|
|
This chapter provides information on the AccessPro PC card. The information is organized into the following sections:
The AccessPro PC card is a full-featured multiprotocol router card that can be installed in an IBM or compatible PC equipped with either an ISA bus or EISA bus.
This series of PC-compatible router cards is based on Cisco 2500 series technology. The cards provide scalable wide-area connectivity and flexible full-function multiprotocol routing support. An AccessPro PC card runs autonomously using only its own processing power, expanding the capabilities of a PC server without impacting any existing applications.
Cisco Configuration Builder, an application that is available as an option, can be used to simplify configuration. The application runs in both Microsoft Windows NT and Windows environments.
The AccessPro PC cards also include built-in PC serial port emulation so that you can configure an AccessPro PC card from a PC, in lieu of the serial console port found on Cisco 2500 series products. You can select from four communications ports: COM1, COM2, COM3, or COM4. Access to the console port interface is available through the ISA bus using terminal emulation software (not provided) running on a PC.
There are currently four models of the AccessPro PC card:
Table 208 : AccessPro PC Card Summary of Features
| Characteristic | Features |
|---|---|
| Network interfaces | 1 Ethernet or 1 Token Ring
1 synchronous serial (1E1T) |
| Ethernet interface | IEEE 802.3 10BaseT (RJ-45) |
| Token Ring interface | IEEE 802.5 10BaseT (RJ-45), supports unshielded twisted-pair wiring1 |
| Synchronous serial interfaces | EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21 (NRZ/NRZI2 and DTE/DCE) EIA-530 (NRZ/NRZI and DTE)
All serial cables use a DB-60 chassis connector |
| Auxiliary port | Asynchronous serial (RJ-45, EIA/TIA-232-compatible) |
| PC serial port emulation | COM1, COM2, COM3, and COM4 (selectable) |
| Memory | 4-MB Flash memory (expandable to 16 MB)
32-KB NVRAM Primary memory (DRAM SIMMs) varies with software ordered (expandable to 16 MB) |
| Processor type | 20-MHz Motorola 68EC030 |
| Software | Choice of feature sets:
Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 feature sets (see Table 210) |
| Dimensions (H x L) | 4.8 x 13.3" (12.2 x 33.8 cm) |
Table 209 : AccessPro PC Card Environmental Specifications
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Power requirements | 3.0A @ 5V, 0.5A @ ±12V 30W maximum |
| Operating temperature range | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
| Nonoperating temperature | --40 to 185°F (--40 to 85°C) |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 5 to 95% |

The AccessPro PC card includes the following features:
The AccessPro PC card supports the following software releases:
Table 211 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for Cisco IOS Releases 11.2, 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2.
With the introduction of Cisco IOS Release 11.2, feature sets have been updated to make it easier to select the exact feature sets you need. Feature sets names are simplified and are more consistent across Cisco hardware platforms. In addition, you can add options to the standard feature set offerings. These options provide additional features and value based on the hardware platform selected. Cisco also continues to offer specialized feature sets for key applications.

The Cisco AccessPro PC card offers the following types of feature sets:
Cisco IOS images with 40-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) support may legally be distributed to any party eligible to receive Cisco IOS software. 40-bit DES is not a cryptographically strong solution and should not be used to protect sensitive data.
Cisco IOS images with 56-bit DES are subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) controls and have a limited distribution. Images to be installed outside the U.S. require an export license. Orders may be denied or subject to delays due to U.S. Government regulations. Contact your sales representative or distributor for more information, or send e-mail to export@cisco.com.
