|
|
Working with Your Access Server for the First Time
Refer to this chapter after performing the tasks described in the previous chapter, "Starting Up Your Access Server for the First Time." This chapter will familiarize you with critical components of Cisco access servers while you configure the product for the first time. Spending a few minutes in this chapter just after you start up your access sever will save you time over the long term.
Complete the tasks in this chapter if you are not familiar with any of the following components and configuration tasks on a Cisco access server:
Specifically, this chapter describes the following:
Working with the EXEC Facility, Lines, and Interfaces
This section describes the following information:
Choosing a Method of Connecting to the Network
The prompt that appears when you first log in to an access server (
Router>
) is called the EXEC prompt. When you access the EXEC prompt, you are accessing the EXEC facility and you start an EXEC session. You can log in through the following ports on an access server:
To configure the access server (via the console port) to permit remote clients to dial in through asynchronous interfaces to access network resources (such as printers and file servers). You have two options:
In general, you should give system administrators access to the EXEC facility, but give dialin clients access only to the network. The next section "Permitting Users to Connect Directly to the Network" describes how to enable users to log in to the network without ever seeing the access server.
Permitting Users to Connect Directly to the Network
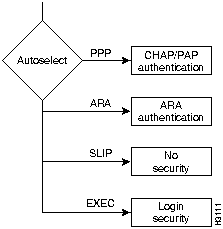
When a user dials through the access server, the Cisco IOS software can detect the incoming protocol automatically if you configure it to autoselect the protocol. You autoselect a protocol by issuing the autoselect ppp or autoselect arap line configuration commands. If the Cisco IOS software detects one of these protocols, it can launch Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) or AppleTalk Remote Access (ARA) sessions automatically.
Figure 2-1 shows the authentication process when autoselect is used.
Figure 2-1 : Flowchart of EXEC Facility and Autoselect Authentication Options
Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3 show examples of what clients (dialin PC or Macintosh users) see when they connect to the network using PPP and ARA.
Figure 2-2 : Client Connection to an IP Network Using Windows 95
After clients using PPP connect to the network, they have access to all IP network resources, such as UNIX hosts, other PCs on the network, or Windows NT servers.
Figure 2-3 : Client Connection to an AppleTalk Network Using ARA 2.0
After users connect to the network via ARA, they have access to all AppleTalk network resources, including AppleShare servers, the public folders of other users, and printers. They can also use ARA as the transport protocol to run IP applications.
Connecting to the EXEC Facility
If you permit users to dial in to the EXEC facility, they can use terminal services (such as Telnet), run an asynchronous protocol over the line, or use one of many other access services. For example, you can enter the ppp command to initiate a PPP session to a device on the network.
To enable users to log in to the EXEC facility, issue the autoselect during-login line configuration command. When the Cisco IOS software detects a carriage return, the user is connected to the EXEC facility. You also access the EXEC facility any time you log in to the access server through the access server to configure it.
There are two primary levels to the EXEC facility:
As the network administrator for an access server, you protect privileged level EXEC mode with a password that only administrators know. You give dialin users access only to user-level EXEC mode so that they can issue commands to connect with other network devices (such as the ppp command).
For an overview of configuration mode, refer to the section, "Accessing Different Command Modes." For information about configuring security, refer to the "Configuring Access Service Security" chapter.
Accessing Different Command Modes
In addition to the EXEC facility, you can access several different command modes on the access server. Each different command mode permits you to configure different components on the access server. Table 2-1 lists the most common components and configuration modes. You configure global parameters in global configuration mode, interface parameters in interface configuration mode, and line parameters in line configuration mode. For information about what you typically configure in line mode versus interface mode, refer to the section "Configuring Asynchronous Interfaces."
