|
|
LightStream 1010 ATM Switch 622 SM/MM Port Adapter Module Configuration Note
Product Numbers: WAI-OC12-1SM=, WAI-OC12-1MM=
This document contains instructions for installing and configuring the 622 single-mode (SM) and the 622 multimode port adapter modules. For a complete description of commands used to configure and maintain the 622 SM/MM port adapter modules, refer to the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Software Configuration Guide and the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Command Reference publications. For complete hardware configuration and maintenance procedures, refer to the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide publication.
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on a CD called Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series. The CD is updated and shipped monthly, so it might be more up-to-date than the printed documentation. To order the Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series CD, contact your local sales representative or call Customer Service. The CD is available both as a single CD and as an annual subscription. You can access Cisco technical documentation on the World Wide Web Universal Resources Locator (URL)
http://www.cisco.com.
Sections in this document include the following:
![]()
What is the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch?
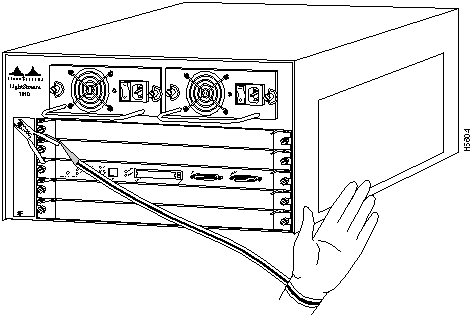
The LightStream 1010 uses a five-slot, modular chassis featuring the option of dual, fault-tolerant, load-sharing power supplies. (See Figure 1.) The central slot in the LightStream 1010 is dedicated to a single, field-replaceable ATM switch processor (ASP) module that supports both the 5-Gbps shared memory and the fully nonblocking switch fabric. The ASP also supports the feature card and high performance reduced instruction set (RISC) processor that provides the central intelligence for the device. The remaining slots support up to four hot-swappable Carrier Modules (CAMs). Each CAM supports up to two hot-swappable Port Adapter Modules (PAMs) for a maximum of eight PAMs per switch, supporting a wide variety of desktop, backbone, and wide-area interfaces.
Figure 1 : Front View of the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch
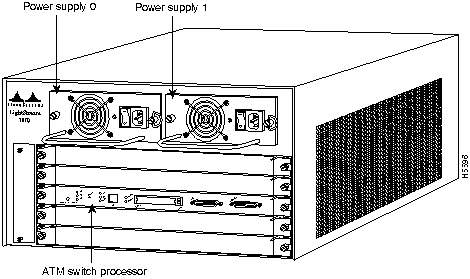
The LightStream 1010 ATM switch provides switched ATM connections to individual workstations, servers, LAN segments, or other ATM switches and routers using fiber-optic, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), and coaxial cable.
The LightStream 1010 ATM switch can accommodate up to 8 OC-12 switched ATM ports in a standard 19-inch (48-centimeter) rack.
Figure 2 shows an example of a network configuration using the LightStream 1010 ATM switch in a high-performance workgroup.
Figure 2 : LightStream 1010 Workgroup Configuration Example
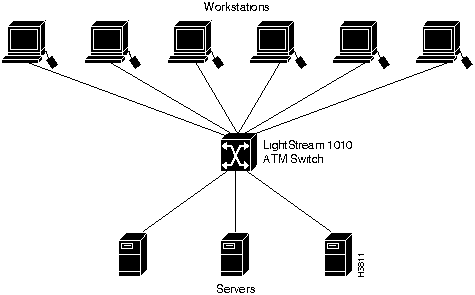
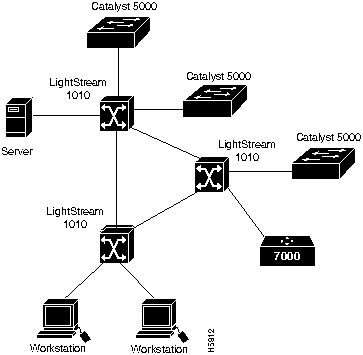
Figure 3 shows an example of a network configuration using the LightStream 1010 ATM switch for a campus backbone.
