|
|
This chapter provides information on Cisco's access server products. The information is organized into the following sections:
http://www.cisco.com. For more information, see the chapter "Documentation."
Cisco access servers include the following products:
The following software applications are used to enable Internet traffic to pass through access servers, use Internet applications, establish remote connections, and control access to networks:

This section compares the features of the Cisco access servers. Table 158 lists the features of Cisco access servers. Table 159 lists the environmental specifications for the Cisco access servers.
Table 158 : Cisco Access Server Series Summary of Features
| Characteristic | Cisco 2500 Series
Access Servers |
Cisco AS5100 Access Server | Cisco AS5200 Access Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported network interfaces | Ethernet
Synchronous serial Asynchronous serial Token Ring |
Ethernet
Synchronous serial Asynchronous serial |
Ethernet
Synchronous serial PRI/T1 |
| Maximum asynchronous connections | 8 or 16 | 48 | 48 |
| Slots available for network interface cards | -- | 16 | 3 |
| Choice of software feature sets | |||
| Cisco IOS Releases
11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 |
IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX Routing IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN1 Desktop Desktop with IBM base functionality Enterprise (includes IBM base functionality) Enterprise/APPN1 Remote Access Server RMON2 |
IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality IP/IPX Routing IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality Desktop Desktop with IBM base functionality Enterprise (includes IBM base functionality) Remote Access Server RMON2 |
IP Routing
IP/IPX Routing Desktop Enterprise RMON2 |
| Cisco IOS
Release 11.2 |
IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/APPN/Plus IP/APPN/Plus 40 IP/APPN/Plus 56 Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/APPN/Plus IP/APPN/Plus 40 IP/APPN/Plus 56 Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/APPN/Plus IP/APPN/Plus 40 IP/APPN/Plus 56 Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
| Flash memory | All Cisco 2500 series access server models include a minimum of 4 MB of Flash memory; however, depending on the Cisco IOS release level shipped with the system, they might require more memory. Refer to Table 175, later in this chapter, for the minimum Flash memory required for each feature set. | All Cisco AS5100 access server models include a minimum of 4 MB of Flash memory; however, depending on the Cisco IOS release level shipped with the system, they might require more memory. Refer to Table 175, later in this chapter, for the minimum Flash memory required for each feature set.3 Each access server card (AS51-16A-E) has one Flash SIMM socket; Cisco 2500 series access servers have two Flash SIMM sockets. | 4-MB boot Flash
8-MB system Flash |
| Memory expandability | All models include the minimum DRAM required by the Cisco IOS release level shipped with the system. Refer to Table 175, later in this chapter, for the minimum DRAM required for each feature set. | All models include the minimum DRAM required by the Cisco IOS release level shipped with the system. Refer to Table 175, later in this chapter, for the minimum DRAM required for each feature set.3 | All models include the minimum DRAM required by the Cisco IOS release level shipped with the system. Refer to Table 176, later in this chapter, for the minimum DRAM required for each feature set. |
| Dimensions
(H x W x D) |
1.75 x 17.5 x 10.56" (4.44 x 44.45 x 26.82 cm) | 7 x 19 x 18.5" (17.78 x 48.26 x 47.21 cm) | 3.5 x 17 x 15" (two rack units) |
| Weight
(average shipping) |
10 lb (4.5 kg) | 54.5 lb (24.4 kg) | 25 lb (11.4 kg) |
| Standard components | Power supply and cord
Console cable RJ-45-to-DB-25 and RJ-4-to-DB-9 adapters Rack-mount /wall-mount kit |
Power supply and cord
Console cable RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter Rack-mount /wall-mount kit |
Power supply and cord
Console cable 2 RJ-48 cables |
| Processor type | 20-MHz 68030 | 20-MHz 68030 | 20-MHz 68030 |
Table 159 : Cisco Access Server Series Environmental Specifications
| Description | Cisco 2500 Series Access Servers | Cisco AS5100 Access Server | Cisco AS5200 Access Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | 40W (135.5 Btu/hour) | Input:
Maximum: 475W (1621 Btu/hour), 4A (AC) or 9.9A (DC) Typical1: 325W (1105 Btu/hour), 2.7A (AC) or 6.8A (DC) Output: 325W +5V, 45A --5V, 2A +12V, 3.5A --12V, 3.5A |
180W (maximum), 135.5 Btus/hour |
| AC Input | 110 to 220 VAC
50 to 60 Hz 1.0 to 0.5A |
Strap selectable:
120V (90 to 132 VAC), 47 to 63 Hz or 240V (180 to 264 VAC), 47 to 63 Hz |
100 to 240 VAC
50 to 60 Hz 1.5 to 3.0A |
| DC Input | --48 VDC (Cisco 2509-DC and Cisco 2511-DC only) | --48 VDC (--42 to --60 VDC) | --48 VDC (--48 to --60 VDC) |
| Operating temperature range | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
| Nonoperating temperature range | --40 to 185°F (--40 to 85°C) | --40 to 185°F (--40 to 85°C) | --40 to 185°F (--40 to 85°C) |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 5 to 95% | 0 to 95% | 5 to 95% |
Table 160 lists the interfaces available for the Cisco access servers.
Table 160 : Cisco Access Server Interfaces
| Model | Ethernet | Token Ring | Serial | Asynchronous | PRI/T1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2509 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 0 |
| 2510 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 0 |
| 2511 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 16 | 0 |
| 2512 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 16 | 0 |
| AS5100 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 481 | 0 |
| AS5201 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
This section describes the available Cisco access servers that you can order.
Cisco 2500 Series Access Servers
The Cisco 2500 series access servers provide a variety of models designed for small office and remote site environments. Each model is a fixed-configuration router that supports at least two interface types. Each access server comes standard with Flash EPROM technology for simplified software maintenance. For software, the Cisco 2500 series access servers offer a wide choice of feature sets, so you can select the appropriate protocol set for your network environment. These feature sets range from IP and bridging-only to a feature set containing the full array of Cisco's software functionality. Table 161 lists the product numbers for the Cisco 2500 series access servers.
Table 161 : Cisco 2500 Series Access Server Product Numbers
| Model | Description | Product umber |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco 2509 | 1 Ethernet port, 2 serial ports, 8 asynchronous ports, AC power supply | CISCO2509 |
| Cisco 2509-DC | 1 Ethernet port, 2 serial ports, 8 asynchronous ports, DC power supply | CISCO2509-DC |
| Cisco 2510 | 1 Token Ring port, 2 serial ports, 8 asynchronous ports,
AC power supply |
CISCO2510 |
| Cisco 2511 | 1 Ethernet port, 2 serial ports, 16 asynchronous ports, AC power supply | CISCO2511 |
| Cisco 2511-DC | 1 Ethernet port, 2 serial ports, 16 asynchronous ports, DC power supply | CISCO2511-DC |
| Cisco 2512 | 1 Token Ring port, 2 serial ports, 16 asynchronous ports, AC power supply | CISCO2512 |
Figure 80 : Cisco 2509 Rear Panel
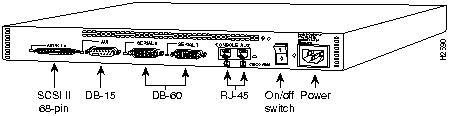
Figure 81 : Cisco 2510 Rear Panel
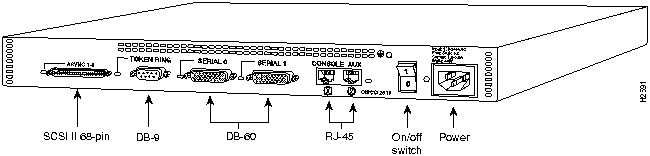
Figure 82 : Cisco 2511 Rear Panel
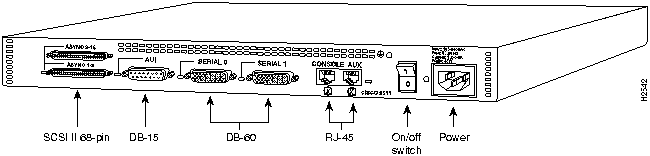
Figure 83 : Cisco 2512 Rear Panel
The Cisco AS5100 access server is a versatile data communications platform that combines in one chassis the functions of a Cisco access server with analog and digital modems, CSUs, and T1 channel banks.
