|
|

This chapter provides information on the Cisco 4000 series routers. It is organized into the following sections:
The Cisco 4000 series consists of the Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, Cisco 4700, and Cisco 4700-M routers. Although the Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 routers are no longer orderable, they are still supported. The Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 routers have been replaced by the Cisco 4500-M and Cisco 4700-M routers.
The Cisco 4000 series routers run Cisco IOS software, Cisco's industry-leading networking software that provides a variety of feature sets. You can choose a feature set that supports your specific protocol environment. Cisco IOS software assures robust, reliable internetworks by supporting both LAN and WAN protocols, optimizing WAN services, and controlling internetwork access. In addition, Cisco IOS software allows centralized, integrated, and automated installation and management of internetworks.
The Cisco 4000 series routers offer Flash EPROM technology as a standard feature. Flash EPROMs enable you to distribute new software releases from a central location. After the software is distributed, the routers can reboot from programs stored in local Flash memory.
All models provide a configurable modular router platform by using network processor modules (NPMs)--individual removable cards used for external network connections. Because the router's modules support many variations of protocols, line speeds, and transmission media, the Cisco 4000 series can accommodate all types of network computing environments. As Cisco introduces new modules, the Cisco 4000 series can be upgraded to keep pace with technological advances. 
This catalog introduces new versions of the high density serial NPM and the 1-port single-mode ATM OC-3c NPM. Both are supported on the 4500, 4500-M, 4700, and 4700-M (but not on the 4000 or 4000-M).
In the case of the high density serial module, 2 new versions have been added, one which mixes 8 low speed serial ports of RS232 with low speed ports of V.35 (NP-2T16S-232V35) and another which mixes 8 low speed serial ports of RS232 with 8 low speed serial ports of X.21 (NP-2T16S-232X21). These are in addition to the V.35, RS232, and X.21 only versions (NP-2T16S-V.35, NP-2T16S-RS232, NP-2T16S-X21).
In the case of the 1-port single-mode ATM OC-3cNPM, we have added a version that supports "long reach" distances (NP-1A-SM-LR) to the current version which supports "intermediate reach" distances (NP-1A-SM).
The Cisco 4000 series routers can support combinations of up to three of the following NPMs:
Figure 43 shows the rear view of the Cisco 4000 series router.
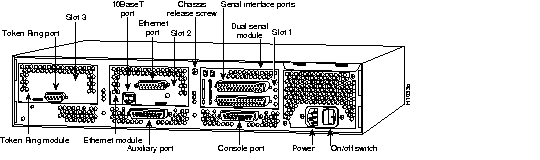
lists a summary of features for Cisco 4000 series routers, and Table 38 lists the environmental specifications.
| Characteristic | Cisco 4500-M | Cisco 4700-M1 |
|---|---|---|
| Supported network interfaces | Ethernet
Token Ring FDDI Serial HSSI High-density serial ISDN BRI Channelized E1/T1 ISDN PRI ATM OC-3c ATM DS-3 ATM E3 | Ethernet
Token Ring FDDI Serial HSSI High-density serial ISDN BRI Channelized E1/T1 ISDN PRI ATM OC-3c ATM DS-3 ATM E3 |
| Slots available for modules | 3 | 3 |
| Software options-- Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus 56 Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 | IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/AppleTalk/DEC) Plus 56 Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 |
| Software options-- Cisco IOS Releases 11.0 and 11.1 | IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX Routing IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality Desktop Desktop with IBM base Enterprise Enterprise/APPN | IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX Routing IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality Desktop Desktop with IBM base Enterprise Enterprise/APPN |
| Processor type | 100-MHz IDT Orion RISC | 133-MHz IDT Orion RISC |
| Flash memory | 4 MB standard, expandable to 8 or 16 MB | 4 MB standard, expandable to 8 or 16 MB |
| Main memory | 16 MB standard, expandable to 32 MB | 16 MB standard, expandable to 32 or 64 MB |
| Shared memory | 4 MB standard, expandable to 8 or 16 MB | 4 MB standard, expandable to 8 or 16 MB |
| Nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM) | 128 KB | 128 KB |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7 in. (8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm) | 3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7 in. (8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm) |
| Weight (average shipping) | 24 lb (10.9 kg) | 24 lb (10.9 kg) |
| Agency approvals | UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2 | UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2 |
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Consumption | 200W (682 BTUs1/hour) |
| Input | 100 to 240 VAC2 |
| Frequency | 47 to 63 Hz |
| Current rating | 3.0A @ 100V; 1.5A @ 240V |
| Operating temperature range | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
| Nonoperating temperature range | -4 to 149°F (-20 to 65°C) |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 5 to 95% |

Cisco 4000 series routers have the following standard features:

The network processor modules available for the Cisco 4000 series routers and their hardware options are described in the following sections:
Cisco 4000 series routers support combinations of up to three network processor modules (NPMs). Table 39 describes the maximum number of each module supported by a specific system and the minimum Cisco IOS software release required for each module. Table 39 also lists product numbers for the NPMs.
