|
|
This chapter includes configuration examples for the Cisco 1020:
Administrative access to the Cisco 1020 is controlled by a password. That is, only network administrators entering the correct password can change the configuration of the unit. The unit is shipped without a password. To set password protection, enter
enable
at the
Username:
prompt and press Return at the
password:
prompt. Enter the new password using the enable password command in the Cisco 1020 Command Reference publication.
Dial-in access through the Cisco 1020 can be controlled for each dial-in site. To set password access for a dial-in site, see the password command in the Cisco 1020 Command Reference publication.
Following is the procedure:
Username:
prompt. Enter enable and press the Return key.
Username:
prompt, check the serial cable between the Async 1 port and the PC.
The commands for the Cisco 1020 configurations are similar. Only minor changes to the configurations are required to enable or disable specific Cisco 1020 functionality.
The first configuration, which is the most common, is used here as the model. Where the commands in configurations 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 differ from that of configuration 1, they are in boldface for ease of identification. In this way, the commands responsible for the specific functionality of a configuration are easily identified.
For purposes of this example configuration:
The following figures show the topology for the example configurations: Figure 4-1 shows example configurations 1 through 4, Figure 4-2 shows example configuration 5, and Figure 4-3 shows example configuration 6.
Figure 4-1 Configurations 1 through 4 Topology
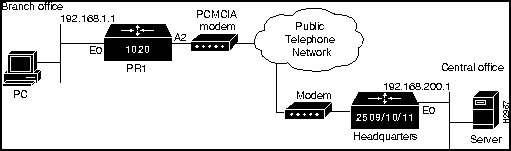
Figure 4-2 Configuration 5 Topology
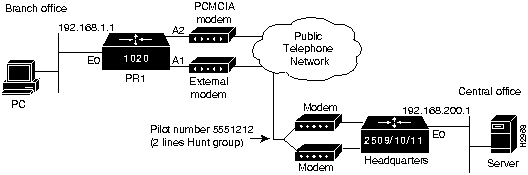
Figure 4-3 Configuration 6 Topology
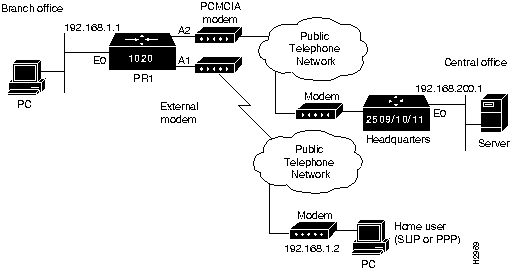
This configuration enables dial-out on demand and allows dial-in on the PCMCIA (Async 2) port. (See Figure 4-1.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant ! IPX option must be purchased from Cisco. option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere modem-def usrv34 "USR V.34 Courier" 115200 "" "AT&F1S0=1&W" "OK" "" ! ! Go to site hq for all unknown networks (default route). ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network F3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 2 ! Incoming/outgoing calls allowed. modem inout dialer rotary-group 2 modem-type usrv34 ! !type the following chat-script as one continuous line ! ! 5551212 is the phone number of the other side. ! pr1 is username on the other side. ! what4ever is our password on the other side. ! 192.168.1.1 is our IP address from Ethernet 0. chat-script hqdial "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT" "" "name:" "pr1" "word:" "what4ever" ">" "ppp 192.168.1.1" ! site hq password what4ever system-script hqdial dial-on demand session-timeout 5 dialgroup 2 encapsulation ppp ! Identifies the IP address on the other end. ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 routing rip ip tcp header-compression ! Novell network number of async link. ipx network F2 ! Must be set to 1 to use one port. max-ports 1 ! ^Z # write # quit
If the system being called supports CHAP and PPP Address Negotiation you can use the following instead:
chat-script hqdial "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT"
If the Cisco 1020 dials out to another system it can either use a chat script to log in, or it can do CHAP. The Cisco 1020 will not authenticate itself using PAP.
