|
|
Configure PIX Firewall using the commands that follow. You can enter commands from your console computer or terminal, or through Telnet or the HTML management interface.
Help information is available by entering a question mark by itself for a listing of all commands, or with a command for command syntax. For example:
pixfirewall> int ? usage: interface ethernet inside|outside 10baseT|100baseTX|auto
You can add comments to your configuration by entering a colon (:) as the first command in a line. Use comments to improve configuration file readability or to make configuration file commands not executable.
You can abbreviate most commands down to the fewest unique characters for a command; for example, you can enter write t to view the configuration instead of entering the full command write terminal, or you can enter en (enable) to start privileged mode and conf t (configure terminal) to start configuration mode.
"Type `?' for a list of commands" Message
To simplify the PIX Firewall interface, the "Type `?' for a list of commands" message displays for a variety of reasons:
pixfirewall(config)# hostname ? usage: hostname <newname>
Sets Private Link key duration. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| minutes | Duration in minutes that a Private Link key is used to encrypt information on the connection. If you enter 0, the duration is set to 10 minutes. The maximum duration is 1215752191 minutes (2345 years). |
Usage Guidelines
The age command specifies the length of time in minutes that a key is active over Private Link. Private Link supports up to seven keys that it selects sequentially to ensure additional security.
See also: link, show age.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# age 0 pixfirewall(config)# show age Private Link Key Aging: 10 minutes
Apply outbound access list to an IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| number | An outbound access list identification number previously created with the outbound command. |
| outgoing_src | Examines the source address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement. Limits access for an inside network address. For example, specify outgoing_src if you want to deny an inside user access to an external web site. |
| outgoing_dest | Examines the destination address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement. Limits access to a particular IP address and service on the Internet. For example, specify outgoing_dest to prevent inside users from accessing a particular external web site. |
Usage Guidelines
The apply command applies the outbound list parameters to permit or deny access from an IP address in your inside network to an IP address in the outside network. Use outbound lists to permit or deny access to system ports.
See also: clear apply, no apply, outbound, show apply, show outbound.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# apply 1 192.168.42.42 10.10.10.42
Add entry to PIX Firewall ARP table. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
inside
|
Network interface that protects the inside network. |
outside
|
Network interface for the unprotected outside network connection to the PIX Firewall. |
| ip_address | IP address for the ARP table entry. |
| mac_address | Hardware MAC address for the ARP table entry. |
| alias | Make this entry permanent. Alias entries do not time out and are automatically stored in the configuration when you use the write command to store the configuration. |
Usage Guidelines
The arp command adds an entry to the PIX Firewall ARP table. ARP is a low-level TCP/IP protocol that resolves a node's physical address from its IP address through an ARP request asking the node with a particular IP address to send back its physical address.
See also: clear arp, no arp, show arp.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# arp 192.168.0.42 0000.0101.0202 pixfirewall(config)# arp 192.168.0.43 0000.0101.0203 alias
Change PIX Firewall ARP table entry duration. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| seconds | Duration that an ARP entry can exist in the ARP table before being cleared. |
Usage Guidelines
The arp timeout command sets the duration that an ARP entry can stay in the PIX Firewall ARP table before expiring. The timer is known as the ARP persistence timer. The default value is
14400 seconds (4 hours).
See also: show arp timeout
Example
pixfirewall(config)# arp timeout 42 pixfirewall(config)# show arp timeout arp timeout 42 seconds
Enable PIX Firewall user authentication. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
inside
|
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on your local network (inside the PIX Firewall). |
outside
|
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on the outside of the PIX Firewall. |
Usage Guidelines
The auth command enables PIX Firewall authentication. The no auth command disables authentication. With the inside or outside argument, you can enable or disable authentication on one side of the PIX Firewall or the other. Without arguments, you can enable or disable authentication on both sides.
For outside connections, a challenge prompt appears during FTP or Telnet sessions as defined by the type of authentication server.
Authorization notes:
authentication_username@remote_system_username
authentication_password@remote_system_password
Example
pixfirewall(config)# auth inside
Specify IP address of authentication server. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| type | Authentication type: radius or tacacs+. |
| server_ip | The IP address of the authentication server. |
| skey | An alphanumeric keyword of up to 127 characters defined by what the authentication server accepts. This is a public key between the client and server for encrypting data between them. The skey value must be the same on both the client and server systems. |
Usage Guidelines
The auth-server command lets you identify the IP address of the authentication server. The authentication server must be on the inside PIX Firewall network interface.
Defines a server for the specified authentication server type. PIX Firewall tries each server in order until it receives an answer for the type of authentication you specify. Refer to the previous auth command description for more information on authentication.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# auth-server radius 192.168.42.20-192.168.42.42
Specify IP address of authentication user. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
type
|
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+ |
ip_address
|
IP address from which or to which access is authenticated. If you want every system in your network to authenticate to this type of server, use 0.0.0.0 for the IP address. You can specify a network IP address by entering zero in each octet of the host portion of the IP address; for example, for a class C address, code 0 in the last octet, such as 192.168.42.0. |
netmask
|
Network mask of ip_address. Always specify a specific mask value. If you want to limit authentication to a single IP address use 255 in each octet; for example, 255.255.255.255. |
Usage Guidelines
The auth-user command lets you provide authentication services for an IP address. For outbound connections, use of auth-user indicates that anyone on the IP address you specify must use authentication when using Telnet, FTP, or HTTP. For inbound connections, auth-user indicates that anyone attempting to access the specified IP address with FTP, Telnet, or HTTP must use authentication.
Refer to the previous auth command description for more information on authentication.
See Also: auth, no auth-user, show auth-user
Example
pixfirewall(config)# auth-user radius 192.168.42.1 255.255.255.0
Clear previous apply of outbound access lists to an IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| number | An outbound access list identification number previously created with the outbound command. |
| outgoing_src | Examines the source address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement. Limits access for an inside network address. For example, specify outgoing_src if you want to deny an inside user access to an external web site. |
| outgoing_dest | Examines the destination address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement. Limits access to a particular IP address and service on the Internet. For example, specify outgoing_dest to prevent inside users from accessing a particular external web site. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear apply command clears an outbound access list created by a previous use of apply.
See also: apply, no apply, show apply.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear apply
Clear PIX Firewall ARP table entry. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
| inside | PIX Firewall inside network interface ARP table. |
| outside | PIX Firewall outside network interface ARP table. |
| ip_address | IP address. |
| mac_address | Hardware MAC address for the ARP table entry. |
| alias | An ARP entry for one host that points to another. These entries are not cleared from the PIX Firewall ARP table during reboots. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear arp command clears the PIX Firewall ARP table. To remove alias entries, specify the alias keyword. You may clear entries by IP or MAC address.
This command is the same as no arp.
See also: arp, no arp, show arp.