| NPM Type | Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700-M1 | Minimum Cisco IOS Software Release Required | Product Numbers | Hardware Restrictions with Other NPMs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-port 10BaseT Ethernet | - | 9.14(1) | NP-1E | No restrictions |
| 1-port 100BaseTX Fast Ethernet | 2 | 11.1(5)2 | NP-1FE | If one NP-1FE is installed, only one ATM or one FDDI module can be installed in the same router.
If two NP-1FEs are installed, you cannot install any ATM or FDDI modules in the same router. Full-duplex mode is supported only when the Fast Ethernet module is the sole high-speed module configured. |
| 2-port 10BaseT Ethernet | 3 | 9.14(1) | NP-2E | No restrictions |
| 6-port 10BaseT Ethernet | 3 | 10.3(6) | NP-6E | No restrictions |
| 1-port Token Ring | 3 | 9.14(5) | NP-1RV2 | No restrictions |
| 2-port Token Ring | 3 | 9.14(5) | NP-2R | No restrictions |
| 1-port single attachment multimode FDDI | 2 | 9.14(1) | NP-1F-S-M | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port dual attachment multimode FDDI | 2 | 9.14(1) | NP-1F-D-MM | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port dual attachment single-mode FDDI | 2 | 9.14(3) | NP-1F-D-SS | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 2-port serial | 3 | 9.14(6) | NP-2T3 | No restrictions |
| 4-port serial | 3 | 10.1 | NP-4T | 4 Mbps maximum speed per interface. |
| 2-port high-speed synchronous and 16-port low-speed sync/async | 2 | 11.2(4)P | NP-2T16S-V.35
NP-2T16S-RS232 NP-2T16S-X21 NP-2T16S-232V35 NP-2T16S-232X21 | Maximum of two 2-port high-speed synchronous and 16-port low-speed synchronous modules can be installed per router.
No restrictions with other modules. |
| 1-port HSSI | 2 | 11.2(5)P | NP-1HSSI | Maximum of two HSSI modules when both are run at high speeds.
Maximum of 12 Mbps per HSSI when two HSSI modules are configured and another high-speed module is also installed. |
| 4-port ISDN BRI | 2 | 10.2 | NP-4B4 | Not compatible with the three PRI modules, unless the PRI modules are configured for channelized service. |
| 8-port ISDN BRI | 2 | 10.2 | NP-8B4 | Not compatible with the three PRI modules, unless the PRI modules are configured for channelized service. |
| 1-port channelized T1/ISDN PRI | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CT1 | When configured for PRI, the NP-CTI is not compatible with the 4- and 8-port ISDN BRI modules.
Is compatible with these modules when configured for channelized service. |
| 1-port channelized E1/ISDN PRI, unbalanced | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CE1U | When configured for PRI, the NP-CE1U is not compatible with the 4- and 8-port ISDN BRI modules.
Is compatible with these modules when configured for channelized service. |
| 1-port channelized E1/ISDN PRI, balanced | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CE1B | When configured for PRI, the NP-CE1B is not compatible with the 4- and 8-port ISDN BRI modules.
Is compatible with these modules when configured for channelized service. |
| 4-port serial E1/G.703 and E1/G.704, unbalanced | 3 | 10.2(4) | NP-4GU | No restrictions |
| 4-port serial E1/G.703 and E1/G.704, balanced | 3 | 10.2(4) | NP-4GB | No restrictions |
| 1-port single-mode ATM OC-3c | 1 | 10.3(4) | NP-1A-SM | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port single-mode ATM OC-3c Long Reach | 1 | 11.2(9)P | NP-1A-SM-LR | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port multimode ATM OC-3c | 1 | 10.3(4) | NP-1A-MM | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port ATM DS-3 | 2 | 11.0(5) | NP-1A-DS3 | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
| 1-port ATM E3 | 1 | 11.0(5) | NP-1A-E3 | Maximum of two high-speed modules can be installed per router. |
Table 40 lists incompatible NPM configurations. The basic rule states that you cannot configure a Cisco 4500 or Cisco 4700 with more than two high-speed NPMs.
