Step 2 Use the dntrk command to down the trunk. Execute dntrk at both ends of the trunk.
Display and print trunk configuration
The network trunk configuration can be displayed on the screen or printed on the printer in a one step process by using any one of the following commands.
- dsptrks---Displays the current trunk configuration and alarm status at a node.
- prttrks---Prints the current trunk configuration and alarm status at a node.
- dspnw---Displays all trunks for each node in a domain.
- prtnw---Prints all trunks for each node in a domain.
Setting Up ATM Trunk Redundancy
ATM trunk redundancy is the T3 and E3 trunk redundancy supported by the AIT and BTM cards on the IPX and IGX, respectively. Redundancy of one of these T3 or E3 trunks can exist between either an AIT and BPX or a BTM and a BPX. The connected BPX card is the BNI. Trunk redundancy cannot exist between IPXs and IGXs. Also, virtual trunking and trunk redundancy are incompatible. This redundancy uses the standard trunk cables rather than a Y-cable. (For all service card sets other than the AIT and BTM, redundancy is managed through the general Y-cable redundancy commands addyred, delyred, and dspyred).
Trunk redundancy depends on the applicable commands, trunk cards in adjacent card slots, and the standard trunk cable. The trunk redundancy commands execute only on the IPX or IGX. The BPX does not require information regarding this feature. ATM redundancy is managed through the following commands.
- addtrkred---Sets up redundancy for a pair of AIT or BTM cards.
- deltrkred---Deletes redundancy for a current redundant pair.
- dsptrkred---Displays all redundant ATM trunk pairs
Using subrate trunk interface control templates
Subrate trunks use an Interface Control Template that specifies the configuration of an output control lead. The template defines which output lead is to be configured and whether the lead is asserted, inhibited, or follows a specified input source. A template for a subrate trunk can be configured individually or copied from the template of another subrate trunk.
Subrate trunk interface control templates are managed through the following commands.
- cnftrkict---Configures an interface control template for a subrate trunk.
- cpytrkict---Copies the template from one subrate trunk and applies to another trunk.
- dsptrkict---Displays the interface control template for a specifies line.
- prttrkict---Prints the interface control template for a specifies line.
Summary of Commands
The following list shows the full name and starting page for the description of each trunk command.
Table 5-2 :
| addtrk
|
Add trunk
|
5-7
|
| addtrkred
|
Add trunk redundancy
|
5-9
|
| cnftrk
|
Configure trunk
|
5-11
|
| cnftrkalm
|
Configure trunk alarm
|
5-17
|
| cnftrkict
|
Configure trunk interface control template
|
5-19
|
| cpytrkict
|
Copy trunk interface control template
|
5-21
|
| deltrk
|
Delete trunk
|
5-23
|
| deltrkred
|
Delete trunk redundancy
|
5-25
|
| dntrk
|
Down trunk
|
5-27
|
| dspcons
|
Display Connections, BPX/ATM Connections Only
|
5-29
|
| dspnw
|
Display network
|
5-31
|
| dsptrkbob
|
Display trunk breakout box
|
5-34
|
| dsptrkcnf
|
Display trunk configuration
|
5-36
|
| dsptrkict
|
Display trunk interface control template
|
5-39
|
| dsptrkred
|
Display trunk redundancy
|
5-41
|
| dsptrks
|
Display trunks
|
5-43
|
| dsptrkstats
|
Display trunk statistics
|
5-45
|
| prtnw
|
Print network
|
5-47
|
| prttrkict
|
Print trunk interface control template
|
5-49
|
| prttrks
|
Print trunks
|
5-50
|
| uptrk
|
Up trunk
|
5-51
|
addtrk
Adds a trunk between two nodes. It must be executed at one of the nodes terminating the line. A trunk must be "added" to the network before it can be used for traffic. Before a trunk can be added to the network, the line must be activated, or "upped", at both ends of the connection using the uptrk command. The addtrk command only has to be entered at one end of the connection. A trunk must be free of major alarms before it can be added. If the addtrk command is used to join two previously separate networks, the local node verifies that all node names in both networks are unique before the trunk is added. In the following situations, the addtrk command cannot be executed:
- Another node is simultaneously attempting to change the network topology by adding or deleting a trunk.
- Another node is notifying all nodes that it has been renamed.
- Another node is currently adding or deleting a connection in the network with the addcon or delcon command.
- There is an unreachable node in the network.
- Two networks are to be joined, and the node names are not unique across both networks
When using the addtrk command, exercise caution when adding a new node to a network or one network to another network. With these particular operations, the user IDs and passwords may be replaced by those in the other network. Consult StrataCom ISC before performing these operations.
Full Name
Add trunk to the network
Syntax
addtrk <slot.port>[.vtrk]
Related Commands
deltrk, dsptrks, uptrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
addtrk 7
Description
Add trunk between node beta slot 7 and node alpha slot 10.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 15:04 MST
PLN Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
7 E1/32 Clear - Line OK alpha.10
9 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.10
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 Major - AIT Missing -
Last Command: addtrk 7
Next Command:
Table 5-3 : addtrk -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the slot and port number of the trunk to add.
|
Table 5-4 : addtrk -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies the virtual trunk number. The maximum on a node is 32. T
he maximum on a T3 or E3 line is 32. The maximum on an OC3/STM1 line is 11.
|
addtrkred
Configures an ATM trunk on an AIT or BTM card set with redundancy by specifying a backup trunk to the primary trunk. This redundancy scheme requires two sets of ATM cards and two T3 or E3 cables. After a primary trunk failure clears, the trunk traffic automatically returns to the primary card set and T3 or E3 line.