Getting Context-Sensitive Help
You can get help in any of the command modes listed in Table 2-1. The help available in the Cisco IOS software describes the syntax for each command or displays the complete name of the command. To get context-sensitive help, type ? (a question mark) at the prompt. There are two types of help available:
You can also type ? at the command prompt and the Cisco IOS software displays all available commands for that command mode. The following example shows sample output for the commands available in privileged EXEC mode:
Refer to the chapter "Configuring the User Interface" in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide for more information about any aspect of working with the user interface in the Cisco IOS software. The Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide is part of the Cisco IOS documentation in Cisco IOS Releases 11.1 and later.
Configuring Asynchronous Interfaces
The Cisco AS5200 is configured with either a Dual T1 PRI card or a Dual E1 PRI card. The T1 PRI or E1 PRI ports to which you connect T1 PRI or E1 PRI lines are located on the back panel of your access server. Remote clients dial in to the network through these T1 PRI or E1 PRI ports.
To enable clients to dial in, configure the following four types of interfaces used for dial in operations: ISDN interface, dialer interface, group asynchronous interface, and asynchronous interface. Asynchronous interfaces correspond to physical terminal (TTY) lines. For example, asynchronous interface 1 corresponds to TTY line 1.
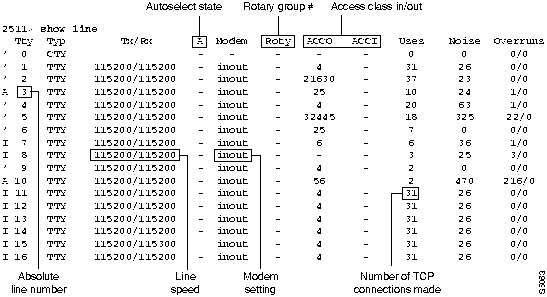
Generally, commands entered in asynchronous interface mode enable you to configure protocol-specific parameters for asynchronous interfaces, whereas commands entered in line configuration mode permit you to configure the physical aspects for the same port. In Figure 2-4, which shows the show line output on a Cisco AS5200, TTY line 1 corresponds with asynchronous interface 1, TTY line 16 corresponds with asynchronous interface 16, and so on.
Figure 2-4 : Show Line Output---TTY Lines and Asynchronous Interfaces
Asynchronous line configuration commands configure ports for the following options:
To enter line configuration mode, first connect to the console port of the access server and enter privileged EXEC mode. Next, enter global configuration mode and then line configuration mode for the asynchronous lines that you want to configure.
The following example of T1 line configuration (E1 is configured for lines 1 through 60) shows the sequence of entering line configuration mode for lines 1 through 48:
Generally, interfaces enable the Cisco IOS software to use routing functions. Specifically, you configure asynchronous interfaces to support PPP connections. You configure interfaces on an access server for the following functions:
Configuring Group Asynchronous Interfaces
To configure multiple asynchronous interfaces at the same time (with the same parameters), you can assign each asynchronous interface to a group and then configure the group. Configurations throughout this guide configure group asynchronous interfaces, rather than configuring each interface separately.
To configure a group asynchronous interface, specify the group async number (an arbitrary number) and the group range (beginning and ending asynchronous interface number). The following example shows the process of creating a group asynchronous interface for asynchronous interfaces 1 through 24 on a Cisco AS5200 access server with a Dual T1 PRI card:
At this point, you have configured asynchronous interfaces 1 through 24 as part of the same group and you are in interface configuration mode for the group asynchronous interface. To enter asynchronous interface configuration mode at any point to configure this group, enter the following command:
First-Time Access Server Configuration Procedures
This section describes the use of Cisco IOS software to configure some fundamental parameters so that PC and Macintosh clients dial into your network to access resources, such as file servers and printers.
This section assumes you have referred to the user guide or installation and configuration guide that accompanied your router and that you have access to user level EXEC mode ( Each step in the subsequent sections show information that appears on the screen before and after you type each command. On-screen text and system responses appear in The 5 lessons, and their content, are shown in the following list:
After you complete the tasks in all 5 lessons, you will have enabled remote PC users to dial in and access IP resources on your network.
