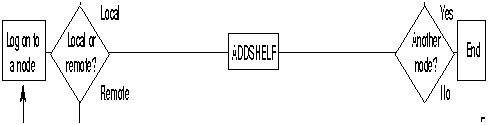
An interface shelf is a non-routing device that drives ATM cells to and from a BPX routing hub in a tiered network. An interface shelf is either an IPX configured as an interface shelf (IPX/AF) or an Axis shelf. For an IPX or IGX to serve as an interface shelf, StrataCom personnel must first configure it for that purpose. Furthermore, the shelves must be configured to use STI cell headers and BPX Addressing Mode (BAM). An Axis must have been brought up in the network before you can add it to the tiered network (for instructions, see the Axis Release 2.0 Reference Manual or a later version of this manual). To add a feeder shelf, use addshelf. To delete a feeder shelf, use delshelf. To view conditions on a feeder trunk, use dspnode. Note that addshelf and addtrk are mutually exclusive commands.
IGX card sets may consist of the following (the x indicates multiple versions of an IGX card type, such as a CVM8):
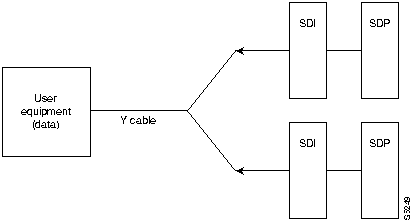
The following illustrates a typical Y-cable connection of primary and secondary card sets for redundancy.
The switching to the standby card takes place only if the secondary card set is in a Standby or a Standby-F state (not if it is Failed). See the dspcds definition for information on these states.
Note Terminating connections is possible at a primary slot only and not at a secondary slot. See the addcon command.
On multi-port card sets, each primary port is connected by a Y-cable to a secondary (redundant) port. Port 1 of the primary card set must be paired to port 1 of the secondary card set, and so on. The following illustrates the cabling for a multi-port card set.
Figure 4-2 :
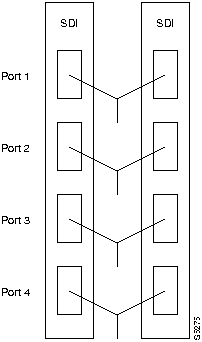
If the secondary card set becomes active, the primary card set becomes the backup. For the primary set to serve as the backup, it must be a complete set and not failed. This applies to single and multi-port cards.
The addyred command is applicable even if the primary and secondary slots are empty. If cards are in place in the primary and secondary slots, the system checks for card compatibility. Two types of incompatibility can occur: back card and jumper or cable. (On SDI, FRI, and FTI cards, jumpers determine whether a port is configured as DCE or DTE. On LDI cards, either a DCE or DTE adapter cable connects to the LDI port, as applicable).
If incompatibilities exist, the following message "Y-Cable Conflict" appears on the screen. Specific conflicts are listed in reverse video in the Y-Cable Redundancy screen. See the dspyred description for more information. V.35 redundancy requires special redundant jumpers on the SDI or FRI cards that are Y-cabled together. Always use the applicable Y-Cable Redundancy Kit for a card.
Controlling External Devices
If your system is configured to control an external device, such as a multiplexer, you can establish a window session to it from the control terminal. While in a window session, any characters you type at the control terminal go to the external device for processing. Any characters generated by the external device appear on the control terminal screen.
The Window to External Device (window) command establishes a window session. You can use this command only if the external device connects to the local node. You can, however, enter the window command during a virtual terminal session so that you have a window session with any external device in the network. To have a window session, execute the virtual terminal (vt) command to place you in the node that is cabled to the device, and then invoke the window command. Before you start a window session, you must have configured the port and the port function with the cnfterm and cnftermfunc commands. In addition, you must know whether the external window device is cabled to a node's Control Terminal (RS-232) port or Aux Port (RS-232) port. The format for the window command is:
- window [a | c]
Enter an a if the external device is attached to the node's Aux Port or c if the device is attached to the node's Control Terminal port. The default for this parameter is Aux Port. To establish a window session with an external device attached to a node's Control Terminal port, enter:
- window c
The system responds by redrawing the terminal screen. You can now enter commands and send data to the external device as if you were locally connected to its Control Terminal port. While in the window session, only commands used to control the external device are recognized. IPX/IGX/BPX commands are not recognized. You might notice a slight transfer delay in transmission, due to the IPX/IGX/BPX bundling of characters before transmitting them. Transfers are delayed until the transfer buffer is filled, or until the keyboard has been inactive for over 50 milliseconds.
To end a window session, enter an escape sequence. Escape sequences are one-to-eight characters in length and are configured with the Configure Terminal Port Function (cnftermfunc) command. For example, if you have specified "signoff" as the escape sequence in the Configure Terminal Port Function, enter the following to end the window session:
- signoff
The default escape sequence is:
- ^^ (SHIFT 66)
If this escape sequence does not work and you do not know the configured escape sequence, leave the keyboard idle for four minutes. After four minutes, the system terminates the window session.
Figure 4-3 : Set-up nodes
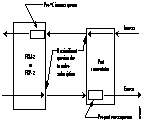
Figure 4-4 : View node configuration

Figure 4-5 : Configure the node interface for a terminal attached to the node
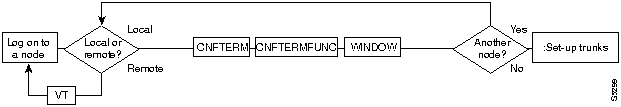
Figure 4-6 : Remove a node from the network

Figure 4-7 : Add an interface shelf to the network
Summary of Commands
The following list shows the full command name and starting page for the description of each node command.
| addalmslot
|
Add an alarm slot
|
4-9
|
| addshelf
|
Add a trunk between the hub node and access shelf.
