|
|

This chapter describes periodic maintenance, troubleshooting, and replacement of major IPX components.
The IPX operating system software takes care of most IPX monitoring and maintenance. Preventive maintenance of IPX hardware is minimal. It consists of the following:
This section contains preventive maintenance information for the IPX.
IPX power supply voltages must be checked on a node equipped with a fully configured set of cards. If a power supply voltage is out of tolerance, the power supplies must be replaced one at a time until the voltage levels are correct. (In older IPX systems, power supplies were adjusted to bring them into tolerance. This is now unnecessary.)
Test points for the power supply voltages for IPX 8 and IPX 16 system are on the SCC. Test points for an IPX 32 system are on both the SCC and LEC expansion card.
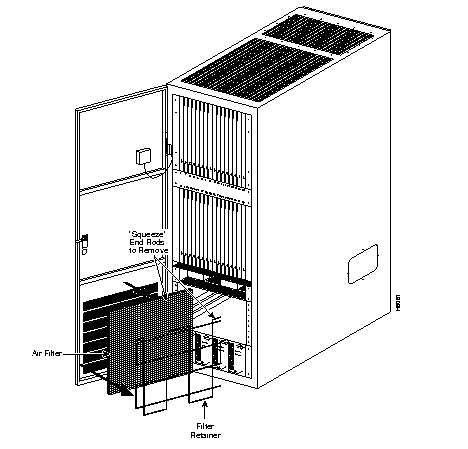
Every two months or more often depending on the environment, inspect the air filter assembly for dust buildup. The air filter assembly requires washing to remove dust. The air filter is located in the door of the IPX 16/32 (Figure 3-1).
Remove and clean the IPX 16/32 air filter, as follows:
Step 1 A filter retainer keeps the air filter in place. To remove the filter, squeeze the ends of the filter retainer inwards, then lift out the filter retainer and filter.
Step 2 Clean the filter with cold water (use mild detergent if the filter is extremely dirty).
Step 3 Allow the filter to dry before returning it to its frame.
Step 4 Install the filter by sliding it into position in the door channel, and slide the filter retainer into the door channel over the filter.
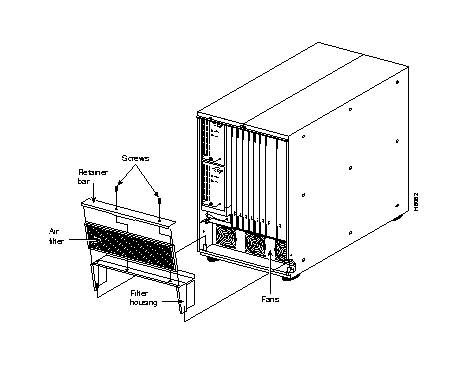
Every two months or more often depending on the environment, inspect the air filter assembly for dust buildup.The air filter sits below the card cage in the IPX 8 cabinet, at the front (Figure 3-2).
Remove and clean the IPX 8 air filter as follows:
Step 1 Open the front door of the IPX 8 cabinet.
Step 2 Locate the air filter assembly at the bottom-front of the IPX 8.
Step 3 A retainer bar at the top of the filter assembly keeps the filter in place (Figure 3-2). Remove the retainer bar by unscrewing the two phillips head machine screws.
Step 4 Grasp the filter and slide it out the top.
Step 5 Clean the filter with cold water (use mild detergent if the filter is extremely dirty).
Step 6 Allow the filter to dry before returning it to its frame.
Step 7 Make sure all three fans are operating. Replace the fan assembly if any fan is not operating properly.
Step 8 Install the air filter by sliding it into the side channels of the filter assembly.
Step 9 Secure the filter retainer bar with the two machine screws.
This section describes elementary troubleshooting procedures and briefly describes the commands for troubleshooting an IPX node. For detailed description of these commands, refer to the Command Reference. This section does not contain an exhaustive set of procedures and does not take into account any of the diagnostic or network tools available to troubleshoot the IPX.
This section contains information about the following:
The IPX runs self-tests continuously to ensure proper function. When the IPX finds an error condition that affects its operation, it downs the affected card or line. It then selects a standby card or redundant line if one is available. In a non-redundant system, no alternate cards are available for the CDP, NTC, ATM, ARC, CIP (upgraded systems), BC-E1, BC-T1, PIC and TXR (upgraded systems), SDP, SDI, LDP, LDI and NPC, so the system comes down if a failure occurs on any of these cards.