Trunk redundancy applies to two trunks. These are a T3 or E3 trunk between:
- An AIT (IPX) and a BNI on a BPX
- A BTM (IGX) and a BNI on a BPX
Specify trunk redundancy at the IPX or IGX only. Primary and backup card sets must be in adjacent slots.
Full Name
Add ATM trunk redundancy
Syntax
addtrkred <primary trunk> <secondary trunk>
Related Commands
deltrkred, dsptrkred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
addtrkred 4 5
Description
Add bandwidth redundancy for the primary ATM trunk in slot 4 with backup from the ATM trunk in slot 5.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 15:15 MST
ATM Line Backup ATM Line
4 5
Last Command: addtrkred 4 5
Next Command:
Table 5-5 : addtrkred -- Parameters
| primary trunk
|
Specifies the slot number of the primary trunk card set.
|
| secondary trunk
|
Specifies the slot number of the secondary trunk card set as backup.
|
cnftrk
A trunk has a default configuration after it is upped with uptrk. Beyond this default configuration, the cnftrk command permits configuration of trunk parameters. This command must be used at both ends of a trunk.
In the display for cnftrk, the current value for each parameter appears on screen. At the command lime prompt for each parameter, the current or default value appears in parentheses and stays the same if you press the Return key without typing any characters. Configurable parameters depend on the trunk type. If a displayed parameter is not available, it appears in half-tone.When you create or edit a job with the addjob or editjob command, respectively, prompts appear for line format and line options when you specify cnftrk in the job.
The parameters RCV Trunk Rate and XMT Trunk Rate apply to standard, physical ATM trunks. These parameters allow a throttling down from the maximum line rate for the trunk type. For ATM trunks terminating on an IPX AIT or an IGX BTM, the RCV Trunk Rate must be adjusted downward to prevent overloading of the bus. In this situation, the rate should be no more than half the total bus bandwidth. (The total is 80,000 cells per second.) The rate could be less if significant numbers of T1 or E1 trunks exist on the same node.
Increments for RCV Trunk Rate and XMT Trunk Rate can be as small as 1 cps (although the node may round up or down). Note that, because a corresponding amount of throttling back must be specified at the other end, cnftrk execution must happen at both ends of the trunk. Therefore, if RCV Trunk Rate is 40,000 cps on the near end, XMT Trunk Rate must be 40,000 cps on the far end of the trunk.
The default value for XMT Trunk Rate is the maximum rate for the back card type. This rate can be throttled down to any number of cells per second that is less than or equal to the physical port rate. If E3 or T2 is selected, the bandwidth is reduced from the T3 rate.
The implementation of XMT Trunk Rate on a virtual trunk differs from the implementation on a physical trunk. On a physical trunk, XMT Trunk Rate limits the rate at which the back card physically generates cells. For a virtual trunk, XMT Trunk Rate does not limit the rate at which the back card generates cells: the line rate stays at the maximum for the line type. However, XMT Trunk Rate is the maximum transmission rate allowed on a virtual trunk. The provider of the virtual trunk service assigns the value for XMT Trunk Rate to the user, and this is the value that must be specified using cnftrk.
For configuring an NTC or NTM trunk, the Subrate interface and Subrate data rate fields are configurable only if the back card is a BC-SR. The choices for interface type are V.11, X.21, V.35, or RS449. The data rate is set to match the subrate facility and must be in the range 64 Kbps to 1.920 Mbps.
The DS0 map is used to define fractional E1 and T1 trunks. It consists of a repeating set of specifications in the form <x[-y[a]]>, where "x" and optional "y" are DS-0 numbers 0 to 23, and the optional "a" indicates alternating. The value of "y" must be greater than that of "x." The values of both "x" and "y" cannot be less than 0 or greater than the maximum number of DS-0s for the line type. In the DS-0 map for unframed E1, use 0-31. For framed E1, use 1-31. For 30 DS-0 E1, use 1-15, 17-31. Normally, the parameters are set after the trunk has been upped but before it has been added to the network with the addtrk command.
The section titled "cnftrk--parameters" in this definition shows required trunk parameters. Virtual trunk parameters are in the section titled "cnftrk - optional parameters." To aid in selecting trunk parameters on a BPX, which are a subset of the total trunk parameters, a list of BPX trunk parameters follows:
|
|
Pass Sync
|
Statistical Reserve
|
|
|
Idle Code
|
Restrict CC Traffic
|
|
|
Link Type
|
HCS Masking
|
|
|
Cable Length
|
Valid Traffic Classes
|
|
|
Transmit Rate
|
Virtual Trunk VPI (virtual trunks only)
|
|
|
Payload Scramble
|
Virtual Trunk Type (virtual trunks only)
|
|
|
Loop Clock
|
Connection Channels (virtual trunks only)
|
Certain parameters can be reconfigured after adding a trunk. Refer to the section "Reconfiguring a trunk."
Full Name
Configure trunk
Syntax
cnftrk <slot.port>[.vtrk] <options for HSSI | E1 | T1 | E3 | T3 | OC3 | E2 | HSSI | SR >
Related Commands
addtrk, dsptrkcnf
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnftrk 8
Description
Configure trunk 8 (an NTC-T1). Enter the parameters to be configured when prompted.
System Response
sw91 TN StrataCom IPX 8 8.2 May 22 1996 16:55 GMT
PLN 8 Configuration T3/636 [96000 cps] AIT slot: 8
Clock Rate: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Transmit Trunk Rate: 96000 cps Restrict PCC traffic: No
Rcv Trunk Rate: 1000 pps Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: Yes recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No cps cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 length: 0-225 ft.
