|
|
Before you install the AccessPro card, read this chapter carefully. It contains important information that will make your installation quicker and easier. This chapter contains the following sections:
Follow these guidelines to ensure general safety:
![]()
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a discharge of stored static electricity that can damage electronic equipment and impair electrical circuitry, resulting in complete or intermittent failures. ESD is increased by the combination of synthetic fibers and dry atmosphere.
Always follow ESD-prevention procedures when removing and replacing components. Ensure that the chassis is electrically connected to earth ground. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted surface of the chassis frame to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis. Always follow the guidelines in the preceding section, "Safety Recommendations."
![]()
![]()
The ports for the Ethernet or Token Ring, serial, and auxiliary connections are located on the rear panel of the main card and the daughter card. (See Figure 2-1, Figure 2-2, Figure 2-3, and Figure 2-4.)
Figure 2-1 Rear-Panel Connectors, Model AP-EC
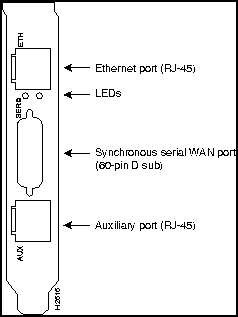
Figure 2-2 Rear-Panel Connectors, Model AP-RC
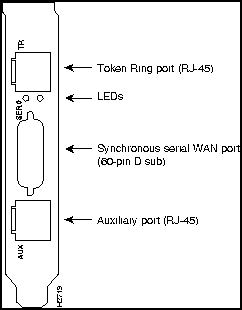
Figure 2-3 Rear-Panel Connectors, Model AP-EBC
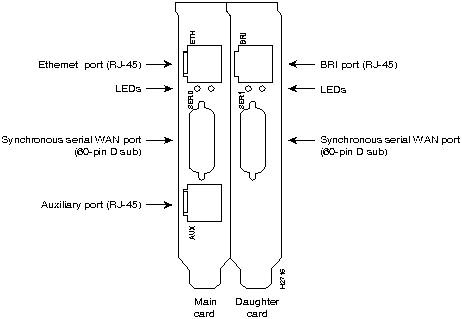
Figure 2-4 Rear-Panel Connectors, Model AP-RBC
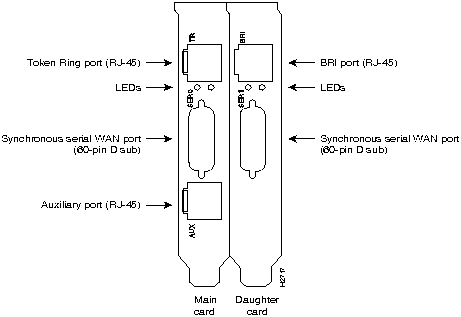
When you set up the LAN and WAN connections, be aware of the distance limitations and potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) as defined by the EIA. Following are the distance limitation specifications for Ethernet 10BaseT, Token Ring RJ-45, BRI, and serial interfaces.
The distance limitation for the IEEE 802.3 specification is a maximum segment distance of 328 feet (100 meters) at a transmission rate of 10 megabits per second (Mbps).
The distance limitation for the IEEE 802.5 specification is a maximum segment distance of 328 feet (100 meters) at a transmission rate of 4 or 16 Mbps.
The specifications for the ISDN BRI cable are listed in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 BRI Cable Specifications
| Specification | High-Capacitance Cable | Low-Capacitance Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance (@ 96 kHz(1)) | 160 ohms/km | 160 ohms/km |
| Capacitance (@ 1 kHz) | 120 nF(2)/km | 30 nF/km |
| Impedance (@ 96 kHz) | 75 ohms | 150 ohms |
| Wire diameter | 0.024" (0.6 mm) | 0.024" (0.6 mm) |
| Distance limitation | 32.8' (10 m) | 32.8' (10 m) |
![]()
![]()
As with all signaling systems, EIA/TIA-232 signals can travel a limited distance at any given bit rate; generally, the slower the data rate, the greater the distance. Table 2-2 shows the standard relationship between baud rate and maximum distance for EIA/TIA-232 signals.
Table 2-2 EIA/TIA-232 Speed and Distance Limitations
| Data Rate (Baud) | Distance (Feet) | Distance (Meters) |
|---|---|---|
| 2400 | 200 | 60 |
| 4800 | 100 | 30 |
| 9600 | 50 | 15 |
| 1200 | 25 | 7.6 |
| 3400 | 12 | 3.7 |
![]()
Balanced drivers allow EIA/TIA-449 signals to travel greater distances than EIA/TIA-232 signals. Table 2-3 lists the standard relationship between baud rate and maximum distance for EIA/TIA-449 signals. These limits are also valid for V.35 and X.21.
Table 2-3 EIA/TIA-449 Speed and Distance Limitations
| Baud Rate | Distance (Feet) | Distance (Meters) |
|---|---|---|
| 2400 | 4,100 | 1,250 |
| 4800 | 2,050 | 625 |
| 9600 | 1,025 | 312 |
| 19200 | 513 | 156 |
| 38400 | 256 | 78 |
| 56000 | 102 | 31 |
| T1, E1 | 50 | 15 |
![]()
When you run cables for any significant distance in an electromagnetic field, interference can occur between the field and the signals on the cables. The construction of terminal plant cabling has two implications:
If you use twisted-pair cables with a good distribution of grounding conductors in your plant cabling, emitted radio interference is unlikely. If you exceed the maximum distances---although we do not recommend that you do this---you will get the best results if you ground the conductor for each data signal.
If you have cables that exceed the recommended distances, or if you have cables that pass between buildings, give special consideration to the effect of lightning strikes or ground loops. The electromagnetic pulse caused by lightning or other high-energy phenomena can easily generate enough energy into unshielded conductors to destroy electronic devices. If your site has experienced this kind of problem, consult experts in lightning suppression and shielding.
![]()
Most data centers cannot resolve the infrequent but potentially catastrophic problems just described without pulse meters and other special equipment. Take precautions to avoid these problems by providing a properly grounded and shielded environment, and pay special attention to issues of electrical surge suppression.
To predict and remedy strong EMI, consult experts in radio frequency interference (RFI).
Access to the console port interface is available through the ISA bus using terminal emulation software running on the PC. To configure the card for console port functionality, refer to the section "Setting COMport Jumpers" in the chapter "Maintaining the AccessPro PC Card."
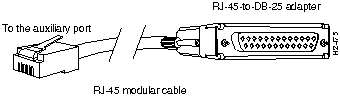
An RJ-45, asynchronous serial, auxiliary port is included on all AccessPro cards. This is a DTE port to which you can attach a CSU/DSU or protocol analyzer for network access. This port connects to external equipment using an RJ-45-to-DB-25 adapter, shown in Figure 2-5. The appendix "Cabling Specifications" lists the pinouts for the auxiliary port.
Figure 2-5 RJ-45-to-DB-25 Adapter
|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.