This section lists specific site preparation specifications for each Cisco product. Included are any special requirements for your system, such as rack-mounting options, special power requirements, or external cable connections (where available or required).
The following is a list of the Cisco products covered in this section:
- Cisco 200 Series, page 17
- Cisco 760 Series, page 18
- Cisco 1000 Series, page 19
- Cisco 2500 Series, page 20
- Cisco 3600 Series, page 22
- Cisco 4000 Series, page 24
- Cisco AS5100 Access Server, page 26
- Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server, page 30
- Cisco 7000 Series and 7500 Series, page 32
- Cisco 7200 Series, page 43
- Cisco LightStream 1010, page 45
- Cisco LightStream 2020, page 48
- Catalyst 1200, page 55
- Catalyst 1700, page 57
- Catalyst 1800, page 59
- Catalyst 1900, page 60
- Catalyst 2000 Series, page 61
- Catalyst 2600, page 64
- Catalyst 2820, page 66
- Catalyst 3000, page 67
- Catalyst 5000, page 69
- Catalyst WS-C1400 Concentrator, page 71
- FastHub 100 Series, page 73
- StrataCom Integrated Gigabit Switch Family, page 74
- StrataCom BPX Service Node, page 76
- StrataCom Multimedia FastPAD Product Family, page 79
- StrataCom Multiprotocol FastPAD Product Family, page 81
Note On-Site Services (OSS) is not responsible for the software configuration for your Cisco product. Service is limited to hardware installation and setup.
The section "
Site Preparation Checklist," on
page 82, contains a checklist you should complete and return to Cisco Systems after you verify the preinstallation requirements discussed in this guide.
This section contains the hardware, software, and external connection requirements for the Cisco 200 series products, which include the Cisco 201, Cisco 202, Cisco 203, and Cisco 204.
Table 15 lists the hardware and software requirements for the Cisco 200 series.
Table 15: Cisco 200 Series Minimum Hardware and Software Requirements
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| PC CPU type
| 80386 or higher
|
| PC type
| Desktop
|
| Memory
| At least 1 MB
|
| PC slot
| One available half-length ISA slot
|
| PC operating system
| DOS version 5.0 or later
|
| Windows
| Version 3.1 or later
|
| Windows for Workgroups
| Version 3.11 or later
|
| Windows 95
| Version 4.0 or later
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco 200 series products.
- One ISDN BRI port with S/T for the Cisco 201 and Cisco 203. Uses an external NT-1 device.
- One U interface for the Cisco 202 and Cisco 204. An NT1 device is integrated with the interface.
This section contains physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 760 series routers, which include the Cisco 765 and Cisco 766.
Table 16 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 760 series routers.
Table 16: Cisco 760 Series Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 1.6 x 8.3 x 9.6 in (4.1 x 21.1 x 24.4 cm)
|
| Weight
| Cisco 765: 1.6 lb. (0.7 kg)
Cisco 766: 1.7 lb. (0.8 kg)
|
| Power supply
| External
|
| Voltage
| 100-250 VAC
|
| Frequency
| 50 to 60 Hz
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 120°F (0 to 50°C)
|
| Storage temperature
| - 30 to 160°F (- 35 to 70°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 20% to 95%, noncondensing
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco 760 series routers.
- ISDN Basic Rate Interfaces (BRIs)
- ISDN S/T using an RJ-45 connector
- ISDN U using an RJ-45 connector
- Ethernet Interfaces supported
- Ethernet 10BaseT using an RJ-45 connector
- Ethernet 10Base2 using a BNC connector
- Ethernet attachment unit interface (AUI) using a DB-15 connector
- Basic telephone service interface using an RJ-11 connector
- Console configuration port using a DB-9F 9-pin female connector
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 1000 series, which includes the following models: the Cisco 1001 LAN Extender, the Cisco 1003, Cisco 1004, and the Cisco 1005 routers.
Table 17 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 1000 series models.
Table 17: Cisco 1000 Series Physical Specifications
| Description
| Design Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 1.75 x 8.0 x 8.3 in (4.5 x 20. x 21 cm)
|
| Weight
| 6.0 lb (2.75 kg)
|
| Input voltage
| 12 VDC
External power supply: 100 to 240 VAC
|
| Frequency
| 50 to 60 Hz
|
| Power dissipation
| 12W (maximum), 135.5 Btus/hour
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| - 40 to 185°F (- 40 to 85°C)
|
| Humidity (noncondensing)
| 10 to 90%
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco 1000 series.
- Ethernet attachment unit interface (AUI) using a DB-15 connector
- Ethernet 10BaseT interface using an RJ-45 connector.
- X.21 synchronous serial, data terminal equipment (DTE) interface, using a DB-15 connector.
- V.35 synchronous serial, nonreturn to zero (NRZ) interface, using a 34-pin connector.
- ISDN BRI interface using an RJ-45 connector. The port is labeled "ISDN S/T" on the Cisco 1003 router and "ISDN U" on the Cisco 1004 router. The Cisco 1004 router includes an integrated NT1 device.
- Synchronous serial port using a DB-60 connector. Supports the following interfaces: EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21, and EIA-530.
- EIA/TIA-232 console port using an RJ-45 connector.
- EIA/TIA-232 console/asynchronous serial port using an RJ-45 connector.
- One external PCMCIA Type-2 slot for an integrated modem, V.34 speed.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 2500 series. The specifications apply to the following Cisco 2500 series models:
- Single LAN routers: 2501, 2502, 2503, 2504, 2520, 2521, 2522, and 2523
- Mission-specific, entry-level routers: 2501CF, 2502CF, 2503I, 2504I, 2520CF, 2520LF, 2521CF, 2521LF, 2522CF, 2522LF, 2523CF, and 2523LF
- Router/hub combinations: 2505, 2507, 2516, 2517, 2518, and 2519
- Access servers: 2509, 2510, 2511, 2512
- Dual LAN routers: 2513, 2514, and 2515
- Modular routers: 2524 and 2525
Table 18 lists the physical specifications for Cisco 2500 series.
Table 18: Cisco 2500 Series Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| Models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: 1.75 x 17.5 x 10.56 in (4.44 x 44.45 x 26.82 cm)
Models 2517 to 2519: 3.0 x 19.0 in (7.62 x 48.26 cm)
|
| Weight (average shipping)
| Models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: 10 lb (4.5 kg)
Models 2517 to 2519: 12.5 lb (5.7 kg)
|
| Power consumption
| For models 2501 to 2525: 40W
|
Input voltage and frequency,
AC power supply
| For models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: 110 to 220 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
For models 2517 to 2519: 90 to 260 VAC, 47 to 63 Hz
|
Input voltage,
DC power supply
| 40 to 72 VDC
|
| Current rating
| For models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: 1.0A at 60 Hz, 0.5A at 50 Hz
For models 2517 to 2519: 5.0A at 60 Hz, 3.5A at 50 Hz
|
| Operating temperature range
| For models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
For models 2517 to 2519: 50 to 95°F (10 to 35°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature range
| For models 2501 to 2516 and 2520 to 2525: - 40 to 185°F (- 40 to 85°C)
For models 2517 to 2519: - 4 to 185°F (- 20 to 85°C)
|
| Humidity (noncondensing)
| For models 2501 to 2525: 5 to 95%
|
| Noise level
| 34 dBa @ 3 ft (0.914 m)
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco 2500 series. The interfaces available for Cisco 2500 series products vary from model to model.
- Asynchronous serial console and auxiliary ports with RJ-45 connectors.
- Synchronous serial interface with a DB-60 connector. The synchronous serial interface supports the following standards in DTE and DCE mode: EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21. The EIA-530 standard is supported in DTE only.
- Ethernet attachment unit interface (AUI) IEEE 802.3 with a DB-15 connector or 10BaseT with an RJ-45 connector.
- Token Ring IEEE 802.5 interface with a DB-9 connector or RJ-45 connector.
- ISDN BRI interface with an RJ-45 connector.
- UTP hub ports with RJ-45 connectors.
- The Cisco 2500 series chassis can be mounted in a 19-inch or 24-inch rack, on a wall, or placed on a desktop.
Only two Cisco 2500 series models include removable WAN modules: the Cisco 2524 and the Cisco 2525. The Cisco 2524 and Cisco 2525 routers provide LAN and WAN access in a modular router platform. The Cisco 2524 router includes an Ethernet (AUI or 10BaseT) LAN connection, and the Cisco 2525 router includes a Token Ring (STP or UTP) LAN connection. Both routers can accommodate up to three WAN modules: two synchronous serial and one ISDN.
The ISDN WAN modules are keyed so that you cannot insert them into the synchronous serial WAN slots. A blank slot cover is installed over unused slots to ensure proper air flow inside the chassis.
The synchronous serial WAN modules include the following external connectors:
- 2-wire switched 56-kbps digital service unit/channel service unit (DSU/CSU) WAN module with an RJ-11 connector.
- 4-wire 56/64-kbps DSU/CSU WAN module with an RJ-48S connector.
- Fractional T1/T1 DSU/CSU WAN module with an RJ-48C connector.
- Five-in-one synchronous serial WAN module with a DB-60 serial connector. The five-in-one synchronous serial interface supports the following signaling standards: EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21, and EIA-530.
The ISDN WAN modules include the following external connectors:
- ISDN BRI WAN module with an RJ-45 connector
- ISDN WAN module, with integrated NT1 device, with an RJ-45 connector
This section contains the physical specifications and the external connection requirements for the Cisco 3600 series, which includes the Cisco 3620 and the Cisco 3640.
Table 19 contains the physical specifications for the Cisco 3600 series products.
Table 19: Cisco 3600 Series Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Input voltage, AC power supply
Current
Frequency
Power dissipation
| 100 to 240 VAC, autoranging
Cisco 3640: 2.0A; Cisco 3620: 1.0A
50 to 60 Hz
Cisco 3640: 140W (maximum); Cisco 3620: 60W
|
| Input voltage, AC power supply
Current
Power dissipation
| 38 to 72 VDC
Cisco 3640: 5.0A; Cisco 3620: 2.5A
Cisco 3640: 140W (maximum); Cisco 3620: 60W
|
| Operating humidity
| 5 to 95%, noncondensing
|
| Operating temperature range
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature range
| -40 to 185°F (-40 to 85°C)
|
| Regulatory compliance
| FCC Part 15 Class B. For additional compliance information, refer to the 3600 Series Public Network Certification document.
|
This section contains external connection requirements for the Cisco 3600 series.
The Cisco 3620 and Cisco 3640 provide the same electrical interface types and modes; however, the Cisco 3620 is a two-slot modular access router, while the Cisco 3640 is a four-slot modular access router. Both routers allow identical LAN and WAN connections that can be configured by means of interchangeable network modules and WAN interface cards.
The Cisco 3620 and Cisco 3640 have the following external connection requirements, depending on the interface modules ordered:
- The EIA/TIA-232 console port is configured as DTE and uses an RJ-45 connector
- The router ships with a cable kit to connect a console (an ASCII terminal or PC running terminal emulation software) to the console port. The console cable kit contains an RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable and RJ-45-to-DB-9 and RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapters (labeled Terminal).
- Synchronous serial interface types, except EIA-530, are available in DTE or DCE format: DTE with a plug connector at the network end and DCE with a receptacle at the network end. V.35 is available in either mode with either gender at the network end. EIA-530 is available in DTE only.
Note The serial WAN interface card uses a universal high-density, 60-pin receptacle. Each universal port requires a serial port adapter cable that determines the port's electrical interface type (EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21) and mode: DTE or DCE. Although all port adapter cables use a universal plug at the quad serial module end, the network end of each cable type uses the physical connectors commonly used for the interface. (For example, the network end of the EIA/TIA-232 port adapter cable is a DB-25 connector, the most widely used EIA/TIA-232 connector.)
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet attachment unit interface (AUI) using a DB-15 connector
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseT using an RJ-45 connector
- Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) and shielded twisted-pair (STP), IEEE 802.5 Token Ring using DB-9 connectors
- Basic Rate Interface (BRI) using RJ-45 connectors; the Network Termination 1 (NT1) circuitry is included in the router
 | Caution To prevent damage to the system, make certain you connect the BRI cable to the BRI connector only and not to any other RJ-45 connector. |
- Channelized E1/Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
- Cisco Systems makes four cables for the CE1/PRI modules. All four have DB-15 connectors on the CE1/PRI end and either BNC, DB-15, Twinax, or RJ-45 connectors on the network end.
- Channelized T1/PRI (on the CT1/PRI module only) using DB-15 connectors (for null-modem and straight-through cabling)
- Channelized T1/PRI-CSU (on the CT1/PRI-CSU module only) using a straight-through RJ-48C-to-RJ-48C cable to connect the T1 port to an RJ-48C jack
Following are the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 4000 series products, which include the Cisco 4000-M, the Cisco 4500-M, and the Cisco 4700-M.
Table 20 contains the physical specifications for the Cisco 4000 series products.
Table 20: Cisco 4000 Series Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7 in (8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm)
|
| Weight
| 24 lb (10.9 kg)
|
| Power (heat) dissipation
| 200W (682.6 Btu/hr)
|
| Input voltage, current, and frequency
| 100 to 240 VAC, 3.0 to 1.5A, 47to 63 Hz
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| - 40 to 185°F (- 40 to 85°C)
|
| Humidity (noncondensing)
| 5 to 95%
|
| Air flow and fan noise
| Fan rated at 31 cfm, at 52 dBa
|
| Agency approvals
| UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2
|
This section contains external connection requirements for the Cisco 4000 network processor modules, along with the other connections on the Cisco 4000 chassis.
All Cisco 4000 series models provide a configurable modular router platform using network processor modules (NPMs), individual removable cards used for external network connections.
The Cisco 4000 series routers can support combinations of up to three of the following NPMs:
- One-, two-, or six-port Ethernet
- Ethernet interface supported: IEEE 802.3 using attachment unit interface (AUI), DB-15 connectors, and 10BaseT using RJ-45 connectors.
