|
|
After you install VlanDirector, you are ready to work with the application and become familiar with its features. VlanDirector is installed as part of CiscoWorks Switched Internetwork solutions (CWSI). Refer to the CD booklet that accompanied the CWSI software CD for system requirements and installation instructions.
This section provides information on network requirements, starting VlanDirector, how to in VlanDirector, and how to understand the VlanDirector network map and views.
Summary of Getting Started Tasks
The following is a list of the tasks to get started with VlanDirector. The procedure for completing each task follows this summary.
Before you install the software, perform the following procedure to verify that your network is set up correctly:
You can start VlanDirector from the UNIX command line, SunNet Manager, or HP OpenView.
Starting VlanDirector from the UNIX Command Line
To start VlanDirector from the UNIX command line, follow these steps:
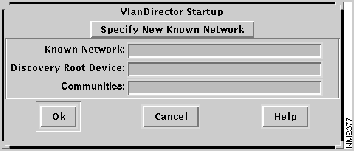
Figure 3-1 : VlanDirector Startup Window
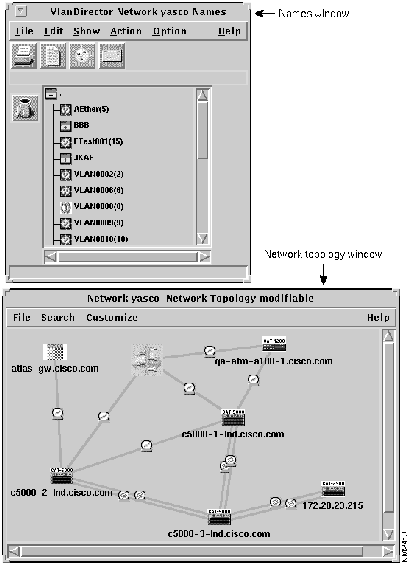
Figure 3-2 : VlanDirector Names and Network Topology Windows after Startup
For additional command line options, refer to Appendix B.
If problems occur when starting VlanDirector, make sure the PATH environment variable includes a path to VlanDirector executables. If you do not want to change your PATH environment variable, you can launch VlanDirector as follows:
When entering this command, replace <install directory> with the directory and path name where VlanDirector is installed.
Starting VlanDirector from SunNet Manager
To start VlanDirector from the SunNet Manager Tools menu, follow these steps:
Figure 3-3 : VlanDirector Startup Window
Starting VlanDirector from HP OpenView
To start VlanDirector from HP OpenView, follow these steps:
Figure 3-4 : VlanDirector Startup Window
VlanDirector combines the following navigational aids to help you become familiar with the user interface and perform VLAN configuration. If you are getting started with VlanDirector, familiarize yourself with these navigational aids before you perform VLAN configuration tasks.
Network maps and VLAN windows allow you to switch between high-level topology maps and detailed device and port views. You can hide or show views depending on which ones you want to use at a particular time. Figure 3-2 shows the windows that are displayed by default when you start VlanDirector.
To display all of the VlanDirector windows, do the following:
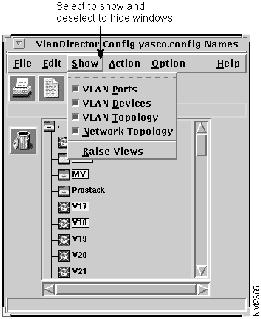
In the Names window, select Show, and then select the four VLAN view options in the Show menu as shown in Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 : Displaying VlanDirector Windows
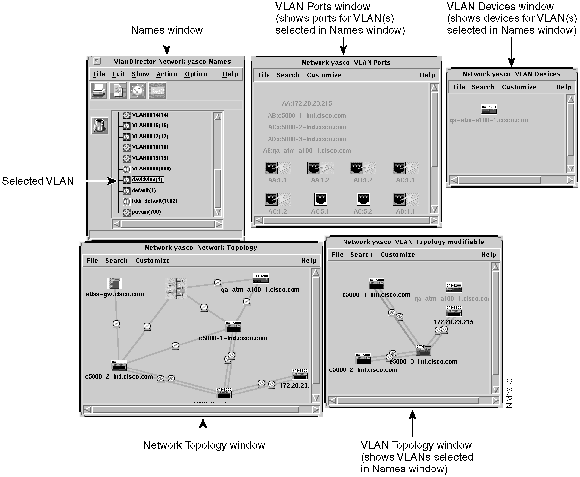
VlanDirector displays all of the topology and device windows as shown in Figure 3-6, and Table 3-1 provides a summary of what you can do from each window.