Example
pixfirewall# clear arp inside
Remove authentication support for IP address. (Configuration mode.)
type ip_address netmask
Syntax Description
type
|
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+. |
ip_address
|
IP address from which or to which access is directed depending on whether the connection is inbound or outbound. |
netmask
|
Network mask of ip_address. Always specify a specific mask value. If you want to limit access to a single IP address use 255 in each octet; for example, 255.255.255.255. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear auth-user command removes authentication access for an IP address. You can remove all access by not specifying options, or you can remove access by authentication type, such as TACACS+, or by type and IP address.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear auth-user tacacs+
Stop authentication access to a server. (Configuration mode.)
type server_ip skey
Syntax Description
| type | Authentication type: radius or tacacs+ |
| server_ip | The IP address of the authentication server. |
| skey | An alphanumeric keyword of up to 127 characters defined by what the authentication server accepts. This is a public key between the client and server for encrypting data between them. The skey value must be the same on both the client and server systems. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear auth-server command specifies that an authentication server is no longer servicing authentication requests. Use this command when you take an authentication server offline or have changed your network topology.
You can remove access to all authentication servers by not specifying options, or you can remove access by authentication type, such as TACACS+, or by type and server IP address.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear auth-server
Remove HTTP access to the PIX Firewall HTML management interface from the specified IP address or all IP addresses. (Configuration mode.)
ip_address [netmask]
Syntax Description
| ip_address | IP address of systems on the inside of the PIX Firewall that are able to access the HTML management interface. You can give access to a maximum of 16 IP addresses. |
| netmask | Network mask of ip_address. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear http command removes HTTP access to an IP address. This is the same as the no http command.
See also: http, show http.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear http
Clear outbound access list. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| num | A tag number for the access list. |
permit
|
Allow the access list to access the specified IP address and port. |
deny
|
Deny the access list access to the specified IP address and port. |
| ip_address | The IP address for this access list entry. |
| netmask | The network mask for comparing with the IP address; 255.255.255.0 causes the access list to apply to an entire class C address. 0.0.0.0 disables all access. |
| port | A port or range of ports that the access list is permitted or denied access to; for example, 1-1024. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear outbound command clears an outbound access list or specific details within it.
See also: apply, no outbound, outbound, show outbound.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear outbound 1
Clear the inside or outside interface's routing table. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| inside|outside | Sets the network default route and path for either the inside or outside interface. |
| static | Clears the static routes. Static routes are those entered manually with the route command. They are stored in the in the configuration when it is saved. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear route command clears the routing table for the specified interface. You can clear both routing tables by entering clear route without the inside or outside keywords. To clear static routes, use the static keyword. To remove an individual route without clearing the entire table, use the no route command.
See also: no route, route, show route
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear route inside static
Clear SNMP contact or location, or stop sending SNMP event information. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| contact | Clear the contact information. |
| location | Clear the PIX Firewall location. |
| host | Stop sending SNMP event information. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear snmp-server contact command deletes the contact information from that which is sent to the SNMP server. The clear snmp-server location command has the same effect for the location. Use these commands when you want to change the text in the contact or location fields; that is, by clearing it and then replacing the information with the snmp-server command.
The clear snmp-server host command stops sending SNMP traps, or you can specify one or more IP addresses to which SNMP traps are not sent.
Using SNMP, you can monitor system events on the PIX Firewall.
See also: no snmp-server, snmp-server, show snmp-server
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear snmp-server location
Stop logging SYSLOG messages. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| ip_address | SYSLOG host IP address. |
| facility | Eight facilities LOCAL0(16) through LOCAL7(23); the default is LOCAL4(20). Hosts file the messages based on the facility number in the message. |
| level | Message type; sets the level above which PIX Firewall suppresses messages to the SYSLOG hosts. Setting the level to 3, for example, allows messages with levels 0, 1, 2, and 3 to display. The default is 3. The levels are:
|
Usage Guidelines
The clear syslog console command disables SYSLOG messages on the console. The clear syslog host command disables sending SYSLOG messages to the specified host. The clear syslog output command stops sending all SYSLOG messages. This command is the same as no syslog.
See also: syslog, show syslog
Example
pixfirewall(config)# clear syslog
Remove PIX Firewall Telnet access from user. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| ip_address | The IP address or network of a host that is authorized to access the PIX Firewall Telnet management interface. |
| netmask | The netmask for the network specified in this Telnet command. This allows multiple machines on a particular IP subnet access to the PIX Firewall management interface. |
Usage Guidelines
The clear telnet command removes Telnet access to an IP address. Up to 16 hosts or networks are allowed access to the PIX Firewall, 4 simultaneously. show telnet displays the current list of IP addresses authorized to access the PIX Firewall. You can use the who command to see which IP addresses are currently accessing the firewall with Telnet.
See also: show telnet, who
Example
Add conduit through firewall for incoming connections. (Configuration mode.)
global_ip port[-port] protocol ip_address [netmask]
Syntax Description
| global_ip | The IP address from the global pool to associate this conduit with. |
| port | Destination port number into which connections are permitted on the inside machine (if using TCP, 25 for SMTP, 80 for HTTP, and so on). 0 means match any port. The port values are defined in RFC 1700. |
| protocol | tcp or udp. |
| ip_address | IP address (host or network) from which to permit incoming connections (0.0.0.0 is any host). |
| netmask | Network mask of ip_address. |
Usage Guidelines
The conduit command creates an exception to the PIX Firewall Adaptive Security mechanism by letting you permit connections from outside the PIX Firewall to hosts on the inside network. Conduits exist on the static translation slots and can be added with the conduit command or through the last parameter of the static command. The conduit command is the recommended method. The no conduit command removes the conduit you specify.
If a conduit is specified as, for example: conduit 192.1.1.1 tcp:192.1.2.2/32-0, the host 192.1.2.2 can access the inside host that is mapped to the global address 192.1.1.1 on any TCP port. The same syntax applies for UDP.
See also: no conduit, show conduit.
Example
The following pair of commands enables only SMTP communication between the UNIX gateway host (10.10.25.10) and an SMTP server on the inside network (192.168.1.49):
pixfirewall(config)# static 10.10.26.147 192.168.1.49 pixfirewall(config)# conduit 10.10.26.147 tcp:10.10.25.10/32-25
To remove the last conduit, issue the following:
pixfirewall(config)# no conduit 10.10.26.147 tcp:10.10.25.10/32-25
Merge current configuration with that on floppy disk. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The configure floppy command merges the current running configuration with the configuration stored on floppy disk. This command assumes that the floppy disk was previously created by the write floppy command.