- One- or two-port Token Ring
- Token Ring interfaces use DB-9 to IEEE 802.5, media attachment unit (MAU) connectors.
- One-port, both single and dual attachment station (DAS), multimode FDDI
- The multimode network processor module connectors are FDDI-standard physical sublayer (PHY) connectors. The media interface connector (MIC) connects to FDDI standard 62.5/125 micron multimode fiber optic cable. The module also has an optical bypass switch connector using a 6-pin DIN connector.
- One-port dual attachment single-mode FDDI
- The XMTR and RCVR ports use simplex, FC-type connectors.
- Two- or four-port synchronous serial
- Serial interfaces supported by these modules: EIA-530, EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21. All can be configured as nonreturn to zero inverted (NRZI), nonreturn to zero (NRZ), and DCE or DTE (except EIA-530, which is DTE only). Serial cables have DB-50 connectors for the two port module, and DB-60 connectors for the four port module.
- Four- or eight-port ISDN BRI
- Uses RJ-45 8-pin connectors.
- One-port channelized T1/ISDN PRI
- Uses a 15-pin, DB-15 connector.
- One-port channelized E1/ISDN PRI (balanced or unbalanced)
- Uses a 15-pin, DB-15 connector.
- Four-port serial G.703 (balanced or unbalanced)
- Uses 15-pin, DB-15 connectors.
- One-port ATM (single-mode or multimode) OC-3c
- Uses a duplex SC connector.
- Uses a duplex SC connector.
This section includes the other external connection requirements for Cisco 4000 series systems.
- The data communications equipment (DCE) console port uses a male DB-25 connection, and the data terminal equipment (DTE) auxiliary port uses a female DB-25 connection. (A standard EIA/TIA-232 cable can be used for either.)
- The Cisco 4000 series chassis can be optionally rack- (standard 19 inch and Telco), slide-, desk- (top or side), or wall-mounted.
This section contains the physical specifications and the external connection requirements for the Cisco AS5100 access server.
Table 21 contains the physical specifications for the AS5100.
Table 21: Cisco AS5100 Access Server Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| AS5100 chassis capacity
| Up to 17 front-loaded NACs, and their associated rear-loaded NICs. Two power supplies (both are required)
|
| Power requirements
| DC power supply nominal -48 VDC (-42 VDC to -60 VDC) with respect to ground
AC power supply nominal 120V (90 to 132 VAC) @ 47 to 63 Hz, or strap-selectable nominal 240V (180 to 264 VAC) @ 47 to 63 Hz
|
| Power supply output (maximum)
| 330W
45A @ +5.2V
2A @ -5 V
3.5A @ +12.2V
3.5A @ -12.2V
|
| Power supply input (maximum)
| 470W
1604 Btus
4A (DC)
10A (DC)
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104oF (0 to 40oC)
|
| Relative humidity
| 0-95% noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| Complies with FCC Part 15 Class A EMI/RFI requirements; complies with FCC Part 68 for nationwide telephone systems; listed by Underwriters' Laboratories (UL), approved by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), and is Department of Communications (DOC) certified
|
Table 22 contains the physical specifications for the AS51 NAC and NIC cards.
Table 22: AS51 NAC and NIC Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
Power requirements
(maximum)
| 4A @ +5 VDC, 6.75W
55 mA @ - 5 VDC, 275 mW
50 mA @ +12 VDC, 600 mW
50 mA @ 12 VDC, 600 mW
|
| Dimensions (L x H)
| NAC: 12.45 x 6.4 in (31.62 x 16.26 cm)
NIC: 4.85 x 6.4 in (12.32 x 16.26 cm)
|
| Certification
| Complies with FCC Part 15, UL-listed, CSA-approved
|
Table 23 contains the physical specifications for the Quad Modem NAC and NIC cards.
Table 23: Quad Modem NAC and NIC Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
Power requirements
(maximum)
| 1.35A @ +5 VDC, 6.75W
55 mA @ -5 VDC, 275 mW
50 mA @ +12 VDC, 600 mW
50 mA @ 12 VDC, 600 mW
|
| Dimensions (L x H)
| NAC: 12.45 x 6.4 in (31.62 x 16.26 cm)
NIC: 4.85 x 6.4 in (12.32 x 16.26 cm)
|
| Certification
| Complies with FCC Part 15, UL-listed, CSA-approved
|
Table 24 contains the physical specifications for the T1 NAC and NIC cards.
Table 24: T1 NAC and NIC Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Power requirements
| 1.5A @ 5 VDC
0.1A @ 12 VDC
5W
|
| Dimensions (L x H)
| NAC: 12.45 x 6.4 in (31.62 x 16.26 cm)
NIC: 4.85 x 6.4 in (12.32 x 16.26 cm)
|
| Heat
| 17 Btus
|
Table 25 contains the physical specifications for the network management NAC card.
Table 25: Network Management NAC Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Power requirements (maximum)
| 3.5A @ +5 VDC
20 mA @ - 5 VDC
50 mA @ +12 VDC
50 mA @ - 12 VDC
|
| Dimensions (L x H)
| 12.45 x 6.4 in (31.62 x 16.26 cm)
|
| Certification
| Complies with FCC Part 15 Class A, FCC Part 68, UL-listed, CSA-approved, and DOC-certified
|
Table 26 contains the physical specifications for the network management Ethernet NIC card.
Table 26: Network Management Ethernet NIC Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Power requirements
| 1.5A @ +5 VDC
50 mA @ +12 VDC
50 mA @ - 12 VDC
|
| Dimensions (L x H)
| 4.85 x 6.4 in (12.32 x 16.26 cm)
|
| Certification
| Complies with FCC Part 15 Class A, FCC Part 68, UL-listed, CSA-approved, and DOC-certified
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the AS5100 access server.
- The AS51 NAC and NIC function together to form 16 asynchronous serial ports using the SCSI II-to-DB-50 breakout cable. The access server module interfaces include Ethernet 10BaseT, asynchronous serial, and synchronous serial. The AS51 NIC provides two 68-pin asynchronous ports that connect to the modem NICs in the Access Server 5100 chassis.
- NAC card
- Ethernet 10BaseT using an RJ-45 connector
- Console port
- The NAC has an RJ-45 console asynchronous serial port. A connection to a terminal uses an RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter. Depending on the adapter used, this port becomes a data communications equipment (DCE) device or a data terminal equipment (DTE) device. To use the terminal as a console you should use a DCE RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter.
- An RJ-45 auxiliary asynchronous serial port is included on the NAC. A connection to a modem for network access uses an RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter. The adapter you use turns this port into a DCE device or a DTE device. A connection to a digital service unit/channel service unit (DSU/CSU) or protocol analyzer uses a DTE RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter.
- Synchronous serial interface port
- Supports the following interfaces: EIA/TIA-530, EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21
- NIC card
- 68-pin asynchronous serial ports
- Each of the two 68-pin asynchronous serial ports supports eight EIA/TIA-232 serial ports. A supplied breakout cable splits each 68-pin port into two 50-pin connectors, which in turn connect to the quad modem NICs.
- Each chassis houses up to 48 high-speed analog or digital modems. Digital modems connect to the phone system by a direct T1 link through the T1 interface card. Analog modems connect to standard telephone lines through the modem interface card.
- The quad modem provides four dial-up modems on a single card. Each modem is capable of supporting V.32 (19.2 kbps) modulation and MNP Levels 1-5 or V.42/V.42 error correction and data compression, or V.34 (28.8 kbps).
- The quad modem EIA/TIA-232 NIC provides the physical interface for four EIA/TIA-232 ports via a 50-pin connector. A breakout cable is provided to adapt this interface to standard DB-25/DB-9 EIA/TIA-232 connectors.
- The T1 NIC and T1 NAC route incoming digital T1 lines to the quad modems.
- The T1 NIC uses RJ-48 connectors. It also provides an RJ-45 connector for the EIA/TIA-232 interface port. The T1 NIC is compatible with an external channel service unit (CSU) if required, and provides a serial interface to the T1 NAC.
- The network management NAC and NIC manage all the devices in the AS5100 access server using SNMP.
- Two power supplies provides AC or DC power input, and supplies DC power to the installed cards via connectors in the midplane. Both power supplies are required in the chassis.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements of the Cisco AS5200 universal access server.
Table 27 lists the physical specifications for the AS5200 access server.
Table 27: Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 3.5 x 17.5 x 15 in two rack units (8.89 x 44.45 x 38.1 cm)
|
| Weight
| 25 lb (11.4 kg)
|
Input voltage, AC power supply
Current frequency
Power dissipation
| 100 to 240 VAC
1.0 to 2.0A50 to 60 Hz
180W (maximum), 135.5 Btus/hour
|
Input voltage, DC power supply
Maximum input current
Typical input current
Power dissipation
Output voltage
| - 48 to - 60 VDC
6.0A
4.0A
180W (maximum)
5.0 VDC
|
Alarm relay rating:
Voltage
Current
Maximum switching power
Maximum switching voltage
|
48 VDC
3A
150W
220 VAC
|
| Operating environment
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| - 40 to 185°F (- 40 to 85°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 5 to 95%, noncondensing
|
| Noise level
| 34 dB @ 3 ft (0.914 m)
|
The Cisco AS5200 access server has a 19-inch modular chassis that accommodates up to three feature cards. The feature cards should be a combination of one or two WAN cards and one or two modem carrier cards.
The types of cards and their external connection requirements are as follows:
- Dual T1 Primary Rate Interface (PRI) card with integrated channel service units (CSUs)
- The dual T1 PRI card routes incoming digital T1 lines to the modem modules. It uses RJ-48C connectors.
- Modem carrier card with one or two 12-port modem cards
- The Cisco AS5200 access server can contain 12, 24, 36, or 48 modem ports installed on two carrier cards in the chassis card slots. Each modem carrier card holds up to two, 12-port modem cards. The modem cards connect through the carrier card and the system backplane to the dual T1 PRI card. Transmission or reception is then accomplished on T1 lines connected to the dual T1 PRI card.
- A serial connection to the modem can be made through the Ethernet attachment unit interface (AUI) port or the serial ports on the chassis.
- A blank slot cover is installed over any unused slots.
Additional external connections for the Cisco AS5200 are as follows:
- Two serial WAN interface ports
- The serial ports on the Cisco AS5200 are five-in-one synchronous serial using 60-pin, D-type connectors. The interface supports EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21 (NRZ/NRZI and data terminal equipment (DTE)/DCE mode), and EIA-530 (NRZ/NRZI and DTE mode).
- One Ethernet LAN port using an AUI, DB-15 connector
- Console port
- An EIA/TIA-232 (RJ-45) console asynchronous serial port connects to a terminal using an RJ-45 cable and an RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter or to a PC using an RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter.
- An EIA/TIA-232 (RJ-45) auxiliary asynchronous serial port can connect to a modem for remote maintenance or other access services. The port uses an RJ-45 roll-over cable with a male modem (MMOD) adapter (labeled "Modem") for this connection.
- The three-pin alarm port is a future enhancement that will connect the Cisco AS5200 to an external audio, visual, or other alarm. The alarm port is not supported by current versions of the system software or the feature cards.
- Two Cisco AS5200 power supplies provide AC or DC power input and supply DC power to the installed cards via connectors in the backplane. Either the AC or DC power supply is required in the chassis.
The following are the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 7000 series and the Cisco 7500 series. The external connection requirements and rack mount requirements are the same for Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series. Physical specifications and power supply requirements vary from system to system. This section includes the following systems: the Cisco 7000 series--the Cisco 7000 and the Cisco 7010; the Cisco 7500 series--the Cisco 7505, Cisco 7507, and the Cisco 7513.
This section includes the physical specifications and power supply requirements of the Cisco 7000.
Table 28 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7000.
Table 28: Cisco 7000 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 19.25 x 17.5 x 25.1 in (48.90 x 44.45 x 63.75 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis only: 76 lb (34.47 kg)1; chassis fully configured: 1 RP2, 1 SP (or SSP), or RSP7000 and RSP7000CI, 7 interface processors, and 2 power supplies: 145 lb (65.76 kg)
|
| Power supply
| 700W maximum
|
| Power (heat) dissipation
| 282W (962.5 Btu/hr), maximum configuration
626W (2136.5 Btu/hr), maximum configuration
530W (1808.9 Btu/hr), typical with maximum configuration
|
| Total power (heat) dissipation
| 1200W (4095.6 Btu/hr)
|
| Input voltage and frequency
| 100 to 240 VAC wide input with power factor corrector (PFC), 50 to 60 Hz
|
| AC input rating
| 12A maximum @ 90 VAC with chassis fully configured (AC-input power supplies)
|
| DC input rating
| - 40 volts (V) minimum, - 48V nominal, - 72V maximum (AC-input power supplies)
|
| Airflow
| Dual blowers rated at a total of 140 cfm, at a noise level of 58 dBa
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90% noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2-950, EN60950, EN41003, AUSTEL TS001, AS/NZS 3260 EMI: FCC Class A, EN55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2
|
1
The weight of the Cisco 7000 requires that two people be available for the chassis installation.
2
RP = Route Processor. SP = Switch Processor. RSP-7000 = 7000 series Route Switch Processor. RSP7000CI = 7000 series Chassis Interface.
The Cisco 7000 contains either one 700W AC-input power supply or one 700W DC-input power supply. A second power supply, identical to the first, can be added for redundant power. These power supplies are automatically load sharing and redundant, which means a second power supply can be installed or replaced without interrupting system operation.
Each power supply should be connected to a separate AC or DC source, so that, in case of an input power line or power supply failure, the second power supply maintains uninterrupted system power. Ideally, an uninterruptible powers source (UPS) would be available for each AC-input power supply.
This section contains the physical specifications and power supply requirements for the Cisco 7010.
Table 29 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7010.