|
4-11
|
| addyred
|
Add Y-cable redundancy
|
4-13
|
| cnfasm
|
Configure ASM card
|
4-15
|
| cnffunc
|
Configure system function
|
4-17
|
| cnfname
|
Configure node name
|
4-20
|
| cnfprt
|
Configure printing functions
|
4-22
|
| cnfterm
|
Configure terminal port
|
4-24
|
| cnftermfunc
|
Configure terminal port functions
|
4-26
|
| cnftmzn
|
Configure time zone
|
4-29
|
| delalmslot
|
Delete alarm slot
|
4-31
|
| delshelf
|
Delete a trunk between a hub node and access shelf
|
4-33
|
| delyred
|
Delete Y-cable redundancy
|
4-35
|
| dspasm
|
Display ASM card configuration
|
4-36
|
| dspcd
|
Display card
|
4-38
|
| dspcds
|
Display cards
|
4-40
|
| dsplancnf
|
Display LAN configuration
|
4-43
|
| dsplmistats
|
Display LMI Statistics
|
4-45
|
| dspnds
|
Display nodes
|
4-47
|
| dspnode
|
Display summary information about interface shelves
|
4-49
|
| dsptermcnf
|
Display terminal configuration
|
4-51
|
| dsptermfunc
|
Display terminal port configuration
|
4-53
|
| dspprtcnf
|
Display print configuration
|
4-55
|
| dsppwr
|
|
4-57
|
| dspyred
|
Display Y-cable redundancy
|
4-59
|
| prtyred
|
Print Y-cable redundancy
|
4-61
|
| upcd
|
Up card
|
4-63
|
| window
|
Window to external device
|
4-65
|
addalmslot
Enables the MAJOR and MINOR alarm indicators on an Alarm Relay Card (ARC) or Alarm Relay Module (ARM) front card. It also configures the slot to provide external alarms from the Alarm Relay Interface (ARI) back card. This command should be used at each node equipped to provide external alarm indications to the customer alarm reporting system. The slot specified for the ARC or ARM may be any shelf slot but is usually the slot farthest to the right.
Upon command execution, the system places the alarm card set in the active state and displays the current alarm status.
Full Name
Add alarm slot.
Syntax
addalmslot <slot number>
Related Commands
delalmslot, dspalms
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
NO
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
addalmslot 16
Description
Enable alarm reporting from slot 16 in a node. (The system then displays alarm status.)
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 14:27 MST
Alarm summary (Configured alarm slots: 16)
Connections Failed: None
Groups Failed: None
PLN Alarms: 1 Major
CLN Alarms: None
Cards Failed: 1
Missing Cards: None
Remote Node Alarms: 1 Major
Remote Domain Alarms: None
Last Command: addalmslot 16
Next Command:
Table 4-1 : addalmslot -- Parameters
| slot number
|
Specifies the slot number of the alarm card set to activate.
|
addshelf
Adds a trunk between a BPX hub node and an interface shelf in a tiered network. The trunk for an interface shelf must be "added" to the network before it can be used for traffic. Before a trunk can be added to the network, the line must be activated (or "upped") on both the interface shelf and the hub node with the uptrk command.
The interface shelf can be either an Axis or an IPX configured as an interface shelf (IPX/AF). If the interface shelf is an IPX, it must be configured as an interface shelf by StrataCom before you add it with addshelf. If the interface shelf is an Axis, it must also already be established in the system through Axis-specific commands. See the Axis Release 2.0 Reference Manual for the procedures.
Interface shelves take only frame relay input on the circuit side and drive one ATM T3 trunk with an interworking connection type (ATFR) on the trunk side. Each IPX/AF or Axis shelf has one T3 trunk connected to an BPX serving as an access hub. Each access hub can support up to 16 T3 trunks to the interface shelves. Attempting to add more than 16 shelves to a hub triggers an error message.
The addshelf command requires that the trunk configuration include STI header format and BPX Addressing Mode (BAM) mode. A trunk must be free of major alarms before it can be added.
Full Name
Add a feeder shelf.
Syntax
addshelf <trunk> <shelf-type> <vpi> <vci>
Related Commands
delshelf, dspnode, dsptrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
addshelf
Description
Add trunk 11.1 as an Axis interface shelf. After the addition, the screen displays confirmation of the addition and shows the name of the shelf. The example already shows the name of the Axis at trunk 11.2 is A242.
System Response
nmsbpx23 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Aug. 16 1996 13:28 PST
BPX Interface Shelf Information
Trunk Name Type Alarm
1.3 AXIS240 AXIS OK
11.2 A242 AXIS OK
This Command: addshelf 11.1
Enter Interface Shelf Type: I (IPX), A (AXIS)
Table 4-2 : addshelf - Parameters
| trunk
|
Specifies the slot and port number of the trunk.
|
| shelf type
|
Specifies the type of interface shelf. I = IPX/AF. A = Axis.
|
| vpi vci
|
Specifies the vpi and vci (Annex G vpi and vci used). For the Axis interface shelf only, the valid range for vpi is 5--14 and for vci is 16 --271. For an IPX/AF interface shelf, the valid range for both vpi and vci is 1--255.
|
addyred
Enables card redundancy for the IPX, IGX, and BPX cards. This command specifies a primary card slot and a secondary (standby) card slot to form a redundant pair. Refer to the section titled "Specifying cable redundancy" at the beginning of this chapter for a list of supported card sets for each node. The following applies to redundant card sets:
- The primary and secondary card sets must be identical.
- Secondary card sets must not currently be active.
- Neither the primary nor secondary card set may already be part of a redundant card set pair.
In both the single and multi-port card sets, if the secondary card set becomes active, the primary card set serves as its backup (assuming the primary card set is complete and not failed). The addyred command can be used even if the primary and secondary slots are empty. If cards reside in the primary and secondary slots, the system checks for card compatibility. Two types of incompatibility can occur: back card and jumper or cable. (On SDI, FRI, and FTI cards, jumpers determine whether a port is configured as DCE or DTE. On LDI cards, either a DCE or DTE adapter cable connects to the LDI port. The IPX Installation Manual, the IGX 16/32 Reference Manual, and IGX 8 Installation Manual describe the jumper positions and cabling.)
If incompatibilities exist (for example, if port 1 on the primary slot is configured as DTE and port 1 on the secondary slot is DCE), the message "Y-Cable Conflict" appears on the screen. Specific conflicts are listed in reverse video in the Y-Cable Redundancy screen. See the dspyred command for more information.
Full Name
Add Y-cable redundancy.