The new feature set tables use the following conventions to identify features:
Table 210 : Cisco IOS Releases 11.2, 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 Feature Sets---AccessPro PC Cards
| Cisco AccessPro PC Card Feature Sets | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | IP Routing | IP/IPX/
IBM/ APPN1 |
IP/IPX Routing2 | Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) | Enterprise3 | |||||||||||||||
| Cisco IOS Release | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 |
| LAN Support | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 24 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)5 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Novell IPX6 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Source-route bridging7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Services | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay SVC Support (DTE) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for
CPP and PPP |
X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ISDN8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PPP9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMDS | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| X.2510 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header11, link and payload compression12 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IP Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| BGP413 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Named IP Access Control List | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NHRP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSPF Not-So-Stubby-Areas (NSSA) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF On Demand Circuit
(RFC 1793) |
X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Other Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AURP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NLSP14 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| RTMP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| SRTP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Management | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration15 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON events and alarms16 | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON full | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Kerberos V client support | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Lock and key | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Network layer encryption
(export controlled 40-bit and 56-bit DES)17 |
Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RADIUS | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Router authentication | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| TACACS+18 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IBM Support (Optional) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| APPN (optional)3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Bisync19 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Caching and filtering | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DLSw+ 20 | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay SNA support (RFC 1490) | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA) Server | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NetView Native Service Point | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| QLLC19 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Response Time Reporter (RTR) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SDLC integration | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization
via local acknowledgment |
Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB7, 21 | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | |
| SRT | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Protocol Translation | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rlogin | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Remote Node22 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ARAP 1.0/2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| ATCP23 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| CPPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| IP pooling | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPX and ARAP on virtual asynch interfaces | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPXCP11 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| MacIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NASI24 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| NetBEUI over PPP | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| PPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services22 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT25 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Xremote | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
Adding a feature set may require you to purchase more memory. Table 211 lists the minimum memory requirements and the product numbers for Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1, 11.0 10.3, and 10.2 feature sets; Table 212 lists the requirements for Cisco IOS Release 10.0 feature sets. The minimum memory requirements listed were chosen for typical branch and remote office applications. If your network is very large or using complex routing protocols, you may need more memory. Configuration analysis and testing are encouraged.
Table 211 : Cisco IOS Software Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements---
AccessPro PC Card
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Releases | |||||||||||
| 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | |||||||
| Feature Set | Product Number1 | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM | Flash | Total DRAM |
| IP | SFAPC-xx.x.x
SWAPC-xx.x.x= |
4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB |
| IP with IBM base | SFAPCS-xx.x.x
SWAPCS-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| IP/IPX | SFAPD-xx.x.x
SWAPD-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| IP/IPX with IBM base | SFAPDS-xx.x.x
SWAPDS-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| Desktop | SFAPB-xx.x.x
SWAPB-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| Desktop with IBM base | SFAPBS-xx.x.x
SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| Enterprise | SFAPA-xx.x.x
SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB |
Table 212 : Access Pro PC Card Minimum Memory Requirements for Cisco IOS Release 10.0
| Cisco IOS Release 10.01 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature Set | Flash
Memory |
Total DRAM
Memory |
| IP | 4 MB | 2 MB |
| IP with IBM base | -- | -- |
| IP/IPX | -- | -- |
| IP/IPX with IBM base | -- | -- |
| Desktop | 4 MB | 6 MB |
| Desktop with IBM base | -- | -- |
| Enterprise | 4 MB | 6 MB |
There are two types of DRAM memory on the AccessPro PC cards: primary and shared (packet). Primary memory is used to store the operating configuration, routing tables, caches, queues, and packets. Shared memory is used to store incoming and outgoing packets. In Table 213, the physical configuration column lists the amount of fixed DRAM and DRAM SIMM memory supported. The system usage lists how the system allocates the total DRAM memory installed.
