|
|

This chapter will help you find solutions, should you be having problems with your router. Begin by attempting to isolate the problem to a specific source.
The following sections describe troubleshooting particular kinds of problems:
Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2 illustrate the LEDs on the front panels of Cisco 700 series routers. See the section, "Front Panel LED Functions," later in this chapter for a detailed description of the LEDs.
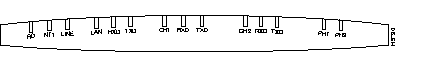
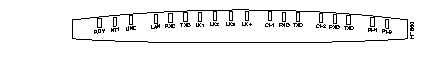
The LEDs on the front panel of Cisco 700 series routers display the activity status of the router as connections are made and as packets are sent and received.
Table 5-1 lists the LEDs and their functions.
There is one LED on the rear panel, the LINK LED. The LINK LED remains lit when the router is
The front panel LEDs can be used for diagnostic purposes. When the router is powered on, it performs a series of self-tests. After these tests are completed, any operational problem is represented by a combination of lit and unlit LEDs.
Table 5-2 lists the combinations of lit and unlit LEDs and their significance.
| RDY | NT-1 | LINE | CH1 | CH2 | Test Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On | Blinking several times per second | See Note1 | Internal NT-1 is unable to synchronize with the ISDN switch | ||
| On | Blinking one time per second | Internal NT-1 is synchronized with the ISDN switch, but is unable to synchronize with the ISDN terminal devices | |||
| On | Waiting for software | ||||
| On | On | On | On | Processor inactive | |
| Processor self-test error | |||||
| On | EPROM2 checksum error | ||||
| On | RAM error | ||||
| On | On | Flash memory error | |||
| On | On | HDLC3 packet chip error | |||
| On | On | Configuration port error | |||
| On | On | On | ISDN interface chip error |
Cisco 760 series routers have 12 to 14 (depending on the model) LEDs on the front panel. Cisco 770 series routers have 15 to 18 LEDs on the front panel. In addition to indicating operating status, LEDs indicate problems that might occur during the power-on process.
During initialization (power-up or reboot), with the switch type set to NI-1, the following message displays:
host> Please wait for TWAIT timer to expire in __ seconds host> Make a call to bypass this timer
The timer value varies from 1 second to 5 minutes. Upon expiration of the time, the router requests a terminal endpoint identifier (TEI) and initiates SPID initialization as usual. If needed, either a voice or data call can be initiated instead of waiting for the timer to expire. This stops the timer immediately and allows initialization to continue.
Note that the call will be successful unless the ISDN line has not been given enough time to rest before power-up or reboot.
The Inband Timeout Violation error message indicates the router cannot communicate with the remote device after an ISDN connection had been established. This might be caused by the speed of the connection. Under some conditions, the router attempts to connect at 56 kbps and the remote device attempts to connect at 64 kbps. The data becomes unusable. Set the speed to 64 kbps, and attempt the connection again.
The following conditions are often caused by router configuration problems:
If the router calls itself, check that the number configured with the set number command is not the same as the number configured with the set directory number command.
ISDN supports two separate logical data channels on the same physical line. If these two numbers are the same, the router might attempt to call itself when on-demand dialing is enabled or if the user issues the call command.
Either of the following messages received on your terminal might indicate a SPID configuration problem:
Channel Not Available Facility Not Subscribed
Check for the following conditions:
If outgoing calls are unsuccessful, check for the following conditions:
You can also try initiating the call manually.
If an outgoing call is initially successful and then rejected, check for the following conditions:
The router places outbound calls without any problems, but cannot receive incoming calls. Verify the following conditions are met:
If you have problems connecting to the 10BaseT Ethernet network, check the node/hub configuration. On Cisco 760 or 770 series routers, this configuration is set with a switch on the rear panel labeled HUB/NODE.
If an error occurs during a software download, a combination of blinking LEDs indicates a problem. An error code is also displayed on the terminal.
Table 5-3 lists the combination of blinking LEDs that indicate an error, along with the error code and a description of the error.