The Cisco AS5100 access server provides the greatest benefit for organizations that need to centralize processing capabilities for remote offices and LANs. It enables organizations to aggregate their modem traffic onto analog or digital telephone lines and route it through the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
The Cisco AS5100 access server is optimized for high-speed modem access, and is ideally suited for all traditional dial-up applications, such as access to a host, electronic mail, file transfer, and dial-in access to a LAN.
The Cisco AS5100 access server is available with the following modems:
Each of the V.32 or V.34 modems is available as digital, analog, or analog/digital.
Figure 84 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server Front Panel
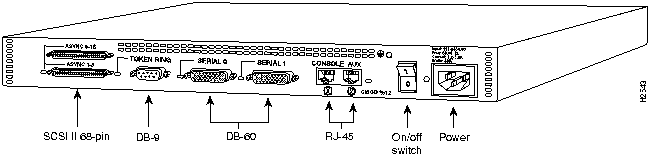
Figure 85 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server Rear Panel
The Cisco AS5100 access server consists of the following components:
The Cisco AS5100 access server is built around a three-bus chassis that can be managed by optional SNMP management software.
The midplane design supports a wide array of NACs and NICs that can be configured and installed in the chassis to meet diverse connectivity needs. The chassis provides 17 connectors in front for NACs, and 17 connectors in the rear for NICs. All NACs and most NICs can support hot-swapping, which allows you to insert and remove cards while the power is on.
Optional AC or DC-powered chassis are available. DC power is supplied to the installed NICs and NACs via connectors in the midplane. All configured chassis from Cisco Systems include two power supplies. One unit provides sufficient power to a fully loaded chassis, and the second provides full redundancy.
The T1 NIC provides a four-wire T1 interface to the Cisco AS5100 access server, and the T1 NAC provides mapping of individual DS0s to the quad modem NACs across the Time Division Multiplexer (TDM) bus.
The T1 NIC is available as a dual-trunk version, which handles up to 48 DS0 channels from two trunks. Each channel carries either a pulse code modulation (PCM)-encoded voice channel or digital data. The T1 NAC supports 64-kbps clear channel operation for data channels, and supports Feature Group B for voice channels. Again, each of the DS0 channels connect to other NACs via the midplane.
The T1 NIC provides RJ-48 connector(s) to terminate the trunk(s). It also provides an RJ-45 connector for the EIA/TIA-232 interface port. The T1 NIC performs all CSU functions including auto equalization and auto gain functions to support 6000 feet of 24-gage shielded cable. This card complies with all Bell Core standards relating to T1 alarms, loopbacks, error detection, and so forth. The T1 NIC is compatible with an external CSU if desired, and provides a serial interface to the T1 NAC.
The T1 NAC allows you to use dial number identification string (DNIS) and automatic number identification (ANI) information provided by the public 950 services, Feature Groups B and D, and enhanced 800 services to route data. Using this call information, the Cisco AS5100 access server chassis can independently configure the specific modems according to the dialed number requirements.
The T1 cards support the following features:
The network management NAC and NIC cards act as proxy agents for the T1 and modem cards in the chassis. The NAC and NIC cards communicate with the T1 and modem cards over a dedicated management bus on the midplane. An SNMP console communicates with the management cards via a serial console port or over a LAN interface. Total Control Manager (TCM) software provides users with easy and immediate access to configuration/management of the modem and T1 card sets.
The access server NAC and associated NIC cards function as a communications server system with 16 asynchronous serial ports, one synchronous serial port, and one 10BaseT Ethernet port. Up to three access server cards can be installed in each Cisco AS5100 access server chassis. Each one is functionally equivalent to a standalone Cisco 2511, with the following exceptions:
Each chassis houses up to 48 high-speed analog or digital modems. Digital modems connect to the phone system by a direct T1 link through the T1 NIC. Modems can be managed with software ranging from a simple terminal interface menu system for device configuration or via SNMP using the network management card.
The quad modem cards provide four dial-up modems on a single card. Each modem is capable of supporting V.32 or V.34 and MNP-5 or V.42/V.42bis error correction and data compression.
The modem can also make use of the DNIS and ANI information provided by the public 950 services, Feature Groups B and D, and enhanced 800 services to customize the configuration of the modem before answering a call. For example, the dialed phone number can be associated with specific applications, and the same modem pool can be dynamically configured on a call-by-call basis to adjust to the requirements of the application.
The Quad EIA/TIA-232 NIC provides the physical interface for four EIA/TIA-232 ports via a 50-pin connector on the rear of the card.
Each EIA/TIA-232 port supports the full complement of EIA/TIA-232 signals necessary for synchronous or asynchronous operation. The ports support operation at speeds up to 115.2 kbps, and provide four serial interfaces to the quad modem NAC.
The modem cards support the following features:
Cisco AS5100 Access Server Network Management Products
The Cisco AS5100 access server uses two network management products:
Cisco AS5100 Access Server Product Numbers
This section contains tables that list Cisco AS5100 access server product numbers. For document product numbers, see the chapter "Documentation" later in this catalog.
Table 162 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server Systems
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Complete chassis, AC, Ethernet network management card, and console cable | AS5101-A |
| Complete chassis, DC, Ethernet network management card, and console cable | AS5101-D |
Table 163 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server System Spares or Options
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| AS5100 16-slot AC chassis | AS51-CHAS-A= |
| AS5100 16-slot DC chassis | AS51-CHAS-D= |
| AS5100 AC-45A power supply | AS51-PWR-A= |
| AS5100 DC-45A power supply | AS51-PWR-D= |
| AS5100 AC fan tray1 | AS51-FAN-A= |
| AS5100 DC fan tray1 | AS51-FAN-D= |
| Cables | See Table 169 |
Table 164 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server Interface Card Sets
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| AS5100 Ethernet network management card set | AS51-NMCS-E= |
| AS5100 dual T1 card set | AS51-2T |
| Quad V.34 digital modem set | AS51-4V34D |
| Quad V.34 analog modem set | AS51-4V34A |
| Quad V.34 analog/digital modem set | AS51-4V34AD |
| Access Server card set---16A, 1E, 1T1 | AS51-16A-E |
Cisco AS5100 Access Server Bundled Systems
Although the Cisco AS5100 access server is a modular chassis that can be customized for your particular networking needs, it is also available in five different bundled systems (fixed hardware configurations) for North America only.