Figure 3-6 : VlanDirector Windows
Table 3-1 : VlanDirector Windows and What They Show
After Discovery, you might want to rearrange your network displays as follows so you can more easily see a network view. To do this, do the following:
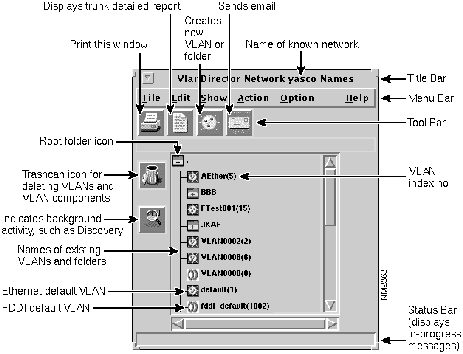
Understanding the Names Window
The Names window displays the names of existing VLANs and folders and enables you to perform many VlanDirector configuration tasks. Use this window to give a name to a new VLAN or to organize groups of VLANs into folders, in the same way that you would organize files into folders or directories.
The Names window also provides menu commands to manage configurations and known networks. Figure 3-7 shows the Names window.
The Names window has the following characteristics:
Menu Bar
The menu bar contains the commands that enable you to work with VLAN configurations, create VLAN names, and control many operating characteristics of the application, such as which network views are displayed.
Tool Bar
Icons in the tool bar include a printer symbol, which prints the Names window; the paper symbol, which opens a Trunk Details Report window; the Create VLAN icon, which opens a create-dialog box for creating a VLAN name or folder; and the Send Email icon, which enables you to report problems or send feedback using email.
Icon Bar -- Left Side of Pane
There are also icons appearing down the left side of the Names window. They include the trash can, the background activity icon, and the discrepancies icon. The background activity icon looks like a magnifying glass and is displayed whenever a process or action is in progress. When the icon is displayed, VlanDirector is performing a discovery of network devices or changing VLANs or their properties.
Central Scrollable Pane -- Names List
VLANs and folder names appear in the central scrollable pane.
Status Bar
The message bar displays textual explanation of a tool bar function whenever you place the pointer over a tool bar icon.
The message bar also displays in-progress status messages whenever you initiate an action.
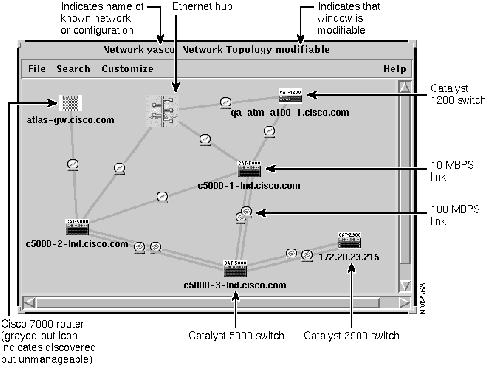
Icons are used to depict devices and links. Device icons include the name and type of the device so you can easily identify it; for example, CAT-5000 indicates a Catalyst 5000 switch. The name of the switch is underneath the icon.
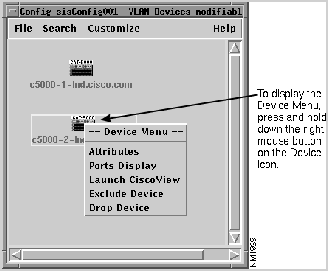
In some views, you can press and hold down the right mouse button on the device icon to display a popup menu listing command options for that device. For example, click on a device on the VLAN Devices window to display a popup menu containing command options for that device.
Figure 3-8 shows the device icons that are used in VlanDirector and what they mean. Figure 3-9 shows the port icons used in VlanDirector.
Figure 3-8 : Network Topology Window Showing VlanDirector Icons
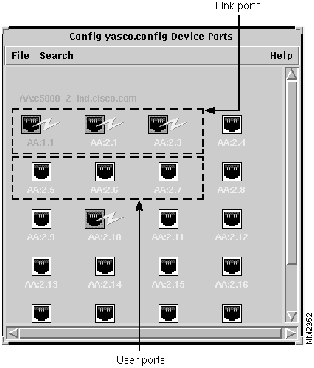
Figure 3-9 : Port Icons in VlanDirector
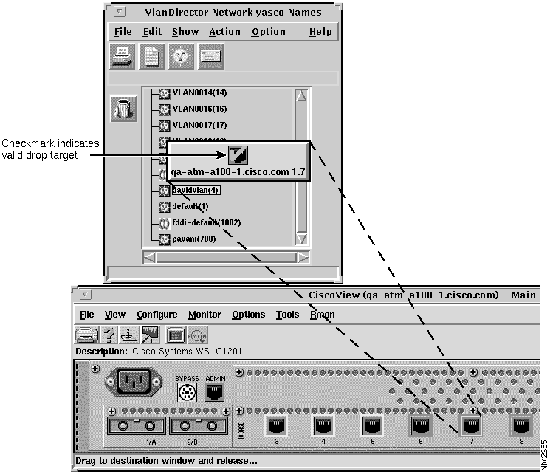
Figure 3-10 : Device Icon Popup Menu VlanDirector enables you to drag and drop icons. To drag and drop an icon to a target, select the icon and then drag it to the target. You can drag or drop a single icon or more than one icon simultaneously. For example, when adding a port to a VLAN, you can drag and drop a port from a CiscoView display to the VLAN name in the Names window or to the VLAN Ports window. Figure 3-11 shows an example of dragging a port from a CiscoView window to the Names window.