| NPM Type | Product Number |
| 1 ATM OC-3c, 1 FDDI, 1 ATM DS-3 or ATM E3 | 1 NP-1A-MM or SM + 1 NP-1F-D-MM/S-M/D-SS + 1 NP-1A-DS3 or E3 |
| 1 ATM OC-3c, 1 Fast Ethernet, 1 ATM DS-3 or E3 | 1 NP-1A-MM or SM + 1 NP-1FE + 1 NP-1A-DS3 or E3 |
| 2 Fast Ethernet and 1 FDDI | 2 NP-1FE + 1 NP-1F-D-MM/S-M/D-SS |
| 2 Fast Ethernet and 1 ATM DS-3 or E3 | 2 NP-1FE + 1 NP-1A-DS3 or E3 |
| 2 Fast Ethernet and 1 ATM OC-3c | 2 NP-1FE + 1 NP-1A-MM or SM |
| 2 ATM OC-3c | 2 NP-1A-MM or SM |
| 3 FDDI | 3 NP-1F-D-MM/S-M/D-SS |
| 1 ATM OC-3c and 2 FDDI | 1 NP-1A-MM or SM + 2 NP-1F-D-MM/S-M/D-SS |
Figure 44 through Figure 60 show the Cisco 4000 series network processor modules.
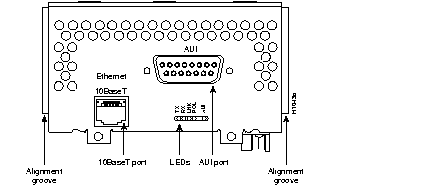
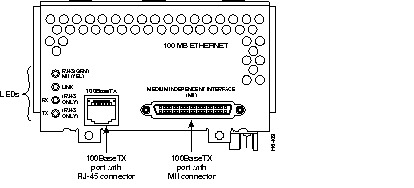
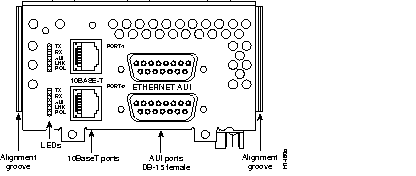
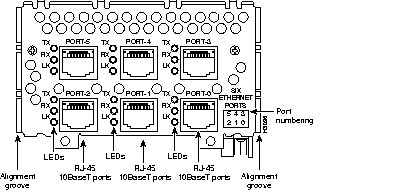
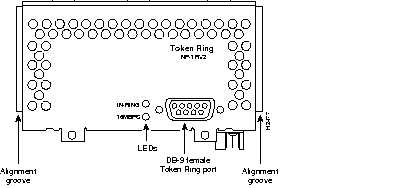
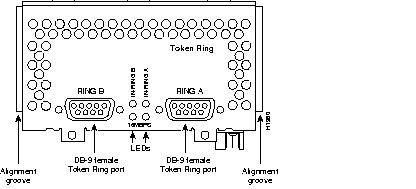
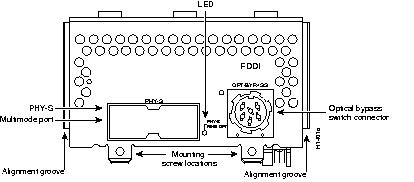
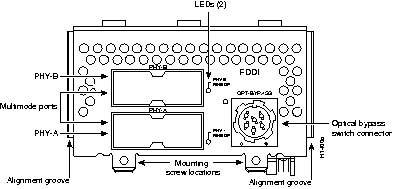
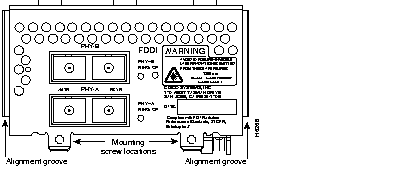
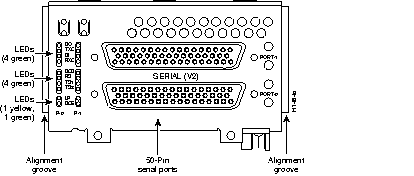
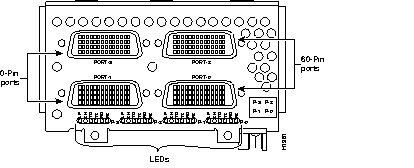

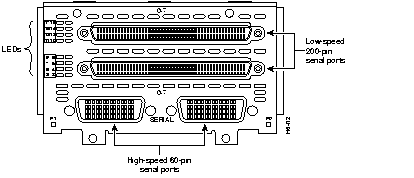

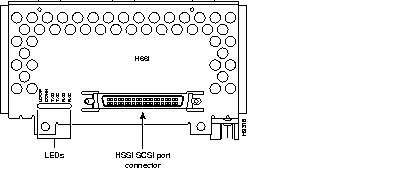
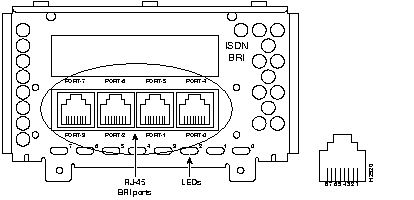
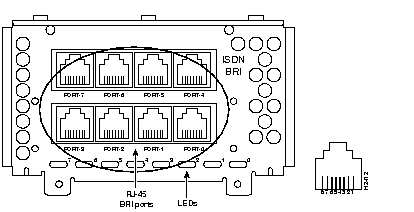
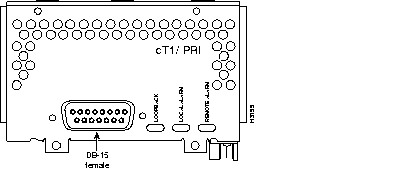
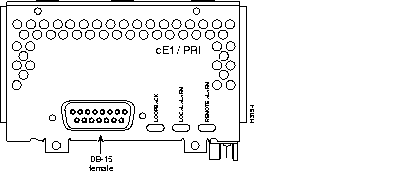
All Cisco 4000 series routers share the same physical design. Each router offers three slots for LAN or WAN connectivity and uses the same optional NPMs and software features for compatibility and investment protection. Three different types of memory are available for the Cisco 4000 series--main memory, shared memory, and system Flash memory. Each type of memory serves a different purpose in routing packets from