Header Type: STI HCS Masking: Yes
Gateway Type: BAM Payload Scramble: No
VPI Address: 0 End supp BData: Yes
VCI Address: 0 End supp FST: Yes
This Command: cnftrk 8
Trunk Rcv Rate (1) (x1000pps) :
Example 2
cnftrk 1.1
Description
Configure trunk 1.1 (an ATM T3).
System Response
batman TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Date/Time Not Set
TRK 1.1 Config T3 [96000 cps] BNI-T3 slot: 1
Restrict CC traffic: No
Transmit Rate: 96000 Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: Yes recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 cps length: 0-225 ft.
Idle code: 7F hex HCS Masking: Yes
Connection Channels: 1771 Payload Scramble: No
Valid Traffic Classes: Frame Scramble: --
V,TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR Virtual Trunk Type: --
Virtual Trunk VPI: --
Virtual Trunk Service: --
This Command: cnftrk 1.1
Transmit Rate [T2=14490, E3=80000, T3=96000, OC3 = 353208](96000):
Example 3
cnftrk 13.1.1
Description
Configure trunk 13.1.1 (a virtual trunk on an ATM T3).
System Response
sw97 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 July 30 1996 11:45 GMT
TRK 13.1.1 Config T3 [2867 cps] BNI-T3 slot: 13
Restrict CC traffic: No
Transmit Rate: 3000 Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: No recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 cps length: 0-225 ft.
Idle code: 7F hex HCS Masking: Yes
Connection Channels: 55 Payload Scramble: No
Valid Traffic Classes: Frame Scramble: --
V,TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR Virtual Trunk Type: CBR
Virtual Trunk VPI: 0
Virtual Trunk Service: 4
Last Command: cnftrk 13.1.1 3000 N N 992 7F 55 V,TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR N TER
RESTRIAL 0 Y N CBR 0
Next Command:
Table 5-6 : cnftrk -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
ALL
|
The number of the trunk to configure.
|
Any valid slot and port.
|
N/A
|
Trunk Identification
|
ALL
|
Displays trunk number, trunk type and bandwidth supplied, and the card type and slot number of the unit supporting the trunk.
|
T3, E3, T1, E1, FT1, subrate, ATM, NTC, NTM, OC3, STM1.
|
none
|
| Rcv TRK Rate
|
ATM
|
IPX MUXBUS bandwidth (in cps) to allocate to AIT card. Not used for BPX nodes.
|
0--80,000 cells/sec.
|
1000
|
| Tx TRK Rate
|
ATM,
BNI
|
Maximum transmit rate in cells per second (cps) over a trunk. Note that defaults for virtual trunks are 1/32
of the default for T3/E3 and 1/11 of the default for OC3/STM1.
|
0--96000 cps for T3
0--80000 cps for E3
0--353,208 cps for OC3
0--14490 for T2
|
96000 for T3
80000 for E3
353,208 for OC3
14490 for T2
|
| Subrate interface
|
PKT
|
Subrate physical interface type
|
X.21 | V.35
|
X.21
|
| Subrate data rate
|
PKT
|
Subrate data rate (Kbps)
|
64--1920
|
1920
|
| DS-0 map
|
PKT
|
DS-0s to use for FT1 bundle. Optional "a" indicates alternating channels to be used.
|
x - y[a]
|
0-31 (E1) 0-23 (T1)
|
| Pass sync
|
ALL
|
Enables the trunk to pass a clock for network synchronization.
|
Yes | No
|
Yes for standard, no for virtual trunks
|
| Loop Clock
|
ALL
|
Loop receive clock back to transmit.
|
Yes | No
|
No
|
Statistical
Reserve
|
ALL
|
This is the trunk bandwidth reserved for internode controller messages.
|
0--10666
|
600 for FastPackets
1000 for ATM cells
992 ATM on BNI
|
| Header Type
|
ATM
|
Defines the ATM cell header type used: UNI, NNI, or STI. See System Manual for a description.
|
UNI | NNI | STI
|
STI
|
| Gateway Type
|
ATM
|
Defines the type of addressing mode for this trunk. See System Manual for a description.
|
BPX - BPX (BAM)
Cloud (CAM)
Simple (SAM)
|
BAM
|
| VPI Address
|
ATM
|
Virtual path address in ATM cell. Must be non-0 for a virtual trunk.
|
0--255
|
0
|
| VCI Address
|
ATM
|
Virtual circuit address in ATM cell.
|
0--65,535
|
0
|
| Idle code
|
ALL
|
HEX data placed in unused payload space of a packet or ATM cell.
|
0--FF (hex)
|
54 (E1)
7F (T1, ATM)
|
| Restrict CC traffic (requires Super User privilege)
|
ALL
|
Restrict node controller messages from a trunk. Restricting CC traffic can cause serious problems in a network. Contact the StrataCom ISC before changing it.
|
Y | N
|
No
|
| Link type
|
ALL
|
Terrestrial or Satellite link.Link Type applies to configuring a route so it can "avoid satellite."
|
T | S
|
T
|
| Line framing
|
PKT
|
T1 line framing
|
D4 | ESF
|
D4
|
| Line coding
|
PKT
|
E1 line coding
T1 line coding
|
HDB3 | AMI
ZCS | B8ZS
|
HDB3
ZCS
|
| Line CRC
|
PKT
|
E1 CRC-4
|
Yes | No
|
No
|
| Recv impedance
|
PKT
|
E1 receive impedance
|
1 = 75W unbalanced
2 = 75W balanced
3 = 120W balanced
|
1
|
Cable type and
cable length
|
PKT
ATM
|
Length and type of cable used for trunk. Designates the software configurable line build-out to match the cable length from the IPX or IGX to the DSX cross-connect.
