|
|

The Cisco 4000 series comprises the original Cisco 4000, the Cisco 4000-M, and the Cisco 4500.
This publication is specific to the orginal Cisco 4000, but includes identification information following to enable you to distinguish which type of system yours is. For information on the Cisco 4000-M and the Cisco 4500, refer the publication Cisco 4000 Series Hardware Installation and Maintenance.
Cisco 4000 series router models provide a configurable modular router platform using network processor modules---individual modules that when installed in the router are ready for external network hardware connections. The Cisco 4000 series provides flexibility, allowing network managers to easily reconfigure the router when needs change.
The original Cisco 4000 front panel is labeled Cisco 4000; both the Cisco 4000-M and the Cisco 4500 are labeled Cisco 4000 Series on the front panel. The rear label of the Cisco 4000 reads Cisco 4000, the Cisco 4000-M reads Cisco 4000-M , and the rear label of the Cisco 4500 reads Cisco 4500.
Figure 11 shows the front panel of the original Cisco 4000 router.
Figure 1-1 Original Cisco 4000---Front View
Figure 12 shows the front panel of the memory-enhanced Cisco 4000.
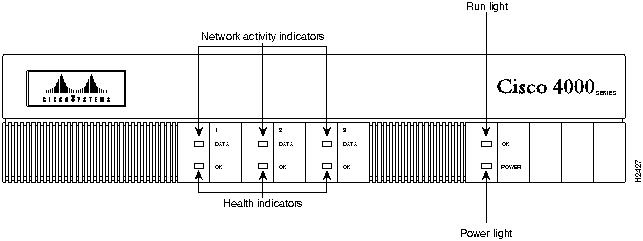
Figure 1-2 Memory-Enhanced Cisco 4000 Series Router---Front View
Table 1-1 Comparison of Cisco 4000 Series Routers
| Memory Feature | Memory-Enhanced Cisco 4000 | Original Cisco 4000 |
|---|---|---|
| Main (CPU-Local DRAM)(1) | 4, 8, 16, 32 MB | 4 or 16 MB |
| Flash | 4 or 8 MB | 2 or 4 MB |
| Shared | 4 MB | 1 or 4 MB |
Design specifications follow:
To successfully operate a multimode FDDI module, the system requires 4 megabytes (MB) of shared memory. The standard shared-memory configuration is 1 MB. For a system that has more than six ports (for example: a system containing dual-Ethernet, four port serial, and dual-serial modules), 4 MB of shared memory is also required.
The Cisco 4000 DC-input power supply is intended for use in DC operating environments.
Table 1-2 Router Specifications
| Description | Design Specification |
|---|---|
| DC-input power | 200W, 40 to 72 VDC |
| Wire gauge for DC-input power connections | 16 AWG(1) |
When using stranded wiring for DC power input, terminate the wiring with approved wiring terminations such as closed loop or spade type with upturned lugs of appropriate size for the wires. The lugs must clamp both the insulation and the conductor.
Table 1-3 lists the router specifications.
Table 1-3 Router Specifications
| Description | Design Specification |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (W x D x H) | 17.6" x 17.7" x 3.4" (44.7 cm x 45 cm x 8.6 cm) |
| Weight | 24 lb (including the chassis and network processor modules) (10.9 kg) |
| Power | 200W, 85--264 VAC, 50--60 Hz |
| Processor | 40-MHz Motorola 68EC030, 32-bit wide |
| CPU-Local DRAM | 4 or 16 MB |
| Shared DRAM | 1 or 4 MB |
| Nonvolatile RAM | 128 KB |
| Network Interface Options | Ethernet, Serial, Token Ring, FDDI |
| Serial Interfaces | RS-232, RS-449, V.35, X.21, NRZ/NRZI, DTE/DCE; EIA-530 DTE |
| Console Port | RS-232 DB-25 female connector |
| Auxiliary Port | RS-232 DB-25 male connector |
| Nonoperating Temperature | -40--185°F (-40--85°C) |
| Operating Humidity | 5--95%, noncondensing |
| Operating Temperature | 32--104°F (0--40°C) |
The router has the following memory systems:
|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.