically
5: reflect horizontally
Example: ncs2snm -q -t 20 -v myview -c /tmp/old -n /tmp/new -s 0.5 -r 2 mymap
The example in the output shows different options you could use with the ncs2snm utility.
The following is an example of the format of the ncs2snm command. Table B-1 describes the options.
hostname%ncs2snmoptionsmymap
| Option | Explanation | Default with No Option |
|---|---|---|
| -h | Help (usage summary). | |
| -v | Print version information. | |
| -p | Purge the current SNM database and load the map file into the current SNM database. | Database is saved and then purged (emptied). |
| -u | Do NOT save the SNM database containing the loaded map that is translated for use in SNM. | Save the loaded map in the SNM database. |
| -q | Query devices using SNMP, including Cisco communications server, AGS+ and IGS routers. | |
| -t time | Specify the SNMP timeout to time seconds. | 10 seconds. |
| -l view | Load the translated map into a view named view. | Home. |
| -c curfile | Save the current database with the name curfile. | /tmp/snm_current.db. |
| -n newfile | Save loaded database as newfile. | /tmp/snm_new.db. |
| -k | Force colors to SNM defaults: blue routers, black networks, and links. | off (use map colors). |
| -s factor | Scale by factor. | 1.0 |
| -r flag | Rotate or reflect based on the key flag. | 0 |
Follow these steps to translate and load a simple NetCentral 1.3 map into SNM.
Step 1: Verify that SNM is running.
Step 2: In the Command Tool or the Shell Tool window, enter the following command, substituting the name of your map file:
hostname% ncs2snm mymap
This command translates the map and loads it into the SNM Home view. Output similar to the following is displayed in the window.
Saving the current SNM database to file /tmp/snm_current.db.
Purging SNM database.
--------------------------------------------------
The managed items from map file <db10> will be added to view <Home>.
Extracting information from map file db10.
# of networks = 3
# of routers = 5.
Adding map elements to SNM database.
adding NETWORK 0: 131.108.3.0.
setting string property <IP_Network_Number> to <131.108.3.0>.
skipping NETWORK 1: 131.108.0.0 has no associated graphical element.
adding NETWORK 2: 131.108.4.0.
setting string property <IP_Network_Number> to <131.108.4.0>.
adding ROUTER 0: ding.Cisco.com as a component.router.
setting string property <IP_Address1> to <131.108.2.5>.
setting string property <IP_Address2> to <131.108.23.5>.
setting string property <SNMP_RdCommunity> to <public>.
setting string property <SNMP_WrCommunity> to <public>.
adding agent <snmp-mibII> proxy system <(null)>.
adding agent <Cisco> proxy system <(null)>.
adding interface 131.108.23.5 mask 255.255.255.0 to view 131.108.23.0
adding interface 131.108.37.5 mask 255.255.255.0 to view 131.108.37.0
...
--------------------------------------------------
Saving the new SNM database to file /tmp/snm_new.db.
Step 3: To preserve a copy of the output of ncs2snm in a file named ncs2snm.mymap.out, enter the following command.
hostname% ncs2snm mymap | tee ncs2snm.mymap.out
Do not add an object with the same name twice to SNM. If your map file has two routers with the same name, a nonfatal error occurs when an attempt is made to add the second one to the database. It will not be added, and the first instance of that object will not be affected. If this occurs, manually create the second object in SNM under a new name. (Note that SNM is not case sensitive).
adding ROUTER 1: ding.Cisco.com as a component.router.
...
adding interface 192.31.7.129 mask 255.255.255.240 to view 192.31.7.128
snmdb_add error 10: Duplicate name.
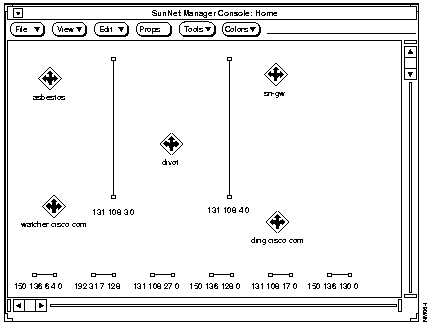
Figure B-2 shows an example map after it was translated and loaded into SNM.