Figure 3 : LightStream 1010 Backbone Configuration Example
622 SM Port Adapter Module Description
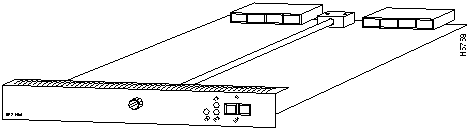
The 622 SM (single-mode) PAM, shown in Figure 4, provides connection to one OC12 interface using a duplex SC SM fiber-optic connector.
Figure 4 : 622 SM Port Adapter Module
622 MM Port Adapter Module Description
The 622 MM (multimode) PAM, shown in Figure 5, provides connection to one OC12 interface using a duplex SC MM fiber-optic connector.
Figure 5 : 622 MM Port Adapter Module
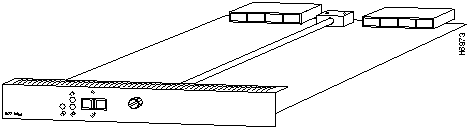
Table 1 lists the 622 single-mode port adapter module specifications:
Table 1 : 622 SM Port Adapter Module Specifications
| Description | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | PAM: 1.2 x 6.5 x 10 in. (3.0 x 16.5 x 25.4 cm) |
| Weight | 1.10 lb (.50 kg)) |
| Operating temperature | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
| Nonoperating temperature | -40 to 167°F (-40 to 75°C) |
| Humidity | 10 to 90%, noncondensing |
| Altitude | -500 to 10,000 ft (-52 to 3,048 m) |
| Interface timing | Loop timing, Stratum 4 accuracy clock for self-timing |
| Port adapter modules (PAM) | PAM with 1SONET STS12c/SDH STM4c single-mode fiber ports, SC connector
(WAI-OC3-4MM) PAM with 1SONET STS12c/SDH STM4c multimode fiber ports, SC connector (WAI-OC3-4SM) |
| Network management | Port Tx and Rx LEDs |
| Mean Time Between Failures | 2.6 years for system configuration |
| Management Information Bases (MIB) | SNMP MIB II (RFC 1213)
Interface table MIB(RFC 1573) AToMIC (RFC 1695) ATM Forum LANE A MIB ATM Forum PNNI MIB SONET MIB (RFC 1595) ATM Forum UNI 30/3.11 ILMI MIB RMON MIB (RFC 1757) Ethernet MIB (RFC 1398) RS-232 MIB (RFC 1659) |
| Maximum
station-to-station cabling distance |
OC-12---8/125-micron single-mode fiber: 9 miles (15 km)
OC-12---862.5/125- and 50/125-micron multimode fiber: .31 miles (500 m) |
| Fiber-optic power levels:
OC-12 Single-mode Output center wavelength Transmit Receive OC-12 Multimode Output center wavelength Transmit optical outpur Receive senstivity |
1274 to 1356 nm Minimum: -15.0 dBm Maximum: -8.0 dBm Minimum: -28.0 dBm Maximum: -8.0 dBm 1270 to 1380 -14 to -20 dBm -14 to -26 dBm |
| Agency approvals | Safety: UL1 1950, CSA2-C22.2 No. 950-93, and EN60950
EMI3: FCC Class A CE Mark, and VCCI Class II with shielded cables |
The eight available CAMs support any combination of network interfaces to provide the following maximum port densities:
You can install any combination of PAMs in any of the eight available PAM slots. There are no restrictions on either the number of modules that can be installed or their proximity to the ASP.
The LEDs on the 622 SM PAM provide status information for the SC fiber-optic interface connection. The LEDs are shown in Figure 6 and described in Table 2.
Figure 6 : 622 SM Port Adapter Module LEDs
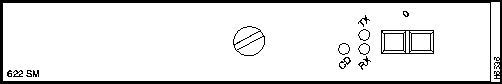
Table 2 : 622 SM Port Adapter Module LED Descriptions
| LED | Description |
|---|---|
| CD (Carrier Detect) | Off---Carrier detect signal not received.