For BPX, the choices are 0--450 feet and over 450 feet. Cable type is not selectable for BPX.
|
1 = 0--220' MAT
2 = 220--440' MAT
3 = 440--655' MAT
4 = 0 -133' ABAM
5 = 133--266' ABAM
6 = 266--399' ABAM
7 = 399--533' ABAM
8 = 533--655' ABAM
1 = 0--133
2 = 255--450'
|
4
1
|
| HCS Masking
|
ATM
BNI
|
Mask the ATM cell header checksum to disable error checking. This applies to E3 and OC3 only.
|
Yes | No
|
Yes
|
| Payload Scramble
|
ATM
BNI
|
Scramble the cell payload.
|
Yes | No
|
Yes for BNI-E3
No for all others
|
| End supp BData
|
PKT
ATM
|
Indicates whether the far end of a trunk supports bursty, frame relay data.
|
Yes | No
|
No
|
| End supp FST
|
PKT
ATM
|
Indicates whether the far end of the trunk supports ForeSight for frame relay.
|
Yes | No
|
No
|
Gateway
Efficiency
|
ATM
|
How many packets to stuff into an ATM cell. Does not apply to BNI.
|
1 | 2 | 3
|
2
|
Table 5-7 : cnftrk -- Optional Parameters
| Connection Channels
|
BNI
|
The maximum number of connection channels per trunk. All virtual trunks on the port share this total. The number of connections added to the port cannot exceed the number of connection channels configured for the port.
|
BNI-T3/E3: max 1771
BNI-OC3: max 15867
|
BNI-T3/E3: 1771
BNI-OC3: 15867
For Virtual Trunks:
BNI-T3/E3: 55
BNI-OC3: 1442
|
| Valid Traffic Classes
|
BNI
|
The valid types of traffic for a virtual trunk. The recommended traffic classes for each virtual trunk types:
On a CBR trunk: ATM CBR, NTS, TS, voice.
On a VBR trunk: ATM VBR and bursty data A.
On an ABR trunk: ATM ABR and bursty data B (ForeSight).
|
V---voice
TS---timestampped
NTS---non-timestampped
FR---frame relay
FST---ForeSight
CBR---constant bit rate
VBR---variable bit rate
ABR---available bit rate
|
|
| Virtual Trunk Type
|
BNI
|
This choice usually comes from the carrier that provides the ATM cloud.
|
CBR, VBR, ABR
|
CBR
|
| Virtual Trunk VPI
|
BNI
|
Virtual Trunks must be configured to have a greater-than-0 VPI before connections are added by addcon. This value usually comes from the carrier that provides the ATM cloud.
|
1--255 for T3/E3
1--63 for OC3 (STM1)
|
|
cnftrkalm
Configures alarm reporting for a trunk. When a trunk are upped and added to the network, alarm reporting is enabled, but cnftrkalm allows disabling of alarms on upped trunks. This can be useful for trunks that are connected to a node but not yet in service or when a trunk has occasional bursts of errors but still functions. When enabled, alarms cause an output from the ARC or ARM card or an indication to StrataView Plus.
Full Name
Configure trunk alarms
Syntax
cnftrkalm <slot.port>[.vtrk] <e | d>
Related Commands
dspalms, dsptrks
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--5
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnftrkalm 7 d
Description
Disable trunk alarms on trunk 7
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 15:21 MST
PLN Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
7 E1/32 Clear - Line OK alpha.10
9 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.10
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 Major - AIT Missing -
Last Command: cnftrkalm 7 d
Next Command:
Table 5-8 : cnftrkalm -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the trunk number.
|
| e
|
Enables the alarm.
|
| d
|
Disables the alarm.
|
Table 5-9 : cnftrkalm -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies the virtual trunk number.
|
cnftrkict
Configures the output lines of an interface control template for a subrate trunk. The following list shows the configurable signals:
Table 5-10 :
| X.21
|
C, I
|
|
| V.35
|
RTS, DTR
|
CTS, DSR
|
| MIL-188
|
IS, LL, RL, RS, SF, SS, TR
|
DM, CS
|
Full Name
Configure trunk interface control template
Syntax
cnftrkict <line> <output> <source>
Related Commands
dsptrkict, prttrkict
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cnftrkict 9 c on
Description
Configure output lead "c" as "on" in the interface control template for subrate trunk 9.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 15:15 MST
Packet Line: 9
Interface: X.21 DTE
Interface Control Template for Trunk Line
Lead Output Value Lead Output Value
C/DTR ON
Last Command: cnftrkict 9 c on
Next Command:
Table 5-11 : cnftrkict -- Parameters
| line
|
Specifies the trunk whose interface control template is to be configured.
|
| output
|
Specifies the output lead to be configured. Configurable output leads vary depending on the type of data interface (X.21, V.35, or MIL-188) used.
|
| source
|
Specifies how the specified output lead is to be configured. The options are as follows:
- On, which means the output lead is asserted
- Off, which means the output lead is inhibited
- l (lower case L) Output follows a local input lead
- Input, which specifies the name of the local input lead that the output lead follows.
Input leads vary depending on the type of data interface (X.21, V.35, or MIL-188) supported.
|
cpytrkict
Copies the interface control template of one trunk to another trunk. Once copied, the control information can be edited with the cnftrkict command. See the cnftrkict description for more information on configuring the trunk interface control templates.