Syntax
addyred <primary slot> <secondary slot>
Related Commands
delyred, dspyred, prtyred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
addyred 25 26
Description
Add Y redundancy to an SDP/SDI card set at slots 25 and 26.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 14:27 MST
Slot Other Front Back Channel Configuration
Slot Type Slot Card Card 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
25 Pri 26 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
26 Sec 25 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
Last Command: addyred 25 26
Next Command:
Table 4-3 : addyred -- Parameters
| primary slot
|
Specifies the slot number of the primary card set.
|
| secondary slot
|
Specifies the slot number of the secondary card set.
|
cnfasm
Allows the user to set various configurable parameters associated with the BPX Alarm and Status Monitor card in slot 15. Since this card is always in slot 15, entering the slot number is unnecessary.
Full Name
Configure ASM card
Syntax
cnfasm
Related Commands
dspasm
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnfasm
Description
Configure parameters for the ASM card.
System Response
D1.jea TRM StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 30 1996 12:25 GMT
[1] Cabinet temp threshold: 50 C [4] Polling interval (msec): 10000
[2] Power A deviation: 6 V [5] Fan threshold (RPM): 2000
[3] Power B deviation: 6 V
ALM ALM
[6] ACO button - [14] BPX card slot -
[7] History button - [15] PSU A failure Y
[8] Cabinet temp Y [16] PSU A removed Y
[9] Power A volt Y [17] PSU B failure Y
[10] Power B volt Y [18] PSU B removed Y
[11] Fan 1 RPM Y
[12] Fan 2 RPM Y
[13] Fan 3 RPM Y
This Command: cnfasm
Which parameter do you wish to change:
cnffunc
Enables or disables a specified node function. Each function has an index number. By entering the command, the index parameter, and the letter "e" or "d," the function is either enabled or disabled.
Full Name
Configure system functions
Syntax
cnffunc <function_index> <e/d>
Related Commands
none
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnffunc 7 e
Description
Enables automatic card testing after card failure detection.
System Response
sw83 VT StrataCom IPX 16 8.2 May 20 1996 13:35 PST
Index Status Function
1 Enabled Automatic CLN/PLN Loopback Test on Local/Remote Alarms
2 Enabled FDP Loopback button
3 Enabled User Command Logging
4 Enabled Automatic Card Reset on Hardware Error
5 Enabled TXR Model D Download
6 Enabled Card Error Record Wraparound
7 Disabled Card Test After Failure
8 Enabled Download From Remote StrataView
9 Enabled Node-by-node Upgrade Compatibility
10 Disabled Logging of conn events in local event log
11 Disabled Logging of conn events in SV+ event log
This Command: cnffunc
Enter index:
Table 4-4 : cnffunc -- Index Parameters
| 1
|
Automatic CLN/TRK Loopback Test on Local/Remote Alarms
|
A remote end loopback is automatically set up on a failed circuit line or trunk. Used to check the health of the back card alarm detection circuitry.
|
enabled
|
| 2
|
FDP Loopback button
|
For IPX/IGX, enables loopback button on SDP card faceplate. (Disable it to prevent accidental operation by contact.)
|
enabled
|
| 3
|
User Command Logging
|
All commands entered by the user is entered in the system log when enabled. When disabled, system log does not become so large but there is no audit trail of operator commands kept.
|
enabled
|
| 4
|
Automatic Card Reset on
Hardware Error
|
The controller card (BCC, NPC, or NPM) issues a hardware reset to card when firmware detects an error during normal operation. This allows the node to return a card to service after a firmware error.
|
enabled
|
| 5
|
TXR Model D Download
|
(Not used)
|
enabled
|
| 6
|
Card Error Record
Wraparound
|
Allows the log entry for each card error to wrap for long entries. When disabled, only first ten failures are logged; others are discarded.
|
enabled
|
| 7
|
Card Test After Failure
|
Indicates card function selftests and background test should continue to be executed after a card has been declared as failing these tests.
|
disabled
|
| 8
|
Download from Remote
StrataView Plus NMS
|
Allows a node to download Software images from a SV+ not directly connected to the node.
|
disabled
|
| 9
|
Node-by-node Upgrade Capability
|
|
enabled
|
| 10
|
Logging of connection events in local event log
|
|
disabled
|
| 11
|
Logging of connection events in SV+ event log
|
|
disabled
|
Table 4-5 : cnffunc -- Parameters
| e/d
|
Enables or disables the previous functions.
|
cnfname
Specifies the name by which a node is known within the network. It may be changed at any time. The new node name is automatically distributed to the other nodes in the network. Node names are case sensitive. For example, an upper-case "A" is not considered to be the same as a lower-case "a". Duplicate names are not allowed in the same network. Node names may be configured from within a job sequence. If the node name is changed and the corresponding name in the job is not changed, the job will not function properly. In the following situations, the cnfname command cannot be executed:
- Another node is attempting to change the network topology by adding or deleting a trunk.
- Another node is notifying all nodes that it has been renamed. Another node is currently adding or deleting a channel connection in the network with the addcon or delcon commands.
- There is an unreachable node in the network.
- The name chosen is already being used for another node in the network.
Full Name
Configure node name
Syntax
cnfname <nodename>
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnfprt, and window
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnfname alpha
Description
Name is changed to alpha. The network topology screen displays indicating the new name. See the dspnw command for more information on the network topology screen.
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 12:02 PST
NodeName Alarm Packet Line Packet Line Packet Line
alpha 10- 7/beta 14- 13/beta
beta MAJOR 7- 10/alpha 9- 10/gamma 13- 14/alpha
15- 15/gamma 20- 11/gamma
gamma MAJOR 10- 9/beta 11- 20/beta 15- 15/beta
Last Command: cnfname alpha
Next Command:
cnfprt
Configures the printing function. To obtain local or remote printing at a node, a printer must connect to the AUX PORT. Also, the configuration must include the correct baud rate and printer type for the port. Use the cnfterm and cnftermfunc commands to do this.
The cnfprt and cnftermfunc commands interact. If the auxiliary port on the node is configured for either an External Device Window or the Network Management Log, a "local" printing configuration automatically changes to "no printing." Printing is not possible because the auxiliary port is being used for another purpose.