Each statement on floppy disk is read into the current configuration and evaluated in the same way as commands entered from a keyboard with these rules:
Example
pixfirewall# configure floppy
Merge configuration with that from flash memory. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The configure memory command merges the configuration in flash memory into the current configuration in RAM. Each statement in flash memory is read into the current configuration and evaluated in the same way as commands entered from a keyboard with these rules:
Example
pixfirewall# configure memory
Start configuration mode. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The configure terminal command starts configuration mode. Exit configuration mode by pressing ^z. After exiting configuration mode, use write memory to store your changes in flash memory or write floppy to store the configuration on floppy disk. Use the write terminal command to display the current configuration.
Example
pixfirewall# configure terminal
Exit privileged mode and return to unprivileged mode. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The disable command exits privileged mode and returns you to unprivileged mode. Use the enable command to return to privileged mode.
Example
pixfirewall# disable pixfirewall>
Start privileged mode. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The enable command starts privileged mode. PIX Firewall prompts you for your privileged mode password. The default password is cisco. Use disable to exit privileged mode. Use enable password to change the password.
Example
pixfirewall> enable Password: ####### pixfirewall# disable pixfirewall>
Set the privileged mode password. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
| password | A password of up to 16 alphanumeric characters, which is not case sensitive. PIX Firewall converts the password to all lowercase. |
Usage Guidelines
The enable password command changes the privileged mode password, for which you are prompted after you enter the enable command. When the PIX Firewall starts and you enter privileged mode, the password prompt appears. The default password is cisco.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# enable password fnord42
Enable access to the optional failover feature. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
active
|
Make a PIX Firewall the primary unit. This argument cannot be used in a configuration file. Only use this command when you need to force control of the connection back to the unit you are accessing, such as when you want to switch control back from a unit after you have fixed a problem and want to restore service to the primary unit. Either enter no failover active on the secondary unit to switch service to the primary or failover active on the primary unit. |
Usage Guidelines
The failover command without an argument indicates that you have connected the optional failover cable from your primary PIX Firewall to a secondary PIX Firewall. Failover works by passing control to the secondary unit should the primary unit fail. The switch between units occurs within
60 seconds of the failure event. The markings on the cable let you choose which unit is primary and which is secondary. Refer to Installing the Failover Connector Assembly and Cable (Document Number 78-3749-01) supplied with the failover cable option for more information about upgrading an existing PIX Firewall unit to accept the failover cable.
Enable the failover feature by adding the failover command (without the active parameter) to the configuration files for both the primary and secondary PIX Firewalls.
When you use Telnet to access the PIX Firewall, only the active unit serves the connection. Use the hostname command on both units to identify a unique name for each unit. Using the host name, you can tell if you are communicating with the primary or secondary unit. If you are using Telnet when a failure occurs, you need to disconnect the Telnet session and restart it to the IP address.
If a failure occurs, the host name in the Telnet command prompt gives you positive acknowledgment that the secondary unit is active. In addition, SYSLOG messages indicate whether the primary or secondary unit failed. Use the show failover command to verify which unit is active.
Aside from the different host names, the configuration files for both units need to be identical.
If you want to force a PIX Firewall to be active or go to standby you can use the failover active or no failover active command. Use this feature to force a PIX Firewall offline for maintenance or to return a failed unit to service.
Use the show failover command to verify the status of the connection and to determine which unit is active.
Failover SYSLOG Messages
In the messages that follow, P|S can be either Primary or Secondary depending on which PIX Firewall is sending the message. Failover messages always have a SYSLOG priority level of 2, which indicates critical condition. Refer to the syslog output command description for more information on SYSLOG messages.
The SYSLOG messages sent to record failover events are:
See also: no failover, show failover.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# failover active
Define IP address in the global pool. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| global_id | An identification number from 1 to 10 that groups global addresses for use by networks on the inside of the PIX Firewall. If there is a single network on the inside of the PIX Firewall, the global_id has no meaning and you use 1. |
| ip_address | One or more IP addresses that the PIX Firewall shares among its connections. Each IP address must be registered with the Network Information Center (NIC). You can specify a range of IP addresses by separating the starting and ending addresses with a dash (-). |
Usage Guidelines
The global command defines the addresses in the global pool. Global pool addresses must be registered with the NIC; they provide an IP address for each incoming and outgoing connection. Always use the nat command with the global command to assign the global_id values to each network.
Configuring the PIX Firewall requires you to specify at least two global IP addresses with the global command. PIX Firewall uses the global addresses to assign a virtual IP address to a connection. When the translate times out (defined by the timeout command), the global address returns to the available pool. If the outside network connects with the Internet, each IP address you specify as a global must be registered with the NIC. The phrases global network and virtual network are synonymous in this document.
When you assign global addresses from the pool for Private Link, select addresses from the start of global pool range. The PIX Firewall allocates IP addresses from the global pool by starting at the end of the range you specify and working backward.
The minimum number of IP addresses you must add to the global pool is 2; for example, 10.10.26.10-10.10.26.11. The maximum is 1 class B network worth of IP addresses. It is not valid to add 1 address; for example, global 10.10.26.20.
Note that the IP addresses assigned to the global pool differ by class type. If you specify a class A address, such as 1.2.3.0, global assigns address 1.0.0.1 through 1.0.255.254 to the global pool; whereas, if you specify a class C address, such as 192.168.42.0, global assigns only the
254 addresses from .1 to .254.
If you are using the same subnet and want to share it between the outside network and the PIX Firewall virtual network, the PIX Firewall causes a proxy-arp for the global pool on the outside network. If you are using global networks that are disjoint from the outside network address, be certain that the networking equipment and computers have a routing table entry for the global network with a next hop of the outside interface of the PIX Firewall.
When you enter the global command and specify a network address, such as 192.168.42.0, the "Some globals not created" message appears if the addresses you requested could not be assigned to the global pool. The firewall cannot assign either the .0 address or the .255 address to the global pool. Use the show global command to view which IP addresses were created.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# global 1 10.10.10.0
Display help information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The help or ? command displays help information about all commands. You can view help on an individual command by entering the command name followed by a question mark.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# age ? age <minutes>
Help information is available on the core commands (not show, no, or clear commands) by entering ? at the command prompt:
pixfirewall(config)# ?
age
apply
arp
auth
auth-server
auth-user
conduit
configure
disable
enable
failover
global
hostname
http
interface
ip
kill
link
linkpath
lnko
lnkopath
nat
outbound
passwd
ping
reload
rip
route
static
snmp-server
syslog
telnet
timeout
who
write
?
