|
|
Saving and Retrieving Known Networks
When you start VlanDirector, it runs the discovery process and creates a known network.
After you have configured VLANs and links on the known network, you can save and retrieve copies of it or later work with the known network again.
This section discusses the uses of known networks and configurations and how to store and retrieve them.
Modifying Known Networks with Discovery
When you start VlanDirector, it automatically performs a discovery of your network.
VlanDirector finds or discovers the devices in the network using Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP). VlanDirector can only discover devices that support CDP. The discovered devices and links between them form a known network. The known network can consist of up to 100 devices. The discovery process stops when it reaches the 100th device.
If your network uses VTP (that is, if one or more switches has VTP enabled), a known network corresponds to the management domain with the same name. This known network includes devices such as non-VTP devices, such as a Catalyst 1200, and devices that have not been initialized, such as a Catalyst 5000 that is capable of running VTP but is not currently running VTP.
VlanDirector displays a map of the discovered network in the VlanDirector Network Topology window. In a known network, devices, links, and ports are updated each time the discovery process is run. The discovery process is run on the interval you specify in the VlanDirector Properties window. The default interval is every 300 seconds.
You can exclude or include certain devices in the topology displays.
Instructions for the following ways to modify the devices to be discovered are provided in this chapter:
Starting Discovery from VlanDirector
To restart the discovery process from VlanDirector, follow these steps:
Excluding a Device from the Known Network
If your known network includes devices that you do not want to manage using VlanDirector, you can exclude them. You might want to exclude them, for example, if your network has more than 100 devices, or you might want to exclude some devices to reduce the number of devices in the specified known network. You can also exclude a device that you do not want to manage in a known network, such as a Catalyst 1200 in a VTP environment.
You can exclude one device or multiple devices simultaneously using the following procedure:
The device is removed from the known network.
Removing a Device from the Known Network
Excluding a device removes it from VlanDirector displays, but the device is retained in the VlanDirector database. If a device has been physically removed from the network, you might also want to remove it from the VlanDirector database. To do this, follow these steps:
The device is removed from the VlanDirector database. However, if a device still exists in the network, it will be discovered the next time the discovery process is run.
Adding a Device Back into the Known Network
You can include a previously excluded device or devices in the known network using the following procedure:
The device will be redisplayed in the VlanDirector displays after the next discovery.
The discovered network will not extend beyond any routers that discovery encounters. You can use the following procedure to discover routers beyond the existing known network.
To extend a known network, complete the following steps:
Changing the Discovery Interval
Depending on the requirements of the configuration you are performing, you might want to change the interval at which the Discovery process is repeated, for example, to reduce the network management traffic on a stable network. The default value is 300 seconds (5 minutes). To change the Discovery interval, follow these steps:
Resolving Network Irregularities
After the discovery process, the Names window might replace the discovery icon (the moving magnifying glass) with a large check mark. This indicates that VlanDirector discovered some discrepancies in the network. You can continue using VlanDirector with discrepancies, but you should evaluate the seriousness of the problem first. A discrepancy is an irregularity that can affect VlanDirector or actual network operation. To examine a discrepancy, in the Names window, select Action>Show Discrepancies, or click the Discrepancy icon in the Names window. After you display the Discrepancy window, the Discrepancy icon disappears.
Gray links in topology displays indicate a discrepancy on the link.
For information on Discrepancies, refer to "Responding to Discrepancies" in Chapter 8.
Routers to other "unmanageable" devices appear but are grayed-out. A device is unmanageable in one of the following situations:
VlanDirector does not discover routers, but includes the router icon and the connections by which CDP found it in the known network.
Using Known Networks or Saved Configurations
You can make changes that are implemented immediately on your network or defer changes until you are ready to implement them. For example, you might want to implement network changes on a particular day of the week for administrative reasons or during the night to minimize network disruption. Configurations can also be used to experiment with a configurations and to save versions for recovery.
For such circumstances, you can save and store images of networks, and later retrieve and apply these configurations to your network. You can also easily switch between known networks and configurations.
A known network depicts the current state of the devices (up to 100), links, ports, protocols, and VLANs in the physical network. A known network corresponds to the management domain you specified on the CLI of at least one switch in your network. If the management domain contains more than 100 devices, the known network will contain only 100 of the devices that are in the management domain.
VlanDirector displays a map of the discovered network in the VlanDirector Network Topology window. In a known network, devices, links, and ports are updated each time the discovery process is run. The discovery process is run on the schedule you specify in the VlanDirector Properties window. The default interval is every 300 seconds.
When using a known network, VlanDirector updates the network and VLAN views as added and deleted devices are discovered.
To create a new known network, follow these steps:
Figure 5-1 : Creating a New Known Network
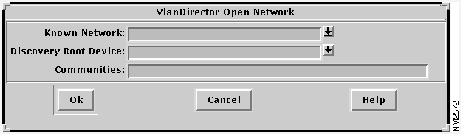
Figure 5-2 : VlanDirector Open Network Window
The discovery process begins and the new network is created.