Establishing a virtual terminal connection with a node does not affect the printing location established for the node that initiates the virtual terminal connection. For example, if node alpha is configured so that all alpha information goes to a printer at node beta and if alpha establishes a virtual terminal connection with node gamma, the results of print commands entered on the alpha keyboard still print at beta. Furthermore, this occurs regardless of the printing location configured for node gamma.
Full Name
Configure printing functions
Syntax
cnfprt <mode> <remote node name>
Related Commands
cnfterm, dsptermfunc
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnfprt
Description
Change the configured printing.
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 13:17 PST
Printing Mode
Remote Printing at beta
Local Printing
No Printing
This Command: cnfprt
Select Local (l), Remote (r), or None (n):
Table 4-6 : cnfprt -- Parameters
| mode
|
Specifies the printing mode. Enter "L" for local printing, "R" for remote printing, and `n' for no printing.
|
| remote node name
|
Specifies the remote node whose printer is used for print commands issued by a user who is physically logged on to this node. This option is only valid when remote printing has been selected. A remote node is one within the domain, but not the node where the command is entered.
|
cnfterm
Configures data transmission parameters for the control and auxiliary ports. The IPX, IGX, and BPX support two RS-232 serial ports on the upper bus expansion card. The top port is called the Control Terminal port. The lower port is called the Auxiliary Port (AUX). Parameters can vary with the equipment connected to the port. The control port may connect to a control terminal, a direct-dial modem, or an external RS-232 device. The auxiliary port may connect to either a printer or an external RS-232 device. Once the data transmission parameters have been set for a port, use the cnftermfunc command to specify the equipment attached to the port. The configuration parameters must match the equipment physically attached to the port.
Full Name
Configure terminal port
Syntax
cnfterm <a/c> <baud> <parity> <num_data_bits> <num_stop_bits>
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnfprt, and window
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnfterm
Description
Configure an auxiliary control port.
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 11:58 PST
Control port Auxiliary port
Baud Rate: 1200 Baud Rate: 9600
Parity: None Parity: None
Number of Data Bits: 8 Number of Data Bits: 8
Number of Stop Bits: 1 Number of Stop Bits: 1
Output flow control: XON/XOFF Output flow control: XON/XOFF
Input flow control: XON/XOFF Input flow control: XON/XOFF
Use DTR signal: Yes DTR signal: Yes
This Command: cnfterm
Select Control port (c) or Auxiliary port (a):
Table 4-7 : cnfterrm -- Parameters
| a/c
|
specifies the port to be configured, where a is the auxiliary port and c is the control port
|
| baud rate
|
specifies the baud rate. Valid baud rates are 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, and 19200 bps
|
| parity
|
specifies parity checking for character transmission to and from the port. Valid parity choices are "E" for even parity, "O" for odd parity, and "N" for no parity
|
| data bits
|
specifies the number of bits to be sent for each transmitted character and the number of bits to be expected for each received character. A "7" indicates seven bits for each character; an "8" indicates eight bits for each character
|
| stop bits
|
specifies the number of stop bits to be sent with each transmitted character and the number of stop bits to be expected with each received character. A "1" indicates one stop bit with each character; a "2" indicates two stop bits with each character
|
| output flow control
|
specifies the output flow control. An "X" specifies XON/XOFF flow control; an "N" specifies no flow control
|
| input flow control
|
specifies input flow control. An "X" specifies XON/XOFF flow control; an "N" specifies no flow control
|
| cts flow control
|
configures cts flow control. An "X" specifies XON/XOFF flow control; an "N" specifies no flow control. This parameter should be turned off if working with modems on a BPX.
|
| use DTR
|
specifies whether the node requires DTR to be asserted to allow or maintain a Login. A "Y" causes the node to require the presence of DTR before allowing a login. A "N" causes the node to ignore DTR entirely
|
cnftermfunc
Configures port functions for the IPX, IGX, or BPX control and auxiliary ports. The IPX and IGX support two RS-232 asynchronous serial ports on the SCC and SCM, respectively. The BPX supports two RS-232 asynchronous serial ports on the LMBCC. In all cases, the top port is the CONTROL TERMINAL port, and the lower port is the AUX PORT. Depending on the desired network configuration, the CONTROL TERMINAL port can connect to a control terminal, StrataView, a direct dial-in modem, or any external RS-232 device. The AUX PORT can connect to a printer, an auto-dial modem to call a control center, or any external RS-232 device.
The interface specified for the port must match the equipment physically attached to the port. The baud rate and other data transmission parameters for the port are set with the cnfterm command. If either port is configured as an external device window, enter the window command to begin a session with the external device.
If the auxiliary port is configured as an autodial modem, designate a "network ID" and a "phone number". Configuring the auxiliary port for an autodial modem enables the following to occur: When a change in alarm status happens anywhere in the network, the autodial modem attached to the auxiliary port dials the specified "phone number". If the call goes to StrataCom's ISC, the alarm is logged under the specified "network ID". With this log, ISC engineers are automatically notified of any problems that occur on the network.
Full Name
Configure terminal port functions
Syntax
cnftermfunc <a/c> <index> [escape_string | (Network_ID Dial_String)]
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnfprt, dsptermfunc
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnftermfunc
Description
Configures an IPX, IGX, or BPX control or auxiliary port.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 14:46 MST
Control port Auxiliary port
1.VT100/StrataView 1.Okidata 182 Printer
2.VT100 2.Okidata 182 Printer with LOG
3.External Device Window 3.Alarm Message Collector
4.External Device Window
5.Autodial Modem
6.VT100
Last Command: cnftermfunc
Next Command:
Last Command: dsplancnf
Next Command:
Example 2
cnftermfunc a TheCustomer 18007674479
Description
Configure an auxiliary port by issuing parameters. The port configuration screen appears with "Autodial Modem" highlighted to indicate that this interface has been chosen for the auxiliary port. When an alarm occurs on the network, the modem will dial 18007674479 to reach the StrataCom ISC. The alarm will be logged on the ISC computer under the name "TheCustomer".