|
Age PIX Private Link keys
Apply outbound lists
ARP table manipulation
User Authorization Enable/Disable
Maintain Authorization Server lists
Maintain IP to Authorization lists
Add/remove conduits to static translations
Configure from terminal, floppy, or memory
Turn off privileged commands
Modify enable password
Administer Failover
Enter global network addresses
Change host name
Add authorized IP addresses for http access to PIX
Interface configuration
Set network number
Terminate a telnet session
Establish an encrypted PIX Private Link
Set the network paths for Private Links
Establish an encrypted PIX Private Link (OLD)
Set the network paths for Private Links (OLD)
Administer Address Translations
Create outbound lists
Modify telnet login password
Source a PING request message
Halt and reload system
RIP table
Set the network default router
Reserve a local to global address translation table entry
Administer SNMP daemon
Log messages to syslog server
Add authorized IP addresses for telnet access to PIX
Set the maximum idle time for translation and connection slots
Show active administration sessions on PIX
Write configuration memory, type 'write ?' for list
?Help list
|
Change the host name in the PIX Firewall command line prompt. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| newname | New host name for the PIX Firewall prompt. This name can be up to
16 alphanumeric characters and is not case sensitive. PIX Firewall converts the host name to all lowercase. |
Usage Guidelines
The hostname command changes the host name label on prompts. The default host name is "pixfirewall." If you have the optional failover feature, assign host names to both PIX Firewall units. Then if a failure occurs and you Telnet to the IP address, the host name in the prompt verifies that the secondary unit is functioning.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# hostname spinner spinner(config)# hostname pixfirewall pixfirewall(config)#
Permit inside IP address access to the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| ip_address | IP address of systems on the inside of the PIX Firewall that are able to access the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. |
| netmask | Network mask of ip_address. If you want to limit access to a single IP address use 255 in each octet; for example, 255.255.255.255. |
Usage Guidelines
The http command lets an IP address access the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. Use no http or clear http to disable management interface access. Use show http to list the information you entered.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# http 192.168.42.42 255.255.255.255
Identify Ethernet board speed and duplex. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| inside | Network interface for inside PIX Firewall network. |
| outside | Network interface for network outside the PIX Firewall. |
| 10baseT | Sets 10Mbit Ethernet and half duplex communications. |
| 100baseTX | Sets 100Mbit Ethernet and half duplex communications. |
| auto | Automatically determines networking speed and sets full duplex communications. |
Usage Guidelines
The interface ethernet command identifies the speed and duplex settings of the network interface boards. The speed setting affects the show blocks command. Refer to Installing Circuit Boards in the Cisco PIX Firewall (Document Number 78-3748-01) for information on installing an Ethernet board. Use no interface ethernet to disable access to the network interface. Use show interface ethernet to view information about the interface.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet inside auto pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet outside auto
Identify Token-Ring board speed. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| inside | Network interface for inside PIX Firewall network. |
| outside | Network interface for network outside the PIX Firewall. |
| 4mbps | 4 megabytes per second data transfer speed. |
| 16mbps | (default) 16 megabytes per second data transfer speed. |
Usage Guidelines
The interface token command identifies the speed of the Token-Ring network interface. Refer to Installing Circuit Boards in the Cisco PIX Firewall (Document Number 78-3748-01) for more information on installing a Token-Ring board. Use no interface token to disable access to the network interface. Use show interface token to view information about the interface.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# interface token inside 16mbps pixfirewall(config)# interface token outside 16mbps
Identify IP address for PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| inside|outside | The inside or outside network interface. |
| ip_address | IP address. |
| [netmask] | Network mask of ip_address. |
Usage Guidelines
The ip address command assigns an IP address to the PIX Firewall. Use the show ip address command to view which addresses are assigned to the inside and outside network interfaces.
Example
pixfirewall(config)# ip address inside 130.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
Terminate a Telnet session. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
| telnet_id | Telnet session ID. |
Usage Guidelines
The kill command terminates a Telnet session. Use the who command to view the Telnet session ID value. When you kill a Telnet session, PIX Firewall lets any active commands terminate and then drops the connection without warning to the user.
See also: show who, telnet
Example
pixfirewall# show who 2: From 10.10.54.0 pixfirewall# kill 2
Specify Private Link connection to PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
| remote_ip_address | IP address of a PIX Firewall running Private Link. |
key-id
|
The key number. Version 3 PIX Firewall supports up to seven Private Link encryption keys. The key_id value can be from 1 to 7. |
| key | The 56-bit key (up to 14 hexadecimal digits) used to seed the encryption chip. This key must be the same on each host end of an encrypted link. The key consists of hexadecimal numbers; for example, fadebac. Select a unique key that is difficult to guess. |
Usage Guidelines
The link command creates an encrypted path between version 3 Private Link equipped PIX Firewall units. You can specify up to seven encryption keys for data access between your unit and the remote unit. The key-ID and key values must be the same on each side of the Private Link. Once you specify the same keys on both sides of the connection, the systems alert each other when a new key takes effect. You can use the age command to specify the number of minutes that a key is in effect.
Specify the link command once for each key you want to specify; for example, if you want seven keys, enter the link command in the configuration seven times.
The PIX Firewall Private Link consists of an encryption card and software that permits PIX Firewall units to provide encrypted communications across an unsecure network such as the Internet. This optional feature is available to domestic customer sites.
PIX Firewall allows up to 64 Private Links. At least two PIX Firewall units are required along with the hardware/software option to use this feature.
Private Link works by checking packets that arrive at the PIX Firewall inside interface. If a route link previously created by the linkpath command exists that matches the destination network address, the packet is encrypted and encapsulated in an AH/ESP frame. The frame has a destination address of the remote PIX Firewall and a source address of the local PIX Firewall. When the packet arrives at the remote PIX Firewall unit, the data in the packet is decrypted and then sent through the inside interface to the original IP address specified. No translation takes place on packets that traverse the PIX Firewall Private Link. The addressing and data remains completely unchanged.
PIX Firewall allows up to 512 link paths.
You can manage remote PIX Firewall units through the Private Link interface.
See also: linkpath, show link
Example
To configure a Private Link, refer to the example setup in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 : Example Private Link Network Diagram
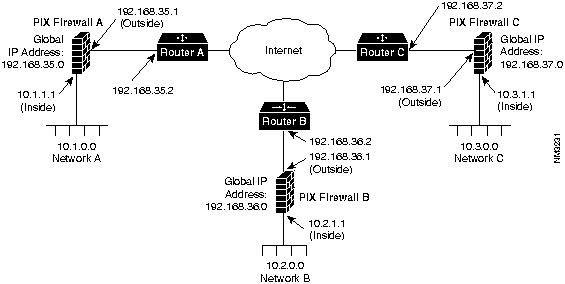
Before configuring Private Link, you would initially configure the systems using the standard commands. To configure PIX Firewall A, use these commands:
pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet inside auto up pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet outside auto up pixfirewall(config)# ip address inside 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 pixfirewall(config)# ip address outside 192.168.35.1 255.255.255.0 pixfirewall(config)# nat 1 0.0.0.0 pixfirewall(config)# global 1 192.168.35.0 pixfirewall(config)# route inside 10.1.1.2 pixfirewall(config)# route outside 192.168.35.2
For this example, assume that PIX Firewall B, the version 2 PIX Firewall, is already configured to have the IP addresses and global IP addresses shown in the illustration, and that it has its Private Link configured to talk to PIX Firewall A and C. Refer to the version 2 Private Internet Exchange Reference Guide (Document Number 78-3362-02) for more information on configuring Private Link.