Total time to complete all 5 lessons can range from 30 minutes to more than an hour. Each lesson takes approximately 10 minutes.
Before you begin, make sure you have completed the following tasks:
Lesson 1, Configuration Basics
In this lesson, you will configure some basic parameters and learn how to work with the command line interface of the Cisco IOS software. This section requires 10 to 15 minutes to complete.
Enter the commands in the following tables to configure basic parameters.
The following output shows statistics for a Cisco IOS 11.2 image running on an access server:
To continue with this lesson, enter the commands listed in the following table:
The following output shows the commands and their definitions available in privileged EXEC mode:
To continue with this lesson, enter the commands listed in the following table:
The following output shows the configuration that you saved when you issued the copy running startup command:
Lesson 2, Configuring T1 PRI Controllers
In this lesson, you will configure some line parameters to enable the access server to work with a modem. This section requires 5 to 7 minutes to complete. For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring Modems" chapter later in this guide.
For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring for ISDN and Analog Calls" chapter in this guide.
At the end of Lesson 1, the
The resulting configuration configures T1 controllers to function with T1 PRI lines. Proceed to Lesson 3.
Lesson 3, Configuring E1 PRI Controllers
In this lesson, you will configure some line parameters to enable the access server to work with a modem. This section requires 5 to 7 minutes to complete. For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring Modems" chapter later in this guide.
For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring for ISDN and Analog Calls" chapter in this guide.
At the end of Lesson 1, the
The resulting configuration configures E1 controllers to function with E1 PRI lines. Proceed to Lesson 3.
Lesson 4, Configuring Access Server Interfaces
In this lesson, you will configure interfaces to enable dial-in to IP networks. This section requires 10 to 15 minutes to complete.
You will configure the following interfaces in this lesson:
You will also enter the following global configuration parameters:
For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring for ISDN and Analog Calls" chapter in this guide.
At the end of Lesson 2, the Ethernet 0 interface is configured with the following commands:
The serial interface is configured with the following commands:
The asynchronous group interface is configured with the following commands:
Enter the following commands to specify the IP address pool and control access by IP protocol
This lesson configured interfaces for dial-in to IP networks. Before you can allow users to dial in to the network, you must configure the modems, which are described in Lesson 4.
Lesson 5, Configuring Access Server Modems
In this lesson, you will configure the access server modems, which will allow users to dial in to your network. This section requires 5 to 7 minutes to complete.
For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring for ISDN and Analog Calls" chapter in this guide.
At the end of Lesson 3, the
The resulting configuration enables clients to dial in to the network to access IP and AppleTalk resources. At this point, you must configure security, or your network will be open to significant security breaches.
Lesson 6, Basic System Security
This lesson uses the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) facility to configure basic local authentication. Local authentication means that an internal username database authenticates users, rather than a remote user authentication (security) server. This section requires 10 to 15 minutes to complete.
For more information about any of the parameters in this lesson, refer to the "Configuring Access Service Security" chapter in this guide.
At the end of Lesson 4, the
You have configured PPP dialin to an IP network and security. Each task in these lessons is described in much greater detail in the subsequent chapters in this guide.
Refer to the next section "Sample Access Server Configuration" to view the configuration resulting from the 5 lessons.
Sample Access Server Configuration
The following Cisco AS5200 configurations show the results of Lessons 1 through 5. These configurations are typically sufficient to enable remote users to dial in as a node on a local network. For additional information, refer to the subsequent chapters in this guide.
T1 Access Server Configuration
The following shows a typical T1 configuration:
E1 Access Server Configuration
The following shows a typical E1 configuration:
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()

Router>
Router> enable
Password:
Router#
Command Mode
Access Method
Prompt
Exit Method
User EXEC
Log in.
Router>
Use the logout command.
Privileged EXEC
From user EXEC mode, enter the enable command.
Router#
To exit back to user EXEC mode, use the disable, exit, or logout command.