Table 4-8 : cnftermfunc -- Parameters
| a
|
Specifies that the auxiliary port will be configured.
|
| c
|
Specifies that the control port will be configured.
|
Table 4-9 : cnftermfunc -- Index Parameters
| Control port
|
1. VT100/StrataView
2. VT100
3. External device window
|
| Auxiliary port
|
1. Okidata 184 printer
2. Okidata 184 printer with LOG
3. Alarm message collector
4. VT100
5. Autodial modem
6. VT100
|
Table 4-10 : cnftermfunc -- Optional Parameters
| escape string
|
Specifies a string of 1 to 8 characters used to terminate a session with an external device. This parameter is valid only for "External Device Window" interfaces. The default escape string is "quit."
|
| network id
|
Specifies a string of 1 to 12 characters used to identify the network during an autodial connection to the StrataCom ISC. This parameter is valid only for "Autodial Modem" interfaces. Any alarm status change in the network is automatically logged at the ISC using this network ID. Contact the StrataCom ISC for the ID to use.
|
| dial string
|
Specifies the telephone number to be dialed when the network is reporting alarm status changes via the autodial modem. This parameter is valid only for "Autodial Modem" interfaces. The "phone number" can be up to 16 characters long and normally consists of digits and commas only. A comma is used to indicate that the autodial modem should pause two seconds before continuing to dial. For example, the number "9,4083700736" would cause the modem to dial a "9", pause two seconds, then dial the remaining digits. Contact the StrataCom ISC for the number to use.
|
cnftmzn
Configures the time zone for the node. Configuring the time zone for a node ensures that the node's time is correct for the local area regardless of the node at which the network date and time are set. Once configured, the time zone for the node is saved in battery-backed memory. After a power failure, a node's date and time are restored if at least one other node in the network has the current time and date.
Full Name
Configure time zone
Syntax
cnftmzn <timezone | g+/- hours>
Related Commands
cnfdate
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example
cnftmzn pst
Description
Configures the time zone to Pacific Standard Time
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 13:19 PST
Last Command: cnftmzn pst
Next Command:
Table 4-11 : cnflmzn -- Parameters
| time zone
|
- gmt (or g) Greenwich Mean Time
- cst (or c) Central Standard Time
- est (or e) Eastern Standard Time
- mst (or m) Mountain Standard Time
- pst (or p) Pacific Standard Time
- yst (or y) Yukon Standard Time
- cdt Central Daylight Savings Time
- edt Eastern Daylight Savings Time
- mdt Mountain Daylight Savings Time
- pdt Pacific Daylight Savings Time
- ydt Yukon Daylight Savings Time
|
hours from Greenwich
Mean Time (GMT)
|
Specifies the difference in hours between local time and Greenwich Mean Time. The range is from -12 to +12 hours. Instead of entering the time zone, you can enter the hours from Greenwich Mean Time. For example, instead of entering pdt for Pacific Daylight Time, you could enter g-7, which is Greenwich Mean Time minus 7 hours.
|
delalmslot
Disables the ARC (IPX) or ARM (IGX) alarm indicators and ARI external alarms. See the addalmslot command for more information on ARC/ARM alarm relays and adding alarm slots.
Upon command execution, the system places the alarm card set in the standby state and displays the current alarm status.
Full Name
Delete an alarm slot
Syntax
delalm <slot number>
Related Commands
addalmslot, dspalms
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
delalmslot 11
Description
Disable the alarm indicators on the ARM card set in slot 11. (The system subsequently displays alarm status.)
System Response
pubsigx1 TN StrataCom IGX 32 8.2 July 16 1996 02:09 GMT
Alarm summary (Configured alarm slots: None)
Connections Failed: None
Groups Failed: None
TRK Alarms: None
Line Alarms: None
Cards Failed: None
Missing Cards: None
Remote Node Alarms: 1 Minor
Remote Domain Alarms: None
Routing Network Alarms: None
Cabinet Fan(s) Failed
FastPAD Node Alarms: None
Last Command: delalmslot 11
Next Command:
Table 4-12 : delamslot -- Parameters
| slot number
|
Specifies the slot number of the alarm card set to activate.
|
|
delshelf
Deletes an interface shelf from a tiered network. Trunks are specified as an IPX/AF or an Axis. Normally, you should execute delshelf only on the BPX hub node. On an IPX, delshelf just lets you turn off LMI if the line to the BPX is not allowing communication. In contrast to deltrk, you can execute delshelf at any time if no connections terminate at the trunk.
Full Name
Delete an interface shelf.
Syntax
delshelf <trunk> | <shelf-name>
Related Commands
addshelf, dspnode
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
delshelf 4.1
Description
Delete shelf trunk 4.1 on an IPX/AF.
System Response
nmsbpx23 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Aug. 16 1996 13:26 PST
BPX Interface Shelf Information
Trunk Name Type Alarm
1.3 AXIS240 AXIS OK
11.2 A242 AXIS OK
Last Command: delshelf A241
Shelf has been deleted
Next Command:
Table 4-13 : delshelf - parameters
| trunk or name
|
Specifies the slot and port number or shelf name of the interface shelf.
|
|
delyred
This command disables the Y redundancy for the card set in the specified primary slot number. If the secondary card slot is being used as the active slot at the time you use the delyred command, the system attempts to switch back to the primary slot. The substitution takes place only if the primary slot card set is complete and the cards are in a Standby or a Standby-F state (not if they are Failed). See the dspcds description for information on card states. See the addyred and dspyred commands for more information on Y-cable redundancy.
Full Name
Delete Y-cable redundancy
Syntax
delyred <primary slot>
Related Commands
addyred, dspyred, prtyred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example
delyred 16
Description
Disable Y-cable redundancy at slot 16.
dspasm
Displays BPX node alarms that, when active, produce an external alarm output (relay closure). These alarms are associated with powering and cooling the node as well as a statistics count. For example, a minor alarm is generated when a fan speed drops below 2000 rpm. Since the single ASM card is always located in slot 15, no card slot need be entered for this command. The ASM alarms are configured with the cnfasm command (SuperUser level)
Full Name
Display ASM card
Syntax
dspasm
Related Commands
cnfasm
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example
dspasm
Description
Display the ASM card parameters.
System Response
D1.jea TRM StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 30 1996 12:24 GMT
ASM Status: Active ASM Alarms
Statistics count: 7 Fan #1 RPM out of range
Statistics timeouts: 0 Fan #2 RPM out of range
Cabinet temperature: 21 C Fan #3 RPM out of range
Power voltage A/B: 0.0 / 0.0 V
PSU Ins Type Rev SerNum Failure
A N N/A N/A N/A N/A
B N N/A N/A N/A N/A
FAN 1 2 3
0000 0000 0000 RPM
Last Command: dspasm
Next Command:
dspcd
Displays the status, revision, and serial number of the card. If a back card is installed, the back card's type, revision, serial number is included. Depending upon the card type, other configuration information may be provided.