To initially configure PIX Firewall C, use these commands:
pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet inside auto up pixfirewall(config)# interface ethernet outside auto up pixfirewall(config)# ip address inside 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 pixfirewall(config)# ip address outside 192.168.37.1 255.255.255.0 pixfirewall(config)# nat 1 0.0.0.0 pixfirewall(config)# global 1 192.168.37.0 pixfirewall(config)# route inside 10.3.1.2 pixfirewall(config)# route outside 192.168.37.2
When you configure a Private Link, follow these steps:
On PIX Firewall A, in the previous illustration, enter these commands to configure the Private Link:
On PIX Firewall C, enter these commands:
Define a Private Link destination IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The linkpath command specifies IP address information for the remote Private Link PIX Firewall. Use show linkpath to view the IP addresses you specify. Use no linkpath to stop access to a Private Link remote firewall. Refer to the link command description for more information about using linkpath.
See also: no linkpath, show linkpath, lnkopath
Example
Define access to an older version 2 Private Link PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The lnko command defines access to a version 2 Private Link PIX Firewall and specifies an encryption key. The PIX Firewall Private Link consists of an encryption card and software that permits PIX Firewall units to provide encrypted communications across an unsecure network such as the Internet. This optional feature is available to domestic customer sites.
Refer to the link command description for more information about using lnko.
See also: lnkopath, show lnko
Example
Specify a version 2 Private Link path to the remote PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The lnkopath command sets the network paths for PIX Firewall version 2 Private Link connections.
See also: show lnkopath, lnko
Example
Associate a network with a pool of IP addresses. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The nat command lets you specify lists of inside hosts that can use the firewall for address translation. You can specify up to 10 global pools of IP addresses. Use nat 0 to enable the identity feature so that address translation is not performed. Use this feature when you have NIC-registered IP addresses on your inside network that you want to be visible on the outside network.
See also: global, no nat, show nat.
Example
Cancel a previous use of the apply command. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no apply command cancels a previous apply statement. All arguments must be specified.
See also: apply, show apply
Example
Erases the contents of the PIX Firewall ARP table. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no arp command clears the PIX Firewall ARP table. This command does not clear aliased ARPs unless you specify alias. You may remove individual entries by specifying either the IP or MAC address.
This command is the same as clear arp.
See also: arp, clear arp, show arp
Example
Suspend user authentication services. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no auth command suspends user authentication for both inside and outside, or you can selectively disable it by interface. Use show auth to view the state of authentication. Use auth to restart authentication. Refer to the auth command description for more information on user authentication.
See also: auth, show auth
Example
Remove access to authentication server. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no auth-server command removes knowledge of all authentication servers, or you can remove servers by type, or type and server IP address. Use show auth-server to view which servers are specified in the configuration.
See also: auth-server, show auth-server
Example
Disable user authentication for IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no auth-user command disables user authentication access to the PIX Firewall. Use show auth-user to view which IP addresses have access to user authentication.
See also: auth-user, show auth-user
Example
Remove a conduit. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no conduit command removes conduits to static translations. To remove groups of conduits, you must specify the global IP address, the port, and the protocol. You can also delete individual conduits by specifying the IP address and network mask. Use the show conduit command to view which conduits remain.
The conduit command lets you permit connections from outside the PIX Firewall to hosts on the inside network. Conduits exist on the static translation slots and can be added with the conduit command. The conduit command is the recommended method.
Example
Turn failover off or force PIX Firewall into standby mode. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no failover command without an argument turns the optional failover feature off. With the active argument, no failover forces a PIX Firewall into standby mode. The failover feature works by passing control to a secondary PIX Firewall should the primary unit fail.
Use show failover to view the status of the connection and to determine if the failover cable is connected to both units.
Refer to the description of the failover command for more information on this feature.
See also: failover, show failover
Example
Remove IP address from the global pool. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no global command removes IP addresses from the global pool.
Example
Remove IP address access to the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no http command lets you deny an IP address access to the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. This command is the same as clear http.
After you enter no http, current HTML sessions can view the pages in the network browser's memory, but if the user tries to reload the configuration interface, the network browser returns an error message and the screen goes blank.
If you immediately re-enter the http command, the network browser restores access to the HTML management interface. Use the reload command in the browser to display the pages.
See also: http, show http, passwd
Example
Disable Private Link connection. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no link command disables a Private Link connection. Use show link to view link information. Refer to the description of the link command for more information on Private Link.
Removing the last key removes the link. You can only remove the link if all linkpath statements have already been removed.
See also: link, show link
Example
Disable Private Link destination IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no linkpath command disables a Private Link connection to a remote PIX Firewall. Use show linkpath to view connection status. Refer to the description of the link command for more information on Private Link.
Improper use of this command can yield the error message "Path does not exist." This results from the no linkpath command being used for a link not previously created.
See also: link, linkpath
Example
Disable access to an older version 2 Private Link PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no lnko command disables access to a version 2 Private Link PIX Firewall. Use show lnko to view Private Link status. Refer to the description of the link command for more information on Private Link.
See also: link, lnko, lnkopath
Example
Disable a version 2 Private Link path to the remote PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no lnkopath command disables the network paths for PIX Firewall version 2 Private Link connections.
See also: show lnkopath, lnko
Example
Disassociate a network with a pool of IP addresses. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no nat command disables a previous occurrence of the nat command.
See also: nat, show nat
Example
Removes an access list previously created with outbound. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no outbound command removes an access list. Use show outbound to view status.
See also: outbound, show outbound
Example
Disables RIP updates. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The rip command enables IP routing table updates from received RIP (Routing Information Protocol) broadcasts. Use show rip to display the current RIP settings. Use no rip to disable PIX Firewall IP routing table updates. The default is to disable all RIP functionality.
Example
Remove an entry from the routing table. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no route command lets you remove an entry from the routing table. To remove a static entry, use the static keyword. Static routes are routes previously entered with the route command.
Example
Stops the PIX Firewall from sending SNMP event information. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no snmp-server command clears a previously specified snmp-server statement. Use this command to either erase the information from what SNMP receives or to change an existing statement by clearing it and re-entering it with the snmp-server command.
Using SNMP, you can monitor system events on the PIX Firewall.
Example
Disable local IP address to a global IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no static command disables a permanent mapping (static translation slot) between a local IP address and a global IP address in the virtual pool. A static address is a permanent mapping from one of the global, registered IP addresses to a local IP address inside the private network. Use show static to view static statements in the configuration.