Green---Carrier detect signal received. |
| RX (Receive) | Off---No cells received.
Flashing green---Cells being received: pulse rate increases with data rate. Red---Alarm (LOF1, LCD2, AIS3). |
| TX (Transmit) | Off---No cells received.
Flashing green---Cells being transmitted: pulse rate increases with data rate. Flashing yellow---Loopback. Steady yellow---Alarm FERF4. |
The LEDs on the 622 MM PAM provide status information for the SC fiber-optic interface connection. The LEDs are shown in Figure 7 and described in Table 3.
Figure 7 : 622 MM Port Adapter Module LEDs Table 3 : 622 MM Port Adapter Module LED Descriptions
When preparing your site for network connections to the switch, you need to consider a number of factors related to each type of interface:
ATM Connections The maximum distances for ATM network segments and connections depend on the type of transmission cable used, for example, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), single-mode, or multimode fiber-optic cable.
Networking standards set the maximum distances between stations using fiber-optic and UTP cable. The maximum cable lengths are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 : ATM Maximum Transmission Distances
For Further Reference
The following publications contain information on determining attenuation and power budget:
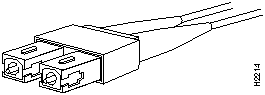
For fiber-optic traffic over SM or MM, use the SC-type connector (Figure 8) to connect the 622 SM PAM and 622 MM PAM with the external ATM switch.
To see translated versions of this warning, refer to the appendix "Translated Safety Warnings" in the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide.
Figure 8 : Fiber-Optic Network Interface Connector (SC Type) The following guidelines will help to ensure your safety and protect the equipment. This list is not inclusive of all potentially hazardous situations that you may be exposed to as you install the module, so be alert.
The supervisor engine, modules, and redundant (second) power supplies are designed to be removed and replaced while the system is operating without presenting an electrical hazard or damage to the system. Before removing a redundant power supply, ensure that the first supply is powered on. However, you must shut down the system before removing or replacing any of the replaceable components inside the front panel, for example, the backplane. Never install equipment that appears damaged.
Follow these basic guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
In addition, use the guidelines that follow when working with any equipment that is disconnected from a power source but still connected to telephone wiring or other network cabling.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which occurs when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, can result in complete or intermittent failures. Each PAM consists of a printed circuit card that is fixed in a metal carrier. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, connectors, and a handle are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the cards from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap whenever you handle the PAMs. Handle the carriers by the handles and the carrier edges only; never touch the cards or connector pins.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
Figure 9 : Placement of Electrostatic Discharge Wrist Strap All PAMs support hot-swapping, which allows you to install, remove, replace, and rearrange the PAMs without turning off the system power. When the system detects that a PAM has been installed or removed, it automatically runs diagnostic and discovery routines, acknowledges the presence or absence of the PAM, and resumes system operation without any operator intervention.
The hot-swap feature allows you to remove and replace modules while the system is operating; you do not need to notify the software or shut down the system power. All CAMs and PAMs (except for the ASP) support hot-swapping.
Each CAM contains a bus-type connector that mates with the system backplane. Each card connector consists of a set of tiered pins, in three lengths. The pins send specific signals to the system as they make contact with the backplane. The system assesses the signals it receives and the order in which it receives them to determine what event is occurring and what task it needs to perform, such as reinitializing new interfaces or shutting down removed ones.
For example, when inserting a CAM, the longest pins make contact with the backplane first, and the shortest pins make contact last. The system recognizes the signals and the sequence in which it receives them. The system expects to receive signals from the individual pins in this logical sequence, and the ejector levers help to ensure that the pins mate in this sequence.
When you remove or insert a PAM, the backplane pins send signals to notify the system, which then performs as follows:
Hot-swap functionality enables you to add, remove, or replace PAMs with the system online, which provides a seamless method to users on the network, maintains all routing information, and ensures session preservation.