Global configuration
From privileged EXEC mode, enter the config terminal command.
Router(config)#
To exit to privileged EXEC mode, use the exit or end command or press Ctrl-Z.
Interface configuration
Enter the interface type number command, such as interface ethernet 0.
Router(config-if)#
To exit to global configuration mode, use the exit command. To exit directly to privileged EXEC mode, press Ctrl-Z.
Line configuration
Enter the line start-number end-number command, such as line 1 48.
Router(config-line)#
To exit to global configuration mode, use the exit command. To exit directly to privileged EXEC mode, press Ctrl-Z.
Router(config)# arap ?
callback Enable callback of ARAP connections
logging Turn on logging of ARAP connections
network Internal Appletalk Network For Arap Clients
Router(config)# arap
Router(config)# ar?
arap arp
Router(config)#
Router# ?
Exec commands:
access-enable Create a temporary Access-List entry
access-template Create a temporary Access-List entry
bfe For manual emergency modes setting
clear Reset functions
...
write Write running configuration to memory, network, or
terminal
x3 Set X.3 parameters on PAD
xremote Enter XRemote mode
5200> enable
5200# configure terminal
5200(config)# line 1 48
5200(config-line)#
Router>
). You can change the host name to any name you wish by using the hostname global configuration command. For example, to change the name of a host from Router to 5200, you would issue hostname 5200 at the global configuration prompt.
5200(config)# interface group-async 1
5200(config-if)# group-range 1 24
Building configuration...
5200(config-if)#
5200(config)# interface group-async 1
5200(config-if)#
Router>
).
Press RETURN to get started
" appears. This is not an error. If this message appears, press Return and the
Router>
prompt appears again. Lesson 1 shows you how to change this timeout interval.
screen font
. Commands that you are instructed to type appear in examples as
boldface screen font
.
![]()
Command
Purpose
Router>
enable
Password:
Router#
Either or return to privileged EXEC mode (represented by
Router#
). If you are in user EXEC mode (represented by the
Router>
prompt), enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command. If an enable password has been set, you are prompted for a password. If none has been set, you are not prompted for a password. If you are in any other mode, type exit and press Return until the
Router#
prompt appears.
Router#
config term
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Enter global configuration mode. The abbreviated command config term represents the command configure terminal. You can abbreviate commands by entering the minimum number of characters that uniquely identify the command.
Router(config)#
hostname 5200
5200(config)#
Change the name of the access server to a meaningful name. Substitute your own name for 5200.
5200(config)#
enable secret guessme
5200(config)#
Enter a secret enable password. This password provides access to privileged EXEC mode. When a user types enable at the EXEC prompt (
Router>
or
5200>
), they must enter the enable secret password to gain access to configuration mode. Substitute your own enable secret instead of using the guessme password.
5200(config)#
line con 0
5200(config-line)#
exec-timeout 0 0
5200(config-line)#
exit
5200(config)#
Enter line configuration mode to configure the console port, which you are connected to. You can see when you enter line configuration mode, because the prompt changes to
5200(config-line)#
. Prevent the access server's EXEC facility from timing out if you do not type any information on the console screen for an extended period. Exit back to global configuration mode.
5200(config)#
exit
5200#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Exit back to privileged EXEC mode. If you have altered any parameters while in global configuration mode (or any other command mode), the message "
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
" appears. This is normal and does not indicate an error condition.
5200#
show version
Display statistics about the Cisco IOS software image loaded on your access server, as well as available memory (NVRAM and Flash), and available interfaces.
5200# show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 3000 Software (IGS-J-L), Version 11.2(1.0), RELEASED SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 23-Oct-96 15:18 by susingh
Image text-base: 0x0303CE40, data-base: 0x00001000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 4.14(9.1), SOFTWARE
5200 uptime is 3 minutes
System restarted by power-on
System image file is "igs-j-l", booted via flash
5200 (68030) processor (revision D) with 8192/4096K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID 02007583, with hardware revision 00000000
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV Inc).
Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.0.
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface.
50 Serial network interfaces.
48 terminal lines.
2 Channelized T1/PRI ports.
128K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of processor board System flash (Read ONLY)
4096K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write)
Configuration register is 0x2102
AS5200>
Command
Purpose
5200#
configure terminal
5200(config)#
?
Get help about all commands available in global configuration mode. The output that follows is based on the igs-j-l software image shown in the output of the show version command. Your output can differ and depends on your image type.
5200(config)# ?
Configure commands:
aaa Authentication, Authorization and
Accounting.
access-list Add an access list entry
alias Create command alias
appletalk Appletalk global configuration commands
arap Appletalk Remote Access Protocol
... (some output deleted for brevity)
username Establish User Name Authentication
vines VINES global configuration commands
vpdn Virtual Private Dialup Network
vty-async Enable virtual async line configuration
x25 X.25 Level 3
x29 X29 commands
xremote Configure XRemote
5200(config)#
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
arap ?
callback Enable callback of ARAP connections
logging Turn on logging of ARAP connections
network Internal Appletalk Network For Arap Clients
5200(config)# arap
Get help about all keywords and arguments associated with the arap global configuration command. The help system lists each argument and describes it. To find out if there are additional arguments with this command, you can type any portion of the command followed by a space and a question mark, as shown in the next step.
5200(config)#
arap network ?
<1-65279> Network number
Get help about the arap network command. The system displays the range of network numbers you can select for an ARA network. For more information about any command in the Cisco IOS software, you can refer to the Cisco IOS software command references.
5200(config)#
exit
5200#
Exit back to privileged EXEC mode.
5200#
copy running startup
Building configuration...
[OK]
5200#
Copy the contents of your running configuration (what you have just entered) to the startup configuration for the access server. The Cisco IOS software displays
[OK]
, indicating that the copy process was successful. The full name of the command is copy running-config startup-config.
5200#
show startup-config
Display your startup configuration. If you want to view your current configuration (if it differed from your running configuration), issue the show running-config command.
5200# show startup-config
Using 419 out of 32762 bytes
!
version 11.2
service slave-log
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname 5200
!
enable secret 5 $1$oiqW$zIoVcK4tkGdpoBarDXcFz0
username jim password 7 04091E020A
!
interface Ethernet0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
shutdown
no fair-queue
!
no ip classless
!
!
line con 0
line 1 8
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
5200#
prompt appeared, and this is where you start Lesson 2. Enter the commands in the following tables to configure modems.
Command
Purpose
5200#
configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
5200(config)#
Enter global configuration mode and accept configuration commands from the console.
5200(config)#
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
Enter the Telco switch type
5200(config)#
controller T1 0
[or]
5200(config)#
controller T1 1
5200(config-controller)#
Enter controller configuration mode to configure a T1 controller port. The T1 controller ports are 0 and 1. The ports are labeled on the Dual T1 PRI card.
5200(config-controller)#
framing esf
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the framing type for the T1 line. The framing type must match you Telco's offering.
5200(config-controller)#
linecode b8zs
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the line code type for the T1 line. The line code must match your Telco's offering.
5200(config-controller)#
clock source line primary
[or]
5200(config-controller)#
clock source line secondary
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the clock source for the T1 line. Configure one T1 line to serve as the primary or most stable clock source line. The other T1 line is configured as the secondary clock source line.
5200(config-controller)#
pri-group timeslots 1-24
5200(config-controller)#
Enter how you want to configure all 24 channels.
5200(config-controller)#
exit
5200(config)#
Exits controller configuration mode.
5200#
prompt appeared, and this is where you start Lesson 2. Enter the commands in the following tables to configure modems.
Command
Purpose
5200#
configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
5200(config)#
Enter global configuration mode and accept configuration commands from the console.
