|
|

As your Resource Manager network inventory and user base grow, you need to perform certain system administration tasks to accommodate that growth. This chapter describes some of the features Resource Manager provides to help you with these tasks.
The following sections are presented in this chapter:
Perform storage management tasks to ensure you have a set of database backups in case your current database becomes corrupted or otherwise unusable.
Use a directory naming scheme that indicates your backup dates in case you need to restore the database. You should create a separate directory for each back up. The backup directory must be writeable by the user bin on Solaris systems. The backup process creates three files:
The px.db file is your database backup. The px.log file is a log of database transactions. Without the px.log file, you cannot restore your database. The CRM_filebackup.tar file contains a collection of backup files created by Resource Manager applications.
Scenario: You have imported devices into your Resource Manager database and you need to back up the database.
You can back up your database immediately or you can schedule it for later.
Make several directories to store your backup files. For example, if you want to perform backups weekly, use a naming convention that indicates the dates of the backups, such as:
You should create a separate directory for each back up. Store a single set of backup files in each directory. Each time you perform a back up, Resource Manager stores the most current px.db and px.log files and other files specified by Resource Manager components in that directory.
To back up the database, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select System Admin > Back Up Data.
The Back Up message appears, providing information about the backup procedure.
Step 3 Read the message, then click Next.
The Back Up dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-1.)
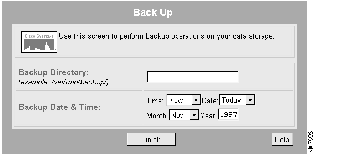
Step 4 Enter the fully qualified pathname name of a backup directory.
 | Caution Store back ups in a partition other than the one hosting the run-time database. If that partition becomes corrupted, your back up could also become corrupted if it resides on the same partition. |
Step 5 Enter the backup date and time, then click Next.
If you select Now, the database is backed up immediately.
Scenario: You discover your run-time database is corrupted and you want to restore the database.
To restore the database, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select System Admin > Restore Data.
The Restore message appears.
Step 3 Read the message, then click Next.
The Restore dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-2.)
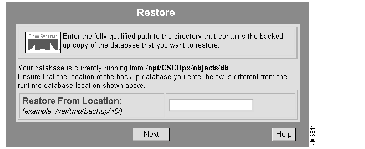
Step 4 Enter the fully qualified pathname of the directory containing the backed up database you want to use.
The database in that directory will be copied over your current database.
Scenario: You notice the file system containing the Resource Manager database is filling up and you need to move the current run-time database to a new location.
To move the database, perform the following procedure:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select System Admin > Move Data.
The Move message appears.
Step 3 Read the message, then click Next.
The Move dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-3.)
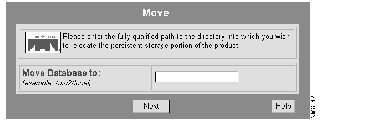
Step 4 Enter the fully qualified pathname of the directory to which you want to move the current run-time database.
 | Caution The entire application except for the web server will be shut down as part of this process. Be sure you are not running any critical tasks when you move the Resource Manager database. |
Step 5 Click Next.
The database is moved and restarted by Resource Manager.
Several of the network management and application management operations provided by Cisco Resource Manager are potentially disruptive to the network (for example, software image downloads) or the Cisco Resource Manager application itself (for example, stop a process, move the database) and need to be protected. To prevent such potentially disruptive operations from being used accidentally or maliciously, Resource Manager includes two-level security that allows access to such features only to users who can authenticate themselves.
The security features depend on the platform you are using.
Cisco Resource Manager for Solaris uses the Apache web server security mechanism. When Login is clicked, the user must enter a username and password. Administrator access is given if the user enters a valid username and password and is a member of the appropriate Apache group. Once logged in, the user remains logged in until the browser that initiated the login is completely closed.
Cisco Resource Manager for Windows NT uses the Windows NT user IDs and passwords and adds a plug-in for the Microsoft Internet Information Server (MSIIS) that manages authentication and protects specific URLs from unauthorized access.
Because the Windows NT version uses the Windows NT user system, Resource Manager does not provide the tools to add or delete users or change passwords. It relies on the Windows NT User Manager to perform these tasks.
Resource Manager enables the administrator to allow and disallow users access to administrator-level operations. A user must be an existing Windows NT user before access to administrator-level operations is allowed. Once such access is allowed, the user must log in as the allowed Windows NT user and use the password associated with that user. A user who is not on the allowed list will not be able to log in and therefore will not have access to protected operations. Once logged in, the user remains logged in until the browser that initiated the login is completely closed.
You can add and delete users and change passwords (Solaris systems) or allow and disallow users (Windows NT systems) by performing the tasks described in the following sections.
Scenario: Your company has just hired a new employee to help manage the network and you want to give the employee administrator-level privileges.
To add a user, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select User Accounts > Add Users.
The Add Users dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-4.)
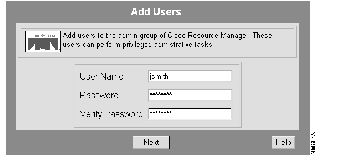
Step 3 Enter the username, password, and password verification, then click Next.
A confirmation message appears.
Scenario: An employee in the Resource Manager administration group has left your company. You need to delete the employee from the administrator-level user list.
To delete users, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select User Accounts > Delete Users.
The Delete Users dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-5.)
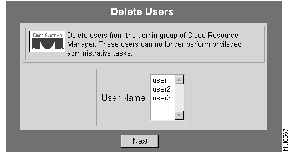
Step 3 Select the name of the user you want to delete from the list, then click Next.
A confirmation message appears.
Scenario: To ensure that your Resource Manager network is secure, you decide to change administrator-level passwords.
To change a password, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select User Accounts > Change Passwords.
The Change Passwords dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-6.)
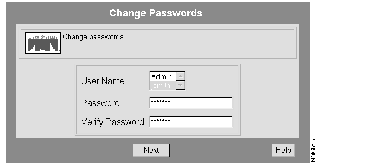
Step 3 Enter the username, new password, and password verification, then click Next.
The password is changed.
Scenario: You want to give administrator-level privileges to a user on the network.
To allow a user, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select User Accounts > Allow Users.
The Allow Users dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-7.)
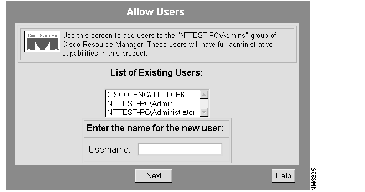
Step 3 Select a username from the List of Existing Users, then click Next.
A confirmation message appears.
Scenario: You want to disallow administrator privileges for a user on the network.
To disallow users, perform the following steps:
Step 1 
Log in with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Click Admin on the button bar, then select User Accounts > Disallow Users.
The Disallow Users dialog box appears. (See Figure 7-8.)
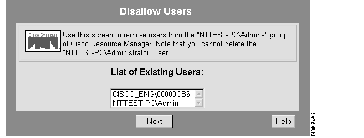
Step 3 Select a username from the List of Existing Users, then click Next.
A confirmation message appears.
|
|