When you insert a new PAM, the system runs a diagnostic test on the new interfaces and compares them to the existing configuration. If this initial diagnostic fails, the system remains offline for another 15 seconds while it performs a second set of diagnostic tests to determine whether or not the PAM is faulty and if normal system operation is possible.
If the second diagnostic test passes, which indicates that the system is operating normally and the new PAM is faulty, the system resumes normal operation but leaves the new interfaces disabled.
If the second diagnostic test fails, the system crashes, which usually indicates that the new PAM has created a problem in the bus and should be removed.
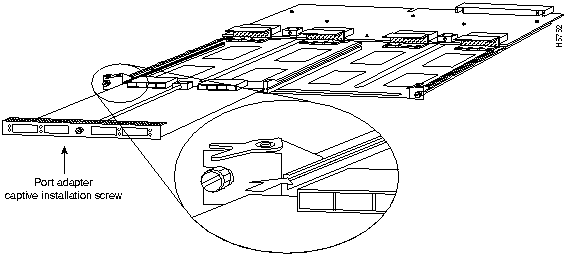
You need a 3/16-inch flat-blade screwdriver to remove any filler (blank) PAMs and to tighten the captive installation screws that secure the CAMs and PAMs in their slots. Whenever you handle CAMs and PAMs, you should use a wrist strap or other grounding device to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. See the section "Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage" in the chapter "Preparing for Installation" in the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide.
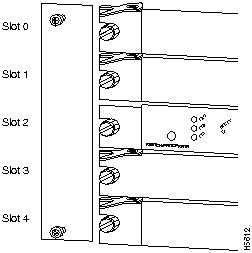
You can install CAMs in any of the four CAM slots numbered 0 through 4 from top to bottom when viewing the chassis from the front as shown in Figure 11. (The middle slot (number 2) contains the ASP, which is a required system component.) Blank CAM and PAM fillers are installed in CAMs or PAM slots without CAMs or PAMs to maintain consistent airflow through the module compartment. Refer to the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide for information about installing the CAM.
Following are detailed steps for removing PAMs and successfully performing hot-swap.
Figure 12 : PAM Carrier Installation Sample Screen Display for Hot-Swapping Procedure
When you remove and replace CAMs and PAMs, the system provides status messages on the console screen. The messages are for information only. In the following sample display, you can follow the events logged by the system when a PAM was removed from slot 3/0. When the PAM is reinserted, the system marks the module as ready again.
Port Adapter Module Configurations
The PAMs support different media and interface types. The configuration commands used with these different PAMs vary according to PAM type. For complete PAM configuration information, refer to the publications LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Configuration Guide and LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Command Reference.
After you install the module, use the following information to configure the module and the individual interfaces on the 622 MM/SM modules. In the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide the section "LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Hardware" contains an overview of the port and module numbering scheme used to configure the 622 PAMs. The section "Configuring the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch" describes how to configure the ports on the FDDI or CDDI module. The section "Confirming the Installation" describes the procedures you should use to confirm that the 622 PAMs are configured correctly.
Each interface (or port) in the switch is designated by several different types of addresses. The physical interface address is the actual physical location (card/subcard/port) of the interface connector within the chassis. The system software uses the physical addresses to control activity within the switch and to display status information. These physical card/subcard/port addresses are not used by other devices in the network; they are specific to the individual switch and its internal components and software.
The following sections describe how the LightStream 1010 switch assigns and controls both the physical (card/subcard/port) and Media Access Control (MAC)-layer addresses for interfaces within the chassis.