See also: conduit, show static
Example
Stop logging SYSLOG messages. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no syslog console command disables SYSLOG messages on the console. The no syslog host command disables sending SYSLOG messages to the specified host. The no syslog output command stops sending all SYSLOG messages. The no syslog command is the same as clear syslog.
See also: syslog, show syslog
Example
Disable IP address Telnet access to the PIX Firewall. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The no telnet command lets you disable Telnet access to the PIX Firewall. The show telnet command displays the current list of IP addresses authorized to access the PIX Firewall. Use the who command to view which IP addresses are currently accessing the firewall. The no telnet command is the same as the clear telnet command.
See also: telnet, who
Example
Creates an access list for controlling Internet use. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The outbound command creates an access list that determines how inside IP addresses can access outside activities. Use with the apply command to specify whether an access list applies to the outside network, or to downloading information from a remote source to the inside network.
See also: apply, show outbound
Example
The following commands prevent host 192.168.1.49 from accessing the World Wide Web (port 80).
If your employees are spending too much time examining GIF images on a particular site with two web servers, you can use the following lines to restrict this access:
Set password for Telnet and HTML access.
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The passwd command sets a password for Telnet and HTML access. Use show passwd to view this password.
See also: enable password, show passwd
Example
passwd athensge0rg1a
Determine if other IP addresses are visible from the PIX Firewall. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The ping command determines if the PIX Firewall has connectivity or if a host is available on the network. The command output shows if the response was received; that is, that the host exists on the network. If the host is not responding, ping displays "no response received." Use show interface to ensure that the PIX Firewall is connected to the network and has connectivity.
Example
The command displays three attempts to reach the specified address:
Reboots and reloads the configuration from flash memory. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The reload command reboots the PIX Firewall and reloads the configuration from flash memory.
Example
Changes RIP settings. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The rip passive command enables IP routing table updates from received RIP (Routing Information Protocol) broadcasts. Use show rip to display the current RIP settings. Use no rip to disable PIX Firewall IP routing table updates. The default is to enable IP routing table updates.
RIP default broadcast is possible on either the inside interface.
The rip default passive command causes the PIX Firewall to broadcast default route messages on the specified interface.
Examples
Enter a static route for the specified interface. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
Use the route command to enter static routes for an interface. To enter a default route, set dest_net_ip and netmask to 0.0.0.0. All routes entered using the route command are stored in the configuration when it is saved. Refer to the write command for more information.
Example
View command information. (Differs by mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show command without arguments or the show ? command lets you view the names of the show commands and a description.
Example
Show activation key and number of user licenses. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show actkey command displays the activation key and number of licensed users for your PIX Firewall. When you install new software, PIX Firewall prompts you for an activation key. Use this command to view the activation key after you have completed the installation. Write this number down in the space that follows so that it is available the next time you upgrade your unit:
Example
Show duration of Private Link key aging. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show age command shows the current length of time that a Private Link key encrypts communications between the local and remote PIX Firewall units. Refer to the link command for more information on Private Link.
Example
View outbound access list to an IP address. (Unprivileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The show apply command lets you view outbound access lists collectively or you can search for lists by number or with the outgoing_src or outgoing_dest keywords.
See also: apply
Example
Display ARP table. (Unprivileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The show arp command without arguments displays all inside and outside network interfaces' ARP tables, aliased or not. show arp inside displays all inside arps, aliased or not. show arp inside ip displays the IP address if it exists. show arp inside 0 alias displays all aliased ARP entries for the inside network interface ARP table (0 is used as a place holder for wild card). show arp inside 0 mac finds and displays the ARP entry that matches the MAC address.
Example
Display number of seconds that an ARP entry can remain in the ARP table. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show arp timeout command lets you view the number of seconds that an ARP entry remains in the ARP table before expiring. Set the duration with the arp command. The default is
Example
Show status of PIX Firewall user authentication. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show auth command lists the status of PIX Firewall user authentication on each interface:
See also: auth
Example
Show IP address of authentication server. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show auth-server command output lists the following information:
Example
Show IP address information for user authentication. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show auth-user command output lists the following information:
See also: auth, auth-user
Example
Show system buffer utilization. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show blocks command lists system buffer utilization.
Example
Show conduit through firewall for incoming connections. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show conduit command output contains the following information:
Example
View configuration in flash memory. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show config command displays the configuration in flash memory. Use write term to view the current configuration in RAM.
See also: write term
Example
Show status of optional failover feature. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show failover command lists the following information:
See also: failover
Example
View global commands in the configuration. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show global command lists the contents of the global command statements in the configuration.
See also: global
Example
View which IP addresses can access the PIX Firewall HTML management interface. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show http command lists the IP addresses that can access the PIX Firewall HTML management interface.
See also: http
Example
Display hardware identification values. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show hw command lets you view hardware identification information.
Example
View network interface information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show interface command lets you view network interface information for both Ethernet and Token-Ring depending on which is installed in your PIX Firewall. This is the first command that you should use whenever you are attempting to get connectivity with the rest of your network.
The information in the display is as follows:
Example
Display the IP address of the PIX Firewall. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show ip address command displays the IP address of the PIX Firewall. The inside or outside keywords in the display indicate the interface to which the IP address is assigned.
Example
View Private Link remote IP address and interface status. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show link command lets you view the remote Private Link's IP address, each encryption key, and the number of packets sent and transmitted ("nn out, nn in").
Example
View Private Link connection information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show linkpath command lets you view the IP address of the outside interface on the remote PIX Firewall ("Foreign IP"), the IP address of the network served by the remote firewall, and the network mask of the foreign network.
Example
View version 2 Private Link information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show lnko command lets you view the IP of the outside interface on the remote PIX Firewall ("Foreign IP"), the local IP address, and the encryption key.
See also: lnko, lnkopath
Example
View version 2 Private Link information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show lnkopath command lets you view the remote IP address, the remote network address, and the network mask.
See also: lnko, linkopath
Example
View nat statement information from the configuration. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show nat command lets you view the contents of the nat statements in the configuration.
See also: nat
Example
Show system memory utilization. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show memory command displays a summary of the maximum physical memory and current free memory available to the PIX Firewall operating system. Everything in PIX Firewall is preallocated and the number of free memory should never change.
Example
View outbound statement information in configuration. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show outbound command lets you view the contents of the previously entered outbound statements in your configuration.
See also: outbound
Example
View the password you entered with the passwd command. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show passwd command lets you view the password you entered with the passwd command. This password permits access to the PIX Firewall with the Telnet command and to the HTTP configuration facility, which you access with a network browser such as Netscape Navigator.
See also: passwd, enable password, telnet, http, write term
Example
Display processes. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show processes command displays a summary listing of running processes. Processes are lightweight threads requiring only few instructions to switch. In the listing, PC is the program counter, SP is the stack pointer, STATE is the address of a thread queue, Runtime is the number of milliseconds that the thread has been running, SBASE is the stack base address, Stack is the current number of bytes used and the total size of the stack, and Process lists the thread's function.