Table 29: Cisco 7010 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 10.5 x 17.5 x 17 in (26.67 x 44.45 x 43.18 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis only (power supply and fan array): 46 lb (20.87 kg)
Chassis fully configured: 1 RP1, 1 SP (or SSP), or RSP7000 and RSP7000CI, 3 interface processors: 70 lb (31.75 kg)
|
| Power supply
| 600W maximum
|
| Power dissipation
| 550W maximum configuration, 540W typical with maximum configuration
|
| Heat dissipation
| 715W (2440 Btu/hr)
|
| Input voltage and frequency
| 100 to 240 VAC wide input with power factor corrector (PFC), 50 to 60 Hz
|
AC input rating
(AC-input power supply)
| 9A maximum at 100 VAC, 4A maximum at 240 VAC with chassis fully configured
|
DC input rating
(DC-input power supply)
| - 40 volts DC (VDC) minimum in North America (- 56V in Europe)
- 48 VDC nominal in North America (- 60V in Europe)
- 52 VDC maximum in North America (- 75V in Europe)
|
| Airflow
| Six muffin fans (fan array), side to side through chassis
|
| Operating temperatures
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) and - 4 to 149°F (- 20 to 65°C) for nonoperating temperature
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2-950, EN60950, EN41003, AUSTEL TS001, AS/NZS 3260EMI: FCC Class A, EN60555-2, EN55022 Class B, VDE 0878 Part 3, 30 Class B Immunity: EN55101/2 (ESD), EN55101/3 (RFI), EN55101/4 (Burst), EN55101/5 (Surge), EN55101/6 (Conducted), IEC77B (AC Disturbance)
|
1
RP = Route Processor. SP = Switch Processor. RSP-7000 = 7000 series Route Switch Processor. RSP7000CI = 7000 series Chassis Interface.
The Cisco 7010 comes equipped with one 600W AC-input power supply or one 600W DC-input power supply. The AC-input power supply operates on AC input power and supplies DC power to the internal components. The DC-input power supply operates on DC input power and supplies DC power to the internal components.
The AC power receptacle (or DC-input terminal block), power on/off switch, and status LED are on the interface processor end of the power supply. A modular power cord connects the AC power supply to the site power source. A cable retention clip on the power supply AC receptacle prevents the cable from being pulled out accidentally. The DC-input is supplied by a three-lead, 8-AWG cable you provide.
Inside the AC-input or DC-input power supply, two small fans draw cooling air through the power supply interior. The air flows in one side of the supply and out the other side, following the same direction as the chassis cooling air.
This section includes the physical specifications and power supply requirements of the Cisco 7505.
Table 30 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7505.
Table 30: Cisco 7505 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| High-speed backplane
| 5-slot, 1.067-Gbps CyBus: 4 interface processor slots plus the RSP slot
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 10.5 x 17.5 x 17.0 in (26.67 x 44.45 x 43.18 cm)
Chassis depth including power cord and cable management fixture is 19 in (48.26 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis only (including power supply and fan array): 46 lb (20.87 kg)
Chassis fully configured with RSP1 and 4 interface processors: 70 lb (31.75 kg)
|
| Power dissipation
| 600W maximum configuration with AC-input power supply
600W maximum configuration with DC-input power supply
540W typical with maximum configuration
|
| Heat dissipation
| 715W (2440 Btus/hr)
|
| AC-input voltage
| 100 to 240 volts AC (VAC), wide input with power factor corrector (PFC)
|
| Frequency
| 50 to 60 Hz
|
| AC-input current
| 9A maximum @ 100 VAC
4A maximum @ 240 VAC at 600W
|
| DC-input voltage
| -40 volts DC (VDC) minimum in North America (-56 VDC in the Europe Community)
-48 VDC nominal in North America (-60 VDC in the Europe Community)
-52 VDC maximum in North America (-72 VDC in the Europe Community)
20A maximum at -48 VDC and 16A maximum @ -60 VDC
|
| DC voltages supplied and maximum, steady-state current ratings for AC- and DC-input
| +5.2 VDC @ 75 amps (A)
+12 VDC @ 15A
- 12 VDC @ 3A
+24 VDC @ 5A
|
| DC-input cable
| 8 AWG (American Wire Gauge); recommended minimum wire gauge
|
| DC-input hold-up time
| 10 milliseconds (ms) of output after the DC input has been interrupted
|
| Airflow
| Side-to-side through chassis by variable-speed, 6-fan array
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| -4 to 149°F (-20 to 65°C)
|
| Relative humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
The Cisco 7505 comes equipped with one 600W AC-input power supply or one 600W DC-input power supply. The AC-input power supply operates on AC-input power and supplies DC power to the internal components. The DC-input power supply operates on DC-input power and supplies DC power to the internal components.
The AC power receptacle (or DC-input terminal block), power on/off switch (or circuit breaker-type switch on the DC-input power supply), and status LED are on the interface processor end of the power supply. A modular power cable connects the AC-input power supply to the site AC power source. A cable retention clip on the power supply AC receptacle prevents the cable from being pulled out accidentally. The DC-input is supplied by a three-lead, 8-AWG cable that you provide.
Inside the AC-input or DC-input power supply, two small fans draw cooling air through the power supply interior. The air flows in one side of the supply and out the other side, following the same direction as the chassis cooling air.
This section includes the physical specifications and power supply requirements of the Cisco 7507.
Table 31 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7507.
Table 31: Cisco 7507 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| High-speed backplane
| 1.067-Gbps CyBus (the 7507 has dual CyBuses), 7 slots
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 19.25 x 17.5 x 25.1 in (48.90 x 44.45 x 63.75 cm)
Chassis depth including power cable is 28 in (71.12 cm).
|
| Weight
| Chassis only: 76 lb (34.47 kg)
Chassis fully configured with 2 RSP2s, 5 interface processors,
and 2 power supplies: 145 lb (65.76 kg)
|
| DC-input voltage
| -40 volts direct current (VDC) minimum
-48 VDC nominal
-72 VDC maximum
|
| DC voltages supplied and steady-state maximum current ratings
| +5.2V @ 100 amps (A)
+12V @ 15A
-12V @ 3A
+24V @ 5A
|
| DC-input power
| 1000 watts (W)
|
| DC-input power supply hold-up time specification
| 10 milliseconds (ms) of output after the input has been interrupted
|
| DC-input wiring
| 8 AWG (American Wire Gauge) wire, which you provide
|
| Power supply
| 700W maximum (AC-input and DC-input power supplies)
|
| Power dissipation
| 626W maximum configuration, 530W typical with maximum configuration
|
| Heat dissipation
| 1200W (4100 Btu/hr)
|
| Input voltage
| 100 to 240 VAC wide input with power factor correction (PFC)
|
| Frequency
| 50 to 60 Hz (hertz) autoranging
|
| AC current rating
| 12A maximum at 100 VAC, 6A maximum at 240 VAC with the chassis fully configured
|
| Airflow
| 140 cfm (cubic feet per minute) through the system blower
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| -4 to 149°F (-20 to 65°C)
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
The Cisco 7507 contains either one 700W AC-input power supply or one 700W DC-input power supply. An optional second power supply, identical to the first, can be added for redundant power. These power supplies are automatically load-sharing and redundant, which means a second power supply can be installed or replaced without interrupting system operation.
Each power supply should be connected to a separate AC or DC source, so that, in case of an input power line or power supply failure, the second power supply maintains uninterrupted system power. Ideally, an uninterruptible powers source (UPS) would be available for each AC-input power supply.
This section includes the physical specifications and power supply requirements of the Cisco 7513.
Table 32 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7513.
Table 32: Cisco 7513 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Backplane
| 13-slot, two 1.0677-Gbps CyBuses: 11 interface processor slots plus the two RSP2 slots
|
Dimensions
(H x W x D)
| 33.75 x 17.5 x 22 in (85.73 x 44.45 x 55.88 cm)
Chassis width including rack-mount flanges is 18.93 in (48.1 cm)
Chassis depth including power cord and cable management fixture is 24 in (60.96 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis with blower module: 75 lb (34.02 kg)
Chassis with blower module and 1 power supply: 100 lb (45.36 kg)
Chassis with blower module and 2 power supplies: 125 lb (56.7 kg)
Chassis with blower module, 2 power supplies, and all slots filled: 160 lb (72.58 kg) Each processor module weighs 2.5 lb (1.13 kg)
|
| Power dissipation
| 1600W with a maximum configuration and one AC-input power supply
1600W with a maximum configuration and one DC-input power supply
1700W nominal with a maximum configuration and two AC- or DC-input power supplies
|
| Heat dissipation
| 1600W (5461 Btu/hr)
|
| AC-input voltage and current
| 100 VAC1 at 16 amps (A) maximum2 wide input with power factor correction (PFC)
240 VAC at 7A maximum
|
| Frequency
| 50/60 Hz
|
| AC-input cable
| 12 AWG (American Wire Gauge), with three-leads, an IEC-320 receptacle on the power supply end, and a country-dependent plug on the power source end
|
| DC-input voltage and current
| -48 VDC3 nominal, at 35 amps (A) in North America
(-60 VDC at 35A in the E.C.)
|
| DC-input cable
| 8 AWG recommended minimum, with three conductors rated for at least 194°F (90°C)
|
| DC voltages supplied and maximum, steady-state current (AC- and DC-input)
| +5.2 VDC @ 75 A
+12 VDC @ 15A
-12 VDC @ 3A
+24 VDC @ 5A
|
| Airflow and noise level
| Through chassis by variable-speed blower; 62 to 70 dBA
|
| Temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C), operating; - 4 to 149°F (- 20 to 65°C), nonoperating
|
| Relative humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
1
VAC = volts alternating current.
2
Each AC-input power supply operating at 120 VAC requires a dedicated 20A service and a 20A receptacle.
3
VDC = volts direct current.
The Cisco 7513 contains either one 1200W AC-input power supply or one 1200W DC-input power supply. An optional second power supply, identical to the first, can be added for redundant power. These power supplies are automatically load sharing and redundant, which means a second power supply can be installed or replaced without interrupting system operation. Each power supply should be connected to a separate AC or DC source, so that, in case of an input power line or power supply failure, the second power supply maintains uninterrupted system power. Ideally, an uninterruptible power source (UPS) would be available for each AC-input power supply.
Note The Cisco 7513 requires that a 20-amp (A) service be available at your site. Wiring codes prevent 20A plugs from being used with most equipment rack power strips. The installation must comply with all applicable codes. The ground bond fastening hardware should be of compatible material and preclude loosening, deterioration, and electro chemical corrosion of hardware and joined material. Installation is approved for use with copper conductors only. Attachment of the chassis ground receptacles to the central office or other interior ground system should be made with a Number 6 AWG copper ground conductor as a minimum. The Cisco 7513 chassis employs two threaded, M4 x .7 chassis ground receptacles. These receptacles are intended to be bonded directly to the central office or other interior ground system, and are located on each side of the rear of the chassis. The chassis ground receptacles require M4 bolts and locking hardware, which are not included.
Follow these precautions and recommendations when planning power connections to the router:
- Check the power at your site before installation and periodically after installation to ensure that you are receiving clean power. Install a power conditioner if necessary.
- Provide redundant power sources for each power supply installed in the chassis.
- For AC-input installations, install an uninterruptible power source where possible.
- Install proper grounding to avoid damage from lightning and power surges.
- For both AC-input and DC-input installations, observe the power specifications listed in Table 32.
The AC-input-powered chassis operating at 120 VAC requires, at the minimum, a 20-amp service, with a 20-amp receptacle at the power source. The power cable supplied with the chassis uses a 20-amp plug. Figure 1 shows the cable features needed to connect the 20-amp plug to your AC source.
Figure 1: 20-amp AC Power Cable Connector, Plug, and 20-amp Receptacle
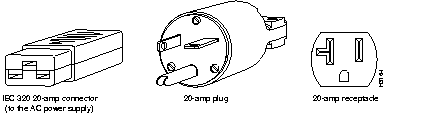
Note Wiring codes prevent 20A plugs from being used with most equipment rack power strips.
The DC powered chassis requires a minimum 35A dedicated service (at - 48VDC). We recommend that you use an 8 AWG, highly flexible, stranded cable for the DC power connections. The stranded cable should be routed through conduit at your site, and the conduit should attach to the terminal block cover on the power supply. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2: Terminal Block Cover
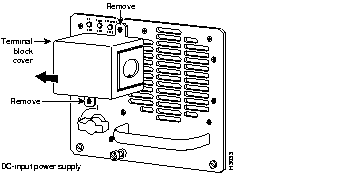
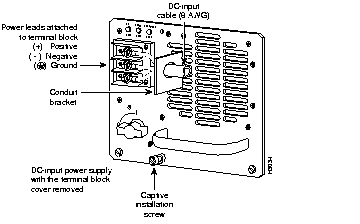
Figure 3 shows the conductor preparation for the DC-input cable connections.
Figure 3: DC Power Cable Connection to Terminal Block
This section lists the external connection requirements for the Cisco 7000 series and 7500 series.
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Interface Processor (AIP)
- All AIP interfaces are full duplex. Use the appropriate ATM interface cable to connect the AIP to an external ATM network.
- The AIP supports the following interface connectors:
- Transparent Asynchronous Transmitter/Receiver Interface (TAXI) multimode fiber optic using a MIC connector
- SONET/SDH using simplex or duplex SC connectors
- SONET/SDH using ST2 connectors
- E3 using a coaxial BNC connector
- DS3 using a coaxial BNC connector
- Ethernet Interface Processor (EIP)
- Each Ethernet port on the EIP requires a connection to an Ethernet transceiver with a transceiver cable, or to an attachment unit with an AUI. Some Ethernet transceivers, usually 10BaseT, can connect directly to the EIP port.
- Fast Ethernet Interface Processor (FEIP)
- The MII port can be connected to your network directly with an MII cable, or can be connected through a 100BaseT or 100BaseF transceiver.
- RJ-45 ports do not require a transceiver.