Making Changes to a Known Network
When you make changes to a known network, you can implement the changes immediately, or defer changes until you are ready to implement them. By default, VlanDirector applies changes immediately.
Sometimes this might not be desirable, as in the following examples.
In these circumstances, you can switch from working with a known network to a temporary configuration in which you can cautiously make changes and preview the changes before you apply them to the network. To operate in this temporary configuration mode, turn the Automatic Installation feature in VlanDirector to Off.
Turning Automatic Installation Off
Automatic Installation is On by default. To turn Automatic Installation Off, follow these steps:
When you are making changes change with the Auto Install option off, you are switched to a temporary configuration. Subsequent changes are made to the temporary configuration. After you are satisfied with the changes that you make, you can then apply changes to the known network as follows: In the Names Window, select Action>Install All or Action>Install Selection.
If you select Action>Install All, the temporary configuration is dropped and you switch back to the known network. If you enter Action>Install Selection, the temporary configuration is retained and you continue to work in the temporary configuration.
To change a temporary configuration to a saved configuration, select File>Save As Configuration, and specify the name for the saved configuration.
A saved configuration is a copy of the devices, ports, links, and VLANs of a known network which is not updated by the discovery process. It does not necessarily reflect the current state of the network and its devices. You might want to use a saved configuration as a master image of your network, or you might want to use a specific configuration on the network on certain days or times in the week.
To create a configuration, select File>Save As Configuration in the Names window. When VlanDirector operates on a saved configuration, it shows only the modifications you have made in the configuration and not the current state of devices in the network.
Configurations can be created, modified, and retrieved.
You can operate on an existing saved configuration, save a known network as a saved configuration, and save a temporary configuration as a saved configuration.
Summary of Differences between Known Network and Configuration
Table 5-1 summarizes the differences between a known network and a configuration.
Table 5-1 : Differences Between Known Networks and Configurations
Determining Your Mode of Operation
You can work in any one of the three modes, depending on your management requirements. You can determine which mode you are in by checking the window title on any of the views that you are currently working with. The title bar indicates the current mode. If you are working with a known network, the title bar includes the word Network. If you are working with a configuration, the title bar includes the word Config. If you are working with a temporary configuration, it includes the word Config and a name starting with .vlv, for example, .vlvAAA03694.
Storing and Retrieving Configurations and Known Networks
You can create and retrieve known networks and configurations.
To create a new known network, follow these steps:
Retrieving a Saved Known Network
To retrieve a saved known network, follow these steps:
Saving a Known Network as a Configuration
To save a known network as a configuration, follow these steps:
A configuration is created from the known network.
To delete unwanted known networks from a list of saved, known networks, follow these steps:
The known network is deleted.
To delete unwanted configurations from a list of saved configurations, follow these steps:
Saving a Temporary Configuration as a Configuration
To save a temporary configuration as a configuration, follow these steps:
To copy a configuration, follow these steps:
You can compare an existing configuration with a known network or another configuration. For example, if you made changes to a network configuration that then caused network problems, you might want to compare to a different configuration that did not result in those problems. To compare two configurations, or a configuration and a known network, do the following
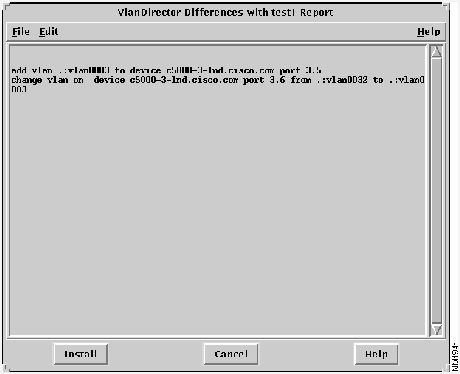
The VLAN Director Differences Report is displayed as shown in Figure 5-3, indicating the differences in the configurations.
Figure 5-3 : VlanDirector Differences Report Interpreting the VlanDirector Differences Report
The VlanDirector Differences Report shows the differences between the saved configuration and your current configuration. For example, the report in Figure 5-3 indicates that the following changes need to be made to the current configuration to make it identical to the saved configuration:
Port 5 on Slot 3 of the device C5000-3-lnd.cisco.com must be made a member of the VLAN named vlan0003.
Port 6 on Slot 3 of the device C5000-3-lnd.cisco.com must be removed from the VLAN named vlan0032 and made a member of the VLAN named vlan0003.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
Known Network
Configuration
Created by discovery
Created from a known network or other configuration
Reflects the active or running network
Reflects a "snapshot" of the known network at the time that the configuration is created
Automatically updated by discovery
Not updated by discovery
Title bar includes the word "network"
Title bar includes the word "config"
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()