Full Name
Display card
Syntax
dspcd <slot number>
Related Commands
dncd, dspcds, resetcd, upcd
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example
dspcd 6
Description
Display status of the card in slot 6. The response shows a port capacity of 44, which is the maximum number of ports on a Port Concentrator Shelf. Therefore, the FRP in this case is an FRP-2. The interface type is X.21.
System Response
minnow TN StrataCom IPX 8 8.2 Aug. 13 1996 08:00 PST
Detailed Card Display for FRP in slot 6
(Global RAM: 4 Mbytes)
Status: Standby (Front Card Supports V.35, X.21)
Revision: FA06 (Front Card Supports Port Concentrator)
Serial Number: 165187 (Front Card Supports NNI, CLLM)
Port Capacity: 44 (Front Card Supports ATFR/CGW)
Backplane Installed
Backcard Installed
Type: FRI-X21
Revision: P01
Serial Number: 155558
Last Command: dspcd 6
Next Command:
dspcds
Displays the cards in a shelf, front and back, with their type, revision, and status. For front and back card sets, the status field applies to the cards as a set. A letter "T" opposite a card indicates that it is running self-test. A letter "F" opposite a card indicates that it has failed a test. If lines or connections have been configured for a slot, but no suitable card is present, the display will list the missing cards at the top of the screen. If a special backplane is installed or if a card was previously installed, empty slots are identified as "reserved".
For an IPX 32 or IGX 32, the screen initially displays only the upper shelf with a "Continue?" prompt. Typing "y" to the prompt displays the cards in the lower shelf. The command dspcds followed by the letter "L" (for lower shelf) displays card status for just the lower shelf. For an IPX 8 or IGX 8, the display screen uses only the left column to display cards for slots 1 through 8. The status and update messages that appear are as follows:
| · Active
|
Card in use, no failure
|
| · Active---F
|
Card in use, failure(s) detected
|
| · Active---T
|
Card active, background test in progress
|
| · Active---F-T
|
Card active, minor failures detected, background test in progress
|
| · Standby
|
Card idle, no failures
|
| · Standby---F
|
Card idle, failure(s) detected
|
| · Standby---T
|
Card idle, background test in progress
|
| · Standby---F-T
|
Card idle, failure(s) detected, background test in progress
|
| · Failed
|
Card failed
|
| · Down
|
Card downed by user
|
| · Down---F
|
Card downed, failure(s) detected
|
| · Down---T
|
Card downed, failure(s) detected, background test in progress
|
| · Mismatch
|
Mismatch between front card and back card
|
| · Update *
|
Configuration RAM being updated from active PCC
|
| · Locked*
|
Incompatible revision of old software is being maintained in case it is needed
|
| · Dnlding*
|
Downloading new system software from the active PCC adjacent node of from StrataVIew
|
| · Dnldr*
|
Looking to adjacent nodes or StrataView for software to load or software needs not specified by user
|
In the preceding messages, as asterisk (*) means additional status designation for BCC and NPC cards. "F" flag in the card status indicates that a non-terminal failure was detected. Cards with an "F" status are activated only when necessary (for example, when no other card of that type is available). Cards with a "Failed" status are never activated.
Full Name
Display cards
Syntax
dspcds [l]
Related Commands
dncd, dspcds, resetcd, upcd
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspcds
Description
Display status on all cards.
System Response
night TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 July 6 1996 14:56 PST
FrontCard BackCard FrontCard BackCard
Type Rev Type Rev Status Type Rev Type Rev Status
1 Empty 9 Empty
2 ASI-E3 AMD Empty Standby-F 10 Empty
3 Empty 11 Empty
4 BNI-T3 BBA T3-3 P04 Active 12 Empty
5 Empty 13 Empty
6 Empty 14 Empty
7 Empty reserved for BCC 15 ASM ABA LMASM AC Active
8 BCC AMC LMBCC P04 Active
Last Command: dspcds
Next Command:
Example 2
dspcds l
Description
Display status of cards on the lower shelf of an IPX 32 (the option "l" means "lower").
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 14:37 MST
Missing Cards: 1 ATM, 1 T3
FrontCard BackCard FrontCard BackCard
Type Rev Type Rev Status Type Rev Type Rev Status
17 PCC HDB Standby 25 SDP BA RS232 AK Active-T
18 Empty 26 SDP BF RS232 AK Standby-F
19 FRP DFB FRI-V35 BC Active-F 27 Empty
20 ATM HM03 Empty Failed 28 Empty
21 Empty 29 Empty
22 CDP AAB Empty Unavail 30 Empty
23 Empty 31 Empty
24 Empty reserved for SDP 32 Empty
Last Command: dspcds l
Next Command:
Table 4-14 : dspcds -- Parameters
| l
|
Directs the system to display status of the cards on just the lower shelf of an IPX 32 or IGX 32.
|
dsplancnf
Displays the addresses and configuration for the LAN Ethernet. The description of the cnflan command has an explanation of the items that appear in the dsplancnf display.
Full Name
Display LAN interface configuration
Syntax
dsplancnf
Related Commands
cnflan
Attributes
| Privilege
|
5
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsplancnf
Description
Display the LAN configuration for the current node.
System Response
sw81 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 May 21 1996 10:51 PST
Active IP Address: 192.187.210.139
IP Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
IP Service Port: 5120
Default Gateway IP Address: 192.187.210.1
Maximum LAN Transmit Unit: 1500
Ethernet Address: 00.C0.43.00.06.91
Type State
LAN READY
TCP UNAVAIL
UDP READY
Telnet READY
TFTP READY
TimeHdlr READY
SNMP READY
Last Command: dsplancnf
Next Command:
dsplmistats
Displays Annex G LMI statistics for the trunk that connects an IPX/AF interface shelf to the hub node. To execute this command from the IPX/AF, the user must telnet to the IPX/AF. This command can provide information to help analyze problems that may arise while setting up a tiered network.