Note A single 100BaseT port adapter can use either the RJ-45 (or optical fiber) connection or the MII connection. If you have two port adapters on your FEIP, you can use either one of the two connections on each port adapter, but not both connections on each port adapter simultaneously.
- Token Ring Interface Processor (TRIP)
- Token Ring MAU connectors provide a direct connection between the TRIP and the ring.
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Interface Processor (FIP)
- Both single-mode and multimode, single and dual attachment connections are available and can be combined on one FIP. Fiber optic cable connects directly to FIP ports using SC connectors for single mode and MIC connectors for multimode. Single-mode uses separate transmit and receive cables. Multimode uses one transmit/receive cable for each physical sublayer (PHY) interface.
- Optical bypass switch connector (6-pin DIN) on the Multimode/Multimode interface.
- Fast Serial Interface Processor (FSIP)
- All FSIP ports support any available interface type and mode. The serial adapter cable determines the electrical interface type and mode of the port to which it is connected. E1-G.703/G.704, EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21 interfaces are available in data terminal equipment (DTE) mode with a plug at the network end and in DCE mode with a receptacle at the network end. EIA-530 is available only in DTE mode with a plug.
- High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI) Interface Processor (HIP)
- The HIP port functions as a DTE when it is connected to a DSU for a standard HSSI connection; it can also be connected to a collocated router with a null-modem cable. Connecting the router to an HSSI network uses an HSSI interface cable between the HIP port and the DSU. HSSI cable ends are identical.
- Channel Interface Processor (CIP)
- The CIP has two channel adaptors, a bus and tag adapter and an ESCON adapter. The bus and tag adapter is called a Parallel Channel Adapter (PCA), and the ESCON adapter is called an ESCON Channel Adapter (ECA). The PCA uses 78-pin connectors for a Y cable. The ECA uses a fiber optic ESCON cable with duplex connectors.
- Multichannel Interface Processor (MIP)
- Two standard T1 serial cables can be used to connect the MIP: null-modem and straight-through. These interface cables are used to connect your MIPs to additional MIPs or to external CSUs, respectively.
- You must use null-modem cables for MIP-to-MIP connections and straight-through cables for MIP-to-CSU connections. The T1 cables used to connect the MIP with external T1 equipment have DB-15 male connectors on each end.
- Four types of E1 cable can be used to connect the MIP: BNC, Twinax, DB-15, and RJ-45. The E1 cables used to connect the MIP with external E1 equipment have a DB-15 male connector on the MIP end.
- Versatile Interface Processor (VIP)
- The VIP uses port adapters that provide the following electrical interfaces: synchronous serial using EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21 DTE and DCE cables, and EIA-530 DTE cables only; IEEE 802.5 Token Ring using RJ-45, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseT using RJ-45, IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet 100BaseTX and 100BaseFX using MII and RJ-45 or MII and SC-type optical fiber.
- Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2)
- The VIP2 uses port adapters that provide the following electrical interfaces: synchronous serial using EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21 DTE and DCE cables, and EIA-530 DTE cables only; IEEE 802.5 Token Ring using RJ-45; IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseT using RJ-45; IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseFL using ST-type multimode, optical fiber; IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet 100BaseTX and 100BaseFX using MII and RJ-45 or MII and SC-type optical fiber; and single-mode and multimode FDDI using MIC and SC-type optical fiber.
Note The VIP2 requires that the Cisco 7000 series system has the 7000 Series Route Switch Processor (RSP7000) and the 7000 Series Chassis Interface (RSP7000CI) installed.
- The data communications equipment (DCE) console port uses a male DB-25 connection, and the data terminal equipment (DTE) auxiliary port uses a female DB-25 connection. (A standard EIA/TIA-232 cable can be used for either.)
The Cisco 7000 series and 7500 series operate as either freestanding or rack-mounted units. An optional rack-mount kit is available for mounting the chassis in an EIA-310C standard 19-inch equipment rack or in a Telco-type rack. When the system is not mounted in a rack, place it on the floor or on a sturdy platform. Do not stack the chassis on other Cisco 7000 series, 7500 series, or any other equipment.
Note The Cisco 7000, Cisco 7507, and Cisco 7513 use the same rack-mount kit, but have different rack-mounting applications and requirements, which are discussed in the documentation that ships with the rack-mount kit.
Following are the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Cisco 7200 series. The Cisco 7200 series includes the Cisco 7204 and Cisco 7206 routers.
Table 33 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco 7204 and the Cisco 7206 routers.
Table 33: Cisco 7204 and Cisco 7206 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 5.25 x 16.8 x 17 in (13.34 x 42.67 x 43.18 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis fully configured with a network processing engine, I/O controller, 6 port adapters, 2 power supplies, and a fan tray: ~50 lbs (22.7 kg)1
|
| Heat dissipation
| 370W (1262 Btu2)
|
| AC-input voltage
| 100-240 VAC3 wide input with power factor correction
|
| AC-input current rating
| 5A4 maximum at 110 VAC and 2.5A maximum at 240 VAC with the chassis fully configured
|
| AC-input cable
| 18 AWG5 three-wire cable, with a three-lead IEC-320 receptacle on the power supply end, and a country-dependent plug on the power source end
|
| DC-input voltage
| -48 VDC6 nominal in North America
-60 VDC nominal in the European Community
|
| DC input current rating
| 14A maximum at -48 VDC
|
| DC-input cable
| 14 AWG (2.08 mm2) recommended minimum, with at least three conductors rated for at least 140°F (60°C).
|
| DC voltages supplied and maximum, steady-state current ratings
| +5.2V @ 30A
+12.2V @ 9A
-12.0V @ 1.5A
+3.5V @ 13A
|
| Frequency
| 50/60Hz7
|
| Airflow
| ~80 cfm8
|
| Temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) operating; -4 to 149°F (-20 to 65°C) nonoperating
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90% noncondensing
|
1
We suggest that two people be available for the chassis installation.
2
Btu = British thermal units.
3
VAC = volts alternating current.
4
A = ampere.
5
AWG = American Wire Gauge.
6
VDC = volts direct current.
7
Hz = hertz.
8
cfm = cubic feet per minute.
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco 7204 and Cisco 7206 routers.
- Input/Output Controller (I/O controller)
- The I/O controller has two EIA/TIA-232 ports: a DCE-mode console port and a DTE-mode auxiliary port. The console port is a DCE DB-25 receptacle for connecting a data terminal, which you will use to configure the interfaces and bring up the router.
- The auxiliary port is a DTE DB-25 plug for connecting a modem or other DCE device (such as a CSU/DSU or other router) to the router. A standard EIA/TIA-232 cable can be used for the auxiliary and console ports.
- The MII connector supports IEEE 802.3u interfaces compliant with the 100BaseX and 100BaseT standards. The single MII connection requires an external transceiver that permits connection to multimode fiber for 100BASE-FX or 100BaseT4 physical media.
- Port adapters
- The Cisco 7204 and the Cisco 7206 routers use port adapters that provide the following electrical interfaces:
- Synchronous serial using EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, and X.21 DTE and DCE cables, and EIA-530 DTE cables only
- IEEE 802.5 Token Ring using RJ-45 connections
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseT using RJ-45 connections
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseFL using ST-type multimode, optical fiber connections
- IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet 100BaseTX and 100BaseFX using MII and RJ-45 or MII and SC-type optical fiber connections
- Single-mode and multimode FDDI using MIC and SC-type optical fiber connections
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the LightStream 1010 ATM switch.
Table 34 lists the physical specifications for the Cisco LightStream 1010.
Table 34: Cisco LightStream 1010 Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| Chassis: 10.5 x 17.2 x 18.1 in (26.7 x 43.7 x 46.1 cm); standard 19-inch rack mount
ASP1 and CAM: 1.2 x 14.4 x 16.0 in (3.0 x 36.6 x 40.6 cm)
PAM2: 1.2 x 6.5 x 10 in (3.0 x 16.5 x 25.4 cm)
|
| Weight
| Empty: 43 lb (19.5 kg)
Fully loaded: approximately 85 lb (39 kg) (depends on loading)
|
| Power supply
| Maximum power budget: 9.8A @ 115 VAC, 60 Hz 4.9A @ 230 VAC, 50 Hz
Auto sensing limits: 100-127/200-240 VAC, 8/4A, 47-63 Hz
Maximum wattage: 376 watts (W)
|
| Altitude
| - 500 ft to 10,000 ft (- 52 m to 3,048 m)
|
| Temperature
| 32° F to 104° F (0° C to 40° C)
|
| Relative humidity
| 10 to 90% noncondensing
|
| Safety certifications
| UL 1950
EN 60950
CSA-C22.2 No. 950-93
Electromagnetic emissions certifications
FCC Class A (Part 15)
EN 55022 Class B
CE Mark
VCCI Class II
|
1
ASP = ATM Switch Processor.
2
PAM = Port adapter module.
The LightStream 1010 uses a five-slot chassis with an ATM backplane and fan tray. It has the following external connection requirements:
- ATM Switch Processor (ASP)
- Console and Auxiliary (AUX) serial port
- Two asynchronous EIA/TIA-232 serial ports on the ASP, the console and auxiliary ports, provide the means for connecting a terminal, modem, or other device for configuring and managing the system. A data communications equipment (DCE) EIA/TIA-232 (female connector) receptacle console port on the ASP provides a direct connection for a console terminal.
- The adjacent data terminal equipment (DTE) EIA/TIA-232 (male connector) plug auxiliary port supports flow control and is often used to connect a modem, a channel service unit (CSU), or other optional equipment for Telnet management of the attached device.
- The Ethernet management RJ-45 port can be used to connect a management workstation and enables SNMP management of the LightStream 1010 switch.
- Feature card
- The feature card is a daughter card of the ASP module and implements a number of value-add capabilities over and above the base switch mechanisms.
- Port adapter module carrier
- The port adapter module carrier (CAM) can be installed in any slot, except slot number 2, in the LightStream 1010 and allows any combination of port adapter modules (PAMs) to be installed with a maximum of two PAMs per CAM. Port adapters are numbered 0 and 1, with 0 on the left, facing the rear of the switch.
- 155-MM port adapter module
- Provides connections for four multimode fiber optic interfaces using four duplex SC connectors.
- 155-SM port adapter module
- Provides connections for four single-mode fiber optic interfaces using SC connectors.
- 155-UTP port adapter module
- Provides connections to four UTP interfaces using RJ-45 connectors.
- Provides connections to two DS-3 interfaces using BNC coaxial connectors.
- Provides connections to two E3 interfaces using BNC coaxial connectors.
- 622-SM port adapter module
- Provides a connection to an OC12 interface using a duplex SC, single-mode, fiber optic connector.
- The high-speed backplane operates at 5 Gbps. The backplane provides the connection between the power supplies, the ASP, the port adapter modules, and the backbone. The backplane slots are numbered 0 through 4, with 0 at the top of the card cage and 4 at the bottom.
The LightStream 1010 ATM switch comes equipped with one 350W AC-input power supply. An optional second power supply, identical to the first, can be added for redundant power. Dual power supplies are automatically load sharing and redundant, which means that a second power supply can be installed or replaced without interrupting system operation.
When two power supplies are installed and both are turned on, each concurrently provides about half of the required power to the system. If one of the power supplies fails, the second power supply immediately ramps up to full power to maintain uninterrupted system operation. Load sharing and fault tolerance are automatically enabled when the second power supply is installed; no software configuration is required.
Each power supply can be connected to a separate AC source so that, in case of an input power line or power supply failure, the second power supply maintains uninterrupted system power.
The field-replaceable system fan assembly provides cooling air for the ASP, interface modules, and backplane. The fan assembly is located inside the chassis.
An internal fan in each power supply draws cooling air from the front of the chassis through the power supply and out the rear of the chassis. An air dam keeps the power-supply airflow separate from that of the rest of the chassis, which is cooled by the fan assembly.
When you are facing the front of the chassis, the fan assembly draws cool air from the right side of the chassis to cool the modules. The exhaust air is forced out the left side of the chassis.
Sensors on the ASP monitor the internal chassis air temperatures. If the air temperature at the sensor exceeds a desired threshold, the environmental monitor displays warning messages.
This section contains the physical specifications, external connection requirements, power supply requirements, and ventilation requirements for the Cisco LightStream 2020 ATM switch.
Table 35 lists the dimension and environmental specifications for the LightStream 2020.
Table 35: LightStream 2020 Switch Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 26.07 x 18.91 x 24.73 in (66.2 x x 48.0 62.8 cm)
|
| Operating temperature at sea level (760 mm Hg)1
| 41o to 104o F (5o to 40o C)
|
| Relative operating humidity
| 10% to 90% noncondensing
|
| Altitude1
| Up to 10,000 feet (3048 m)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| - 4o to 140o F (- 20o to 60o C)
|
| Nonoperating humidity
| 10% to 95% noncondensing
|
| Air quality
| The LightStream 2020 is designed to run in a noncorrosive, relatively dust-free environment.
|
1
Reduce the maximum operating temperature by 1o F (.56 o C) for every 1000 feet (304.8 m) of altitude above 10,000 feet (3048 m).
Table 36 shows how to calculate the weight of a LightStream 2020 system.
Table 36: Calculating the Weight of a LightStream 2020
| System Configuration
| Weight
|
|---|
| Base system/AC power1
| 96.0 lb (43.6 kg)
|
| Redundant base system2/AC power
| 118.0 lb (53.6 kg)
|
| Base system/DC power
| 91.0 lb (41 kg)
|
| Redundant base system/DC power
| 108.0 lb (49 kg)
|
Optional components:
Interface module (up to 9 modules)
Fantail3 (up to 18 fantails)
|
3.75 lb (1.7 kg)
1.9 lb (0.9 kg)
|
Example:
Base system/AC power
With 4 medium-speed modules (4 x 3.75 lb)
With 2 low-speed modules (2 x 3.75 lb)
With 4 fantails (4 x 1.9 lb)
|
96.0 lb
15.0 lb
07.5 lb
07.6 lb
|
| Total weight
| 126.1 lb
|
1
Base system includes chassis, two blowers, power supply, disk assembly, network processor module, and switch card.