Table 165 describes the Cisco AS5100 access server bundled systems. Enterprise software can be ordered for bundled systems ending in "EN," and Remote Access Server software can be ordered for bundled systems ending in "RAS."
Table 165 : Cisco AS5100 Access Server Bundled Systems
| Description | Included Items | Bundled System Product Number |
|---|---|---|
| 48-port digital V.34 modem system with AC power supply and Cisco IOS Enterprise software feature set | 1 17-slot AC chassis (AS51-CHAS-A=)
2 45A power supplies (AS51-PWR-A=) 1 fan tray (AS51-FAN-A=) 1 Ethernet network management card set (AS51-NMCS-E=) 1 console cable (ACS-2500ASYN) 1 U.S. power cord (AS-KIT-US) 1 dual T1 card set (AS51-2T) 12 quad V.34 digital modem card sets (AS51-4V34D) 3 access server card sets (AS51-16A-E), which include 6-MB DRAM (2 MB soldered and 4 MB on SIMM) and 8-MB Flash memory on each access server card set 3 CiscoRemote Plus software user licenses |
AS51AC-48V34D-EN |
| 48-port digital V.34 modem system with DC power supply and Cisco IOS Enterprise software feature set | 1 17-slot DC chassis (AS51-CHAS-D=)
2 45A power supplies (AS51-PWR-D=) 1 fan tray (AS51-FAN-A=) 1 Ethernet network management card set (AS51-NMCS-E=) 1 console cable (ACS-2500ASYN) 1 U.S. power cord (AS-KIT-US) 1 dual T1 card set (AS51-2T) 12 quad V.34 digital modem card sets (AS51-4V34D) 3 access server card sets (AS51-16A-E), which include 6-MB DRAM (2 MB soldered and 4 MB on SIMM) and 8-MB Flash memory on each access server card set 3 CiscoRemote Plus software user licenses |
AS51DC-48V34D-EN |
| 48-port digital V.34 modem system with AC power supply and Cisco IOS Remote Access Server software feature set | 1 17-slot AC chassis (AS51-CHAS-A=)
2 45A power supplies (AS51-PWR-A=) 1 fan tray (AS51-FAN-A=) 1 Ethernet network management card set (AS51-NMCS-E=) 1 console cable (ACS-2500ASYN) 1 U.S. power cord (AS-KIT-US) 1 dual T1 card set (AS51-2T) 12 quad V.34 digital modem card sets (AS51-4V34D) 3 access server card sets (AS51-16A-E), which include 6-MB DRAM (2 MB soldered and 4-MB on SIMM) and 4-MB Flash memory on each access server card set 3 CiscoRemote Plus software user licenses |
AS51AC-48V34D-RAS |
| 16-port digital V.34 modem system with AC power supply and Cisco IOS Enterprise software feature set | 1 17-slot AC chassis (AS51-CHAS-A=)
2 45A power supplies (AS51-PWR-A=) 1 fan tray (AS51-FAN-A=) 1 Ethernet network management card set (AS51-NMCS-E=) 1 console cable (ACS-2500ASYN) 1 U.S. power cord (AS-KIT-US) 1 dual T1 card set (AS51-2T) 4 quad V.34 digital modem card sets (AS51-4V34D) 1 access server card set (AS51-16A-E), which includes 6-MB DRAM (2 MB soldered and 4 MB on SIMM) and 8-MB Flash memory 1 CiscoRemote Plus software user license |
AS51AC-16V34D-EN |
| 16-port digital V.34 modem system with AC power supply and Cisco IOS Remote Access Server software feature set | 1 17-slot AC chassis (AS51-CHAS-A=)
2 45A power supplies (AS51-PWR-A=) 1 fan tray (AS51-FAN-A=) 1 Ethernet network management card set (AS51-NMCS-E=) 1 console cable (ACS-2500ASYNC) 1 U.S. power cord (AS-KIT-US) 1 dual T1 card set (AS51-2T) 4 quad V.34 digital modem card sets (AS51-4V34D) 1 access server card set (AS51-16A-E), which includes 6-MB DRAM (2 MB soldered and 4 MB on SIMM) and 4-MB Flash memory 1 CiscoRemote Plus software user license |
AS51AC-16V34D-RAS |
Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server
The Cisco AS5200 universal access server is a versatile data communications platform that provides the functions of an access server, a router, and digital modems in a single modular chassis. The Cisco AS5200 is intended for Internet Service Providers (ISPs), telecommunications carriers, and other providers that offer managed Internet connections, as well as small- to medium-sized sites that provide both digital and analog access to users on an enterprise network. By terminating both analog and digital calls on the same chassis simultaneously, the Cisco AS5200 provides you with a clear, simple, and easy migration path from today's predominantly analog dial-in services to tomorrow's digital dial-in services.
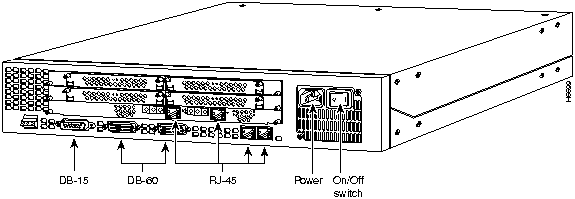
Figure 86 : Cisco AS5200 Access Server Front Panel

Figure 87 : Cisco AS5200 Access Server Rear Panel
Cisco AS5200 Access Server Summary of Benefits
The unique combination of Cisco IOS software and the Cisco AS5200 access server mixed-media platform results in a host of benefits for network managers.
Universal Access
The Cisco AS5200 universal access server is the first product in an entire line of universal access solutions offered by Cisco Systems. Universal access is more than just providing connections from ISDN or asynchronous modems; it is also the ability to perform the following:
The Cisco AS5200 access server provides universal access for small- to medium-sized dial-in sites. This access enables you to save money by using one trunk line, instead of two, for all calls, which reduces the number of system components and operational costs. The Cisco AS5200 access server also supports the widest array of networking and routing protocols available in the industry. Not only does the Cisco AS5200 access server support remote node and remote LAN dial-in protocols, but it also supports all of the Cisco IOS-supported routing protocols.
Scalability
The scalability and manageability of a network are a concern for all network managers. With Cisco IOS Software Release 11.2, the Cisco AS5200 access server will support call aggregation among multiple chassis. Using multichassis, Multilink PPP, Cisco Systems has developed the means to aggregate multiple calls terminated on multiple servers. Network managers will have the ability to stack multiple AS5200 access servers for high-density applications.
Another important feature of scalability is managing the components of a growing network. The Cisco AS5200 access server supports both the command line interface and the CiscoWorks graphical user interface (GUI). Network managers can collect statistics from the modems, upgrade your modem software, group modems for configuration, soft- or hard-busy-out modems, and even monitor call-in-progress signals from individual modems, all from the same platform they already use to manage their routers.
Security
Cisco IOS software provides tight security in the core network, and with the Cisco AS5200 access server, extends that core security to mixed-media dial-in sites. Some of the features supported by the Cisco IOS are access lists, violation logging, Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+), and RADIUS.
WAN Optimization
Cisco offers a wide array of WAN optimization features, including compression, routing filters, snapshot, bandwidth-on-demand, and dial-on-demand routing. These features help control WAN costs---the largest single cost of operating an internetwork.