Full Name
Copy trunk interface control template
Syntax
cpytrkict <source_trunk> <destination_trunk>
Related Commands
cnftrkict, dsptrkict
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
cpytrkict 9 11
Description
Copy the interface control template for trunk 9 to trunk 11.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 15:15 MST
Packet Line: 9
Interface: X.21 DTE
Interface Control Template for Trunk Line
Lead Output Value Lead Output Value
C/DTR ON
Last Command: cpytrkict 9 11
Enter destination line number:
Table 5-12 : cpytrkict -- Parameters
| source trunk
|
Specifies the trunk number of the interface control template information to be copied.
|
| destination trunk
|
Specifies the trunk number to which the interface control template information will be copied.
|
deltrk
Deletes a trunk. Because deleting a trunk removes the communication path between two nodes, using deltrk may split a network into two separate networks. If deltrk execution splits the network, it causes deletion of connections using the deleted trunk.
If both nodes on the trunk are reachable, executing deltrk is necessary on only one node. If a trunk is deleted on a node while the node at the other end is unreachable, the unreachable node does not detect the deletion, so be sure to delete the trunk at both nodes in this case.
After deletion, the trunk still carries framing signals and can generate alarms for counting, but no traffic can go across it. To remove the trunk completely, use dntrk after the deltrk command.
In the following situations, the node does not allow deltrk to execute:
- Another node is attempting to change the network topology by adding or deleting a trunk.
- Another node is notifying all other nodes that it has a new node name.
- Another node is adding or deleting a channel connection in the network with the addcon or delcon command.
Full Name
Delete trunk from a network
Syntax
deltrk <slot.port>[.vtrk]
Related Commands
addtrk, dntrk, dspnw, dsptrks uptrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
deltrk 7
Description
Delete trunk 7 from the network.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 15:02 MST
PLN Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
7 E1/32 Clear - Line OK -
9 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.10
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 AIT - AIT Missing -
Last Command: deltrk 7
Next Command:
Table 5-13 : deltrk -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the physical trunk number.
|
Table 5-14 : deltrk -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies the virtual trunk portion of the trunk identifier.
|
deltrkred
Removes BTM/AIT trunk redundancy. Removing the backup card is possible without causing alarms after deltrkrd executes. This command operates on an IPX or IGX node with a redundant AIT or BTM card se.
Full Name
Delete ATM trunk redundancy
Syntax
deltrkred <backup ATM trunk number>
Related Commands
addtrkred, dsptrkred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
deltrkred 5
Description
Remove ATM trunk redundancy for the card set in slot 5.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
ATM Line Backup ATM Line
7 8
Last Command: deltrkred 5
Next Command:
Table 5-15 : deltrkred -- Parameters
| Backup trunk number
|
Specifies of the ATM card set assigned as the backup.
|
dntrk
Downs a trunk, after which the line no longer has framing nor statistics gathering. Before it can be downed with dntrk, a trunk must be removed from the network with deltrk (or delshelf in a tiered nets).
Full Name
Down trunk
Syntax
dntrk <slot.port>[.vtrk]
Related Commands
addtrk, deltrk, uptrk, dsptrks
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
dntrk 9
Description
Deactivate trunk 9
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 3 1996 10:53 MST
From Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 Major - AIT Missing -
Last Command: dntrk 9
Next Command:
Table 5-16 : dntrk -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the physical trunk.
|
Table 5-17 : dntrk -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies a virtual trunk number (applies to BNI only). T3/E3 range is 1--32. OC3 range is 1--11.
|
dspcons
Displays a summary of connections on an IPX, IGX, or BPX. The fields displayed in the dspcons screens are the following:
| · Local Channel
|
The connection's channel at this node.
|
| · Remote NodeName
|
The name of the node at the other end of the connection.
|
| · Remote Channel
|
The connection's channel at the remote node.
|
| · State
|
The state of the connection(s) as follows:
|
| OK
|
Not routed, but trying
|
| Down
|
Downed (not supported for ATM connections)
|
| OK(Dn)
|
Waiting for onhook to occur to allow courtesy down to
|
|
|
take place or connection(s) which have been courtesy
|
|
|
downed using the dncon command (not supported for
|
|
|
ATM connections)
|
| · Compress
|
IPX or IGX-only. Shows the type of compression, if any.
|
| · Code
|
IPX or IGX-only. Shows the line coding for the connection.
|
| · Type
|
The type of connection (CBR = constant bit rate for voice, VBR = variable bit rate for frame relay or synchronous data rate, ATFR = frame relay to ATM interworking, ATFST = frame relay to ATM interworking with ForeSight).
|
| · Rate
|
The bandwidth assigned the connection in cells/sec (ATM) or Kbits/sec (other).
|
Full Name
Display connections for ATM connections on a BPX node.
Syntax
dspcons [start_channel] [nodename] [state] [type] [+d]
Related Commands
addcon, delcon
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspcons
Description
Display ATM connections on a BPX.
System Response
sw53 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 April 24 1996 22:57 GMT
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Avoid COS O
4.1.2.1 sw53 4.3.2.1 Ok atfst
4.1.2.2 sw53 4.3.2.2 Ok atfst
4.1.2.3 sw53 4.3.2.3 Ok atfst
4.1.2.4 sw53 4.3.2.4 Ok atfst
4.1.2.5 sw53 4.3.2.5 Ok atfst
4.1.2.6 sw53 4.3.2.6 Ok atfst
4.1.2.7 sw53 4.3.2.7 Ok atfst
4.1.2.8 sw53 4.3.2.8 Ok atfst
4.1.2.9 sw53 4.3.2.9 Ok atfst
4.1.2.10 sw53 4.3.2.10 Ok atfst
4.1.2.11 sw53 4.3.2.11 Ok atfst
4.1.2.12 sw53 4.3.2.12 Ok atfst
4.1.2.13 sw53 4.3.2.13 Ok atfst
This Command: dspcons
Continue?