5200(config)#
isdn switch-type primary-net5
Enter the European Telco switch type
5200(config)#
controller E1 0
[or]
5200(config)#
controller E1 1
5200(config-controller)#
Enter controller configuration mode to configure a E1 controller port. The E1 controller ports are 0 and 1. The ports are labeled on the Dual E1 PRI card.
5200(config-controller)#
framing crc4
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the framing type for the E1 line. The framing type must match you Telco's offering.
5200(config-controller)#
linecode hdb3
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the line code type for the E1 line. The line code must match your Telco's offering.
5200(config-controller)#
clock source line primary
[or]
5200(config-controller)#
clock source line secondary
5200(config-controller)#
Enter the clock source for the E1 line. Configure one E1 line to serve as the primary or most stable clock source line. The other E1 line is configured as the secondary clock source line.
5200(config-controller)#
pri-group timeslots 1-31
5200(config-controller)#
Enter how you want to configure all 24 channels.
5200(config-controller)#
exit
5200(config)#
Exits controller configuration mode.
5200(config)#
prompt appeared, and this is where you start Lesson 3. Enter the commands in the following table to enable clients to dial in to IP networks.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
interface ethernet 0
5200(config-if)#
Enter Ethernet interface configuration mode.
5200(config-if)#
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0
Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
5200(config-if)#
no shutdown
Do not shut down the interface.
5200(config-if)#
exit
5200(config)#
Configure interactive mode on the asynchronous interfaces.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
interface serial0:23
[or]
5200(config)#
interface serial1:23
5200(config-if)#
Enter serial interface configuration mode. Once you configure the T1 controller, two corresponding D channel serial interfaces are instantly created. Serial interface 0:23 is the D channel for the T0 controller, and serial interface 1:23 is the D channel for T1 controller. You must configure each serial interface to receive incoming and send outgoing modem signaling.
5200(config-if)#
ip address 172.16.254.253 255.255.255.0
Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
5200(config-if)#
isdn incoming-voice modem
Configure all incoming voice calls to go to the modems.
5200(config-if)#
encapsulation ppp
Enable the point-to-point protocol (PPP) to run on the set of interfaces in the group.
5200(config-if)#
dialer-group 1
Assign the serial interface to dialer group 1 to control dialing access to the interface. Access is controlled by a combination of protocol and access list define in the dialer-list command.
5200(config-if)#
ppp multilink
5200(config-if)#
ppp authentication chap pap
Enable CHAP and PAP authentication on the serial interface.
5200(config-if)#
exit
5200(config)#
Exit serial interface configuration mode.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
interface group-async 1
5200(config-if)#
Place all asynchronous interfaces in a single group, so that you configure the same parameters quickly on all interfaces at one time. This example assigns asynchronous interfaces 1 through 24 to group asynchronous interface 1. You can see that you have entered interface configuration mode, because the prompt changed to
5200(config-if)#
.
The number you use with the group-range command depends on the number of asynchronous interfaces you have on your access server. That is, if your access server has 48 asynchronous interfaces, you can specify group-range 1 48. If 60, specify group-range 1 60.
5200(config-if)#
ip unnumbered ethernet 0
To conserve IP addresses, configure the asynchronous interfaces as unnumbered and assign the IP address of the Ethernet interface to them.
5200(config-if)#
encapsulation ppp
Enable the point-to-point protocol (PPP) to run on the set of interfaces in the group.
5200(config-if)#
async mode interactive
Configure interactive mode on the asynchronous interface.
5200(config-if)#
peer default ip address pool default
Assign a common IP address pool. PPP packets coming through an asynchronous line and ISDN line share this common IP pool.
5200(config-if)#
ppp authentication chap pap
Enable CHAP and PAP authentication on the interface.
5200(config-if)#
group-range 1 24
Define the group range of the interface.
5200(config-if)#
exit
5200(config)#
Exit the interface configuration mode.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48
Assign a pool of IP addresses (in this example, from 172.16.254.1 to 172.16.254.48), all of which are on the same IP subnet. If your access server has 60 modems, the IP address pool is 172.16.254.1 to 172.16.254.60.