Single Vendor Support
With the Cisco AS5200 access server, the router, access server, integrated CSUs, and modems are all supported by Cisco's world class 7-days-a-week, 24-hours-a-day global support team.
Compatibility
With the CSU, modems, routers, and access server components integrated in one chassis, the Cisco AS5200 access server has been designed to avoid incompatibility concerns that plague multibox, multivendor installations, and for seamless interoperability among its integrated components. Fewer individual pieces of equipment reduce configuration and incompatibility issues.
Cisco AS5200 Access Server Feature Cards
The following feature cards are available for the Cisco AS5200 access server. These cards are not hot swappable.
Dual T1/PRI Card
Each Cisco AS5200 access server must have one dual T1/PRI card installed in the chassis. The system does not support more than one of these cards. This card provides the channelized interface necessary to handle digital and analog calls that are terminated in the unit. The card is software switchable between channelized T1 and ISDN PRI. You can configure the card so that both ports are channelized T1, or both ports are ISDN PRI, but not one of each. If you configure the card to support ISDN PRI, it can terminate analog modem calls and ISDN BRI calls. The card determines which type of call is coming in by reading the Q.931 signaling in the ISDN D channel associated with each PRI line. In dual PRI mode, the card can handle 23 B channels plus one D channel on each line, for a total of 46 B channels and 2 D channels. The ability to combine more than one PRI line's signaling into one D channel (47B + 1D), which is known as NFAS, is not currently available.
Carrier Card
The carrier card can hold up to two 12-port modem modules. You can configure a Cisco AS5200 access server to support up to two carrier cards. If you order a Cisco AS5200 access server with modems, it must have one carrier card for each two modem cards ordered.
Microcom Select V.34 12-Port Module
The Select modem module contains 12 manageable modems. These modems are Flash based, so you can upgrade their microcode remotely. You can order up to two of these modules with a carrier card. These modems support real time call-in-progress monitoring. No additional memory is required to support this feature.
The Cisco AS5200 access server supports multiple modem technology and provides centrally managed modem capabilities---key requirements for service providers and enterprises building large dial-in pools. The Cisco AS5200 access server features an open modem architecture of Microcom modems. This enables you to maximize modem coverage with higher performance while leveraging your installed technology base. The Cisco AS5200 access server offers the most complete modem management capabilities, providing network managers with one solution at a central management location. For example, the same management platform is used to manage both routers and modems, significantly streamlining network management. In addition, incoming modem calls can be managed in progress rather than after the call. This allows for fast troubleshooting and analysis.
Microcom Reliable V.34 12-Port Module
The reliable modem module contains 12 unmanageable modems. These modems are Flash based, so you can upgrade their microcode remotely. These modems are not upgradable to Select modems. You can order up to two of these modules with a carrier card. These modems cannot support real time call-in-progress monitoring---the ability to determine the state of a modem at any point in time.
Carrier Card with Two Microcom Modules
You can order a carrier card with two Select or Reliable modem modules.
Table 166 lists the product numbers for the Cisco AS5200 access server.
Table 166 : Cisco AS5200 Access Server Product Numbers
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Ethernet AS5200 chassis with AC power supply | AS5201 |
| Ethernet AS5200 chassis with DC power supply | AS5201-DC |
| Ethernet AS5210 bundled system includes an Ethernet (AS5201) chassis with AC power supply, 48 Reliable modems, a dual T1 card, and IP only software | AS5210 |
| Ethernet AS5210 bundled system includes an Ethernet (AS5201) chassis with DC power supply, 48 Reliable modems, a dual T1 card, and IP only software | AS5210-DC |
| Dual T1/PRI card | AS52-2CT1 |
| Carrier card | AS52-MC1 |
| Carrier card with two Microcom Select modules | AS52-24B-MCOM-V34/R |
| Carrier card with two Microcom Reliable modules | AS52-24B-MCOM-V34 |
| Microcom Reliable V.34 12-port module | AS52-12-MCOM-V34 |
| Microcom Select V.34 12-port module | AS52-12-MCOM-V34/R |
| AS5210 Reliable modem upgrade to Microcom
Select modems |
AS5210-MCOM-SEL-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to IP/IPX software | AS5210-IP/IPX-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to DT software | AS5210-DT-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to enterprise software | AS5210-ENT-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to IP/modem software | AS5210-IP/RM-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to IP/IPX/modem software | AS5210-IP/IPX/RMN-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to DT/modem software | AS5210-DT/RM-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to enterprise/modem software | AS5210-ENT/RM-UPGD |
| AS5210 upgrade to enterprise/RMON/modem software | AS5210-ENT/ARM-UPGD |
Hardware Options for All Access Servers
The Cisco access server series supports the hardware options listed in the following tables. If a product number ends with an equal sign (=), the item can be ordered only as a spare. If a product number does not end with an equal sign, the item can be ordered as a spare or as a configurable part of a system order.
| Option | Cisco 2500 Series Access Servers | Cisco AS5100 Access Server |
|---|---|---|
| 19" rack-mount kit | ACS-2500RM-19= | -- |
| 24" rack-mount kit | ACS-2500RM-24= | -- |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-2509/12= | -- |
| 4-MB DRAM | MEM-1X4D | -- |
| 4-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X4D= | MEM-1X4D= |
| 8-MB DRAM | MEM-1X8D | -- |
| 8-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X8D= | -- |
| 16-MB DRAM | MEM-1X16D | MEM-1X16D |
| 16-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X16D= | MEM-1X16D= |
| 4-MB Flash SIMM | MEM-1X4F | -- |
| 4-MB Flash SIMM (spare) | MEM-1X4F= | MEM-1X4F= |
| 4- to 8-MB Flash SIMM upgrade | MEM-1X8F-U1 | MEM-1X8F-DFB-U1, 2 |
| 8-MB Flash SIMM | MEM-1X8F | MEM-1X8F |
| 8-MB Flash SIMM (spare) | MEM-1X8F= | MEM-1X8F-DFB=2 |
| 8-MB Flash SIMM | MEM-1X8F-U | -- |
| Dual-sided 16-MB Flash SIMM | -- | MEM-1X16F-DFB3 |
| Dual-sided 16-MB Flash SIMM (spare) | -- | MEM-1X16F-DFB=3 |
Table 168 : Cisco AS5200 Access Server Hardware Options
| Option | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Memory Upgrades | |
| 4-MB shared DRAM upgrade (for total of 8 MB) | MEM-8S-52= |
| 12-MB shared DRAM upgrade (for total of 16 MB) | MEM-16S-52= |
| 4-MB main DRAM upgrade (for total of 8 MB) | MEM-8M-52= |
| 12-MB main DRAM upgrade (for total of 16 MB) | MEM-16M-52= |
| 4-MB boot Flash upgrade (for total of 8 MB) | MEM-8BF-52= |
| Spares | |
| Dual T1/PRI card | AS52-2CT1= |
| Carrier card with two Microcom Select modules | AS52-24B-MCOM-V-34/R= |
| Carrier card with two Microcom Reliable modules | AS52-24B-MCOM-V-34= |
| Carrier card | AS52-MC1= |
| Microcom Select V.34 12-port module | AS52-12-MCOM-V34/R= |
| Microcom Reliable V.34 12-port module | AS52-12-MCOM-V34= |
| AS5200 modem blank panel | AS52M-BLANK= |
| AS5200 blank panel | AS52-BLANK= |
| Options for the AS5210 Bundled System | |
| AS5210 modem upgrade to Microcom Select module | AS5210-MCOM-SEL-UPGD |
Table 169 : Cisco Access Server Cables
| Cables1 | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Synchronous serial2 | |
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232MT |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232FC |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449MT |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449FC |
| EIA-530 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-530MT |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35MT |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35FC |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21MT |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21FC |
| Auxiliary/console port cable kit2 | ACS-2500ASYN |
| Asynchronous serial | |
| 8lead octal cable and 8 male DB-25 modem connectors | CAB-OCTAL-KIT |
| 8lead octal cable (68-pin to 8 male RJ-45 connectors) | CAB-OCTAL-ASYNC |
| 8lead octal cable and 8 female DB-25 terminal connectors | CAB-OCTAL-FDTE |
| 8-lead octal cable and 8 male DB-25 modem connectors | CAB-OCTAL-MODEM |
| Male DB-25 modem connector | CAB-25AS-MMOD |
| Female DB-25 terminal connector | CAB-25AS-FDTE |
| 8 female RJ-45 to female RJ-45 adapters | CAB-ADPTRS-RJ45 |
| Cisco AS5100 cables | |
| 8A cable from card set to two quad modem cards3 | CAB-AS51-8= |
This section describes the Cisco IOS software releases and other software options available for Cisco access servers.