Example
View the RIP listening status on your PIX Firewall. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show rip command lets you view the status of RIP listening on the PIX Firewall. The display contains the following information:
See also: rip
Example
View PIX Firewall routing table. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show route command lets you view the route information.
The output display contains the following information:
Example
View PIX Firewall SNMP location, contact, and host information from configuration. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show snmp-server command lists the following information:
See also: snmp-server
Example
View static information in the configuration. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show static command lets you view the static information you entered in the configuration.
See also: static
Example
View previously sent SYSLOG events. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show syslog command lets you view previously sent SYSLOG events. The facility value tells the host where to file the messages. Refer to the description of the syslog output command for more information.
The levels are:
See also: clear syslog, syslog output
Example
View which IP addresses have Telnet access to the PIX Firewall. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show telnet command lets you view which IP addresses can access the PIX Firewall with Telnet. Use the who command to view which of these IP addresses are currently using the PIX Firewall.
See also: telnet, who, kill
Example
Displays the maximum idle time for translation and connection slots. (Configuration mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show timeout command lets you view the idle time for connection and translation slots. If the connection or translation slot has not been used for the idle time specified, the resource is returned to the free pool. The minimum idle time for both xlate and conn is 5 minutes. TCP connection slots are freed within 60 seconds after a normal connection close sequence.
See also: timeout
Example
View PIX Firewall version. (Unprivileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The show version command lets you view the version of your PIX Firewall software.
Example
where: pv is the point release version and nnn is the release number
Shows active HTTP and Telnet administration sessions on PIX Firewall. (Unprivileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The show who command shows the PIX Firewall tty_id and IP address of each HTTP and Telnet client currently logged into the PIX Firewall. This command is the same as the who command.
See also: http, kill, telnet
Example
View translation slot information. (Unprivileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The show xlate command displays the contents of the translation slots.
Example
Provide SNMP event information. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
This command causes the PIX Firewall to send SNMP traps so that the firewall can be monitored remotely. Use snmp-server host to specify which systems receive the SNMP traps. You can specify up to five systems and all must be on the inside network of the firewall. PIX Firewall converts the contact and location information to lowercase.
Use snmp-server contact and snmp-server location to specify your name and the location of the PIX Firewall so that hosts receiving SNMP traps can contact you if monitored problems occur.
Using SNMP, you can monitor system events on the PIX Firewall.
The PIX Firewall SNMP MIB-II groups available are System, Interfaces, and SNMP.
The PIX Firewall SNMP traps available to an SNMP server are:
Use CiscoWorks Windows (Product Number CWPC-2.0-WIN) or any other SNMP V1, MIB-II compliant browser to receive SNMP traps and browse the MIB. SNMP traps occur at UDP port 162. Up to five hosts can receive SNMP traps. SNMP events can be read, but information on the PIX Firewall cannot be changed with SNMP.
Example
Map local IP address to a global IP address. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The static command creates a permanent mapping (static translation slot) between a local IP address and a global IP address in the virtual pool. A static address is a permanent mapping from one of the global, registered IP addresses to a local IP address inside the private network. Static addresses are recommended for internal network service hosts, such as an SMTP server. Use show static to view static statements in the configuration.
See also: conduit, show static
Example
View SYSLOG messages on the PIX Firewall console. (Configuration mode.)
Usage Guidelines
Displays syslog messages on the console port. Use no syslog console to stop the display. Refer to the description of syslog output for more information on SYSLOG.
See also: no syslog console
Example
Define which hosts are sent SYSLOG messages. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The syslog host command lets you specify up to 16 host IP addresses to which SYSLOG messages are sent. Use no syslog host to remove a host from the receiving list. Use show syslog to view the current hosts. Refer to the description of syslog output for more information on SYSLOG.
Example
Start sending SYSLOG notification messages. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The syslog output command configures the facility and level of SYSLOG messages. Because network devices share the eight facilities, syslog output lets you set the facility marked on all messages. Messages are sent to the SYSLOG host over UDP. The syslog output command also starts sending messages onto the network. Use the syslog host command to specify which systems receive the messages.
You can use show syslog to view previously sent messages.
PIX Firewall generates SYSLOG messages for system events, such as security alerts and resource depletion. SYSLOG messages may be used to create email alerts and log files, or displayed on the console of a designated host using UNIX SYSLOG conventions. The log host must be on the internal network.
A PC WinSock version of syslogd also will work.
PIX Firewall sends SYSLOG messages to document the following events:
Logging is enabled by configuring the PIX Firewall with the IP address of the log host.
Configuring a UNIX System for SYSLOG
To configure a UNIX system to accept SYSLOG messages:
Examples of PIX Firewall SYSLOG messages resemble the following:
Example
Allow inside IP address to configure the PIX Firewall from Telnet. (Privileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The telnet command lets you decide who can configure the PIX Firewall from Telnet. Up to 16 hosts or networks are allowed access to the PIX Firewall, four simultaneously. The show telnet command displays the current list of IP addresses authorized to access the PIX Firewall. Use no telnet or clear telnet to remove Telnet access from a previously set IP address. Use the who command to view which IP addresses are currently accessing the firewall.
With Telnet, you can configure the PIX Firewall from the inside network or over Private Link.
See also: clear telnet, no telnet, show telnet, who
Examples
Sets the maximum idle time for translation and connection slots. (Configuration mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The timeout command sets the idle time for connection and translation slots. If the connection or translation slot has not been used for the idle time specified, the resource is returned to the free pool. The minimum idle time for both xlate and conn is 5 minutes. TCP connection slots are freed within 30 seconds after a normal connection close sequence.
Use show timeout to display the current timeout settings.
See also: show timeout
Examples
Shows active Telnet administration sessions on PIX Firewall. (Unprivileged mode.)
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines
The who command shows the PIX Firewall tty_id and IP address of each Telnet client currently logged into the PIX Firewall. This command is the same as the show who command.
See also: http, kill, telnet
Example
Clear the contents of flash memory. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The write erase command clears the flash memory configuration. To clear the current running configuration, use write erase and then reload to reboot the PIX Firewall.
Example
Store the current configuration on floppy disk. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The write floppy command stores the current running configuration on floppy disk. Use configure floppy to replace the current configuration with what you saved on floppy disk. The write floppy command assumes that the floppy disk is formatted for an IBM computer; however, once you use write floppy to write to the disk, its contents can only be accessed with the PIX Firewall.
See also: configure floppy
Example
Save current configuration in flash memory. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The write memory command saves the current running configuration to flash memory. Use configure memory to replace the current configuration with the image you saved in flash memory.
See also: configure memory
Example
View current configuration on console. (Privileged mode.)