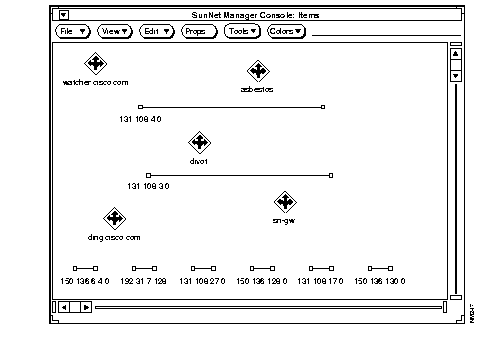
By default, the ncs2snm utility loads your map file into the Home view that is accessible from the option in SNM. To load a map file into a subview, use the -v option to name the desired subview. This subview will be created within the Home view.
For example, if your network is known locally as ournet and your map file is named mymap, then you can load your map file into a view named ournet. Use the following command:
hostname% ncs2snm -v ournet mymap
To load multiple map files into multiple views, use ncs2snm once for each map file. Specify the -p option to keep the database from being purged for each additional map you wish to merge. When you are done loading all the views, you can save the composite database containing all the views.
hostname%ncs2snm -l ournet1hostname%ncs2snm -l ournet2 -phostname%ncs2snm -l ournet3 -p
Use SNM menus to save the current SNM database.
The ncs2snm utility saves the current SNM database as the file
/tmp/snm_current.db. To save the file under a different name, use the
-c filename option.
For example, to translate and load the map file mymap1, save the current SNM database as an ASCII file. In the following example, the directory is /home/me, and the name for the new ASCII file with the SNM database is mynet.db:
hostname% ncs2snm -c /home/me/mynet.db mymap1
The ncs2snm utility normally saves the database containing the loaded map to /tmp/snm_new.db. To save it to another file, specify the filename using the -n filename option. In the following example, the loaded file
is mymap1, and the saved database is map.db in the home directory
/home/me:
hostname% ncs2snm -n /home/me/map.db mymap1
 | Caution To remove old database files (because SNM requires the file /tmp/snmdb.rpcid.userid) use the following command: |
hostname% rm /tmp/snm*.db
Avoid using the rm /tmp/snm* command, which deletes all files in that directory including the /tmp/snmdb.rpcid.userid file.
You may not wish to save and purge the current SNM database. For instance, you may wish to load your NetCentral 1.3 map file into a view in an existing SNM database. The -p option disables saving and purging of the current database. The file /tmp/snm_current.db (or the file specified by the -c option) then becomes irrelevant.
To disable the automatic saving of the SNM database containing the loaded map files, use the -u option. The file /tmp/snm_new.db (or the file specified by the -n option) then becomes irrelevant.
By default, the ncs2snm utility translates all routers in NetCentral 1.3 maps into SNM generic router icons.
To find out which devices in the map are Cisco routers, run the ncs2snm utility with the -q option.
Using the -q option causes map translation to consume more time, but the resulting map will be explicit.
hostname% ncs2snm -q mymap1
If you enable queries,the ncs2snm utility sends an SNMP query to each router to try to find out what type of device it is. If it is a communication server, Cisco AGS, or Cisco IGS, the device will be recognized and the appropriate SNM icon will be used to identify the device. Cisco protocol translators are translated as communication servers, and other routers and routing servers are translated as generic routers.
When a router is queried, the default timeout is ten seconds per router. You can specify the timeout time in seconds by using the -t option as shown below:
hostname% ncs2snm -q -t 30 mymap1
In the previous example, 30 seconds was the default timeout.
Queries use the SNM agent na.snmp on the local host (the system where the ncs2snm utility is running). Queries will function only if this agent is available and exists in your path.