2
Redundant base system includes chassis, two blowers, two power supplies, two disk assemblies, two network processor modules, and two switch cards.
3
All low-speed and serial interface modules require fantails. T3, E3, and E1 CEMAC modules might also require fantails, depending on mode of operation.
To ensure that your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system is capable of maintaining the proper operating temperature range for your LightStream 2020 switch, refer to the heat dissipation information provided in Table 37.
Table 37: LightStream 2020 Power Consumption/Heat Dissipation
| Component
| Power Consumption
| Heat Dissipation
|
|---|
| Base system
| 335W
| 1145 Btu/hr
|
| Redundant base system
| 445W
| 1525 Btu/hr
|
Optional components:
Low-speed modules
Medium-speed modules
Packet modules
Cell modules
|
65W
65W
55W
30W
|
225 Btu/hr
225 Btu/hr
190 Btu/hr
105 Btu/hr
|
| Maximum configuration1
| 965W
| 3325 Btu/hr
|
1
Redundant base system with 8 low-speed or medium-speed modules.
Table 38 lists the power requirements of the LightStream 2020.
Table 38: LightStream 2020 Site Power Requirements
| Power Option
| Voltage
| Current
|
|---|
| AC
| 100 to 240V
| 20A to 10A
|
| DC
| 48V
| 24A
|
Table 39 lists the AC power ratings for the LightStream 2020.
Table 39: LightStream 2020 AC Power Ratings
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Inlet power connector
| IEC 320 C20
|
| Input voltage frequency phase
| 100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz single
|
| Input current
| 16A to 8A
|
| Power consumption1
| 975W maximum
|
| Heat dissipation
| 3330 Btu/hr maximum
|
1
See
Table 37 for additional power-related information.
Table 40 lists the DC power ratings for the LightStream 2020.
Table 40: LightStream 2020 DC Power Ratings
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Input connections
| Support for up to 2 separate - 48 VDC input feeds via 3-position terminal blocks
|
| Input voltage
| - 43 to - 60VDC
|
| Input current
| 24A
|
| Power consumption1
| 975W maximum
|
| Heat dissipation
| 3330 Btu/hr maximum
|
1
See
Table 37 for additional power-related information.
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Cisco LightStream 2020. External connectors attach to access cards and fantails on the interface modules of the LightStream 2020.
The cell line card is designed to support up to 15 ports. It supports the following access cards and fantails:
- OC-3c multimode access card (OC3AC MM) uses duplex SC connectors for up to two ports
- OC-3c single-mode access card (OC3AC SM) uses ST connectors for up to two ports
- E3 access card (E3AC)
- E3ACs are available in 8-port or 4-port versions. Each port has two SMB connectors.
- The E3 access card contains internal digital service units/channel service units (DSU/CSUs) that can connect directly to an E3 line. E3 access card ports can also connect LightStream 2020 nodes directly at distances up to 1250 feet (381 meters).
- T3ACs are available in 8-port or 4-port versions. Each port has two SMB connectors. Each connector is cabled to a 75-ohm BNC coaxial connector on the fantail that provides DS3-compliant connections.
- Each access card contains internal DSU/CSUs that can connect directly to a leased T3 line. T3 access card ports can also connect LightStream 2020 nodes directly at distances up to 900 feet (274 meters).
- Certain interface modules support more ports than can be accommodated on the access cards. T3/E3 fantails provide ports for cell line card/T3 modules and cell line card/E3 modules.
- T3/E3 fantails are available in four-port and eight-port versions.
- The fantail has 8 or 16 BNC connectors, one for transmitting (TX) and one for receiving (RX) on each port. The fantail measures 1.75 inches (1 rack unit, or 4.5 cm) high by 19 inches (48.3 cm) wide. It is designed to fit standard 19-inch equipment racks. Each T3/E3 fantail includes a special cable harness to connect the fantail to its access card.
The packet line card supports the following access cards:
- The Ethernet access card operates in conjunction with a packet line card. Each card supports up to eight IEEE 802.3 Ethernet ports. There are a total of ten connectors for the eight ports.
- Six of the ports have a single RJ-45 female connector (ports 1 to 6)
- Two of the ports have two connectors: an RJ-45 female connector and a DB-15 female connector (ports 0 and 7)
- These ports support the following interfaces:
- 10BaseT twisted pair Ethernet (RJ-45)
- 10Base5 (thick wire) Ethernet (DB-15 attachment unit interface [AUI])
- 10Base2 (thin wire) Ethernet (DB-15 AUI)
- 10BaseFL (fiber) Ethernet (DB-15 AUI)
Note Only one of the two connectors for each of these ports can be used at a time.
- Fiber Ethernet access card
- Each fiber Ethernet access card supports up to eight 802.3 Ethernet 10BaseFL ports. For each port, the fiber Ethernet access card has two ST connectors that support a multimode fiber interface. One connector is for the receive channel and the other is for the transmit channel. There are a total of 16 connectors on the card.
- Each FDDI access card supports two multimode FDDI ports. Each port consists of two media interface connectors (MIC), keyed and labeled as MIC A and MIC B. One 6-pin DIN connector per port is provided for an optional optical bypass cable.
- T1 and E1 circuit emulation access cards
- The circuit emulation access cards have a single 50-pin champ (or "telco") I/O connector, to which you attach a fanout device to support up to eight ports. The necessary connectors are provided by fantail devices.
- The E1 fantail provides 75-ohm ports for E1 circuit emulation access card modules. The fantail measures 3.27 inches (8.3 cm) high by 19 inches (48.3 cm) wide. It is designed to fit standard 19-inch equipment racks. Two versions of the E1 fantail are available:
- E1 fantail with BNC connectors
- E1 fantail with SMZ connectors
- Each E1 fantail supports up to 12 ports with 24 connectors--one for transmitting and one for receiving on each port. (E1 fantails currently support a maximum of eight ports because the circuit emulation access card supports a maximum of eight ports.)
- The serial access card supports up to eight full-duplex serial I/O ports that can be frame forwarding ports, Frame Relay ports, or a combination of the two. To accommodate those ports, the card has two 100-pin connectors. These connectors can be attached to interface-specific fantails (V.35, EIA/TIA-449, or X.21) that hold the connectors for the I/O ports.
- Access to T1 (DS1) or E1 lines is accomplished through the use of external data service units and channel service units (DSUs/CSUs) connected to EIA/TIA-232 ports on theV.35 or EIA/TIA-449 fantails.
- Each line on the serial access card includes a separate interface to control the external DSU/CSU. The control interface is supported by 9-pin male connectors for each port on the V.35 and EIA/TIA-449 fantails. (X.21 lines do not require DSU/CSU control ports.)
- A low-speed line card configured as an edge card provides eight full-duplex serial lines. The card supports Frame Forwarding and Frame Relay interfaces, and a single card can have any mix of Frame Relay and Frame Forwarding ports. Physical line interfaces include V.35, X.21, and EIA/TIA-449.
- External DSU/CSU for the low-speed line card
- Access to T1 (DS1) or E1 lines is accomplished through the use of external DSUs/CSUs connected to fantails over V.35 or EIA/TIA-449 serial interfaces.
- Each line on the low-speed line card includes a separate interface to control the external DSU/CSU. The control interface is supported by 9-pin male connectors for each port on the V.35 and EIA/TIA-449 fantails. (X.21 lines do not require DSU/CSU control ports.)
- The V.35/EIA/TIA-449/X.21 low-speed access card operates in conjunction with the low-speed line card. The card supports up to eight I/O ports. To accommodate those ports, the card has two 100-pin connectors. These connectors can be attached to interface-specific fantails (V.35, EIA/TIA-449, or X.21) that hold the connectors for the I/O ports.
- Serial and low-speed fantails
- Certain interface modules support more ports than can be accommodated on the access cards. The necessary connectors are provided by fantail devices. Fantails provide ports for serial interface modules and low-speed interface modules. Serial speed fantails measure 1.75 inches (1 rack unit or 4.5 cm) high by 19 inches (48.3 cm) wide, and weigh 2 lb (0.9 kg). They are designed to fit standard 19-inch equipment racks.
- Three types of fantails are available for these modules:
- The V.35 fantail has four V.35 data terminal equipment (DTE) ports, using four ISO 2593 connectors.
- The EIA/TIA-449 fantail has four EIA/TIA-449 DTE ports, using male DB-37 connectors.
- The X.21 fantail has eight X.21 ports, using female DB-15 connectors.
- Using switches on the X.21 fantail, each X.21 port can be set to either DTE or DCE mode. The connectors on the fantail are female, the standard for DCE. If you set an X.21 port to be a DTE, you must attach a 15-pin male-to-male gender converter to change the connector on the fantail from female to male.
- DSU/CSU control ports
- In addition to the four port connectors, each V.35 and EIA/TIA-449 fantail has four 9-pin male D-type EIA/TIA-232 connectors for DSU/CSU control ports, also known as craft ports. X.21 fantails do not have DSU/CSU connectors.
This section describes medium-speed line and access cards.
- A single access card for each medium-speed edge card supports two ports. (No fantails are needed for medium-speed edge ports.) Three medium-speed access cards are available; one supports DS3/T3 lines, and the other two support E3 lines. The medium-speed edge card handles ATM UNI traffic between the LightStream 2020 network and other ATM devices.
- A single access card for each medium-speed trunk card supports two ports. (No fantails are needed for medium-speed trunk ports.) Three medium-speed access cards are available; one supports DS3/T3 lines, and the other two support E3 lines. All cards labeled MSC on the bulkhead are functionally equivalent.
- E3 medium-speed access card
- E3 medium-speed access cards, labeled MSAC, support up to two ports each. Each port has two 75-ohm BNC coaxial connectors that provide G.703-compliant connections. One connector is for the receive channel (Rx), and the other is for the transmit channel (Tx).
- T3 medium-speed access card
- T3 medium-speed access cards, labeled MSAC, support up to two ports each.
- Each T3 medium-speed access card has four 75-ohm BNC coaxial connectors that provide DS3-compliant connections. Each port consists of two connectors: one for the receive channel (Rx) and one for the transmit channel (Tx).
- Each access card contains internal DSU/CSUs that can connect directly to a leased T3 line. T3 access card ports can also connect LightStream 2020 nodes directly at distances up to 900 feet (274 meters).
The network processor access card supports one Ethernet port and a pair of serial ports.
In an LightStream 2020 switch, a bulk power tray unit converts power from an external source to bulk DC voltage before distributing DC power to the individual function and switch cards. The nominal voltage of the bulk power unit is -48 VDC.
There are up to two power trays in each chassis; each power tray is a field replaceable unit (FRU). If there are two power trays, both are connected to a 48-volt rail so that either tray can drive the entire system.
The power tray slots, designated A (on top) and B (on the bottom), are accessible from the rear of the chassis.
LightStream 2020 systems are available with two power options:
- AC-powered systems for sites with alternating current (100 to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz)
- AC power supplies accept input power over a continuous range from 100 VAC to 240 VAC at 50 or 60 Hz. No adjustment or configuration is required. Each AC power tray has one recessed male power inlet that conforms to IEC standard 320 C20; it requires a power cord with an IEC 320 C19 connector.
- If a system has two power trays, the trays must be plugged into separate electrical circuits for true redundancy.
- DC-powered systems for sites with direct current (-48 VDC)
- DC-powered LightStream 2020 systems accept power over a continuous range from -43 VDC to - 60 VDC. No adjustment or configuration is required. Power from an external -48 VDC source is brought into the system by the DC power tray.
- DC-powered LightStream 2020 systems do not use detachable power cords; they must be permanently wired to a DC power source by qualified service personnel. Systems with the optional second power tray can be wired from a dual power feed.
The LightStream 2020 chassis takes in cooling air from the front. Air is drawn up through the chassis and is exhausted at the back and the right side by blower units.
There are two blowers located at the top of the chassis in each LightStream 2020 system. One blower is accessible from the front and the other from the rear. Each blower is an FRU. During normal operation, both blowers should be running. If one blower fails, the system can continue to operate; however, the failed blower should be replaced as soon as possible.
In addition to the main air flow through the chassis, each bulk power tray in an AC-powered system contains its own fans.
The cooling system operates properly only when all cards, bulkheads, filler panels, covers, and components are in place. Removing these items disrupts the flow of air through the chassis, which can cause the system to shut down components to prevent damage from overheating.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1200 series switch. The Catalyst 1200 includes four models: WS-C1201, WS-C1202, WS-C1211, and WS-C1212.
Table 41 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 1200 series switch.
Table 41: Catalyst 1200 Series Switch Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 2.7 x 17.4 x 16 in (6.96 x 44.2 x 40.6 cm)
|
| Weight
| 17 lb (7.7 kg)
|
| AC and DC voltage and current
| 100 to 120 VAC, 2.0A maximum, 60 Hz
200 to 240 VAC, 1.0A maximum, 50 Hz
12A @ +5 VDC, 1A @ +12 VDC, 0.5A @ -12 VDC
|
| Power consumption
| 80W, maximum (273.04 Btu/hr)
|
| EMI1 certifications
| FCC Class A (47 CFR, Part 15)
CISPR 22 Class A
VDE Class A
VCCI Class 1
|
| Safety approvals
| UL: 1950
CSA-C22.2 No. 950-M89
IEC 950
|
|
|
|
FDDI transmit power levels:
Single-mode fiber
Multimode fiber
| Average optical power:
Maximum: - 4.0 dBm
Minimum: - 7.0 dBm2
Maximum: - 14.0 dBm
Minimum: - 18.5 dBm
|
FDDI receive power levels:
Single-mode fiber
Multimode fiber
|
Average optical sensitivity: - 33 dBm
Average maximum input power: - 14 dBm
Average optical sensitivity: - 34 dBm
Average maximum input power: - 14 dBm
|
1
EMI = electromagnetic interference.