This section describes ISDN BRI standard cause values that might be received from the ISDN switch when using Cisco 700 series routers. These values are sent from the ISDN switch to the router to indicate ISDN call status.
Although ISDN service providers generally define cause messages with decimal values, Cisco 700 series routers display the hexadecimal (or hex) translation of the decimal value.
Table 5-4 lists the ISDN BRI cause values, the hexadecimal translation, the cause message, and a short definition of the cause message.
| Cause Value1 | Hex Value1 | Cause Message | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0001 | Unassigned number | The ISDN number was sent to the switch in the correct format; however, the number is not assigned to any destination equipment. |
| 2 | 0002 | No route to specified transit network | The ISDN exchange is asked to route the call through an unrecognized intermediate network. |
| 3 | 0003 | No route to destination | The call was routed through an intermediate network that does not serve the destination address. |
| 6 | 0006 | Channel unacceptable | The service quality of the specified channel is insufficient to accept the connection. |
| 7 | 0007 | Call awarded and delivered | The user is assigned an incoming call that is connected to a channel with an established call. |
| 16 | 0010 | Normal call clearing | Normal call clearing has occurred. |
| 17 | 0011 | User busy | The called system acknowledges the connection request, but is unable to accept the call because all B channels are in use. |
| 18 | 0012 | No user responding | The connection cannot be completed because the destination does not respond to the call. |
| 19 | 0013 | No answer from user (user alerted) | The destination responds to the connection request, but fails to complete the connection within the prescribed time. The problem is at the remote end of the connection. |
| 21 | 0015 | Call rejected | The destination is capable of accepting the call, but rejected the call for an unknown reason. |
| 22 | 0016 | Number changed | The ISDN number used to set up the call is not assigned to any system. (If an alternate address is assigned to the called equipment, it might be returned in the diagnostic field of this message.) |
| 26 | 001A | Non-selected user clearing | The destination is capable of accepting the call, but rejected the call because it was not assigned to the user. |
| 27 | 001B | Destination out of order | The destination cannot be reached because the interface is not functioning correctly, and a signaling message cannot be delivered. This might be a temporary condition, but could last for an extended period of time. For example, the remote equipment might be turned off. |
| 28 | 001C | Invalid number format | The connection could be established because the destination address was presented in an unrecognizable format or because the destination address was incomplete. |
| 29 | 001D | Facility rejected | The facility requested by the user cannot be provided by the network. |
| 30 | 001E | Response to STATUS ENQUIRY | The status message was generated in direct response to the receipt of a status inquiry message. |
| 31 | 001F | Normal, unspecified | Reports the occurrence of a normal event when no standard cause applies. No action required. |
| 34 | 0022 | No circuit/channel available | The connection cannot be established because no appropriate channel is available to take the call. |
| 38 | 0026 | Network out of order | The destination cannot be reached because the network is not functioning correctly, and the condition might last for an extended period of time. An immediate reconnect attempt will probably be unsuccessful. |
| 41 | 0029 | Temporary failure | An error occurred because the network is not functioning correctly. The problem will be resolved shortly. |
| 42 | 002A | Switching equipment congestion | The destination cannot be reached because the network switching equipment is temporarily overloaded. |
| 43 | 002B | Access information discarded | The network cannot provide the requested access information. |
| 44 | 002C | Requested circuit/channel not available | The remote equipment cannot provide the requested channel for an unknown reason. This might be a temporary problem. |
| 47 | 002F | Resource unavailable, unspecified | The requested channel or service is unavailable for an unknown reason. This might be a temporary problem. |
| 49 | 0031 | Quality of service unavailable | The requested quality of service (as defined by CCITT2 recommendation X.213) cannot be provided by the network. This might be a subscription problem. |
| 50 | 0032 | Requested facility not subscribed | The remote equipment supports the requested supplementary service, but only by subscription. |
| 57 | 0039 | Bearer capability not authorized | The user requested a bearer capability (BC) that the network provides, but that the user is not authorized to use. This might be a subscription problem. |