For SNM to work properly, use Domain Name Service (DNS) or at least have all host names in your local hosts table. To avoid name resolution problems, ncs2snm queries routers using the address of their first interface. If no interfaces are listed, an attempt is made to query the router by name. The program ncs2snm prints messages so you can see the queries' progress and results.
asking router ding.Cisco.com its type using address 131.108.23.5 ...
adding ROUTER 0: ding.Cisco.com as a component.Cisco-AGS.
setting string property <IP_Address1> to <131.108.2.5>.
...
asking router sri-gw its type using address 192.31.7.29 ...
adding ROUTER 1: sri-gw as a component.Cisco-IGS.
...
asking router asbestos its type using its name (no known interface addresses) ...
adding ROUTER 3: asbestos as a component.router.
If you get NETMGT errors, check to see if SNM's is in your path and is operating correctly. Also, check to see if your network is experiencing connectivity problems. These problems may cause the ncs2snm utility to run for an extended period of time. You may interrupt the ncs2snm utility program, fix the problem, and start again. You may elect to translate maps rapidly without queries, making all routers generic.
The ncs2snm utility translates objects using the colors from the map file. If you specify -k on the command line, map file colors are ignored and SNM default values are used. The color defaults are black for networks and links, and blue for devices.
Some translated NetCentral 1.3 maps may appear too cramped or too spread out in the SNM Console window. Use the -s factor scaling option to customize the map. The scaling factor must be in the range 0.2 to 5.0. Values outside this range will be replaced with the nearest in-range value.
If your NetCentral 1.3 map mymap1 is spread out when you first run the ncs2snm utility, you can shrink the coordinates by using the following command:
hostname% ncs2snm -s 0.7 mymap1
Figure B-3 shows how a map displays when this command is used.
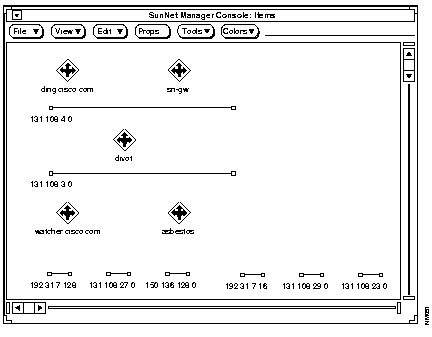
The various networks continue to appear at the bottom of the Home view because they are added with default coordinates. SNM places all icons and views with default coordinates after those with specified coordinates. The scaling and rotation provided by ncs2snm applies only to objects with specified coordinates.
If the translated mymap1 looks cluttered, use the following command to spread the elements across the window.
hostname% -s 1.5 mymap1
Figure B-4 shows an example of an expanded map.
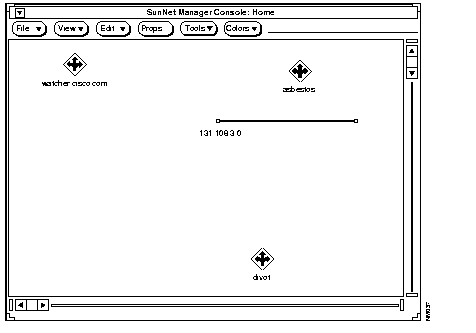
You may experiment by running the ncs2snm utility several times. You will have to move or delete /tmp/snm_current.db and /tmp/snm_new.db each time (or specify new files each time).
Some NetCentral 1.3 maps may have been created in landscape mode. The -r option (together with a flag) allows for rotation or horizontal/vertical flipping of a map. The flag values are shown in Table B-2.
| Flag Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | No rotation |
| 1 | 90 degree counterclockwise rotation |
| 2 | 180 degree rotation |
| 3 | 90 degree clockwise rotation |
| 4 | Reflect (flip) vertically |
| 5 | Reflect (flip) horizontally |
To rotate your translation of mymap1 by 90 degrees counterclockwise, use the following command:
hostname% ncs2snm -r 1 mymap1
Figure B-5 shows a map that is rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise.