Note that all Cisco AS5100 access server cards (AS51-16A-E) must use the same Cisco IOS release level and feature set.
With the introduction of Cisco IOS Release 11.2, feature sets have been updated to make it easier to select the exact feature sets you need. Feature sets names are simplified and are more consistent across Cisco hardware platforms. In addition, you can add options to the standard feature set offerings. These options provide additional features and value based on the hardware platform selected. Cisco also continues to offer specialized feature sets for key applications.

Cisco access servers offer the following types of feature sets:
Cisco IOS images with 40-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) support may legally be distributed to any party eligible to receive Cisco IOS software. 40-bit DES is not a cryptographically strong solution and should not be used to protect sensitive data.
Cisco IOS images with 56-bit DES are subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) controls and have a limited distribution. Images to be installed outside the U.S. require an export license. Orders may be denied or subject to delays due to U.S. Government regulations. Contact your sales representative or distributor for more information, or send e-mail to export@cisco.com.
The new feature set tables use the following conventions to identify features:
| Cisco 2500 Series and AS5100 Access Server Feature Sets | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | IP Routing | IP/IPX/
IBM/ APPN1 |
IP/IPX Routing2 | Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) | Enterprise3 | |||||||||||||||
| Cisco IOS Release | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 |
| LAN Support | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 24 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)5 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Novell IPX6 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Source-route bridging7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Services | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay SVC Support (DTE) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay traffic shaping | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for
CPP and PPP |
X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ISDN8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PPP9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMDS | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| X.2510 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header11, link and payload compression12 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IP Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| BGP413 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Named IP Access Control List | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NHRP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSPF Not-So-Stubby-Areas (NSSA) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF On Demand Circuit (RFC 1793) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Other Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AURP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NLSP14 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| RTMP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| SRTP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Management | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration15 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON events and alarms16 | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON full | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Kerberos V client support | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Lock and key | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| MAC security for hubs17 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Network layer encryption
(export controlled 40-bit and 56-bit DES)18 |
Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RADIUS | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Router authentication | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| TACACS+19 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IBM Support (Optional) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| APPN (optional)3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Bisync20 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Caching and filtering | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DLSw+ 21 | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay SNA support
(RFC 1490) |
Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA) Server | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NetView Native Service Point | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| QLLC20 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Response Time Reporter (RTR) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SDLC integration | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization via local acknowledgment | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB22, 23 | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | |
| SRT | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Protocol Translation | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rlogin | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Remote Node24 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ARAP 1.0/2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| ATCP25 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| CPPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| IP pooling | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPX and ARAP on virtual asynch interfaces | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPXCP11 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| MacIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NASI26 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| NetBEUI over PPP | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| PPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services24 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT27 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Xremote | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Cisco 2500 Series and AS5100
Remote Access Feature Set |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Remote Access Server | ||||
| Cisco IOS Releases | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 |
| Platforms Supported | |||||
| Cisco 2509-2512
AS5100 access server |
X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN Support | |||||
| AppleTalk 1 and 21 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| DECNet IV | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)2 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | X |
| Novell IPX3 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Source-route bridging | -- | -- | -- | -- | X |
| WAN Services | |||||
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay | X | X | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for CPP and PPP | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PPP4 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| X.255 | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | |||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand6 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header7, link and payload compression8 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header8 and link compression | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IP Routing | |||||
| BGP | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| EGP | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X |
| NHRP | -- | -- | X | X | -- |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Other Routing | |||||
| AURP | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | X | X | X | X | X |
| RTMP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | |||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Management | |||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration9 | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON events and alarms10 | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | |||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X |
| Lock and Key | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| RADIUS | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| TACACS+11 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Protocol Translation | |||||
| LAT | X | X | X | X | X |
| PPP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | X | X | X | X | X |
| X.25 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Remote Node12 | |||||
| ARAP 1.0/2.0 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| ATCP | X | X | X | X | -- |
| CPPP | X | X | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X | X | -- |
| IP pooling | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPX and ARAP on virtual asynch interfaces | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPXCP13 | X | X | X | X | X |
| MacIP | X | X | X | X | X |
| PPP | X | X | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services12 | |||||
| LAT14 | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | X | X | X | X | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X | X | X |
| Xremote | X | X | X | X | X |
Table 172 : Cisco IOS Release 11.2 and 11.1---Cisco AS5200 Access Server Feature Sets
| Cisco AS5200 Access Server Feature Sets | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | IP Routing | IP or
IP/Modem |
Desktop | Desktop or
Desktop/ Modem |
Enterprise1 |
Enterprise or Enterprise/ RMON/Modem |
| Cisco IOS Release | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.2 | 11.1 |
| LAN Support | ||||||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 22 | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)3 | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Novell IPX4 | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Source-route bridging (SRB) | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging5 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| WAN Services | ||||||
| ATM LAN emulation: Rate queues for SVC per subinterface | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- |
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Frame Relay | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay SVC Support (DTE) | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- |
| Frame Relay traffic shaping | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for CPP and PPP | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| ISDN6 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| PPP7 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMDS | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | -- | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| X.258 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | ||||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header9, link and payload compression10 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IP Routing | ||||||
| BGP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| BGP411 | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| EGP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Named IP Access Control List | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | Plus | -- |
| NHRP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSPF Not-So-Stubby-Areas (NSSA) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| OSPF On Demand Circuit (RFC 1793) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Other Routing | ||||||
| AURP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| NLSP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| RTMP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| SRTP | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | ||||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Management | ||||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration12 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | X | -- | X | -- |
| Modem Management | Plus | X | Plus | X | Plus | X |
| RMON events and alarms13 | Plus | X | Plus | X | Plus | X |
| RMON full | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | Plus | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | ||||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Kerberos V client support | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- |
| Lock and key | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| MAC security for hubs | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RADIUS | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TACACS+14 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IBM Support (Optional) | ||||||
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| Bisync | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| Caching and filtering | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| DLSw+ 15 | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Frame Relay SNA support (RFC 1490) | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA) Server | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | -- |
| NetView Native Service Point | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| QLLC | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| Response Time Reporter (RTR) | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | -- |
| SDLC integration | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| RFC 1795 | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization
via local acknowledgment |
Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB16 | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| SRT | Plus | -- | Plus | -- | X | X |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Protocol Translation | ||||||
| LAT | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Rlogin | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Remote Node17 | ||||||
| ARAP 1.0/2.0 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ATCP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| CPPP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IP pooling | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX and ARAP on virtual asynch interfaces | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| IPXCP11 | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| MacIP | -- | -- | X | X | X | X |
| NASI18 | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NetBEUI over PPP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services17 | ||||||
| LAT19 | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Xremote | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X |
The Remote Monitoring (RMON) MIB (RFC 1757) allows you to monitor all nodes and their interaction on a LAN segment. Standard Cisco IOS Release 11.1 feature sets provide support for RMON events and event groups only. If you prefer more network management support, you can order an enhanced RMON feature set that includes full support for the following nine groups: statistics, history, alarms, hosts, hostTopN, matrix, filter, capture, and events. Table 173 describes the contents of the enhanced IP/RMON, IP/IPX/RMON, and Enterprise/RMON feature sets.