Table 5-18 : dspcons -- Optional Parameters
slot.port.VPI.VCI
slot.port.DLCI
|
Specifies the connection after which the display begins. Without a starting channel specification (the default), the display begins with the first connected channel.
|
dspnw
Displays the network topology in tabular form. Alarms appear in a column, and added trunks (by addtrk) appear to the right to the node name. Each trunk entry shows the local back card slot number and the node name and back card slot number on the other end of the line. Note the following conventions:
- ~ indicates that the trunk is a satellite line.
- Flashing entry indicates a failed line.
- Blinking node name indicates a node executing downloader software.
If the network has more nodes and trunk connections than are currently on the screen, a "Continue?" prompt appears. Press the Return key to display other parameters, or enter "n" to exit the command.
Full Name
Display network
Syntax
dspnw [+b | -b] [+z | -z]
Related Commands
dspnds, prtnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dspnw
Description
Display the network topology in tabular form.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
NodeName Alarm Packet Line Packet Line Packet Line
alpha 10- 7/beta 14- 13/beta
beta MAJOR 7- 10/alpha 9- 10/gamma 13- 14/alpha
15- 15/gamma
gamma MAJOR 10- 9/beta 15- 15/beta
Last Command: dspnw
Next Command:
The display shows a network containing the nodes alpha, beta, and gamma. The word "Major" on the right of "gamma" and "beta" (see Alarm column) indicates the existence of alarm conditions such as loss of signal.
The "10-9/beta" listed to the right of node gamma indicates that trunk 10 on node gamma connects to node beta as trunk 9. The "7-10/alpha" listed to the right of node beta indicates that trunk 7 on node beta connects to node alpha as trunk 10. If the two trunk numbers are separated by an tilde (~) in place of a dash (-), the display is indicating a satellite. The following illustrates a map of this network.
Figure 5-1 : dspnw Example
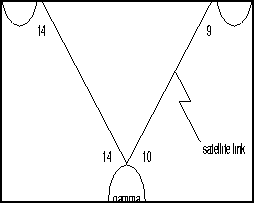
Table 5-19 : dspnw -- Optional l Parameters
| +b
|
Display only the lines that support bursty data.
|
| -b
|
Display only the lines that do no support bursty data.
|
| +z
|
Display only the lines that use ZCS encoding.
|
| -z
|
Display only the lines that do not use ZCS encoding.
|
dsptrkbob
Displays the state of all inputs from subrate line equipment to an IPX or IGX and the state of all outputs from the node to the subrate line equipment. Display updates can occur at an optional, user-specified interval. Otherwise, the display remains on-screen until Delete is pressed or the display times out. The system default for updating the display is every 5 seconds. In the case of a disabled trunk, its number appears in dim, reverse video. See cnftrkict for configuration details.
Full Name
Display trunk breakout box
Syntax
dsptrkbob <line> [interval]
Related Commands
cnftrkict, dsptrkict
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
dsptrkbob 9
Description
Display the breakout for subrate trunk 9.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 April 15 1996 15:15 MST
Packet Line: 9
Interfaces: X.21 DTE
Inputs from Line Equipment Outputs to Line Equipment
Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State
RxD 4/11 Idle TxD 2/9 Active
I/DSR 5/12 On C/DTR 3/10 On
S/RxC 6/13 Active
Last Command: dsptrkbob 9
Hit DEL key to quit:
Table 5-20 : dsptrkbob -- Parameters
| trunk
|
Specifies the subrate trunk.
|
Table 5-21 : dsptrkbob -- Optional Parameters
| interval
|
The number of seconds between updates of the breakout box display. The range is 1--60.
|
dsptrkcnf
Displays trunk configuration. The parameter values that dsptrkcnf displays have been set with cnftrk or are default values.
Full Name
Display trunk configuration
Syntax
dsptrkcnf <slot.port>[.vtrk]
Related Commands
cnftrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptrkcnf 8
Description
Display the configuration for trunk 8. Trunk 8 is an NTC/BC-T1 trunk.
System Response
sw91 TN StrataCom IPX 8 8.2 May 22 1996 16:09 GMT
PLN 6 Configuration T3/3 [1000 pps] AIT slot: 6
Clock Rate: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Transmit Trunk Rate: 96000 cps Restrict PCC traffic: No
Rcv Trunk Rate: 1000 pps Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: Yes recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No pps cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 length: 0-225 ft.
Header Type: STI HCS Masking: Yes
Gateway Type: BAM Payload Scramble: No
VPI Address: 0 End supp BData: Yes
VCI Address: 0 End supp FST: Yes
Last Command: dsptrkcnf 6
Next Command:
Example 2
dsptrkcnf 1.1
Description
Display the configuration for trunk 1.1 (an ATM trunk).
System Response
batman TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 Date/Time Not Set
TRK 1.1 Config T3 [96000 cps] BNI-T3 slot: 1
Restrict CC traffic: No
Transmit Rate: 96000 Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: Yes recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 cps length: 0-225 ft.