2
dBm - decibels per milliwatt.
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1200 switch:
- Administrative interface port: EIA/TIA-232 data communications equipment (DCE) using an RJ-45 connector (straight-through modular cables only).
- 8-port Ethernet interface with the following connectors:
- 10BaseT (WS-C1201)-using RJ-45 connectors
- 10BaseF (WS-C1211)-using ST-type connectors
- A/B port card slot for the following dual attachment station (DAS) interfaces:
- Multimode FDDI using media interface connectors (MICs)
- Single-mode FDDI using ST-type connectors
- CDDI/MLT-3 using category 5, UTP modular, RJ-45 connectors (cross-connect modular cables only)
- For network connections using FDDI-to-CDDI twisted-pair connections, you will need the optional CDDI-FDDI translator.
- To connect CDDI to shielded twisted-pair (STP), use an impedance-matching balance/unbalanced (balun) device.
- Modems
- The EIA/TIA-232 standard is supported at data rates from 50 to 38,400 baud.
- Request To Send (RTS), Clear To Send (CTS), and Data Terminal Ready (DTR) signals are supported.
- Optical bypass switch connector (6-pin DIN).
- The stackable unified management port is out-of-band Ethernet 10BaseT using a female, RJ-45, UTP connection. The stackable unified management port uses an RJ-45, modular, cross-connect cable when connecting to end systems; and straight-through cable when connecting to hubs. You can connect the stackable unified management port to an Ethernet 10BaseT hub for Telnet, File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and SNMP management connection to the switch.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1700 Ethernet desktop switch
Table 42 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 1700 switch.
Table 42: Catalyst 1700 Switch Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 5.25 x 12.28 x 19" (13.34 x 31.19 x 48.26 cm)
|
| Weight
| 18 lb (8.2 kg)
|
| Reliability
| 50,000 hours MTBF
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104ºF (0 to 40ºC)
|
| Operating humidity
| 10% to 90%, noncondensing
|
| Operating altitude
| Up to 10,000 feet
|
| Power consumption
| 60W
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1700.
- 24 personal Ethernet ports, using RJ-45 connectors
- The personal Ethernet ports require 10BaseT compatible Category 3, 4, or 5 unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded twisted-pair (STP) wiring. The attached workstation must be within 100 meters of the Catalyst 1700 (10BaseT requirement) and have standard 10BaseT adapters and software installed.
- One general Ethernet port
- The port has three available connectors that each support different cabling types:
Note Only one general Ethernet connector can be plugged in at a time.
- An RJ-45 connector. It uses 10BaseT compatible UTP or STP wiring. The attached network or device must be within 100 meters of the Catalyst 1700.
- A BNC connector. It uses 10Base2 compatible thin coaxial cable and can be up to 185 meters in length.
- A female 15-pin attachment unit interface (AUI) connector. It interfaces to an external thick coaxial, thin coaxial, 10BaseT or fiber optic transceiver. The external transceiver can be attached via an 802.3 compatible AUI cable, which can be up to 50 meters in length. Supported network and device distances will vary depending on the type of transceiver used.
- Two Fast Ethernet ports using RJ-45 connectors
- Fast Ethernet ports require Category 5 UTP cabling. The attached server, workstation, or hub must be within 100 meters of the port. The server or workstation must have a 100BaseX compatible adapter installed.
Note Only one port can be connected to a network. The rest must be connected to individual stations.
- One serial EIA/TIA-232 port using a 9-pin male subminiature connector (for configuration and management)
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1800 Ethernet desktop switch.
Table 43 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 1800 switch.
Table 43: Catalyst 1800 Physical Specifications
| Specification
| Description
|
|---|
| Temperature
| 32° to 104° F (0° to 40.0°C) ambient room temperature
|
| Relative humidity
| 0% to 90% noncondensing
|
| Electrical power
| 60 to 120 watts (W); 90-230 V @ 50-60 Hz
|
| Power supply
| 1 or 2 replaceable units
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| Standalone: 3.5 x 17 x 21 in (89 x 432 x 534 mm)
Rack-mount: 3.5 x 19 x 21 in (89 x 483 x 534 mm)
|
| Weight
| 40 lbs
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1800.
- A 9-pin, male, management port that functions as a DTE port. This port enables attachment of a console terminal or terminal emulator that is used to customize the switch's configuration, monitor switch activity and status, and test the switch. Console access can be either local, by direct attachment to the EIA/TIA-232 port, or remote, through a modem connection. The EIA/TIA-232 port automatically detects the baud rate of the terminal to which it is attached.
- The switched Token Ring ports use shielded RJ-45 connectors, supporting either Category 3 and Category 5 UTP cables and Type 1 STP cables. Each port is autosensing and autoconfiguring for 4-Mbps or 16-Mbps ring speeds and UTP or STP cabling.
- Eight or 16 IEEE 802.5 Token Ring or 12 Token Ring interfaces with 1 FDDI (using the FDDI Uplink module).
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1900 Ethernet desktop switch.
Table 44 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 1900 switch.
Table 44: Catalyst 1900 Physical Specifications
| Characteristic
| Description
|
|---|
| Operating temperature
| 32-104°F (0-40°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 10% to 90%
|
| Operating altitude
| Up to 10,000 feet
|
| Power consumption
| 65 watts (W)
|
| Input voltage
| 90 to 250 V @ 50 to 60 Hz
|
| Reliability
| 50,000 hours MTBF
|
| Weight
| 10.5 lb (4.78 kg)
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 1.73 x 17.5 x 15.3 in (4.39 x 44.45 x 38.86 cm)
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 1900.
- A 9-pin, male, management port that functions as a DTE port. This port enables attachment of a console terminal or terminal emulator that is used to customize the switch's configuration, monitor switch activity and status, and test the switch. Console access can be either local, by direct attachment to the EIA/TIA-232 port, or remote, through a modem connection. The EIA/TIA-232 port automatically detects the baud rate of the terminal to which it is attached.
- 25 switched Ethernet ports: 24 10BaseT and one AUI
- The 10BaseT ports use RJ-45 connectors to connect to single workstations, 10BaseT hubs, or any 10BaseT compatible device. The attached devices use standard 10BaseT adapters and wiring. Port 25, located on the back panel, supports an alternative AUI connection using a DB-15 connection for attachment to a thick coaxial, thin coaxial, or a fiber optic media transceiver.
- Two fixed 100BaseT ports using RJ-45 connections
- Each 100BaseT port is internally switched to the other Catalyst 1900 ports. One or both of these can be set to collision-free full-duplex mode for full-duplex operation.
This section includes the physical specifications and the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 2000 series switches. The Catalyst 2000 series consists of three models: the Catalyst 2100, Catalyst 2800, and the Catalyst 2900.
Table 45 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 2100 and Catalyst 2800 switches.
Table 45: Catalyst 2100 and Catalyst 2800 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 5.25 x 19 x 12.28 in (13.34 x 48.26 x 31.2 cm)
|
| Weight
| Catalyst 2100: 18 lb (8.17 kg)
Catalyst 2800: 23 lb (10.4 kg)
|
| Input voltage
| 90 to 250V @ 50 to 60 Hz
|
| Power consumption
| Catalyst 2100: 60W
Catalyst 2800: 110W
|
| Operating altitude
| up to 10,000 ft (3048 m)
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
|
| Operating relative humidity
| 10% to 90% noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| UL 1950, CE, CSA 22.2, LR100902, TUV, EN60950, FCC Class A, EN55022A
|
Table 46 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 2900 switch.
Table 46: Catalyst 2900 Switch Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 3.4 x 17.25 x 23 in (8.5 x 43.8 x 58.4 cm)
Chassis depth including cable guide is 21.64 in (55.0 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis: 41 lb (18.6 kg)
|
| DC voltages supplied and steady-state maximum current ratings
| +5V @ 30A+12V @ 2A+24V @ 0.2A
|
| Power supply
| 175W maximum (AC-input power supplies)
|
| Power dissipation
| 240W maximum configuration.
|
| Heat dissipation
| 240W (818 Btu1per hour)
|
| Input voltage
| 100-240 VAC wide input with power factor corrector
|
| Frequency
| 47-63 Hz autoranging
|
| AC current rating
| 3A maximum at 100-240 VAC
|
| Airflow
| 95 cfm2 through the system fan assembly
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| -40 to 167°F (-40 to 75°C)
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| Safety: UL3 1950, CSA4-C22.2 No. 950-93, and EN60950EMI11: FCC Class A (47 CFR, Part 15),CE Mark, EN55022 Class B and VCCI Class 2 with shielded cables
|
1
Btu = British thermal units.
2
cfm = cubic feet per minute.
3
UL = Underwriters Laboratory.
4
CSA = Canadian Standards Association.
This section contains the external connection requirements for Catalyst 2000 series switches.
This section lists the external connection requirements for Catalyst 2100 and Catalyst 2800 switches.
- Twenty-five 10BaseT ports, twenty-four of which require RJ-45 connectors. The twenty-fifth port uses an AUI connector.
- Two 100BaseTX ports (Catalyst 2100), which require RJ-45 connectors.
- EIA/TIA-232(1) management console port that uses a DB-9 connector.
- Two high-speed expansion slots (Catalyst 2800):
- The high-speed expansion slots accept the field-installable modules for the Catalyst 2800. The field modules require the following external connections:
- 100BaseTX module: uses RJ-45 connectors.
- 100BaseFX module: uses ST connectors.
- FDDI module: uses MIC connectors.
- CDDI module: uses RJ-45 connectors.
This section contains the external connection and ventilation requirements for the Catalyst 2900.
The Catalyst 2900 is a 2-slot, 14-port, fixed-configuration switch that fits in a standard 19-inch rack. One of the two slots is for the supervisor module; the other slot is for a 10/100BaseTX or 100BaseFX module. The modules have the following external connections:
- Supervisor engine module
- Console port using a DB-25 female connector.
- Two 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet ports provide (100BaseTX category 5 UTP) Fast Ethernet interfaces operating in full- or half-duplex mode. The Ethernet ports use either RJ-45 or MII connections. If two cables are connected to the same port, the MII is the default connection.
- 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet switching module
- The 10/100-Mbps Fast Ethernet switching module (10/100BaseTX 12 port) provides connections to 12 switched 10/100-Mbps (10/100BaseTX Category 5 UTP) full- or half-duplex Fast Ethernet interfaces using 12 RJ-45 female connectors.
- Fast Ethernet switching module
- The Fast Ethernet switching module (100BaseFX 12 port) provides connection to 12 switched 100-Mbps (100BaseFX fiber optic) full- or half-duplex Fast Ethernet interfaces using 12 SC fiber optic connections.
- The system fan assembly provides cooling air for the supervisor engine module, interface module, and power supply. The fan assembly is located inside the chassis compartment. Facing the front of the chassis, the fan assembly draws cool air from the right side to cool the modules. The exhaust air is forced out the left side of the chassis.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 2600.
Table 44 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 2600.
Table 47: Catalyst 2600 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| Standalone: 3.5 x 17.3 x 14 in (89 x 440 x 356 mm)
Rack-mount: 3.5 x 19 x 14 in (89 x 483 x 356 mm)
|
| Weight
| 17 lbs (7.7 kg)
|
| Reliability
| 50,000 hours MTBF
|
| Power consumption
| 100 watts (W)
|
| Operating altitude
| Up to 10,000 feet
|
| Operating temperature
| 50° to 104°F (10° to 40°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 8% to 80%
|
| Electrical power
| 0.2 kVA
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for Catalyst 2600:
- A 9-pin, male, management port that functions as a DTE port. This port enables attachment of a terminal or terminal emulator that is used to customize the switch's configuration, monitor switch activity and status, and test the switch. Console access can be either local, by direct attachment to the EIA/TIA-232 port, or remote, through a modem connection. The EIA/TIA-232 port automatically detects the baud rate of the terminal to which it is attached.
- The base unit of the Catalyst 2600 has 16 shielded RJ-45 connectors for Token Ring connection. These ports allow half-duplex (HDX) or full-duplex (FDX) connections to other switches, hubs, or end nodes and support the IBM cabling system via 150-ohm, shielded twisted-pair (150-ohm STP) or 100- or 120-ohm twisted-pair via Category 3, 4, or 5 cables.
- IEEE 802.5 Token Ring connector
- Table 48 and Table 49 specify the maximum supported lobe lengths for the following types of cables. An additional 33 ft (10 m) per lobe length is allowed to accommodate patch cables, unless otherwise specified.
Table 48: Lobe Lengths for 150-Ohm Shielded Media
| Ring Speed
| Types 1 and 1a, Types 2 and 2a
| Type 8
| Type 9
|
|---|
| 4 Mbps
| 2460 ft (750 m)
| 1234 ft (376 m)
| 1640 ft (500 m)
|
| 16 Mbps
| 952 ft (290 m)
| 480 ft (146 m)
| 656 ft (200 m)
|
Note Subtract 33 ft (10 m) from the allowed Type 1 or 2 distance each time a 8 ft (2.4-m) patch cable is replaced by a Type 6, 30 ft (9-m) patch cable on that lobe.
Table 49: Lobe Lengths for 100-/120-Ohm Shielded or Unshielded Cable
| Ring Speed
| 100-Ohm Type 3
| 100-Ohm Category 3
|
|---|
| 4 Mbps
| 328 ft (100 m)
| 820 ft (250 m)
|
| 16 Mbps
| Not Supported
| 328 ft (100 m )
|
Note Unshielded media requires appropriate filtering.
Table 50: Lobe Lengths for 100- and 120-Ohm Shielded or Unshielded Cable
| Ring Speed
| 100- or 120-Ohm Category 4
| 100- or 120-Ohm Category 5
|
|---|
| 4 Mbps
| 1148 ft (350 m)
| 1148 ft (350 m)
|
| 16 Mbps
| 656 ft (200 m)
| 656 ft (200 m)
|
Note Unshielded media requires appropriate filtering.