| 58 | 003A | Bearer capability not presently available | The network normally provides the requested BC, but not at the present time. This might be due to a temporary network problem or to a subscription problem. |
| 63 | 003F | Service or option not available, unspecified | The network or remote equipment was unable to provide the requested service option for an unspecified reason. This might be a subscription problem. |
| 65 | 0041 | Bearer capability not implemented | The network cannot provide the bearer capability (BC) requested by the user. |
| 66 | 0042 | Channel type not implemented | The network or the destination equipment does not support the requested channel type. |
| 69 | 0045 | Requested facility not implemented | The remote equipment does not support the requested supplementary service. |
| 70 | 0046 | Only restricted digital information bearer is available | The network is unable to provide unrestricted digital information BC. |
| 79 | 004F | Service or option not available, unspecified | The network or remote equipment is unable to provide the requested service option for an unspecified reason. This might be a subscription problem. |
| 81 | 0051 | Invalid call reference value | The remote equipment received a call with a call reference that is not currently in use on the user-network interface. |
| 82 | 0052 | Identified channel does not exist | The receiving equipment is requested to use a channel that is not activated on the interface for calls. |
| 83 | 0053 | A suspended call exists but this call identity does not | The network received a call resume request. The call resume request contained a Call Identify information element that indicates that the call identity is being used for a suspended call. |
| 84 | 0054 | Call identity in use | The network received a call resume request. The call resume request contained a Call Identify information element that indicates that it is in use for a suspended call. |
| 85 | 0055 | No call suspended | The network received a call resume request when there was not a suspended call pending. This might be a transient error that will be resolved by successive call retries. |
| 86 | 0056 | Call having requested call identity has been cleared | The network received a call resume request. The call resume request contained a Call Identity information element, which once indicated a suspended call. However, the suspended call was cleared either by timeout or by the remote user. |
| 88 | 0058 | Incompatible destination | Indicates that an attempt was made to connect to non-ISDN equipment, for example, to an analog line. |
| 91 | 005B | Invalid transit network specified | The ISDN exchange was asked to route the call through an unrecognized intermediate network. |
| 95 | 005F | Invalid message, unspecified | An invalid message was received, and no standard cause applies. This is usually due to a D-channel error. If this error occurs systematically, report it to your ISDN service provider. |
| 96 | 0060 | Mandatory information element is missing | The receiving equipment received a message that did not include one of the mandatory information elements. This is usually due to a D-channel error. If this error occurs systematically, report it to your ISDN service provider. |
| 97 | 0061 | Message type non-existent or not implemented | The receiving equipment received an unrecognized message, either because the message type was invalid or because the message type was valid but not supported. Cause 97 is due to either a problem with the remote configuration or a problem with the local D channel. |
| 98 | 0062 | Message incompatible with call state or message type non-existent | The remote equipment received an invalid message, and no standard cause applies. Cause 98 is due to a D-channel error. If this error occurs systematically, report it to your ISDN service provider. |
| 99 | 0063 | Information element nonexistent or not implemented | The remote equipment received a message that includes information elements, which were not recognized. This is usually due to a D-channel error. If this error occurs systematically, report it to your ISDN service provider. |
| 100 | 0064 | Invalid information element contents | The remote equipment received a message that includes invalid information in the information element. This is usually due to a D-channel error. |
| 101 | 0065 | Message not compatible with call state | The remote equipment received an unexpected message that does not correspond to the current state of the connection. This is usually due to a D-channel error. |
| 102 | 0066 | Recovery on timer expiry | An error-handling (recovery) procedure was initiated by a timer expiration. This is usually a temporary problem. |
| 111 | 006F | Protocol error, unspecified | An unspecified D-channel error when no other standard cause applies. |
| 127 | 007F | Interworking, unspecified | An event occurred, but the network does not provide causes for the action that it takes. The precise problem is unknown. |
| UNKNOWN | - | Unknown or local error | An event occurred, but the network does not provide causes for the action that it takes. The precise problem is unknown. |
|
|