Table 213 : Shared and Primary DRAM Memory---AccessPro PC Cards
| Physical Configuration | System Usage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total DRAM Memory | Fixed DRAM1 | DRAM SIMM | Shared DRAM Memory | Primary DRAM Memory |
| 2 MB | 2 MB | -- | 1 MB | 1 MB |
| 6 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB | 2 MB | 4 MB |
| 10 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB | 2 MB | 8 MB |
| 18 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB | 2 MB | 16 MB |
Cisco IOS Feature Set Upgrades

Cisco IOS Release 11.2 for the Cisco AccessPro PC card allows software upgrades that cross multiple feature sets. This will require you to order multiple feature set licenses. The following is an example:
You have a Cisco AccessPro PC card installed in your IBM or compatible PC running the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 IP Routing feature set. You want to upgrade to the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 Enterprise Plus 56 feature set. You are crossing two feature sets: one to get from IP to Enterprise, and one to get to the Plus 56 feature set. To complete the upgrade, use the following guidelines:
Feature sets for Cisco IOS Releases 11.2 can be upgraded as described in Table 214.
Table 214 : Cisco IOS Upgrades for Cisco IOS Release 11.2---
AccessPro PC Cards
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number1, 2 |
|---|---|
| Plus
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FLAP-P= and
SWAPAP-xx.x.x= SWAPBP-xx.x.x= SWAPCP-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 40
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FLAP-W= and
SWAPAW-xx.x.x= SWAPBW-xx.x.x= SWAPCW-xx.x.x= |
| Plus 56
with Enterprise with Desktop(IP/IPX/AT/DEC) with IP |
FLAP-Y= and
SWAPAY-xx.x.x= SWAPBY-xx.x.x=, or SWAPCY-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FLAP-CB= and SWAPB-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise | FLAP-CA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) to Enterprise | FLAP-BA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop (IP/IPX/AT/DEC) | FLAP-DB= and SWAPB-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FLAP-DA and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
Feature sets for Cisco IOS Releases 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 can be upgraded as described in Table 215. To order an upgrade, you must use two product numbers; one represents the upgrade license and the other represents the software. For example, to upgrade from an IP feature set to an IP feature set with IBM base functionality, order product number FRAP-CCS= (the upgrade license) and SWAPCS-xx.x.x= (the software).
Table 215 : Cisco IOS Release 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 Software Upgrades---AccessPro PC Card
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number1 |
|---|---|
| IP to IP with IBM base functionality | FRAP-CCS= and SWAPCS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX | FRAP-CD= and SWAPD-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FRAP-CDS= and SWAPDS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop | FRAP-CB= and SWAPB-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FRAP-CBS= and SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise | FRAP-CA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FRAP-CSDS= and SWAPDS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FRAP-CSBS= and SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Enterprise | FRAP-CSA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FRAP-DDS= and SWAPDS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop | FRAP-DB= and SWAPB-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FRAP-DBS= and SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FRAP-DA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FRAP-DSBS= and SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Enterprise | FRAP-DSA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FRAP-BBS= and SWAPBS-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise | FRAP-BA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop with IBM Base to Enterprise | FRAP-BSA= and SWAPA-xx.x.x= |
Table 216 lists product numbers used to upgrade Cisco IOS Release 10.0 feature sets.