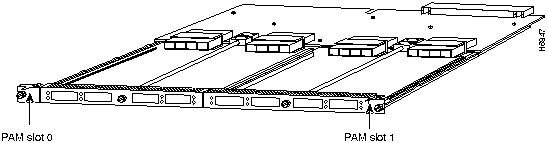
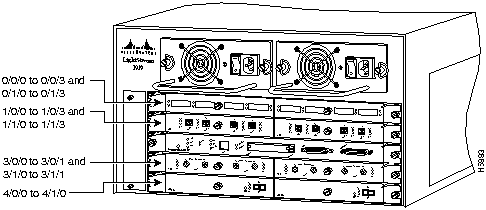
In the LightStream 1010 switch, the port ID specify the actual physical location of each PAM port on the front of the switch. (See Figure 14.) The address is composed of a three-part number in the format card/subcard/port. The first number identifies the slot in which the module is installed. Module slots are numbered 0 to 4 from top to bottom. The second number identifies the subcard or PAM number. The PAMs are numbered 0 and 1 with 0 being the left PAM facing the front of the switch. The third number identifies the physical port number on the module. The port numbers always begin at 0 and are numbered from the left port to the right port, facing the front of the switch. The number of additional ports (/1, /2, and so on) depends on the number of ports available on the module.
Interface ports maintain the same port ID regardless of whether other modules are installed or removed. However, when you move a module to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new slot number. For example, on a 4-port 155 UTP PAM in chassis slot 1 in PAM slot 0, the address of the left port is 1/0/0 and the address of the right port is 1/0/3. If you remove the 4-port 155 UTP PAM from slot 1 and install it in slot 4, the addresses of those same ports become 4/0/0 and 4/0/3.
Figure 13 : ATM Interface Port ID Address Examples
You can identify module ports by physically checking the card/subcard/port location on the front of the switch. You can also use software commands to display information about a specific interface, or all interfaces, in the switch. To display information about every interface, use the show interface command without parameters. To display information about a specific interface, use the show interface command with the interface type and port address in the format show interface atm card/subcard/port. This command is described in the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Command Reference publication.
622 SM/MM Configuration Defaults
When the switch is powered on initially without any previous configuration data, the ATM interfaces are configured automatically on the physical ports. ILMI and the physical card type are used to automatically derive the ATM interface type, UNI version, maximum VPI and VCI bits, ATM interface side, and ATM UNI type.
Default ATM Interface Configuration Without Autoconfiguration
If ILMI has been disabled or if the connecting end node does not support ILMI, the following defaults are assigned to all interfaces:
The following defaults apply to the OC12 PAM:
You can accept the default ATM interface configuration or overwrite the default interface configuration using the command line interface commands. These commands are described in the section "Configuring Virtual Connections" in the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch Software Configuration Guide.
To test the configuration refer to the section "Confirming the Installation" in the LightStream 1010 ATM Switch User Guide.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
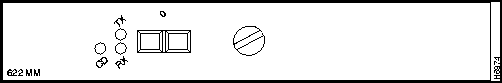
LED
Description
CD (Carrier Detect)
Off---Carrier detect signal not received.
Green---Carrier detect signal received.
RX (Receive)
Off---No cells received.
Flashing green---Cells being received: pulse rate increases with data rate.
Red---Alarm (LOF1, LCD2, AIS3).
TX (Transmit)
Off---No cells received.
Flashing green---Cells being transmitted: pulse rate increases with data rate.
Flashing yellow---Loopback.
Steady yellow---Alarm FERF4.
1 LOF = loss of frame
2 LCD = loss of cell delineation
3 AIS = alarm indication signal
4 FERF = far-end receive failure
Transceiver Speed
Cable Type
Maximum Distance between Stations
622 Mbps
Single-mode fiber
9 miles (15 km)
622 Mbps
Multimode fiber
.31 miles (500 m)
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Unconfigured PAMs installed for the first time start up in the shutdown state. The system identifies them as present but unconfigured. Each must be manually configured from the command line.1
![]()
![]()
![]()
Switch#
%OIR-6-REMCARD: Card removed from slot 3/0, interfaces disabled
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface 155UTP 3/0, changed state to administratively down
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface 155UTP 3/0, changed state to administratively down
Switch#
%OIR-6-INSCARD: Card inserted in slot 3/0, interfaces administratively shut down
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface 155UTP 3/0, changed state to up
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface 155UTP 3/0, changed state to up


Footnotes
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()