In Cisco IOS Release 11.2, the feature RMON full is available in the Plus feature sets.
Table 173 : Cisco IOS Release 11.1---RMON Platform-Specific Feature Sets
| RMON Platform-Specific Feature Sets1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Features
|
IP/RMON Routing | P/IPX/RMON Routing | Enterprise/
RMON |
| Cisco IOS Releases | 11.1 | 11.1 | 11.1 |
| Platforms Supported | |||
| Cisco 2500 series routers: Ethernet models 2501, 2503, 2505, 2507, 2509, 2511, 2513, 2514, 2516, 2518, 2520, 2522, 2524
AS5100 access server |
X | X | X |
| LAN Support | |||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 2 | -- | -- | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging | X | X | X |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | X |
| GRE | X | X | X |
| IP | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X |
| Novell IPX | -- | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging2 | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | X |
| WAN Services | |||
| Frame Relay | X | X | X |
| HDLC | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | X | X |
| ISDN3 | X | X | X |
| PPP4 | X | X | X |
| SMDS | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X |
| X.255 | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | |||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X |
| Header6, link and payload compression7 | X | X | X |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X |
| IP Routing | |||
| BGP | X | X | X |
| EGP | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | X |
| NHRP | X | X | X |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X |
| PIM | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | X |
| Other Routing | |||
| AURP | -- | -- | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | X | X |
| NLSP | -- | X | X |
| RTMP | -- | -- | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | X |
| SRTP | -- | -- | X |
| Management | |||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration | X | X | X |
| RMON nine-group Ethernet8 | X | X | X |
| SNMP | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X |
| Security | |||
| Access lists | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | X |
| Lock and key | X | X | X |
| MAC security for hubs9 | X | X | X |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X |
| RADIUS | X | X | X |
| TACACS+ | X | X | X |
| IBM Support (Optional)10 | |||
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | X | X | X |
| Bisync | X | X | X |
| Caching and filtering | X | X | X |
| DLSw+ | X | X | X |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | X |
| Frame Relay SNA support (RFC 1490) | X | X | X |
| NetView Native Service Point | X | X | X |
| QLLC | X | X | X |
| SDLC integration | X | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | X | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | X | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization
via local acknowledgment |
X | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB | X | X | X |
| SRT | X | X | X |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | X |
| Protocol Translation | |||
| LAT | -- | -- | X |
| PPP | -- | -- | X |
| Rlogin | -- | -- | X |
| Telnet | -- | -- | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | X |
| X.25 | -- | -- | X |
| Remote Node11 | |||
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X |
| ATCP | -- | -- | X |
| CPPP | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X |
| IP pooling | X | X | X |
| IPX on virtual asynch interfaces | -- | X | X |
| IPXCP6 | -- | X | X |
| MacIP | -- | -- | X |
| NASI12 | -- | X | X |
| NetBEUI over PPP | X | X | X |
| PPP | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services11 | |||
| LAT13 | -- | -- | X |
| Rlogin | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X |
| Xremote | -- | -- | X |
Memory Options and Software Product Numbers
Table 174 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for the Cisco 2500 series and AS5100 access servers for Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Table 175 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for the Cisco 2500 series and AS5100 access servers for Cisco IOS Releases 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2. For additional details about how to order software updates and upgrades, see the section "Cisco IOS Feature Set Upgrades" later in this chapter.
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | ||||
| Feature Set | Product Number1 | Access Server Model | Flash | Total DRAM |
| IP | SF25C-11.2.1 SW25C-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 4 MB | 2 MB2 |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| IP Plus | SF25CP-11.2.1 SW25CP-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| IP Plus 40 | SF25CW-11.2.1
SW25CW-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| IP Plus 56 | SF25CY-11.2.1
SW25CY-11.2.1 |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop | SF25B-11.2.1 SW25B-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop Plus | SF25BP-11.2.1
SW25BP-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop Plus 40 | SF25BW-11.2.1
SW25BW-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop Plus 56 | SF25BY-11.2.1
SW25BY-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise | SF25A-11.2.1 SW25A-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise Plus | SF25AP-11.2.1 SW25AP-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise Plus 40 | SF25AW-11.2.1 SW25AW-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise Plus 56 | SF25AY-11.2.1 SW25AY-11.2.1= | 2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus | SF25ANP-11.2.1
SW25ANP-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 16 MB | 8 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 | SF25ANW-11.2.1
SW25ANW-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 16 MB | 8 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 | SF25ANY-11.2.1
SW25ANY-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 16 MB | 8 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| ISDN | SF25I-11.2.1
SW25I-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 4 MB | 2 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| CFRAD | SF25F-11.2.1
SW25F-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 4 MB | 2 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| LANFRAD | SF25LF-11.2.1
SW25LF-11.2.1= |
2500 series | 4 MB | 2 MB |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | ||
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Releases | ||||||||||
| 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | |||||||
| Feature Set | Product Number1 | Access
Server Model |
Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM |
| IP | SF25C-xx.x.x
SW25C-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| IP with IBM base | SF25CS-xx.x.x
SW25CS-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| IP/IPX | SF25D-xx.x.x
SW25D-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| IP/IPX with IBM base | SF25DS-xx.x.x
SW25DS-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| IP/IPX with IBM base and APPN2 | SF25DSN-xx.x.x
SW25DSN-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 8 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop | SF25B-xx.x.x
SW25B-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| Desktop with IBM base | SF25BS-xx.x.x
SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | ||
| Enterprise | SF25A-xx.x.x
SW25A-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB |
| AS5100 | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | ||
| Enterprise with APPN2 | SF25AN-xx.x.x
SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
2500 series | 16 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Remote Access Server | SW25E-xx.x.x= | 2500 series | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB |
| AS5100 | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | ||
| IP and RMON2, 3 | SF25CR-xx.x.x
SW25CR-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 4 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP with IBM and RMON 2, 3 | SF25CSR-xx.x.x
SW25CSR-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP/IPX and RMON2, 3 | SF25DR-xx.x.x
SW25DR-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP/IPX with IBM and RMON2, 3 | SF25DSR-xx.x.x
SW25DSR-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 8 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise and RMON2, 3 | SF25AR-xx.x.x
SW25AR-xx.x.x |
2500 series | 8 MB | 6 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| AS5100 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
Table 176 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for the Cisco AS5200 access server for Cisco IOS Releases 11.2 and 11.1.