one interface to another. The benefit of this architecture is that the system can read program instructions or routing table data from main memory at the same time as it is moving packets between interfaces (using shared memory), thus increasing overall system performance and lowering network latency.
You can change memory configurations in the Cisco 4000 series to accommodate internetworking demands. The memory requirements are driven by the following three factors:
The Cisco 4000 series runs from an image stored in main DRAM. This memory is also used by the system for tables and stacks. The amount of main memory required is determined by the size of the image and by the configuration of the internetwork. Cisco regularly publishes product bulletins that detail what memory is required for any particular Cisco IOS feature subset, and also releases documentation that specifies what memory is needed.
The Cisco 4000 series routers use shared DRAM (also known as packet memory) for handling user data. The recommended amount of shared memory is determined by the type and number of physical or virtual interfaces supported by the router. Other factors that impact the amount of required shared memory are the type of routing selected and the degree of throughput to the various interfaces.
The standard configuration for shared DRAM is 4 MB for the Cisco 4000 series. This is sufficient for most configurations with fewer than 24 physical or virtual interfaces. For routers with 24 or more interfaces or B channels (for example, NP-9B, CT1, and CE1), upgrading to a minimum of 8 MB of shared memory is required.
Table 41 lists the minimum shared memory requirements for NPMs used in Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500, and Cisco 4700 series routers.