Full Name
Display Annex G LMI statistics
Syntax
dsplmistats
Related Commands
none
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX/AF
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsplmistats
Description
Display the LMI statistics for the trunk attached to the hub.
System Response
batman StrataCom IPX/AF 8.2 Jan. 30 1996 18:04 PST
Annex G LMI Statistics for slot:1 port:1
VPI.VCI: 0.0 Lmi enabled Lmi polling enabled
Invalid Pdu Rx: 0 Status Polling Timer (T396) : 10
Invalid Pdu Len Rx: 0 Status Enquiry Timer (T393) : 10
Unknown Pdu Type Rx: 0 Max Status Enquiry Retry (N394): 5
Unknown IE Type Rx: 0 Update Status Timer (T394) : 10
Bad Transaction Rx: 0 Max Update Status Retry (N395) : 5
Status Rx: 1384 Spc Polling Timer : 3
Status Enq Tx: 1384 Spc Retry Timer : 0
Status Enq Rx: 1384 Spc Retry Counter : 1
Status Tx: 1384 Node Status Retry Timer : 0
Status Ack Rx: 8 Node Status Retry Counter : 0
Update Status Tx: 8 Node Status Polling Timer : 2
Update Status Rx: 8
Status Ack Tx: 8
Last Command: dsplmistats
Next Command:
Table 4-15 : dspnds -- Optional Parameters
| domain number
|
Specifies the domain number (1 to 8) for which to display nodes. Only the nodes within the specified domain are displayed. If the number does not match a valid domain number, the message "No domain with this number" is displayed.
|
dspnds
Displays the name, type, and alarm status of all nodes within the domain of the node executing the command. The nodes are grouped per domain, with one domain per display. The remote node alarm status is provided only on a domain basis. Therefore, the user must virtual terminal (vt) to the remote node to get specific alarm information.
If a node is in alarm, its name is highlighted and the alarm type (major/minor), is displayed. A major alarm will be a flashing word. A junction node is identified with "Yes" printed under the Jct column.
Full Name
Display all nodes
Syntax
dspnds [+n | -p | -d | domain]
Related Commands
dspnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspnds
Description
Display the alarm status of all nodes within the domain.
System Response
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:42 PST
NodeName Alarm
alpha MAJOR
beta MAJOR
gamma MAJOR
Last Command: dspnds
Next Command:
Table 4-16 : dspnds -- Optional Parameters
| +n
|
The node number, which requires super user privilege to assign.
|
| -p
|
Specifies that the display include the type of controller card in the node. The types are BCC, NPM, and so on.
|
| -d
|
Specifies that the display include the type of node for each named node. The type is either IPX, IGX, or BPX.
|
| domain number
|
Specifies the domain number (1 to 8) for which to display nodes. Only the nodes within the specified domain are displayed. If the number does not match a valid domain number, the message "No domain with this number" is displayed.
|
dspnode
Displays a summary of the interface shelves.
This command can isolate the shelf where an alarm has originated. The routing nodes in a network do not indicate the interface shelf where an alarm condition exists, so execute dspnode on a hub node to find out which interface shelf originated the alarm.
The first example shows a screen display with dspnode executed on a BPX. The second example shows a screen with dspnode executed on an IPX/AF. When executed on an IPX/AF, dspnode shows the name of the hub node and the trunk number. Note that to execute a command on an IPX/AF, you must either use an attached control terminal or telnet to the IPX/AF.
Full Name
Display interface shelves.
Syntax
dspnode
Related Commands
addshelf, delshelf, dsptrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX/AF, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
dspnode
Description
Display information about the interface shelves (executed on the BPX hub node).
System Response
sw53 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 July 21 1996 15:09 GMT
BPX Interface Shelf Information
Trunk Name Type Alarm
1.1 sw89 IPX/AF OK
1.2 SW93Axis AXIS UNRCH
1.3 SW77Axis AXIS MAJ
3.1 sw92 IPX/AF OK
3.2 sw91 IPX/AF OK
3.3 sw90 IPX/AF OK
4.1 sw24 IPX/AF MIN
4.3 sw25 IPX/AF MIN
Last Command: dspnode
Next Command:
Example 2
dspnode
Description
Display information about the trunk to the hub node (executed on an IPX/AF).
System Response
sw24 TN StrataCom IPX 8 8.2 July 24 1996 10:59 GMT
BPX Switching Shelf Information
Trunk Name Type Alarm
8 sw53 BPX MAJ
Last Command: dspnode
Next Command:
dsptermcnf
Displays the configuration for the control port and auxiliary port at a node. It includes all the asynchronous communications parameters that are specified using the cnfterm command.
Full Name
Display terminal port configurations
Syntax
dsptermcnf
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnftermfunc, dsptermfunc
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptermcnf
Description
Display the terminal port configuration data.
System Response
batman TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 26 1996 02:55 PST
Control port Auxiliary port
Baud Rate: 9600 Baud Rate: 9600
Parity: None Parity: None
Number of Data Bits: 8 Number of Data Bits: 8
Number of Stop Bits: 1 Number of Stop Bits: 1
Output flow control: XON/XOFF Output flow control: XON/XOFF
Input flow control: XON/XOFF Input flow control: XON/XOFF
CTS flow control: No CTS flow control: Yes
Use DTR signal: Yes Use DTR signal: Yes
Last Command: dsptermcnf
Next Command:
dsptermfunc
Displays the port functions configured by the cnftermfunc command.
Full Name
Display terminal port functions
Syntax
dsptermfunc
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnftermfunc, dsptermcnf
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptermfunc
Description
Display the terminal port configuration data.
System Response
swstorm TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:42 PST
Control port Auxiliary port
1. VT100/StrataView 1. Okidata 182 Printer
2. VT100 2. Okidata 182 Printer with LOG
3. VT100
4. Alarm Message Collector
5. External Device Window
6. Autodial Modem
Last Command: dsptermfunc
Next Command:
dspprtcnf
Displays printing configuration for the node. The three printing modes, `remote', `local' and `no' are listed and the currently selected mode is highlighted. If remote printing is selected, the node name where the remote printer is located also appears. If this node name is flashing, the node is unreachable.