Table 51: Lobe Lengths for 100-/120-Ohm Shielded or Unshielded Cable
| Ring Speed
| 100-OhmType 3
| 100-Ohm Category 3
| 100- or 120-Ohm Category 4
| 100- or 120-Ohm Category 5
|
|---|
| 4 Mbps
| 328 ft (100 m)
| 820 ft (250 m)
| 1148 ft (350 m)
| 1148 ft (350 m)
|
| 16 Mbps
| Not Supported
| 328 ft (100 m)
| 656 ft (200 m)
| 656 ft (200 m)
|
Note Unshielded media requires appropriate filtering. A Token Ring network supports up to 260 attaching devices or nodes on a single network when using 150-ohm shielded media (type 1, 1A, 2, or 2A). When cable segments in the network are 100 or 120 ohm, this number is decreased to 132 (72 if using any 4-Mbps-only adapters or filters).
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 2820.
Table 45 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 2820.
Table 52: Catalyst 2820 Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 3.34 x 17.5 x 12.4 in (8.76 x 44.45 x 31.5 cm)
|
| Weight
| 13 lbs (5.90 kg)
|
| Reliability
| 50,000 hours MTBF
|
| Power consumption
| 110 watts (W)
|
| Operating altitude
| Up to 10,000 ft
|
| Operating temperature
| 32-104°F (0-40°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 10% to 90%
|
| Input voltage
| 90 to 250 V @ 50 to 60 Hz
|
Following are the external connection requirements for Catalyst 2820.
- This 9-pin, male, management port functions as a DTE port. This port enables attachment of a terminal or terminal emulator that is used to customize the switch's configuration, monitor switch activity and status, and test the switch. Console access can be either local, by direct attachment to the EIA/TIA-232 port, or remote, through a modem connection. The EIA/TIA-232 port automatically detects the baud rate of the terminal to which it is attached.
- 25 switched Ethernet ports: 24 10BaseT using RJ-45 connections and one AUI using a DB-15 connection.
- The Ethernet 10BaseT ports can connect to single workstations, 10BaseT hubs, or any 10BaseT compatible device. The attached devices use standard 10BaseT adapters and wiring. Port 25, located on the back panel, supports an alternative Ethernet AUI connection for attachment to a thick coaxial, thin coaxial, or a fiber optic media transceiver.
- Two high-speed expansion slots supporting 100BaseT, FDDI, and future ATM modules.
- The high-speed expansion slots are compatible with Catalyst 2820 field-replaceable modules and provide high-bandwidth connections to backbones, servers, and other high-performance devices. Each expansion slot is internally switched to all other Catalyst 2820 ports.
- 100BaseTX module: uses unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable
- 100BaseFX module: uses single-mode, SC-type, optical fiber
- FDDI module: dual attachment station (DAS) and single attachment station (SAS), uses multimode optical fiber cable (with MICs)
- CDDI module: SAS, uses Category 5 UTP cable
The following sections describe the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 3000 system, which consists of the Catalyst 3000 switch and the Catalyst 3000 Matrix.
Table 53 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 3000 system.
Table 53: Catalyst 3000 System Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Mounting
| 19-inch rack-mount
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| Catalyst 3000 switch: 3.5 x 17 x 13.4 in (8.76 x 43 x 34 cm)
Catalyst Matrix: 3.5 x 17 x 13.4 in (8.75 x 43 x 34 cm)
|
| Weight
| Catalyst 3000 switch: 17 lb (7.7 kg)
Catalyst Matrix: 14 lb (6.35 kg)
|
| Input
| 90 to 264 VAC autoranging
|
| Frequency
| 47 to 63 Hz
|
| AC current rating
| Catalyst 3000 switch: 1.5A @ 120V;.75A @ 220V
Catalyst Matrix: 1.0A @ 120V;.5A @ 220V
|
| Operating temperature range
| 50 to 104°F (10 to 40°C)
|
| Storage temperature
| -13 to 167°F (-25 to 75°C)
|
| Operating humidity
| 8 to 80% noncondensing
|
| Storage altitude
| 40,000 ft
|
| Emissions
| FCC Class A (Part 15), EN55022 A, VCCI Class 1, CE Mark
|
| Agency Approvals
| UL1950, ULC, EN 60950
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst 3000 switch and the Catalyst 3000 Matrix.
The Catalyst 3000 16-port switch is a stackable switch with the following external connection requirements:
- Sixteen 10BaseT Ethernet ports using RJ-45 connectors (ports 1-15 always MDI-X, port 16 can be MDI or MDI-X)
- One EIA/TIA-232 console port
- One AUI DB-15 SwitchProbe port
- One SCSI-2 port
- Two expansion module slots. The expansion modules require the following external connections:
- 100BaseTX module: using RJ-45 connectors
- 100BaseFL module: using ST-type connectors
The Catalyst Matrix is an 8-port crosspoint matrix switch used to connect from three to eight 16-port switches to create a single-stack entity.
The Catalyst Matrix has eight I/O stack ports using 50-pin SCSI-2 type connectors (one per port).
The following section describes the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst 5000 series switch.
Table 54 lists the physical specifications for the Catalyst 5000 series switch.
Table 54: Catalyst 5000 Series Switch Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specifications
|
|---|
| Backplane
| 1.2-Gbps1, 5 module connections
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 10.4 x 17.25 x 18.4 in (26.4 x 43.1 x 46.0 cm)
Chassis depth including cable guide is 21.64 in (55.0 cm)
|
| Weight
| Chassis only: 43 lb (19.5 kg)
Chassis fully configured with 1 supervisor engine module, 4 switching modules,
and 2 power supplies: 84 lb (39 kg)
|
| DC voltages supplied and steady-state maximum current ratings
| +5V @ 70A
+12V @ 2A
+24V @ 0.2A
|
| Power supply
| 376W maximum (AC-input power supplies)
|
| Power dissipation
| 350W maximum configuration, 110W typical with maximum configuration
|
| Heat dissipation
| 563W (1919 Btu2/hr)
|
| Input voltage
| 100 to 240 VAC wide input with power factor corrector
|
| Frequency
| 47 to 63 Hz autoranging
|
| AC current rating
| 8A maximum at 100-127 VAC, 4A maximum at 200 to 240 VAC with the chassis fully configured
|
| Airflow
| 95 cfm3 through the system fan assembly
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)
|
| Nonoperating temperature
| - 40 to 167°F (- 40 to 75°C)
|
| Humidity
| 10 to 90%, noncondensing
|
| Agency approvals
| Safety: UL4 1950, CSA5-C22.2 No. 950-93, and EN60950
EMI6: FCC Class A (47 CFR, Part 15),CE Mark, EN55022 Class B and VCCI Class 2 with shielded cables
|
1
Gbps = gigabits per second.
2
Btu = British thermal units.
3
cfm = cubic feet per minute.
4
UL = Underwriters Laboratory.
5
CSA = Canadian Standards Association.
6
EMI = electromagnetic interference.
This section contains the external connections for the Catalyst 5000 modules and ports.
- The Catalyst 5000 is a five-slot rack-mounted chassis with one slot dedicated to the supervisor engine module and a combination of modules that support online insertion and removal (OIR). External connections for the modules follow:
- The supervisor engine module has two Fast Ethernet ports. Each port has two connectors, one MII and one RJ-45.
Note If two cables are connected to the same port, the MII is the default connection.
- 10BaseT 24-port Ethernet switching module uses two 50-pin Telco connectors.
- 10BaseFL 12-port Ethernet switching module uses ST-type connectors.
- 10/100BaseTX 12-port 10/100-Mbps fast Ethernet switching module using RJ-45 connectors.
- 100BaseTX 12-port fast Ethernet switching module using RJ-45 connectors.
- 100BaseFX 12-port fast Ethernet switching module using ST-type fiber optic connectors.
- ATM LAN emulation module (UTP) using RJ-45 connectors.
- ATM LAN emulation module (single-mode and multimode fiber) using SC-type connectors.
- CDDI module (UTP) using RJ-45 connectors.
- FDDI module MMF (multimode fiber) using MIC connectors and (on A/B port card option) an optical bypass switch (9-pin DIN) connector.
- FDDI module SMF (single-mode fiber) using ST-type connectors and (on A/B port card option) an optical bypass switch (9-pin DIN) connector.
- EIA/TIA-232 data terminal equipment (DTE) port using an EIA/TIA-232 data communications equipment (DCE) console cable with DB-25 plugs at one end.
The Catalyst 5000 376W AC-input power supply uses a power factor corrector that allows it to operate on input voltage and current within the ranges of 100 to 240 VAC and 47 to 63 Hz.
A second, identical power supply is also installed in the chassis configured with the redundant power option. Redundant power ensures that power to the chassis continues uninterrupted in the event that one power supply fails. It can also provide uninterrupted power in the event a power line fails, so long as the power supplies receive power from separate power lines.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the Catalyst WS-C1400 concentrator.
Table 55 lists the physical specifications for the WS-C1400 concentrator.
Table 55: WS-C1400 Concentrator Physical Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 2.7 x 18 x 16 in (6.86 x 45.72 x 40.64 cm)
|
| Weight
| 16 lb (7.3 kg)
|
| Power requirements
| 3A @ 110 VAC, 60 Hz (WS-C1400)
1.6A @ 220 VAC, 50 Hz (WS-C1400)
|
| Power consumption
| FDDI: 90W (maximum) (WS-C1400)
CDDI: 110W (maximum) (WS-C1400)
|
| Agency approvals
| CDDI/FDDI: FCC Class A (47 CFR, Part 15)
CDDI/FDDI: CISPR 22 Class A
FDDI: VDE Class B
|
| Safety
| UL: 1950
CSA-C22.2 No. 950-M89
IEC 950
|
| Mounting
| Desktop
19-inch rack (hardware included)
Wall-mount (hardware included with optional kit)
|
FDDI transmit power levels:
Single-mode fiber
Multimode fiber
| Average optical power:
Maximum: -4.0 dBm
Minimum: -7.0 dBm
Maximum: -14.0 dBm
Minimum: -18.5 dBm
|
FDDI receive power levels:
Single-mode fiber
Multimode fiber
|
Average optical sensitivity: -33.0 dBm
Average maximum input power: -14.0 dBm
Average optical sensitivity: -34 dBm
Average maximum input power: -14 dBm
|
This section contains the external connection requirements for the Catalyst WS-C1400 concentrators:
- Administrative interface port: EIA/TIA-232 data communications equipment (DCE) using an RJ-45 connector (straight-through cables only).
- The WS-C1400 has two line card slots. Each slot can support one of the five optional CDDI and FDDI line cards.
- Following are the optional line cards and their connection requirements:
- WS-X1441: eight multimode FDDI ports using MIC connectors
- WS-X1444: eight multimode FDDI ports using ST connectors
- WS-X1450: two multimode FDDI ports using MIC connectors, and CDDI/MLT-3 ports using RJ-45 connectors
- WS-X1455: ten single-mode FDDI ports using SC connectors
- WS-X1483: CDDI/MLT-3 ports using RJ-45 connectors
- For network connections using FDDI-to-CDDI twisted-pair connections, you will need the optional CDD-FDDI translator.
Note To connect CDDI to shielded twisted-pair (STP), you must use an impedance-matching balance/unbalanced (balun) device.
- The chassis can be placed on a desktop, or rack-mounted in a standard 19-inch rack.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the FastHub 100 Series repeaters. The FastHub 108T and the FastHub 104T (hereafter referred to as FastHub 108T/104T) are 100BaseT-compatible, standalone, unmanaged, Class II Fast Ethernet repeaters. The eight-port FastHub 108T and the four-port FastHub 104T both support the 100BaseTX physical layer.
Table 56: FastHub 100 Series Technical Specifications
Reliability
| 50,000 hours MTBF
|
| Operating temperature
| 32 to 104° Fahrenheit (0 to 40° Celsius)
|
| Operating humidity
| 5% to 80%
|
| Power consumption
| FastHub 108T: 25 watts (W)
FastHub 104T: 15 watts (W)
|
| Input voltage
| 90 to 240 V @ 50 to 60 Hz
|
| Weight
| FastHub 108T: 3.8 lbs [1.7 kg]
FastHub 104T: 3.6 lbs [1.6 kg]
|
| Width
| 6.3 in (16 cm)
|
| Depth
| 9.4 in (24 cm)
|
| Height
| 2.05 in (5.2 cm)
|
The FastHub 100 Series repeaters' 100BaseTX ports provide connectivity to 100BaseTXdevices using Category 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling.
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the StrataCom Integrated Gigabit Switch (IGX) product family, which consists of the IGX 8, IGX 16, and IGX 32 multiservice ATM switches. The IGX provides the same core ATM capabilities and advanced networking features as the StrataCom BPX Service Node.
Table 57 lists the StrataCom IGX physical specifications.