| Network Processor Module | Minimum Shared Memory |
|---|---|
| Cisco 4000 Router | |
| NP-1E | 0.1 MB |
| NP-2E, NP-2T | 0.2 MB |
| NP-2R, NP-4T | 0.4 MB |
| NP-4B | 4.0 MB |
| NP-8B | 8.0 MB |
| NP-CT1, NT-CE1U, NT-CE1B (PRI) | 8.0 MB |
| NP-CT1, NT-CE1U, NT-CE1B (Channelized mode) | 0.5 MB |
| NP-1F-S-M, NP-1F-D-MM, NP-1F-D-SS | 2.0 MB |
| Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 Routers | |
| NP-2E, NP-2T | 0.4 MB |
| NP-2R, NP-4T, NP-GU, NP-4GB | 0.6 MB |
| NP-6E | 1.2 MB |
| NP-4B | 4.0 MB |
| NP-8B | 8.0 MB |
| NP-CT1, NT-CE1U, NT-CE1B (PRI) | 8.0 MB |
| NP-CT1, NT-CE1U, NT-CE1B (Channelized mode) | 0.5 MB |
| NP-1F-S-M, NP-1F-D-MM, NP-1F-D-SS, NP-1A-SM, NP-1A-SM-LR, NP-1A-MM, NP-1A-DS3, NP-1A-E3 | 2.0 MB |
| 2 NP-1F-S-M, NP-1F-D-MM, NP-1F-D-SS | 3.0 MB |
| NP-1FE | 1.5 MB |
| NP-1HSSI | 1.0 MB |
| NP-2T16S | 0.6MB |
The Cisco 4000 series software images are stored and compressed in system Flash memory. Flash memory is more reliable than traditional diskette-resident system software and provides maximum availability and easy software upgrades and maintenance. The Cisco 4000 series routers are shipped with a default of 4 MB of system Flash memory. This is adequate for most Cisco IOS software feature sets and leaves room for future image growth. However, certain feature sets require 8 MB of system Flash memory. With Cisco IOS Release 11.2, for example, the 4500-M requires 8 MB of system Flash memory for the Enterprise feature Set.
Most of the Cisco 4000 series support 4, 8, and 16 MB of system Flash memory. You might need to order more system Flash memory than the minimum required to store multiple images for the Cisco 4000 series router itself, and to store images for other routers so that the Cisco 4000 series can be used as a TFTP server for other Cisco routers.
The following types of memory are also used in the Cisco 4000 series, but they are not critical components that drive the minimum memory requirements for the system.
The Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700 store their boot images in the system Flash memory. The standard configuration of 4 MB is sufficient for use on these platforms. Currently no upgrades are offered.
The Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700 store a small software image in the boot helper Flash, which is also called XBoot Flash memory. This memory is in the form of Flash SIMMs. The XBoot image is used to boot the Cisco IOS software across a network. You might need to boot across the network when there is no image in the system Flash or the image has been corrupted. The standard configuration of 4 MB is sufficient for use on these platforms. You only need to upgrade the XBoot image to the latest version when support for booting over a network is required using an unrecognized NPM. For example, if you have added a new NPM that was not available when your system was originally shipped, you need to upgrade the XBoot image. New XBoot images can be downloaded from Cisco Connection Online (CCO).
The boot image is stored in EPROM on the Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M routers. This boot image is called RXBoot. The Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M boot EPROMs are 2 MB. The boot EPROM provides the same functionality on the Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M as the boot helper Flash provides on the Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, Cisco 4700, and Cisco 4700-M. The boot helper Flash simplifies the process of upgrading software images. Rather than changing the EPROMs when you want to load a new image, you can simply download a new image, using TFTP, into the onboard Flash memory.
The ROMMON performs initialization tasks in the Cisco 4000 series. It performs power diagnostics and sets variables after checking memory sizes. After this is completed, the main image is booted (as a default) from system Boot Flash (for the Cisco 4500 and the Cisco 4700) and from the boot EPROM (for the Cisco 4000). If you have configured your system to boot from XBoot, ROMMON boots from the secondary image. You cannot configure the amount of ROMMON memory available.
The Cisco 4000 series offers the hardware, memory, and NPM cable options listed in Table 42, and the power supply options listed in Table 43. If a product number ends with an equal sign (=), the item can be ordered only as a spare. If a product number does not end with an equal sign, the item can be ordered as a spare or as a configurable part of a system order. If a Cisco 4000 series product number ends with -CH, the item is available either through the Cisco authorized reseller channel, or through your local Cisco sales office. Other hardware options can also be ordered through the Cisco authorized reseller channel.