Idle code: 7F hex HCS Masking: Yes
Connection Channels: 1771 Payload Scramble: No
Valid Traffic Classes: Frame Scramble: --
V,TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR Virtual Trunk Type: --
SVC Channels: 0 Virtual Trunk VPI: --
SVC Bandwidth: 0 cps Virtual Trunk Service: --
Last Command: dsptrkcnf 1.1
Next Command:
Example 3
dsptrkcnf 13.3.1
Description
Display the configuration for virtual trunk 13.3.1.
System Response
sw97 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 June 22 1996 07:34 GMT
TRK 13.3.1 Config T3 [2867 cps] BNI-T3 slot: 13
Restrict CC traffic: No
Transmit Rate: 3000 Link type: Terrestrial
Subrate interface: -- Line framing: --
Subrate data rate: -- coding: --
Line DS-0 map: -- CRC: --
Pass sync: No recv impedance: --
Loop clock: No cable type:
Statistical Reserve: 992 cps length: 0-225 ft.
Idle code: 7F hex HCS Masking: Yes
Connection Channels: 55 Payload Scramble: No
Valid Traffic Classes: Frame Scramble: --
V,TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR Virtual Trunk Type: CBR
Virtual Trunk VPI: 1
Virtual Trunk Service: 3
Last Command: dsptrkcnf 13.3.1
Next Command:
Table 5-22 : dsptrkcnf -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the physical slot and port number of the trunk.
|
Table 5-23 : dsptrkcnf -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies the virtual trunk number. The maximum value on a node is 32. The maximum on a T3 or E3 line is 32. The maximum for user traffic on an OC3/STM1 trunk is 11. (See also the section called "Setting Up a Virtual Trunk" at the front of this chapter.)
|
dsptrkict
Displays interface control information for the subrate trunks. The displayed information includes:
- Specified line.
- Associated leads and their status (i.e., on or off)
- Whether output follows a local input.
- Name of the local or remote input lead that the output lead follows.
To see a list of configurable outputs, and information on how to configure an output, see the cnftrkict command. Disabled trunks have their trunk number displayed in dim, reverse video on the screen.
Full Name
Display trunk interface control templates
Syntax
dsptrkict <line>
Related Commands
cnftrkict, prttrkict
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptrkict 9
Description
Display subrate for the trunk 9 interface control template.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
Packet Line: 9
Interface: X.21 DTE
Interface Control Template for Trunk Line
Lead Output Value Lead Output Value
C/DTR ON
Last Command: dsptrkict 9
Next Command:
dsptrkred
Displays the backup and primary cards for ATM trunks. It is used for information purposes such as auditing nodes for configurations.
Full Name
Display ATM trunk redundancy
Syntax
dsptrkred [trunk]
Related Commands
addtrkred, deltrkred
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--4
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptrkred
Description
Display all ATM trunks with redundancy.
System Response
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.2 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
ATM Line Backup ATM Line
4 5
7 8
Last Command: dsptrkred
Next Command:
Table 5-24 : dsptrkred -- Optional Parameters
| ATM trunk number
|
Specifies the slot number of the primary or backup ATM card set to display. Without this optional entry, the screen displays all primary and backup ATM trunks.
|
dsptrks
Displays basic trunk information for all trunks on a node. This command applies to both physical only and virtual trunks. The displayed information consists of:
- Trunk number, including the virtual trunk number if applicable
- Line type (E1, T3, or OC3, for example)
- Alarm status
In addition, for trunks that have been added to the network with the addtrk command, the information includes the node name and trunk number at the other end. Trunks that have a "--" in the Other End column have been upped with uptrk but not yet added on both ends with addtrk. For disabled trunks, the trunk numbers appear in reverse video on the screen.
Full Name
Display trunks
Syntax
dsptrks
Related Commands
addtrk, deltrk, dntrk, dspclns, uptrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
No
|
Example 1
dsptrks
Description
Display information on the trunk configuration and alarm status for the trunks at a node. The trunk numbers with three places represent virtual trunks.
System Response
sw53 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 April 24 1996 23:03 GMT
TRK Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
1.1 T3 Clear - OK sw89(IPX/AF)
1.2 T3 Clear - OK -
1.3 T3 Clear - OK -
2.1.1 OC3 Clear - OK -
3.1 T3 Clear - OK sw92(IPX/AF)
3.2 T3 Clear - OK sw91(IPX/AF)
3.3 T3 Clear - OK sw90(IPX/AF)
4.1 T3 Clear - OK sw24(IPX/AF)
4.2 T3 Clear - OK swstorm/1.1
4.3 T3 Clear - OK sw25(IPX/AF)
13.1 T3(E3) Clear - OK -
13.2.1 T3 Clear - OK -
13.2.2 T3 Clear - OK -
13.2.3 T3 Clear - OK -
Last Command: dsptrks
Next Command:
dsptrkstats
Displays the trunk port status, ATM cell loss counts, cell payload errors, and cell header errors for the specified trunk port. The table that follows lists the other statistics. By including the optional clear parameter, dsptrkstats execution clears these statistics.
Table 5-25 :
| Cells dropped due to BFrame parity err.
|
A parity error was detected in one or more of the P bits in the BFrame header or in the BIP-16 parity check for the header causing the cell to be dropped.
|
| Cell header mismatch error count.
|
A count of cells received by a BNI in this slot.port with an incorrect header address for that card.
|
| First mismatch cell header VPI/VCI.
|
This displays the VPI/VCI address of the first header mismatch to be received by the card in this slot.port.
|
| BFrame cell data payload error.
|
A separate BIP-16 parity check is used for the payload data. This number represents the number of errors detected by this parity check. This does not necessarily cause a cell to be dropped.
|
| BFrame cell loss due to admin access.
|
Internal to the BNI card is an administrative processor. This statistic is a count of the cells that were lost in an internal administrative shuffle.
|
Full Name
Display trunks statistics
Syntax
dsptrkstats <slot.port> [clear]
Related Commands
cnftrkstats, dsptrkerrs
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
No
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
dsptrkstats 1.1
Description
Display cell statistics for ATM trunk 1.1.