Table 216 : Cisco IOS Release 10.0 Software Upgrades---
AccessPro PC Card
| Upgrade1 | Product Number |
|---|---|
| IP to Desktop2 | SWAP-10.0.xCB= |
| IP to Enterprise3 | SWAP-10.0.xCA= |
| Desktop to Enterprise4 | SWAP-10.0.xBA= |
The AccessPro AP-EC contains the following ports:
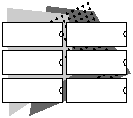
Figure 100 : Model AP-EC AccessPro PC Card
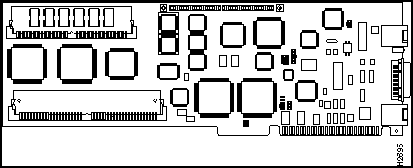
Figure 101 : Model AP-EC AccessPro Rear Panel
The AccessPro AP-RC contains the following ports:
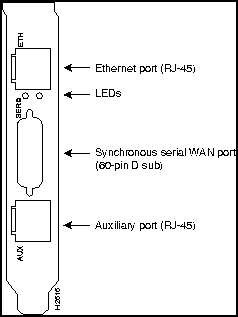
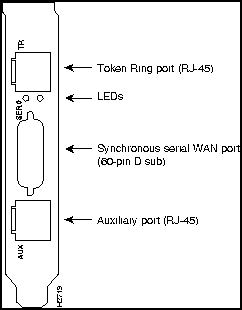
Figure 102 : Model AP-RC AccessPro PC Card
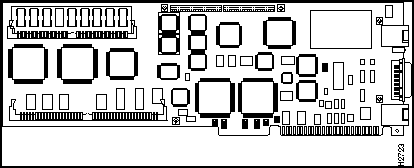
Figure 103 : Model AP-RC Rear Panel
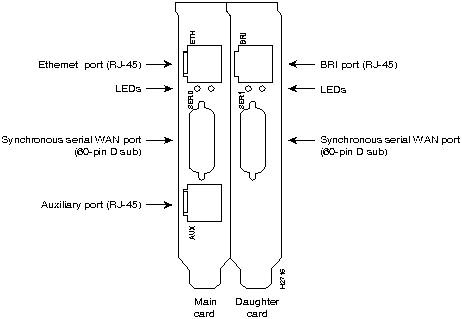
The AccessPro AP-EBC contains the following ports:
Note that Model APEBC comprises a Model APEC AccessPro card with a daughter card mounted on the noncomponent side, as shown in Figure 104.
Figure 104 : AccessPro Card and Daughter Card
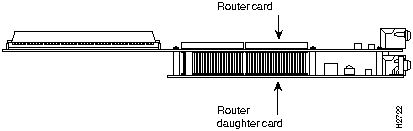
Figure 105 : Model AP-EBC Rear Panel
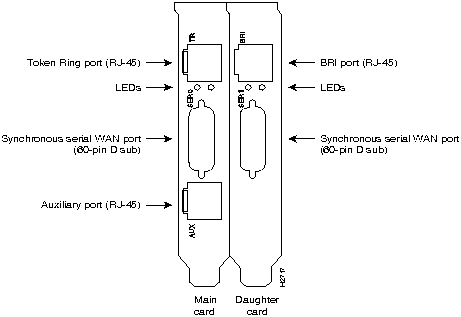
The AccessPro AP-RBC contains the following ports:
Note that Model APRBC comprises a Model APRC AccessPro card with a daughter card mounted on the noncomponent side, as shown in Figure 104.
Figure 106 : Model AP-RBC Rear Panel
The options for the AccessPro PC card include cables, memory, and software upgrades. For cable illustrations, refer to the section "Specifications" in the chapter "Cables and Transceivers" later in this catalog. Table 217 lists the cable options, and Table 218 lists the memory options.
Table 217 : AccessPro PC Card Cable Options
| Cables | Product Number |
|---|---|
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232MT |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232FC |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449MT |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449FC |
| EIA-530 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-530MT |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35MT |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35FC |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21MT |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21FC |
| Auxiliary/console port cable kit | ACS-2500ASYN |
Table 218 : AccessPro PC Card Memory Options
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| 4-MB DRAM | MEM-1X4D |
| 4-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X4D= |
| 8-MB DRAM | MEM-1X8D |
| 8-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X8D= |
| 16-MB DRAM | MEM-1X16D |
| 16-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-1X16D= |
| 4-MB Flash SIMM (spare) | MEM-1X4F= |
| 4- to 8-MB Flash memory upgrade | MEM-1X8F-DFB-U1, 2 |
| 8-MB dual Flash bank SIMM (spare) | MEM-1X8F-DFB=2 |
| 16-MB dual Flash bank SIMM | MEM-1X16F-DFB |
| 16-MB dual Flash bank SIMM (spare) | MEM-1X16F-DFB=3 |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.