Table 57: IGX Physical Specifications
| Characteristic
| Description
|
| Platforms
| IGX 8
8-slot unit, rack mount or free-standing
1.2 Gbps cell switching bus
CISPR B EMI certified
IGX 16
16-slot unit, rack mount or free-standing
1.2 Gbps cell switching bus
CISPR B EMI certified
IGX 32
32-slot unit, rack mount or free-standing
1.2 Gbps cell switching bus
CISPR B EMI certified
|
| Power
| Distributed 48V DC power conversion on modules
220/240 VAC AC-DC converter, 1:N redundant
|
| Control processors
| Network Processor Module (NPM) 68040 CPU
System Clock module (SCM), internal or external clocking
|
| Alarm modules
| Alarm Relay module (ARM)
8 normally open contacts
6 normally closed contacts
|
| Voice service modules
| Channelized Voice and Data module (CVM)
32-, 24- and 16-Kbps ADPCM voice compression (ITU G.721, G.723 and G.726)
Voice activity detection (VAD)
Integrated FAX/high-speed modem detection and echo cancellation
Supports T1, E1, Japanese TTC interfaces
|
| Circuit switched data service modules
| High-speed Data module (HDM)
Up to 4 channels, each up to 1.344 Mbps
Supports EIA/TIA-232, V.35, EIA/TIA-422, EIA/TIA-449, X.21/V.36 interfaces
Repetitive pattern suppression to 128 Kbps
Low-Speed Data module (LDM)
Up to 8 channels, totaling 8x19.2 Kbps
Supports EIA/TIA-232 interface
Repetitive pattern suppression to 19.2 Kbps
|
| Frame Relay service modules
| Frame Relay module (FRM)
Up to four channels, totaling 2.048 Mbps
Conforms with
CCITT 1.122 (ANSI T1/S1)
T1.606--Services description of Frame Relay bear service
T1.606 addendum--Congestion management
T1.617 (Annex D)--Signaling specification for Frame Relay
T1.618--Core aspects of Frame Relay
Includes fully standard handling of DE, FECN and BECN bits
Supports V.35, EIA/TIA 422, EIA/TIA 449, X.21/V.36, and T1/E1 (channelized and nonchannelized) interfaces
|
| Network trunking modules
| Network Trunking front module (NTM)
Trunk speeds from 128 Kbps to 2.048 Mbps
Supports T1/E1, Japanese Y trunk interfaces
Broadband ATM Trunk module (BTM)
ITU 53-byte cell standard
Supports T3/E3 and HSSI interfaces
Multipoint logical trunking over ATM service
FastPAD Trunk module (FTM)
FastDLC, FrameClass, Frame Relay service compatible, protocol
FastPAD trunk speeds from 9.6 Kbps to 512 Kbps
Supports V.35, T1, E1, X.21 interfaces
|
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) transport service, flexible clocking, and circuit switched data service modules are features of circuit switched data services. IGX systems provide circuit switched data connectivity for legacy data transport through transparent, fixed delay, fixed throughput, zero discard point-to-point data connections over ATM. Speed options range from 1200 bps to 2.048 Mbps (asynchronous from 1.2 Kbps to 19.2 Kbps) using standard RS232, V.35, X.21, T1 and E1 interfaces. The IGX supports both dedicated port and channelized circuit emulation (from voice service circuit interfaces).
All IGX Frame Relay ports interoperate with IGX and BPX ATM ports. Standards-compliant Frame Relay services from StrataCom IGX systems achieve high throughput, low delay, low discard, connectivity for LAN interconnect and legacy FRAD traffic. Port speed options range from 56 Kbps to 2.048 Mbps. Standard interfaces include V.35, X.21, channelized T1 and channelized E1, for up to 31 logical ports per physical port.
The ATM line module includes the following features:
- T3/E3
- Port (UNI 3.0)
- Trunk
- CBR, VBR, ABR
This section contains the physical specifications and external connection requirements for the StrataCom BPX Service Node broadband ATM switch.
Table 58 lists StrataCom BPX Service Node physical specifications.
Table 58: BPX Service Node Physical Specifications
| Characteristic
| Description
|
| 15 module slots
| 2 slots reserved for redundant control and switch modules
1 slot reserved for Alarm Status Monitor (ASM) module
12 slots for general-purpose function modules
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 22.75 x 17.72 x 27 in (57.8 x 45 x 68.6 cm)
19 in (48.3 cm) rack mountable
|
| Power requirements
| -48V DC or 208/240V AC input
1400W dissipation (max)
|
| Crosspoint switch fabric
| Switch capacity of 20 Gbps
12 800-Mbps switch ports that can support up to OC-12 cell rate
Arbiter establishes up to 20 million cell connections per second
|
| Network interfaces
| T3 (44.736 Mbps) with PLCP per TA-TY-000773
OC-3 (155.520 Mbps) with SONET framing per ANSI T1.105
E3 (34.368 Mbps) per ITU-T Rec. G.804
STM-1 (155.520 Mbps) with SDH framing per ITU-T Rec. G.708
OC12/STM-4 (622.08 Mbps), complies with SONET standards
Bellcore GR-253-CORE, ANSI T1.105; complies with SDH standards ITU-T G.708 and G.709; ITU-T G.957 and G.958
|
| Common network interface features
| Up to 16 programmable queues for class-based or VP/VC-based queuing
Queues programmable by maximum queue depth, minimum service bandwidth, maximum service bandwidth, cell loss priority (CLP) thresholds, EFCI thresholds
ForeSight closed-loop, rate-based congestion management
Fully compliant ABR VS/VD implementation
Explicit rate (ER) marking
EFCI marking
|
| Broadband service interfaces
| Conformance to ATM Forum Specification v3.1:
T3/DS3 UNI (44.736 Mbps)
OC-3 UNI (155.520 Mbps) SONET
OC-12 UNI (622 Mbps) SONET
E2 UNI (34.368 Mbps)
STM-1 UNI (155.520 Mbps) SDH
STM-4 UNI (622 Mbps) SDH
|
| Optional redundancy
| All components are optionally redundant to 100% system redundancy including the control processor, crosspoint switch, network interfaces, service interfaces, critical backplane signals, power supplies, power modules, and cooling fans
|
| Network management
| Interfacing to network management is provided by SNMP connection via:
1 802.3 AUI interface for local connection to StrataView Plus
2 asynchronous control/printer ports
|
| Alarms, indicators, and controls
| Major node alarm, minor node alarm, alarm cut-off and history indicators
Visual and audible (major and minor) relay closures provided for connection to central office alarm system, including power supply status indicators and LAN activity indicator
Each interface module has a minimum of three visual indicators: Active (green), Standby (yellow), and Fail (red)
|
| Node synchronization
| Stratum 3 clock per ATT PUB 62411
Software programmable source: internal clock, transmission line, auxiliary port to an external clock source
|
ATM Service Interface (ASI) modules provide standard interfaces for connecting to cell-based customer premise equipment (through an ATM UNI standard user interface) or to non-StrataCom networks (through an NNI network interface). ASI modules support native ATM sessions at speeds of T1/E1, n x T1/E1 Inverse Multiplex ATM (IMA), T3/E3, OC3/STM-1, and OC12/STM-4.
Broadband Network Interface (BNI) modules connect the BPX Service Node to other BPX or StrataCom IGX and IPX nodes. These modules support up to 16 classes of service and network trunk interfaces including T1/E1, n x T1/E1 IMA, T3/E3, OC3/STM-1, and OC12/STM-4.
The BXM cards provide standard interfaces for connecting to cell-based customer premises equipment via ATM User-Network Interface (UNI) or to non-Cisco networks via Network-to-Network (NNI).
There are two high-density BXM cards for the BPX:
- BXM 155: Up to 8 OC-3/STM-1 native ATM access and trunk ports per card
- BXM 622: Up to 2 OC-12/STM-4 native ATM access and trunk ports per card
BXM cards also support ATM-Frame-Relay network interworking, service interworking, and enable configuration of PVCs or SVCs for the same service classes that are supported by the ASI modules. With BXM, the BPX supports up to 16 independent classes of service to protect your hardware investment as the industry defines additional traffic types.
Note BXM cards will be available at a future date.
The AXIS interface shelf operates in the BPX Service Node and supports a wide range of services from a single platform. This enables organizations to reduce equipment costs, fully utilize trunking resources, protect their investments in existing premise equipment, and rapidly deploy new services as required. AXIS modules adapt incoming data to 53-byte ATM cells using industry-standard ATM Adaption Layers (AAL) for transport over the ATM network.
Services below 34 Mbps are provided on the AXIS shelf, and interfaces supported include the following:
- Frame Relay
- High-speed Frame Relay
- ATM Frame UNI
- SMDS
- T1/E1 ATM UNI
- n x T1/E1 IMA UNI
- Circuit emulation
- ISDN switched access
Note AXIS aggregates traffic from as many as 80 T1 or E1 ports onto a single port of a multiport broadband trunk card. This high port density maximizes use of the BPX Service Node high-capacity switch fabric. Each 9-inch rack-mount shelf supports up to 80 DS1 or E1 ports or more than 2,000 64-Kbps users. AXIS has a compact footprint that minimizes the space required within central offices. The BPX Service Node supports up to 16 AXIS interface shelves.
This section contains the specifications and external connection requirements for the StrataCom Multimedia FastPAD and FastPAD Micro products, which provide voice and data integration over Frame Relay or leased line networks.
Table 59 lists the base unit specifications for the Multimedia FastPAD family products:
Table 59: Multimedia FastPAD Base Unit Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| FastPAD
|
|
| Dimensions (H x W x D)
| 5.25 x 17 x 18 in (13.34 x 43.18 x 45.72 cm)
|
| Weight
| 30 lbs (13.61 kg)
|
| Data ports, 5 RS-232
| DB25F (async to 9.6 kbps, sync to 48 kbps)
High-speed synchronous port (to 64 kbps)
Standard: RS-232, optional: V.11, V.35, RS 449
|
| FastPAD Micro
|
|
| Dimensions (H xW x D)
| 5.25 x 8.5 x 18 in (13.34 x 21.59 x 45.72 cm)
|
| Weight
| 12 lbs (5.44 kg)
|
| Data ports 1, RS-232
| DB25F (async to 9.6 kbps, sync to 48 kbps)
One high-speed synchronous port (to 64 kbps)
Standard: RS-232, optional: V.11, V.35, RS 449
|
| FastPAD and FastPAD Micro
|
|
| EMI emissions
| Class B
|
| Temperature
| 32to 122º F (0 to 50º C)
|
| Humidity
| 0 to 90%, noncondensing
|
| Voltage
| 94 to 240 VAC
-48 VDC (FastPAD only)
|
| Power consumption
| 200W
|
| Trunk protocol
| CCITTI. 122, ANSI T1.606, Frame Relay compatible
|
| Data rates
| 9.6 kbps to 512 kbps
|
| Interfaces
| RS-232C, V.35, X.21
|
The standard FastPAD base unit configuration can support up to six data channels: five low-speed V.24 ports for data rates of up to 9.6 kbps (asynchronous) and 48 kbps (synchronous), and one high-speed synchronous port that can be configured as V.35/X.21/V.11 to supports data rates of up to 64 kbps. The standard configuration for the high-speed data port is V.24. This port can be configured to V.35, X.21, or V.11 through the use of optional internal adapter cards.
The FastPAD base unit also comes standard with a trunk port that supports data rates up to 128 kbps. Like the synchronous data port, the standard configuration for the trunk port is V.24. This port is also configurable to V.35, X.21, or V.11 through the use of the optional internal adapter cards.
The FastPAD base unit has eight expansion slots which can be used for either the Voice/FAX expansion interface or the Frame Relay access module. The FastPAD base unit is available with either AC or DC redundant power options. The AC power option supports a voltage range from 94 to 240 VAC. The DC power option supports standard -48 VDC power.
The standard FastPAD Micro base unit configuration can support up to three data channels; one low-speed V.24 port for data rates to 9.6 kbps (asynchronous) and 48 kbps (synchronous), and one high-speed synchronous port that can be configured as V.35/X.21/V.11 for data rates to 64 kbps. The standard configuration for the high-speed data port is V.24. The port can be configured to V.35, X.21 or V.11 through the use of optional internal adapter cards.
The FastPAD Micro base unit also comes standard with a trunk port that supports data rates up to 128 kbps. Like the synchronous data port, the standard configuration for the trunk port is V.24. It is also configurable to V.35, X.21, or V.11 through the use of the optional internal adapter cards.
The FastPAD Micro base unit has four expansion slots which can be used for either the Voice/FAX expansion interface or the Frame Relay access module. The FastPAD Micro base unit is available with AC power only, supporting a voltage range from 94 to 240 VAC. It is not available with a redundant power option.
This section contains the specifications and external connection requirements for the StrataCom Multiprotocol FastPAD product family, which includes the FastPADmp6, FastPADmp, FastPADmp12, FastPADmpr12, and FastPADmpr24.
The Multiprotocol FastPAD products can support both asynchronous and synchronous connections, and PSTN and ISDN backup.
The Multiprotocol FastPAD products use a connector-and-cable interface system that allows many different connections of interfaces such as V24/V28, V.11, V.35, X.24, and X.21, which might co-exist on the same product. Also available are ISDN terminal adapters and G.703 adapters.
Table 60 lists the interface specifications for the Multiprotocol FastPAD products.
Table 60: Multiprotocol FastPADmp Products Specifications
| Description
| Specification
|
|---|
| Synchronous line speeds
| 600 bps to 1 Mbps (FastPADmp6, FastPADmp)
600 bps to 2 Mbps (FastPADmp12, FastPADmpr12, and FastPADmpr24 only)
|
| Asynchronous line speeds
| 75 bps to 38.4 kbps
|
| Transputer connections
| 20 Mbps serial link to four nearest-neighbor modules
|
| Interfaces
| V24/V28, V.11, V.35, ISDN, G.703 nonchannelized
|
| FastPADmp6 interfaces
| 3 each, fixed V24/V28 DCE interfaces, speeds below 19.2k guaranteed
2 each, variable V.11 or V24/V28 DCE interfaces, up to 1.5 Mbps
1 each, variable V11/ V24/ V28/ V35/ ISDN DTE/DCE interface, line speeds up to 1.75 Mbps
|
| FastPADmp interfaces
| 12 each, variable V11/ V24/ V28/ V35 DTE/DCE interface, line speeds up to 1.75 Mbps
|
| FastPADmp12 interfaces
| 2 each, variable V11/ V24/ V28/ V35 DTE/DCE interface, line speeds up to 2.3 Mbps
|
| FastPADmpr12 and FastPADmpr24 interfaces
| 2 each, variable V11/ V24/ V28/ V35 DTE/DCE interface, line speeds up to 2.3 Mbps
|
| Loading
| On 12-port modules, aggregate line speed on any three consecutive ports cannot exceed the maximum line speed of the unit
|