The FAIL light on a card indicate that the system has found the card defective in some mode and now considers it as a failed cards. In this situation you would use Table 3-1 to find the cause and obtain the information on replacing the failed component.
 | Caution When using Table 3-1 for troubleshooting, call StrataCom ISC before performing any disruptive testing or repairs on the IPX. This ensures that you have isolated the correct problem area. It also enables ISC personnel to provide assistance in performing the necessary procedures. |
| Symptom | Probable Cause | Remedy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1.
| No indicators on IPX boards lit- console screen blank. | 1. | IPX power switch switched off. | 1. | Switch on power switch. |
| 2. | IPX breaker tripped reset the breaker | 2. | Switch off, then switch on the power switch to the Check to see if any overload condition exists (shorted connections, crow-barred power supplies). | ||
| 3. | IPX power cord dislodged from plug into 208 or 240 VAC receptacle. | 3. | Reconnect power cord | ||
| 4. | Power supplies not functioning. | 4. | Replace power supplies | ||
2. | Front card FAIL indicator lit | 1. | Front card failed: ·CDP card ·NPC card ·ARC card ·NTC card ·AIT card ·SDP card ·LDP card ·FRP card ·FTC card ·MT3 card | 1. | Check alarm status of card and remove and replace the front card. |
| NOTE: If an NPC fails in a non-redundant IPX system, the system must be rebooted. | |||||
| Note: CIP is used in pre- 7.0 systems. | |||||
| 3. | Front card indicator lit - replacement card does not fix problem. | 1. | Backplane defective. | 1. | If a new card does not fix problem, the backplane may be suspect (uncommon failure). Contact the Stratacom ISC. |
| 4. | SDI card FAIL indicator lit. | 1. | SDI card failed:
·SDI (RS232) card ·SDI (RS449) card ·SDI (V.35) card | 1. | Check alarm status of card remove and replace the SDI card. |
| 5. | ATM, ARC, CDP, LDI, BC-E1 or BC-T1 FAIL indicator lit-replacement card does not fix problem. | 1. | LB backplane defective. | 1. | If new card does not fix the problem, contact Stratacom ISC. |
| NOTE: All cards plug into the system backplane. If the backplane is defective, it could cause a fault to appear on any card. | |||||
6. | Power Supply FAIL indicator lit. | 1. | Power supply defective. | 1. | Check power supply output Remove and replace power supply if defective. |
2. | SCC wiring or card defective. | 1. | If power supplies output check out, then SCC wiring or card is suspect. | ||
| 2. | Make sure the plug connection to the SCC card is secure; tighten if it is not. | ||||
| 3. | If the plug connection is secure and the Power Supply Monitor FAIL indicator is still lit, then remove and replace the SCC card. | ||||
7. | Power Supply Monitor FAIL indicator lit. | 1. | Defective fan, or fan assembly in enclosure - allowing the temperature in the enclosure to rise above 50× C. | 1. | Check that both fans in power shelf are rotating. |
| 2. | If both fans are not rotating, check the main connection plug to the fan assembly for proper connection, and push in the connector to correct situation. | ||||
| 3. | If only one fan is rotating, check the interconnecting plugs for proper connection, and push in the connector to correct the situation. | ||||
| 4. | If the fans in remedies 2 and 3 above are still not functioning, remove and replace the fan assembly. | ||||
| 2. | Defective temperature sensor wiring or sensor. | 1. | Check the cable plug attached to the system backplane and push in the connector to correct the situation. | ||
|
|
|
| 2. | Check the wiring between the temperature sensor and the SCC board, and re-solder it if necessary. |
| 3. | If neither remedy 1 or 2 above does not cure the problem, remove and replace the temperature sensor. | ||||
3. | Defective power supply fan in power supply allowing the power supply temperatures to rise above 50× C. | 1. | If the fan assembly is functioning correctly, then the power supply assembly fans are suspect. | ||
| 2. | Check to see if the power supply fans are rotating, if not, remove and replace the power supply with the defective fan. | ||||
| 3. | If power supply fans are functioning, then the power supply temperature sensor is defective. Remove and replace the temperature sensor | ||||
4. | Defective SCC card | 1. | If both the enclosure fan assembly and the power supply fans are working correctly (see symptom 6, probable causes 1, 2 and 3), then the SCC card is suspect. | ||
| 2. | Remove and replace the SCC card. | ||||
8. | Console screen blank, IPX indicator lights lit. | 1. | Control terminal switched off. | 1. | Switch on the control terminal. |
| 2. | Control terminal power cord disconnected. | 2. | Reconnect the control terminal power cord to 208/240 VAC power outlet. | ||
| 3. | RS-232 cable loose or disconnected from the Control Terminal port on the SCC, or from the control terminal. | 3. | Reconnect the RS-232 cable to Control Terminal port on the SCC back card or to the control terminal itself. | ||