Figure 3-11 : Example of Drag-and-Drop from CiscoView to VlanDirector In this example, the port is dragged from the CiscoView display to the Names window. Similarly, you can drag multiple ports. Multiple ports are represented by a single port icon.
Sometimes when dragging from CiscoView, you need to drag on the LED rather than the port icon.
To drag and drop an icon, for example, a port:
You can drag and drop multiple items of the same type. To drag and drop more than one item, for example, multiple ports:
When you drag an item to a valid target, the icon that you are dragging displays a checkmark when you have reached a valid target.
When dragging over an invalid target, no checkmark is displayed.
A valid drop target cannot always accept a dropped icon or object. When this occurs, an error message is displayed. For example, if the VLAN Devices, Ports, or Topology window is displaying only one VLAN, it can accept a port from CiscoView. If it is displaying more than one VLAN, it cannot accept the port from CiscoView.
When dragging an item to the trash can, make sure that you move the arrowhead of the pointer attached to the upper-left corner of the dragged icon into the trash can.
Table 3-2 shows a list of common drag-and-drop tasks.
Table 3-2 : Common Drag-and-Drop Tasks
Using CiscoView with VlanDirector
CiscoView is a device management application that enables you to display a graphical representation of each network device, display configuration and performance information, and perform minor troubleshooting tasks.
CiscoView is provided with VlanDirector. Use CiscoView with VlanDirector to add or delete ports to and from a VLAN by dragging and dropping ports from a CiscoView display into a VlanDirector display, as shown in Figure 3-11.
To start CiscoView, do one of the following:
Understanding Colors and Legends in VlanDirector
VlanDirector uses color to indicate port status, VLAN membership, and icon selection.
CiscoView and VlanDirector use the following color-coded scheme to indicate port status.
Magenta -- Testing
Green -- Up
Brown -- Down
Cyan -- Dormant
Red -- Failure
Orange -- Minor Alarm
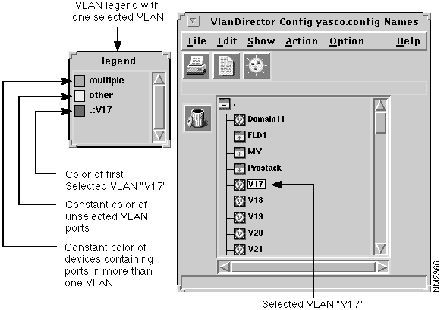
To display the color-coded legend for VLAN membership, in the Names window select Option>Show Legend, if it is not already selected. The Legends window matches colors to selected VLANs. It also displays default colors of brown to identify switches with more than one VLAN defined and light gray to indicate unselected VLANs. When you have only one VLAN selected in the Names, the Legends window shows colors as in Figure 3-12.
Figure 3-12 : Legends Window with One VLAN Selected
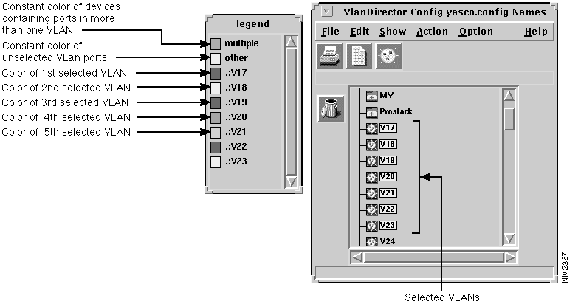
If you have more than one VLAN selected simultaneously, for example, if you have seven VLANs simultaneously selected using the Shift key while selecting, the Legends window shows the color assignment shown in Figure 3-13.
Figure 3-13 : Legends Window with Multiple VLANs Selected
Names of ports and devices in a selected VLAN are displayed in the VLAN Devices, Topology, or Ports window in the appropriate color according to the legend.