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Releases | |||||||||
| Cisco IOS 11.2 | Cisco IOS 11.1 | ||||||||
| Feature Set | Product Number1 | Boot
Flash |
Main
DRAM |
System
Flash |
Shared DRAM | Boot
Flash |
Main
DRAM |
System
Flash |
Shared DRAM |
| IP | SF52C-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| IP/IPX | SF52D-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| Desktop | SF52B-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| Enterprise | SF52A-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| IP/Modem | SF52CR-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| IP/IPX/Modem | SF52DR-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| Desktop/Modem | SF52BR-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| Enterprise/Modem | SF52AR-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
| Enterprise/RMON/
Modem |
SF52ARM-xx.x.x | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB |
There are two types of DRAM memory in the Cisco 2500 series and AS5100 access servers: primary and shared (packet). Primary memory is used to store the operating configuration, routing tables, caches, queues, and packets. Shared memory is used to store incoming and outgoing packets. In Table 177 and Table 178, the physical configuration column lists the amount of fixed DRAM and DRAM SIMM memory supported. The system usage column lists how the system allocates the total DRAM memory installed.
Table 177 : Recommended Shared and Primary DRAM Memory---Cisco 2500 Series Access Servers
| Physical Configuration | System Usage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total DRAM
Memory |
Fixed DRAM1 | DRAM SIMM | Shared DRAM
Memory |
Primary DRAM Memory |
| 4 MB | -- | 4 MB | 2 MB | 2 MB |
| 6 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB |
| 8 MB | -- | 8 MB | 2 MB | 6 MB |
| 10 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB |
| 16 MB | -- | 16 MB | 2 MB | 14 MB |
| 18 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB |
Table 178 : Recommended Shared and Primary DRAM Memory---Cisco AS5100 Access Servers
| Physical Configuration | System Usage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total DRAM Memory | Fixed DRAM1 | DRAM SIMM | Shared DRAM
Memory |
Primary DRAM Memory |
| 6 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB |
| 10 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB |
| 18 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB |
Cisco IOS Feature Set Upgrades
Cisco IOS Release 11.2 for the Cisco access servers allows software upgrades that cross multiple feature sets. This will require you to order multiple feature set licenses. The following is an example:
You have a Cisco 2511 access server running the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 IP Routing feature set. You want to upgrade to the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 Enterprise Plus 40 feature set. You are crossing two feature sets: one to get from IP to Enterprise, and one to get to the Plus 40 feature set. To complete the upgrade, use the following guidelines:
Feature sets for Cisco IOS Releases 11.2 can be upgraded as described in Table 179. Adding a feature set may require you to purchase additional memory. The minimum memory requirements for Cisco 2500 series, AS5100, and AS5200 access servers are listed in Table 177 and Table 178. The minimum memory requirements listed were chosen for typical branch and remote office applications. If your network is very large, using complex routing protocols, or using RMON, you may need more memory. Configuration analysis and testing are encouraged.
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number1, 2 |
|---|---|
| Plus
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FL25-P= and
SW25AP-xx.x.x= SW25BP-xx.x.x= SW25CP-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 40
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FL25-W= and
SW25AW-xx.x.x= SW25BW-xx.x.x= SW25CW-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 56
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FL25-Y= and
SW25AY-xx.x.x= SW25BY-xx.x.x= SW25CY-xx.x.x= |
| Plus and APPN
with Enterprise with IP/IPX/IBM |
FL25-APPN= and
SW25ANP-xx.x.x= SW25DSN-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 40 and APPN with Enterprise | FL25-APPN=, FL25-W=, and SW25ANW-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 56 and APPN with Enterprise | FL25-APPN=, FL25-Y=, and SW25ANY-xx.x.x= |
| CFRAD to IP | FL25-FC= and SW25C-xx.x.x= |
| CFRAD to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FL25-FB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| CFRAD to Enterprise | FL25-FA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| LAN FRAD to IP | FL25-LFC= and SW25C-xx.x.x= |
| LAN FRAD to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FL25-LFB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| LAN FRAD to Enterprise | FL25-LFA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| ISDN to IP | FL25-IC= and SW2525C-xx.x.x= |
| ISDN to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FL25-IB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| ISDN to Enterprise | FL25-IA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FL25-CB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise | FL25-CA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) to Enterprise | FL25-BA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FL25-DB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FL25-DA and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
Feature sets for Cisco IOS Release 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 can be upgraded for the Cisco 2500 series and AS5100 access servers as described in Table 180. To order an upgrade, you must use two product numbers; one represents the upgrade license, and the other represents the software. For example, to upgrade from an IP feature set to an IP feature set with IBM base functionality, order product number FR25-CCS= (the upgrade license) and SW25CS-xx.x.x= (the software). To upgrade to a feature set with APPN, you must first purchase the upgrade license for the desired feature set and then purchase the upgrade license and upgrade software for the APPN feature set.
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number1 |
|---|---|
| IP to IP with IBM base functionality | FR25-CCS= and SW25CS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX | FR25-CD= and SW25D-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR25-CDS= and SW25DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN2 | FR25-CDS=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop | FR25-CB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR25-CBS= and SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise | FR25-CA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-CA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR25-CSDS= and SW25DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN2 | FR25-CSDS=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR25-CSBS= and SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Enterprise | FR25-CSA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-CSA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR25-DDS= and SW25DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN2 | FR25-DDS=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop | FR25-DB= and SW25B-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR25-DBS= and SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FR25-DA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-DA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR25-DSBS= and SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Enterprise | FR25-DSA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-DSA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base and APPN2 | FR25-APPN= and SW25DSN-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR25-BBS= and SW25BS-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise | FR25-BA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-BA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop with IBM base to Enterprise | FR25-BSA= and SW25A-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop with IBM base to Enterprise and APPN2 | FR25-BSA=, FR25-APPN=, and SW25AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/RMON | FR25-R= and SW25CR-x.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IBM/RMON | FR25-CCS=, FR25-R=, and SW25CSR-x.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX/RMON | FR25-CD=, FR25-R=, and SW25DR-x.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-CDS=, FR25-R=, and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-CA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/RMON to IP/IBM/RMON | FR25-CCS= and SW25CSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/RMON to IP/IPX/RMON | FR25-CD= and SW25DR-x.x.x= |
| IP/RMON to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-CDS= and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/RMON to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-CA= and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IBM to IP/IBM/RMON | FR25-R= and SW25CSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IBM to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-CSDS=, FR25-R=, and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IBM to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-CSA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IBM/RMON to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-CSDS= and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IBM/RMON to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-CSA= and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX/RMON | FR25-R= and SW25DR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-DDS=, FR25-R=, and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-CSA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX/RMON to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-DDS= and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX/RMON to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-DA= and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX/IBM to IP/IPX/IBM/RMON | FR25-R= and SW25DSR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX/IBM to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-DSA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| IP/IPX/IBM/RMON to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-DSA= and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-BA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| Desktop/IBM to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-BSA=, FR25-R=, and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
| Enterprise to Enterprise/RMON | FR25-R= and SW25AR-x.x.x= |
Table 181 lists the feature set upgrades for Cisco IOS Release 11.2 and 11.1 and corresponding product numbers for the AS5200 access server. The AS5200 access servers upgrades are ordered as a bundled system that comes with an IP feature set.