If another system dials into the Cisco 1020 and starts sending PPP packets without going through the Username: Password: login sequence, the Cisco 1020 will ask the other system to authenticate itself with PAP, and if that is refused it will ask the other system to authenticate itself with CHAP. If that is refused also then the Cisco 1020 will hang up, since the other system is refusing to authenticate itself.
For best results, set your Cisco 2500 for
ppp authentication chap
.
This configuration enables dial-out only and establishes a continuous connection on the PCMCIA modem. This configuration is shown with no timeout enabled. (See Figure 4-1.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere modem-def usrv34 "USR V.34 Courier" 115200 "" "AT&F1S0=1&W" "OK" "" ! ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network F3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 2 modem out dialer rotary-group 2 modem-type usrv34 ! !type the following chat-script as one continuous line ! chat-script hqdial "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT" "" "name:" "pr1" "word:" "what4ever" ">" "ppp 192.168.1.1" ! site hq password what4ever system-script hqdial dial-on continuous dialgroup 2 encapsulation ppp ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 routing rip ip tcp header-compression ipx network F2 max-ports 1 ! ^Z # write # quit
This configuration enables dial-in only on the PCMCIA modem slot (Async 2). This configuration is shown with no timeout enabled. (See Figure 4-1.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere modem-def usrv34 "USR V.34 Courier" 115200 "" "AT&F1S0=1&W" "OK" "" ! ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 1 ipx network F3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 2 modem in modem-type usrv34 ! site hq password what4ever encapsulation ppp ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 routing rip ip tcp header-compression ipx network F2 ! ^Z # write # quit
This configuration enables a hardwire dial-up network connection on the PCMCIA modem slot (Async 2) using PPP. (See Figure 4-1.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere ! ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network f3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 2 no modem async default ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation PPP ipx network f2 ip tcp header-compression routing rip ^Z # write # quit
This configuration enables multiline load-balance on demand, using a PCMCIA modem slot (Async 2) and a second external modem (connected to the Async 1 port). The answering system must have at least two lines on a rotary for this to work because the site uses the same phone number for both modem dial-outs. (See Figure 4-2.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere modem-def usrv34 "USR V.34 Courier" 115200 "" "AT&F1S0=1&W" "OK" "" ! ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network F3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 1 modem inout dialer rotary-group 2 modem-type usrv34 ! interface async 2 modem inout dialer rotary-group 2 modem-type usrv34 ! !type the following chat-script as one continuous line ! chat-script hqdial "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT" "" "name:" "pr1" "word:" "what4ever" ">" "ppp 192.168.1.1" ! site hq password what4ever system-script hqdial dial-on demand session-timeout 5 dialgroup 2 load-threshold 1000 encapsulation ppp ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 routing rip ip tcp header-compression ipx network F2 max-ports 2 ! ^Z # write # quit
This configuration enables the user "home" to dial into an external modem connected to the Async 1 port and run PPP from home, while enabling dial on demand using the PCMCIA modem to headquarters. (See Figure 4-3.)