5200(config)#
dial-list 1 protocol ip permit
5200(config-if)#
exit
Specify a dial list to control dialing by protocol. In this example, dialing is permitted by anyone using the IP protocol.
5200(config)#
prompt appeared, and this is where you start Lesson 4. Enter the commands in the following table to configure the access server modems.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
line 1 24
5200(config-line)#
Exit from interface configuration mode and return to global configuration mode.
5200(config-line)#
modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdms
Configure the access server modems automatically. A string of modem configuration commands is sent to the modem each time a modem is reset.
5200(config-line)#
transport input all
Allow all protocols to be used when connecting the line.
5200(config-line)#
autoselect ppp
Enable remote IP users running a PPP application to dial in, bypass the EXEC facility, and connect directly to the network.
5200(config-line)#
autoselect during-login
Send a username and password prompt to the user. The autoselect function begins after the user logs in.
5200(config-line)#
modem inout
Enable both incoming and outgoing calls.
5200(config-line)#
stopbits 1
Specify the number of stop bits transmitted per byte.
5200(config-line)#
rxspeed 57600
Set the line receive speed.
5200(config-line)#
txspeed 57600
Set the line transmit speed.
5200(config-line)#
exit
5200(config)#
Exit to global configuration mode.
5200(config)#
prompt appeared, and this is where you start Lesson 5. Enter the commands in the following table to configure basic system security.
Command
Purpose
5200(config)#
aaa new-model
Enable the AAA facility globally on the access server.
5200(config)#
aaa authentication login default local
Define an authentication method list for users logging in to the access server.
5200(config)#
aaa authentication ppp default local
Define an authentication method list for clients using a PPP application to dial in to the network.
5200(config)#
aaa authentication arap default local
Define an authentication method list for clients using ARA to dial in to the network.
5200(config)#
username jim password 2ude
Populate the local username database by specifying a username-and- password pair for every user who needs access to the network.
5200# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
version 11.2
service slave-log
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname 5200
!
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authentication arap default local
aaa authentication ppp default local
enable secret 5 $1$ltBE$Slq0BUs/5mwqw6B4DOapg/
!
username jim password 7 02150C5A110702
!
enable password cisco
!
modem startup-test
no ip domain-lookup
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
!
controller T1 0
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
controller T1 1
shutdown
clock source line secondary
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
shutdown
no fair-queue
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial0:23
ip address 172.16.254.253 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer-group 1
no fair-queue
ppp multilink
ppp authentication chap pap
!
interface Group-Async1
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool default
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap pap
group-range 1 24
!
ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
line con 0
line 1 24
exec
autoselect during-login
autoselect ppp
modem InOut
modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdms
transport input all
stopbits 1
rxspeed 57600
txspeed 57600
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
!
end
5200# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
version 11.2
service slave-log
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname 5200
!
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authentication arap default local
aaa authentication ppp default local
enable secret 5 $1$ltBE$Slq0BUs/5mwqw6B4DOapg/
!
username jim password 7 02150C5A110702
!
enable password cisco
!
modem startup-test
no ip domain-lookup
isdn switch-type primary-net5
!
controller E1 0
framing crc4
clock source line primary
linecode hdb3
pri-group timeslots 1-31
!
controller E1 1
shutdown
clock source line secondary
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
shutdown
no fair-queue
!
interface Serial1
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Serial0:23
ip address 172.16.254.253 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
isdn incoming-voice modem
dialer-group 1
no fair-queue
ppp multilink
ppp authentication chap pap
!
interface Group-Async1
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
async mode interactive
peer default ip address pool default
no cdp enable
ppp authentication chap pap
group-range 1 24
!
ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
line con 0
line 1 31
exec
autoselect during-login
autoselect ppp
modem InOut
modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdms
transport input all
stopbits 1
rxspeed 57600
txspeed 57600
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
!
end
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()