Table 181 : Cisco IOS Software Upgrades---Cisco AS5200 Access Server
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number |
|---|---|
| IP to IP/IPX | AS5210-IP/IPX-UPGD |
| IP to Desktop | AS5210-DT-UPGD |
| IP to Enterprise | AS5210-ENT-UPGD |
| IP to IP/Modem | AS5210-IP/RM-UPGD |
| IP to IP/IPX/Modem | AS5210-IP/IPX/RM-UPGD |
| IP to Desktop/Modem | AS5210-DT/RM-UPGD |
| IP to Enterprise/Modem | AS5210-ENT/RM-UPGD |
A LAT terminal license is required to use with each asynchronous interface to which a LAT terminal is connected. Table 182 lists the licenses available and the corresponding product numbers.
Table 182 : Optional LAT Terminal Licenses
| Description | Cisco Access Server 2500 Series | Cisco Access Server AS5100 |
|---|---|---|
| 8-user LAT terminal license | FS-L8-10.X= | FS-L8-10.X= |
| 16-user LAT terminal license | FS-L16-10.X= | FS-L16-10.X= |
| 48-user LAT terminal license | -- | FS-L48-10.X= |
CiscoRemote is a scalable and comprehensive solution for remote access client software. There are two types of CiscoRemote software: CiscoRemote Lite and CiscoRemote Plus. Both products are optimized for easy installation and tuned for operation with Cisco access servers. CiscoRemote extends the benefits of Cisco IOS software capabilities to the desktop and provides a complete solution when used with Cisco access servers or remote node products (such as the Cisco 201 and Cisco 202).
CiscoRemote Lite provides basic remote node connectivity to an enterprise network. This basic connectivity package includes an installer, dialer, modem discovery, TCP/IP VxD stack, PPP or SLIP over IP or IPX. You can use CiscoRemote Lite with Windows 3.1, Windows for Workgroup, or Windows 95. CiscoRemote Lite is available free of charge on CCO (Cisco Connection Online, URL http://www.cisco.com) for an unlimited number of clients, provided that it is used to dial in to a Cisco device. The software is not licensed for use with any other vendor's hardware.
CiscoRemote Plus combines a complete set of applications for dial-up remote computing in one software package---a complete solution for enterprise network, remote access, and Internet communications. All applications are optimized, tested, and supported by Cisco Systems. CiscoRemote Plus links PCs with other computing resources within an enterprise network or across the Internet. Using CiscoRemote Plus, you can browse the World Wide Web, transfer files, log on to remote hosts, access Internet news groups, or share documents in real-time collaborative sessions.
Table 183 provides a comparison of CiscoRemote Lite and CiscoRemote Plus features. CiscoRemote Plus includes dial-up remote applications such as Remote node accelerator (Powerburst), Remote control (Timbuktu), E-mail (Beyond Mail), Netscape Navigator Browser, Version 2.0, and Document conferencing (DataBeam) that are not provided with CiscoRemote Lite.
Table 183 : CiscoRemote Lite and CiscoRemote Plus---Comparison of Features
| Feature | CiscoRemote Lite (Version 2.0) | CiscoRemote Plus (Version 2.0) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 3.1, Windows for Workgroups, and Windows 95 support1 | X | X |
| One-step installation | X | X |
| Windows-based dialer | X | X |
| TCP/IP protocol (VxD) | X | X |
| PPP/SLIP | X | X |
| Automatic modem detection | X | X |
| LAN driver (NDIS / ODI) for ISDN | -- | X |
| PAP/CHAP | X | X |
| Windows sockets and NetBIOS (APIs) | X | X |
| Telnet and ping | X | X |
| DHCP support | X | X |
| SNMP (MIB II) | X | X |
| Callback RFC 1570 | X | X |
| VJ header compression | X | X |
| Remote node accelerator (Powerburst) | -- | X |
| Remote control (Timbuktu) | -- | X |
| E-mail (Beyond Mail) | -- | X |
| Netscape Navigator Browser, Version 2.0 | -- | X |
| Document conferencing (DataBeam) | -- | X |
| ITU T.120 compatibility | -- | X |
| TN3270 | -- | X |
| TFTP server | -- | X |
| FTP client and server | -- | X |
| Software and user guide on CD | -- | X |
Figure 88 shows a sample net launcher dialog box from CiscoRemote Plus software.
Figure 88 : CiscoRemote Plus Net Launcher Dialog Box
The software also provides the industry's first remote-node accelerator for dramatically improving dial-up performance. CiscoRemote Plus also has LAN support for attached Ethernet devices such as the Cisco 753 router. CiscoRemote Plus provides all these features at a fraction of the cost of the individual components. CiscoRemote Plus is designed for the demands of an enterprise network, yet its ease of use makes it equally well suited to connect an individual at home to the Internet.
Table 184 : CiscoRemote Plus Product Numbers
| Description1 | Product Numbers |
|---|---|
| CiscoRemote Plus for Windows, 1-user license | CISCOREMOTE-V2.0 |
| CiscoRemote Plus, 500-user license | CRPLUS-500-V2.0 |
| CiscoRemote Plus, 1000-user license | CRPLUS-1K-V2.0 |
| CiscoRemote Plus, 5000-user license | CRPLUS-5K-V2.0 |
| CiscoRemote Plus, 10,000-user license | CRPLUS-10K-V2.0 |
| AirSoft software for the PowerBurst Server | PBAGENT-1-V1.0 |
CiscoSecure UNIX Server is a network security server that controls and secures access to a network via dial-up modems or ISDN. It can also secure internal or external access to routers within a network. Network Access security involves three sets of requirements: authentication, authorization, and accounting, referred to as AAA. CiscoSecure utilizes a central database storing user and group profiles of authentication and authorization information. When a user attempts to login to a network, the router communicates with CiscoSecure using the TACACS+ security protocol. CiscoSecure authenticates the user and sets the authorization parameters to determine the user's privilege levels. At the same time it stores accounting information that can be used for security audits or account billing.
Figure 89 displays a view of users and groups in the authentication and authorization (AA) database.
Figure 89 : Users and Groups Displayed in the AA Database
Using CiscoSecure, a network administrator can control the following:
Table 185 provides CiscoSecure UNIX Server specifications.
Table 185 : CiscoSecure UNIX Server Specifications
| Description | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Hardware requirements | UNIX SPARCstation
32-MB RAM 64-MB swap Minimum of 200 MB of free disk space per 1000 users One 3.5-inch floppy drive |
| Software requirements | SunOS 4.1.3/4.1.4
Solaris 2.5 Cisco IOS Release 10.3 or later |
Table 186 lists the CiscoSecure UNIX Server product numbers. Note that ports/sessions means the number of ports when using modems or B channels when using ISDN.
Table 186 : CiscoSecure UNIX Server Product Numbers
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server base unit---16 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-B16 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server base unit---48 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-B48 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server base unit---192 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-B192 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server base unit---1024 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-B1024 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server add-on---16 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-A16 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server add-on---48 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-A48 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server add-on---192 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-A192 |
| CiscoSecure UNIX Server add-on---1024 ports/sessions | CSUS-1.0-A1024 |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.