Note that only relative icon positions are rotated or flipped. The picture as a whole is not rotated or flipped. All text will appear in the usual orientation.
To flip the map vertically so that objects at the top of the map appear at the bottom in SNM, use the following command:
hostname% -r 4 mymap1
This section describes some of the error messages you may see when running ncs2snm.
Error Message: ERROR: no map file specifiedExplanation:
You failed to name a map file.
Recommended Action:
Specify the name of a map file after the ncs2snm command.
Error Message: ERROR: out of memoryExplanation:
ncs2snm ran out of memory. Is your map file huge?
Recommended Action:
Check for sufficient swap space.
Error Message: ERROR: can't access file filename.Explanation:
The program cannot open the map file filename.
Recommended Action:
Check that the map file filename exists, and has the correct permissions (is readable).
Error Message: ERROR: SNM file save error (2, 0, 1)Explanation:
The program cannot save the SNM database.
Recommended Action:
Make sure that you have write permission and sufficient space on the target directory (/tmp is the default).
Error Message: ERROR: Unable to open SNM database, error number: message.Explanation:
The program cannot open the SNM database.
Recommended Action:
Check your SNM installation. The database is usually a subdirectory of/var/adm/snm. The message may explain what the problem is.
Explanation:
The ncs2snm program uses the SNM API to make additions to the database. An error occurred initializing the structure that is used for communicating with SNM.
Recommended Action:
Look at the message, which is the SNM error message. It should tell you more about the problem. The object that is causing problems is named name. If necessary, create the offending object manually in SNM.
Error Message: ERROR: gethostname() call failed?!Explanation:
The ncs2snm utility uses the C function gethostname() to obtain the name of the system it is running. This function call failed.
Recommended Action:
Make sure the hostname command works.
Error Message: ERROR: snmdb_add_to_view error number: message.Explanation:
SNM could not add an object to a view. The ncs2snm output displays information about the object and the view.
Recommended Action:
Manually add the object to the view within SNM.
Error Message: ERROR: snmdb_set_color error number: message.Explanation:
The color of an object could not be set. This information is specified in the ncs2snm output.
Recommended Action:
Set the color manually within SNM.
Error Message: ERROR: snmdb_add error number: message.Explanation:
An object could not be added to the SNM database. You can figure out which object by looking at the surrounding ncs2snm output.
Recommended Action:
An object name duplicates one already added to the SNM database. You may edit the map file and make the name unique (and then run ncs2snm again). The alternative is to manually create the object with a new name in SNM.
Error Message: ERROR: snmdb_set_property (string) error number (property: prop): message.Explanation:
The SNM property prop could not be set. The affected object may be determined from the ncs2snm output.
Recommended Action:
You may use the SNM "Properties..." dialog for the affected object to manually set the desired property.
Error Message: ERROR: snmdb_add_agent error number (agent agent): message.Explanation:
The SNM agent agent could not be specified for an object. The affected object may be determined from the surrounding ncs2snm output.
Recommended Action:
You may use the SNM "Properties..." dialog for the affected object to manually specify the desired agent.
Error Message: NETMGT ERROR: messageExplanation:
The SNM netmgt_ API is being used to perform SNMP router queries. The message message should indicate the problem.
Recommended Action:
Make sure RPC services operate correctly and use the following command
rpcinfo -p
If nothing else works, run with queries disabled. You can later manually specify router types within SNM.
Error Message: ERROR: Can't register callback function.Explanation:
To perform SNMP queries, ncs2snm has to register a callback function with the RPC services provid;er. If it cannot do so, it will not be able to perform SNMP queries. It then prints the above error message and quits.
Recommended Action:
Make sure RPC services operate correctly and use the following command
rpcinfo -p
If nothing else works, run with queries disabled. You can later manually specify router types within SNM.
|
|