System Response
sw53 TN StrataCom BPX 15 8.2 April 24 1996 23:07 GMT
Trunk 1.1 Status: Clear - OK Clrd: 07/24/95 17:31:16
Type Count
Cells dropped due to BFrame parity err 0
Cell header mismatch error count 0
BFrame cell data payload error 0
BFrame cell loss due to disabled chan 0
BFrame cell count(TX) 8316 non-hipri cells - 52
BFrame cell count(RX) 12452
First mismatch cell masked VPI/VCI 0
First mismatch cell full VPI/VCI 0
Last Command: dsptrkstats 1.1
Next Command:
Table 5-26 : dsptrkstats -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the physical part of the logical trunk number.
|
Table 5-27 : dsptrkstats -- Optional Parameters
| clear
|
Directs the system to clear the statistics counters.
|
prtnw
Prints the network topology table. Alarms print in a column, and added trunks (by addtrk) appear to the right to the node name. Each trunk entry shows the local back card slot number and the node name and back card slot number on the other end of the line. Note the following conventions:
- ~ indicates the trunk is a satellite line.
- Flashing entry indicates a failed line.
- Blinking node indicates a node is executing downloader software.
Parameters set Zero Coded Suppression (ZCS) display characteristics. ZCS writes a 1 over the least significant bit of any byte that contains 0s. The purpose is to ensure a minimum occurrence of 1s so that the receiving node can extract timing information. Command uses the same syntax, and prints the same information as is displayed using the dspnw command.
Full Name
Print network
Syntax
prtnw [+b | -b] [+z | -z]
Related Commands
dspnw
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
prtnw
Description
Print the network topology.
System Response
(No screen display, just a printout.)
Table 5-28 : prtnw -- Parameters
| +b
|
Display only the lines that support bursty data.
|
| -b
|
Display only the lines that do no support bursty data.
|
| +z
|
Display only the lines that use ZCS encoding.
|
| -z
|
Display only the lines that do not use ZCS encoding.
|
prttrkict
Prints the interface control template of a subrate trunk. For a list of configurable outputs and configuration steps, see the cnftrkict description. The printed information includes:
- Specified line.
- Associated leads and their status
- Whether output follows a local input
- Name of the local or remote input lead that the output lead follows
Full Name
Print trunk interface control template
Syntax
prttrkict <line>
Related Commands
dsptrkict
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
prttrkict
Description
Print network topology.
System Response
(No screen display, just a printout.)
Table 5-29 : prttrkict -- Parameters
| line
|
Specifies the trunk interface control template.
|
prttrks
Prints the trunk configuration for the node. This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as the dsptrks command. Configuration information for trunks includes the trunk number and the type of line (T3, E3, and so on). For trunks that have been added to the network with the addtrk command, the configuration information also includes the node name and trunk number at the other end of the line.
Note the following printout characteristics:
- Those trunks that show a "--" in the "Other End" column, have been upped with the uptrk command but not yet added with the addtrk command.
- The Other End column shows the node name and slot number of the other end of the trunk.
- Names of disabled trunk appear as light text in the printout.
Full Name
Print trunks
Syntax
prttrks
Related Commands
dsptrks
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--6
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
No
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
YEs
|
Example 1
prttrks
Description
Print trunk configuration for the node.
System Response
(No screen display, just a printout.)
uptrk
Activates (ups) a trunk and, through the presence or absence of the optional vtrk parameter, identifies either a physical or virtual trunk. Note that mixing physical and virtual trunks is not allowed, so changing the trunk type between physical and virtual requires the trunk to be down (dntrk) before changing.
An activated trunk generates line signalling but does not yet carry live traffic. In this state, the node can monitor the trunk for reliability before the trunk is added with addtrk. Once a trunk has shown reliability and is ready to go into service, use addtrk to add the trunk to the network. Subsequently, if the trunk must go out of service, use dntrk. The dntrk command causes the node to reroute any existing traffic if sufficient bandwidth is available.
A trunk cannot be upped if the required cards are not available. Furthermore, if an NTC or NTM is executing self-test, a "card in test" message may appear on-screen. If this occurs, re-enter uptrk.
Full Name
Up trunk
Syntax
uptrk <slot.port>[.vtrk]
Related Commands
addtrk, dntrk
Attributes
| Privilege
|
1--2
|
| Jobs
|
Yes
|
| Log
|
Yes
|
| Node
|
IPX, IGX, BPX
|
| Lock
|
Yes
|
Example 1
uptrk 21
Description
Activate (up) trunk 21---a single-port card, in this case, so only the slot is necessary.
Example 2
uptrk 6.1.1
Description
Activate (up) trunk 6.1.7---a virtual trunk, in this case, which the third digit indicates.
Table 5-30 : uptrk -- Parameters
| slot.port
|
Specifies the slot and port of the trunk to activate. If the card has only one port, the port parameter is not necessary. An NTM, for example, has one port.
|
Table 5-31 : uptrk -- Optional Parameters
| vtrk
|
Specifies the virtual trunk number. The maximum on a node is 32. The maximum on a T3 or E3 line is 32. The maximum for user traffic on an OC3/STM1 trunk is 11 (so more than one OC3/STM1 may be necessary). (See also the section called "Setting Up a Virtual Trunk" at the front of this chapter.)
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()