| 4. | Control terminal malfunctioning. | 4. | Refer to the control terminal manufacturer's manual. | ||
9. | Printer not functioning | 1. | Printer switched off. | 1. | Switch on the printer. |
| 2. | Printer out of paper. | 2. | Renew the paper supply. | ||
| 3. | Printer power cord disconnected. | 3. | Reconnect the printer cord to 208/240 VAC power outlet. | ||
| 4. | RS-232 cable loose or disconnected from the Control Terminal port on the SCC or from the printer. | 4. | Reconnect RS-232 cable to the Control Terminal port on the SCC back card or to the printer itself. | ||
| 5. | Printer malfunctioning. | 5. | Refer to the printer manufacturer's manual. | ||
10. | Modem not functioning. | 1. | Modem switched off | 1. | Switch on the modem. |
| 2. | Modem power cord disconnected. | 2. | Reconnect modem power cord. | ||
| 3. | RS-232 cable loose or disconnected from the Control Terminal port on the SCC, or from the modem. | 3. | Reconnect the RS-232 cable to the Control Terminal port on the SCC back card or the modem itself. | ||
| 4. | Telephone hookup cable disconnected. | 4. | Reconnect the telephone hookup cable. | ||
| 5. | Modem malfunctioning. | 5. | Refer to the modem manufacturer's manual. | ||
| 6. | DIP switches not set correctly. | 6. | Refer to the modem manufacturer's manual. | ||
| 11. | DFM is not functional. | 1. | DFM has been not been enabled by Stratacom. | 1. | Contact the ISC. |
| 12. | DFM has been enabled but still does not function. | 1. | DFM only runs on
speeds up to 64Kbps. | 1. | Readjust the speed. |
| 13. | Background noise or music sounds choppy. | 1. | VAD problem.-VDP needs sensitivity adjustment | Contact the ISC. | |
| 14. | High speed modem drops to low speed. | 1. | ADPCM is taking over. | 1. | Contact the ISC. |
| 15. | Bundled (Frame Relay) connections have failed. | 1. | One or more bundled connections have failed. | 1. | Contact the ISC.
|
The initial mode of troubleshooting the IPX uses the console alarms displayed on the console screen. Table 3-2 provides you with a procedure for isolating the alarms and thereby isolating the fault. Any repair to the IPX must be performed by StrataCom-qualified personnel.
 | Caution When using Table 3-2 for troubleshooting, call the StrataCom ISC before performing any disruptive testing, or attempting to repair the IPX, to ensure that you have isolated the correct problem area, and also to enable ISC to provide you with assistance in performing the necessary procedures. |
The first step in IPX troubleshooting is to check the condition of the system by displaying system-wide alarm conditions. To see a summary of current alarms on an IPX node, use the dspalms command. The alarms summary includes the following:
To display alarms, enter the command dspalms. If the screen indicates a failure, refer to the commands in Table 3-3 to further isolate the fault.
| Failure | Diagnostic Commands |
|---|---|
| Connections | dspcons (display connections) |
| Line Alarms | dspclns (display circuit lines) |
| dsptrks (display trunks) | |
| Cards | dspcds (display cards) |
| Power Monitor | dsppwr (display power supply status) |
| Remote Node | dspnw (display network) |
| Unreachable Nodes | dspnw (display network) |
| Remote Node Alarms | dspnw (display network) |
When a card indicates a failed condition on the alarm summary screen, use the dspcds command to display the status of the circuit cards on a node. The information displayed for each card type includes the card slot number, software revision level, and status of the card.
Table 3-4 lists all possible status descriptions for each card type.
| Card Type | Status | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All card types (including CDP) | Active | Active card | |
| Active--F | Active card with non terminal failure. | ||
| Standby | Standby card | ||
| Standby--F | Standby card with non terminal failure. | ||
| Standby--T | Standby card performing diagnostics. | ||
| Standby--F-T | Standby card with non terminal failure performing diagnostics. | ||
| Failed | Card with terminal failure. | ||
| Unavailable | Card is present but it may be in any of the following states: | ||
| 1. | The node does not recognize the card (may need to be reseated). | ||
| 2. | The card is running diagnostics. | ||
| 3. | A VCD card is paired with a | ||
| VDP and the VDP has failed (upgraded systems). | |||
| Down | Downed card. | ||
| Empty | No card in that slot. | ||
| VDP (upgraded systems) | Same status as for all card types, plus: |
| |
| Active--T | Active card performing diagnostics.
| ||
| NPC | Same status as for all card types, plus: | ||
| Updating | Standby NPC is downloading network configuration from an active NPC. | ||
| NOTE: Red FAIL LED flashes during updating. | |||
| Cleared | NPC is preparing to become active. | ||
| Loading Software | Downloader commands appear when the system is downloading software to the NPC. | ||
To display cards enter the following command:
User-initiated tests are available to diagnose the state of the IPX system, as follows:
Woolpack tests are available to help diagnose the state of the IPX system, as follows:
|
|