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Network Processor Modules (NPMs) | See Table 39. |
| Cisco 4500-M Memory | |
| 4-MB Flash memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-4F= |
| 8-MB Flash memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-8F= |
| 16-MB Flash memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-16F= |
| 8-MB shared memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-8S= |
| 16-MB shared memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-16S= |
| 32-MB main memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4500M-32D= |
| Cisco 4700-M Memory | |
| 64-MB main memory upgrade (spare) | MEM-4700M-64D= |
| Serial Cables for 1-Port Channelized T1/E1/PRI NPM | |
| MIP-CT1: DSX1 to CSU DB-15 straight-through cable, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-7KCT1DB15 |
| MIP-CT1: DSX1 to CSU DB-15 null modem cable, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-7KCT1NULL |
| E1 for 75-ohm, unbalanced connections (with BNC connectors), 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-E1-BNC |
| E1 for 120-ohm, balanced connections (with DB-15 connector), 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-E1-DB15 |
| E1 for 120-ohm, balanced connections (with Twinax connector), 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-E1-TWINAX |
| E1 ISDN PRI cable, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-E1-PRI |
| Serial Cables for 2-Port Serial NPM | |
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NP232T |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NP232C |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NP449T |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NP449C |
| EIA/530 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NP530 |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NPX21T |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NPX21C |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NPV35TV2 |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-NPV35CV2 |
| Serial Cables for 4-Port Serial NPM and 2 High-Speed Ports on NP-2T16S | |
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-232MT |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-232FC |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-449MT |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-449FC |
| EIA/530 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-530MT |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-X21MT |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-X21FC |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-V35MT |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10 ft (3 m) | CAB-V35FC |
| V.35 male cable DCE interface, 10 ft (3m) | CAB-V35MC |
| V.35 female cable DTE interface, 10 ft (3m) | CAB-V35FT |
| Cables for NP2T16S NPM, Low-Speed Ports | |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 male V.35 DTE connectors | CAB-OCT-V35-MT |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 female V.35 DCE connectors | CAB-OCT-V35-FC |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 male EIA/TIA-232.V.24 DTE connectors | CAB-OCT-232-MT |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 female EIA/TIA-232.V.24 DCE connectors | CAB-OCT-232-MC |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 male X21 DTE connectors | CAB-OCT-X21-MT |
| 8-lead octal cable with 8 female X21 DCE connectors | CAB-OCT-X21-MC |
| Cables for HSSI NPM | |
| HSSI cable, male-to-male connectors, 10 ft | CAB-HSI1= |
| HSSI cable, male-to-male null modem cable, 10 ft | CAB-HNUL= |
| Kits | |
| Blank NPM filler card (spare) | ACS-NPPN= |
| Telco/wall-mount kit | ACS-NPWM |
| 19-in. rack-mount kit | ACS-NPRM |
| Redundant Power System | |
| 600W Redundant AC Power System without DC power cables | PWR-600-AC-RPS-NCAB |
| 24-inch rack mount kit | ACS-3640RM-24(=) |
| RPS Field Upgrade for C4000 series | ACS-4000-RPS= |
| RPS 22/18 two-to-one DC power cable | CAB-RPSY-2218(=) |
| RPS 22/18 one-to-one DC power cable | CAB-RPS-2218= |
The Cisco IOS software available for the Cisco 4000 series routers is described in the following sections:
The Cisco 4000 series routers support the following software releases:
The Cisco 4000 series offers the following types of feature sets:
The Cisco IOS feature set tables use the following conventions to identify features:
Software feature packs consist of CD-ROMs that contain Cisco IOS software feature set images and a Windows 95 application, which loads the images onto a router.
Software feature packs are available for most of the Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Table 44 lists the product numbers for feature sets and feature packs available in Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Software feature packs are only available for Cisco IOS Release 11.2 and later releases.
For more information about software feature packs, see the "Cisco IOS Feature Packs" section in the "Cisco IOS Software" chapter earlier in the catalog.
Adding a feature set or feature pack might require you to purchase additional memory. Table 44 lists the software feature set and feature pack product numbers and minimum memory requirements for Cisco IOS Release 11.2.
The minimum memory requirements listed were chosen for typical branch and remote office applications. If your network is very large, using complex routing protocols, or using RMON, you might need more memory. Configuration analysis and testing are encouraged.
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | |||||
| Feature Set | Cisco 4000 Series Model | Product Number | Flash | Main DRAM | Shared DRAM |
IP | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-C-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
IP Plus | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-CP-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
IP Plus 40 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-CW-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | ||
IP Plus 56 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-CY-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Desktop | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-B-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Desktop Plus | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-BP-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Desktop Plus 40 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-BW-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Desktop Plus 56 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-BY-11.2=1 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Enterprise | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-A-11.2=1 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Enterprise Plus | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-AP-11.2=1 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Enterprise Plus 40 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-AW-11.2=1 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
Enterprise Plus 56 | Cisco 4500-M | CD45-AY-11.2=1 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
|
|