The dspprtcnf command displays the current print configuration for the domain where the command is entered. Printing cannot occur across a junction node. Each domain must be configured with a printer for this feature to print whenever needed.
Remote mode indicates that the log for the node prints on the printer at the listed remote node. Local mode indicates that the log for the node prints on the node's printer. No printing mode indicates that the log for the node does not print.
Full Name
Display print configuration
Syntax
dspprtcnf
Related Commands
cnfprt
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspprtcnf
Description
Display the print configuration. The example does not show the highlighted field.
System Response
sw83 TN StrataCom IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 22 1996 16:02 PST
Printing Mode
Remote Printing
Local Printing
No Printing
Last Command: dspprtcnf
Next Command:
dsppwr
Displays the current status of the power supply monitor, the current power supply configuration (which may consist of from one to four power supplies depending on node requirements), and the current cabinet temperature.
On the right side of the screen is displayed the internal cabinet temperature in degrees Centigrade and Fahrenheit. The temperature is displayed as a thermometer and the exact temperature appears at the top of the thermometer.
Full Name
Display power supply status
Syntax
dsppwr
Related Commands
dspcd, dspcds
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsppwr
Description
Display power supply status.
System Response
sw81 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 May 21 1996 13:13 PST
Power Status Cabinet Temperature
ASM Status: Active 22 71
Power voltage A/B: 0 / 49 V C 60 | | 140 F
e | | a
PSU Ins Type Rev SerNum Failure n 50 |--| 122 h
A N N/A N/A N/A N/A t | | r
B Y 240V 0C 29959 None i 40 | | 104 e
g | | n
Fan Status r 30 | | 86 h
a | | e
FAN 1 2 3 d 20 | | 68 i
3300 3360 3240 RPM e `--' t
Last Command: dsppwr
Next Command:
dspyred
Displays information for Y-cable pairings. A single slot can be specified, or all pairings are displayed when no slot is specified. Slot numbers appearing in high intensity indicate active card status. Front card, back card, and channel configuration conflicts appear in reverse video. A conflict occurs when the port interfaces are different for corresponding ports in a redundant slot pair. The output display contains the following information:
- First column (Slot) designates the slot of the displayed card.
- Second column (Slot Type) designates its status, Pri (primary) or Sec (secondary).
- Third column (Other Slot) designates the slot number of the associated Y-redundant card.
- Fourth column (Front Card) designates the type of card in the front slot.
- Fifth column (Back Card) designates the type of card in the back slot.
Remaining columns (Channel Configuration) describe the channel configurations when appropriate.
Full Name
Display Y-cable redundancy
Syntax
dspyred [slot]
Related Commands
addyred, delyred, prtyred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspyred
Description
Display Y-redundancy for all cards.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 14:28 MST
Slot Other Front Back Channel Configuration
Slot Type Slot Card Card 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
25 Pri 26 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
26 Sec 25 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
Last Command: dspyred
Next Command:
prtyred
Prints the Y-cable redundancy configuration for an SDP, LDP, CDP, FRP, FTC, NTC or AIT card on an IPX. On an IGX, the cards are the HDM, LDM, CVM, FRM, FTM, NTM and BTM. On a BPX, the applicable cards are the BCC, ASI, and BNI. This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as the dspyred command. See the dspyred command for details on the format of the command output.
Full Name
Print the Y-cable redundancy
Syntax
prtyred <start slot>
Related Commands
dspyred, addyred, delyred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
prtyred
Description
Print Y-redundancy for all cards (no starting slot entered).
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 14:28 MST
Slot Other Front Back Channel Configuration
Slot Type Slot Card Card 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
25 Pri 26 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
26 Sec 25 SDP RS232 DCE DCE DCE DCE
Last Command: prtyred
Next Command:
upcd
Activates a downed card. If a slot contains a complete card set, both the front and back card are upped. After a card set is upped, it is an available node resource. An upped card goes into either a standby or active. The initial state depends on whether the card is immediately needed.
Full Name
Up card
Syntax
upcd <slot.number>
Related Commands
dncd, dspcds
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
upcd 6
Description
Activate card in slot 6. The NTC card in slot number 6 has been upped. The card status is updated to "Standby."
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 July 15 1996 14:51 MST
Missing Cards: 1 ATM, 1 T3
FrontCard BackCard FrontCard BackCard
Type Rev Type Rev Status Type Rev Type Rev Status
1 PCC HDB Active 9 NTC EL02 T1 P07 Active
2 CDP EB Standby 10 Empty
3 CDP Active 11 Empty
4 Empty 12 Empty
5 Empty 13 Empty
6 NTC EP02 SR P11 Standby 14 Empty
7 NTC EC02 E1 P06 Active 15 Empty
8 Empty 16 Empty
Last Command: upcd 6
Next Command:
Last Command: dsplancnf
Next Command:
Table 4-17 : upcd -- Parameters
| slot number
|
Specifies the card slot number of the card to be upped
|
window
Provides an interface to an external device. To establish a session with an external device, first use the cnftermfunc command to designate the port to serve as the external device window. To begin the session, enter the window command and specify the port. The control terminal screen subsequently clears, after which characters entered at the control terminal go to the external device and vice versa.
Because the IPX/IGX/BPX "bundles" characters together before transmitting them, a slight transfer delay occurs. Transfers are delayed until the transfer buffer is filled or the keyboard is inactive for over 50 milliseconds. To end the session, enter the escape sequence designated with the cnftermfunc command. The default for the escape sequence is ^^ (SHIFT 66).
The window command can be executed over a virtual terminal connection. This makes it possible to control all external devices from a single point in the network.
Full Name
Window to external device
Syntax
window <a/c>
Related Commands
cnfterm, cnftermfunc
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
window a
Description
Connect to a local router attached to the auxiliary port. The following dialogue shows the prompts and example responses.
System Response
Protocol [ip]:
Target IP address: 192.9.202.1
Repeat count [5]:
Datagram size [100]:
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]::
Type escape sequence to abort. ^^
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.9.202.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
.......
Success rate is 100 percent
left #
Table 4-18 : window -- Parameters
| a
|
Specifies a window into external equipment attached to the node's auxiliary port. This is the default connection.
|
| c
|
Specifies a window into external equipment attached to the node's control port.
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()