# configure terminal hostname pr1 ip domain-name eg.com enable password whatUwant option ipx IPXOptionKeyHere modem-def usrv34 "USR V.34 Courier" 115200 "" "AT&F1S0=1&W" "OK" "" ! ip route 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1 1 ! interface ethernet 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network F3 ipx encapsulation sap ! interface async 1 modem in dialer rotary-group 1 modem-type usrv34 ! interface async 2 modem inout dialer rotary-group 2 modem-type usrv34 ! !type the following chat-script as one continuous line ! chat-script hqdial "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT" "" "name:" "pr1" "word:" "what4ever" ">" "ppp 192.168.1.1" ! site hq password what4ever system-script hqdial dial-on demand session-timeout 5 dialgroup 2 encapsulation ppp ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 routing rip ip tcp header-compression ipx network F2 max-ports 1 ! site home password no12gess encapsulation ppp ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 no routing rip ip tcp header-compression ipx network F4 ^Z # write # quit
Here is how you configure a Cisco 2500 series Access Server to accept dialin on Async5 from a Cisco 1020. The Cisco 1020 should use the following chat-script, entered as one continuous line:
chat-script hq "" "ATDT 5551212" "CONNECT" "" "name:" "pr1" "word:" "what4ever" ">" "ppp 192.168.1.1"
An example configuration for the Cisco 2500 Series for use with dial-ins to Async5 follows:
! version 10.2 service timestamps debug uptime ! ! Used for CHAP and to identify site to remote end. hostname hq ! enable password a11powerizmine ! ! Used for CHAP with remote site pr1. username pr1 password what4ever ipx routing 0000.0c0a.2e9a ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network f1 encapsulation sap ! interface Async5 ppp authentication chap ip unnumbered Ethernet0 ip tcp header-compression passive encapsulation ppp async dynamic address async mode interactive ipx network f2 dialer in-band dialer map ip 192.168.1.1 name pr1 dialer map ipx f2.0000.0cc0.5002 name pr1 broadcast dialer-group 1 ! ! To ease doing telnet to line 5. ip host MODEM5 2005 192.168.200.1 ip domain-name eg.com ! ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 ! line 5 ! Presents Username: Password: to match chat script. login local modem InOut rxspeed 38400 txspeed 38400 flowcontrol hardware
An example configuration that allows both dial-in to and dial-out from the 2500.
! version 10.2 ! hostname hq ! enable password whatUwant ! username pr1 password what4ever ipx routing 0000.0c0a.3e2c chat-script cisco-default ABORT ERROR "" "at" "OK" "ATDT\T" TIMEOUT 60 "CONNECT" chat-script pr1 "" "\r\r" "name:" "hq" "word:" "what4ever" ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 ipx network F1 encapsulation sap ! interface Async5 ip unnumbered Ethernet0 ip tcp header-compression encapsulation ppp hold-queue 40 out async dynamic address async mode interactive dialer in-band dialer rotary-group 1 ! interface Dialer1 ip unnumbered Ethernet0 encapsulation ppp ipx network F2 no ipx route-cache ipx watchdog-spoof dialer in-band dialer map ip 192.168.1.1 name pr1 modem-script cisco-default system-script pr1 5558888 dialer map ipx F2.0000.0cc0.500f name pr1 modem-script cisco-default system-script pr1 broadcast 5558888 dialer-group 3 ppp authentication chap ! ip host MODEM5 2005 192.168.200.1 ! ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 Dialer1 ! access-list 10 permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 access-list 800 deny FFFFFFFF F2 access-list 800 permit FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF ipx route F3 F2.0000.0cc0.500f ! dialer-list 3 list 10 dialer-list 3 list 800 ! line 5 login local modem InOut rxspeed 38400 txspeed 38400 flowcontrol hardware
After completing the installation and configuring the IP address, use the ping command to test for connectivity between the Cisco 1020 and a host, by sending an echo request to a host residing anywhere in your network.
192.34.56.5 is alive.
For more information on the ping command and what to expect with no response, refer to the Cisco 1020 Command Reference manual.
Failures in systems are characterized by certain symptoms. Each symptom can be diagnosed based on problems or causes using specific troubleshooting tools. After identifying each cause, a series of actions can solve the problem. Use these steps to develop your troubleshooting process.
When problem solving, consider the following on the Cisco 1020:
If the SYSTEM - OK LED is off, check power and the power cable.
Verify that the LINK - OK LED is lit. This will confirm that the Cisco 1020 is connected to a 10BaseT hub. If the LINK - OK LED is not lit, check the hub and 10BaseT connection and wiring.
The LAN - ACT LED blinks to indicate Ethernet traffic.
For the Ethernet LAN connection, verify that the RJ-45 connector is firmly seated in the Ether 0 connector on the Cisco 1020.
For the WAN connection, verify that the PCMCIA modem is firmly seated in its slot, and that the modular telephone cable is connected to the appropriate phone jack.
Ensure that power is off when you insert the PCMCIA modem.
|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.