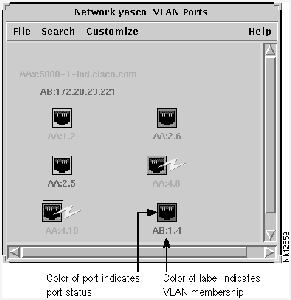
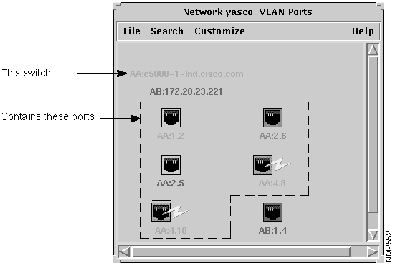
Figure 3-14 is an example of the VLAN Ports window showing port status and VLAN membership.
Figure 3-14 : I dentifying Port Status and VLAN Membership through Color
The VLAN Ports window displays the ports in the VLAN(s) that you selected in the Names window. The names of switches that include VLAN ports are listed on the top left portion of the window. To determine what switch a port belongs to, match the two letters listed at the beginning of the label underneath the port with the corresponding letters in the list of switch names as shown in Figure 3-15.
Figure 3-15 : Identifying Switch Ports VlanDirector uses color to indicate when an icon is selected or active and when certain operations are valid. Items such as folder names appear yellow when selected. Port device and link icons are outlined in yellow when selected.
Similarly, when dragging an icon from one window to another, VlanDirector uses color to indicate where you can drop the icon. For example, when dragging a port icon from CiscoView, VlanDirector indicates which window can accept that port by changing the inside border of the icon from beige to white.
Using the Context-Sensitive Online Help System
The VlanDirector application has an online help system that includes both task-oriented online help and context-sensitive online help on windows and error messages.
After you launch VlanDirector, use the help system to get information about using the VlanDirector interface, navigating within the product, and finding information on a specific topic.
Help is available in the following ways:
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
set cdp enable all
set vtp domain <name>
source <install directory>/etc/install.cshrc
vdirector

-wr private
-rd light -wr day
<install directory>/bin/vdirector
source <install directory>/etc/install.cshrc
snm -i &

-wr private
-rd light -wr day
source <install directory>/etc/install.cshrc
ovw
-wr private
-rd light -wr day
View
What it Shows
Tasks Performed
Names
Existing VLANs and folders
Select VLANs
Create and delete VLANs
Perform VLAN configuration tasks
Show or hide other VlanDirector windows
Network Topology
The discovered known network
Physical devices and physical links between them
Any discovered but unmanageable devices (grayed out)
Display device and link attributes reports
Add links to a VLAN
Launch CiscoView for a device
Exclude and drop devices from discovery
Display device ports window
Change link protocols
VLAN Topology
Devices and links enabled to carry VLANs between them
Add and delete VLAN links
Launch CiscoView
Display Device Ports by VLAN
VLAN Ports
Ports in a VLAN or VLANs selected in the Names window
Differentiates between user and link ports
VLAN membership by port label
VLAN status by color of each port
Launch Device Ports window
Display port attributes
Launch CiscoView
VLAN Devices
VLAN devices for VLAN or VLANs selected in the Names window
Launch Device Ports window
Launch CiscoView
Legends
Colors for selected VLANs
Device Ports Popup
Ports for selected devices
Drag-and-drop ports to a VLAN
Display port attributes
Device Ports by VLAN
Ports for selected VLANs
Task
Drag From
Drag To
Add a port to a VLAN
CiscoView
VLAN Name in the Names window
Device Ports
VLAN Name in the Names window
CiscoView
VLAN Topology, Devices, or VLAN Ports window
Device Ports
VLAN Topology, Devices, or VLAN Ports window
Add a link to a VLAN
Network Topology
VLAN Topology
Network Topology
VLAN Names in Names window
Merge two VLANs
Names (VLAN to be merged)
Names (VLAN 2 or destination VLAN)
Remove a VLAN port
VLAN Ports
Trash can icon in Names window
Device Ports by VLAN
Trash can icon in Names window
Delete a link with a single VLAN
VLAN Topology
Trash can icon in Names window
Delete a link with more than one VLAN
VLAN Topology
Trash can icon in Names window
For this Information
Follow This Path from the Names Window
Display the help system
In the Names window, select Help>Using Help.
Search for information
From the help system's main window, click the Find button and specify any word, or use the Search button to search by topic.
Self-contained help system describing how to use the product features
In the Names window, select Help>Contents.
Version information
In the Names window, select Help>About VlanDirector.
Context-sensitive help on any VlanDirector window
Click the Help button in the window or search within the Help system.
Create a VLAN
Help>Contents>Creating a New VLAN
Managing links
In the Names window, select Help > Contents> Configuring and Working with Links
Error messages
Click Help in the Error Message window.
Making changes to VLANs
In the Names window, select Help > Contents>Modifying and Deleting VLANs.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()