Usage Guidelines
The write terminal command displays the current running configuration on the console computer. Before using this command, set your terminal communications program to store the screen display in a log file, or else once the configuration displays, you can use copy and paste commands to copy it to a file on your console computer.
Use configure terminal to start configuration mode. You can then copy and paste a configuration from a text file into the configuration.
You can also display the current configuration contents with show config, but passwords are not displayed. The write terminal command lists all information in configuration including passwords.
See also: configure terminal, show config
Example
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
(14 hexadecimal digits).
pixfirewall(config)# : Configure for firewall C:
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.37.1 1 fadebac
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.37.1 2 bacfade
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.37.1 3 baabaaa
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.37.1 4 beebeee
pixfirewall(config)# linkpath 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.37.1
pixfirewall(config)# :
pixfirewall(config)# : Configure for firewall B:
pixfirewall(config)# lnko 192.168.36.2 fadebac
pixfirewall(config)# lnkopath 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.36.2
pixfirewall(config)# : Configure for firewall A:
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.35.1 1 fadebac
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.35.1 2 bacfade
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.35.1 3 baabaaa
pixfirewall(config)# link 192.168.35.1 4 beebeee
pixfirewall(config)# linkpath 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.35.1
pixfirewall(config)# :
pixfirewall(config)# : Configure for firewall B:
pixfirewall(config)# lnko 192.168.36.2 fadebac
pixfirewall(config)# lnkopath 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.36.2
dest_net
The IP address of the destination network on the inside interface of the remote PIX Firewall of a Private Link.
netmask
Specifies a subnet mask to apply to dest_net.
remote_ip
IP address of the remote PIX Firewall's outside network interface.
pixfirewall(config)# linkpath
remote_global
IP address from the global address pool.
key
The encryption key. Version 2 PIX Firewall supports one Private Link encryption key. The encryption key can be up to 56 bits in length (14 hexadecimal digits); for example, fadebac.
pixfirewall(config)# lnko 192.168.42.1 0xfaded
dest_net
The IP address of the destination network on the inside interface of the remote PIX Firewall of a Private Link.
netmask
Specifies a subnet mask to apply to dest_net.
remote_global
IP address in the global pool of the remote PIX Firewall in a Private Link environment.
pixfirewall(config)# lnkopath 1.2.3.4 255.255.255.0 192.168.42.1
global_id
A number in the range of 1 to 10 previously specified with the global command. Specify 0 to indicate that no address translation be used with ip_address.
ip_address
IP address of the network to which the global pool pertains.
netmask
Network mask for ip_address. You can use 0.0.0.0 to allow everyone access.
pixfirewall(config)# nat 1 192.168.42.0 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall(config)# show nat
nat 1 192.168.42.0 255.255.255.255
num
An access list number previously created with outbound.
outgoing_src
Use if previously specified with the apply command. outgoing_src causes the firewall to examine the source address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement.
outgoing_dest
Use if previously specified with the apply command. outgoing_dest causes the firewall to examine the destination address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall for access list enforcement.
pixfirewall(config)# outbound 1 deny 192.168.42.2 255.255.255.255 80
pixfirewall(config)# apply 1 outgoing_src
pixfirewall(config)# show apply
apply 1 outgoing_src
pixfirewall(config)# no apply 1 outgoing_src
pixfirewall(config)# show apply
pixfirewall(config)#
inside
PIX Firewall inside network interface ARP table.
outside
PIX Firewall outside network interface ARP table.
ip_address
IP address.
mac_address
Ethernet MAC address for the ARP table entry.
alias
Delete aliased ARP entries (those pointing to another host).
pixfirewall(config)# no arp
inside
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on your local network (inside the PIX Firewall).
outside
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on the outside of the PIX Firewall.
pixfirewall(config)# auth
pixfirewall(config)# show auth
auth outside
auth inside
pixfirewall(config)# no auth
pixfirewall(config)# show auth
no auth outside
no auth inside
type
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+.
server_ip
The IP address of the authentication server.
skey
An alphanumeric keyword of up to 127 characters defined by what the authentication server accepts. This is a public key between the client and server for encrypting data between them. The skey value must be the same on both the client and server systems.
RADIUS must have skey defined.
pixfirewall(config)# show auth-server
auth-server 1.2.3.4 thism0dernw0rld
pixfirewall(config)# no auth-server
pixfirewall(config)# show auth-server
pixfirewall(config)#
type
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+.
ip_address
IP address from which or to which access is directed depending on whether the connection is inbound or outbound.
netmask
Network mask of ip_address.
pixfirewall(config)# show auth-user
auth-user radius 192.168.30.2 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall(config)# no auth-user
pixfirewall(config)# show auth-user
pixfirewall(config)#
global_ip port protocol ip_address [netmask]
global_ip
The IP address from the global pool to associate this conduit with.
port
Destination port number into which connections are permitted on the inside machine (if using TCP, 25 for SMTP, 80 for http, and so on). 0 means match any port.
protocol
tcp or udp.
ip_address
IP address (host or network) from which to permit incoming connections (0.0.0.0 is any host).
netmask
Network mask.
pixfirewall(config)# no conduit 192.168.42.0 25 tcp
active
Force the current PIX Firewall into standby mode.
pixfirewall(config)# no failover
pixfirewall(config)# show failover
Failover Off
This host: Primary - Active
...
pixfirewall(config)# no failover active
pixfirewall(config)# show failover
Failover Off
This host: Primary - Standby
...
pixfirewall(config)#
global_id
An identification number from 1 to 10 that groups global addresses for use by networks on the inside of the PIX Firewall.
ip_address
An IP address or a range of IP addresses previously entered with the global command.
pixfirewall(config)# global 1 192.168.42.0
Some globals not created
pixfirewall(config)# show global
global 1 192.168.42.1-192.168.42.254
pixfirewall(config)# no global 1
pixfirewall(config)# show global
pixfirewall(config)#
ip_address
IP address of systems on the inside of the PIX Firewall that are able to access the PIX Firewall HTML management interface.
netmask
Network mask of ip_address. If you want to limit access to a single IP address use 255 in each octet; for example, 255.255.255.255.
pixfirewall(config)# no http
remote_ip_address
IP address of a PIX Firewall running Private Link.
key-id
The key number. Version 3 PIX Firewall supports up to seven Private Link encryption keys.
key
The 56-bit key (up to 14 hexadecimal digits) used to seed the encryption chip. This key must be the same on each host end of an encrypted link. The key consists of hexadecimal numbers; for example, fadebac. Select a unique key that is difficult to guess.
pixfirewall(config)# no link 1.2.3.4 1
dest_net
The IP address of the destination network on the inside interface of the remote PIX Firewall of a Private Link.
netmask
Specifies a subnet mask to apply to dest_net.
remote_ip
IP address of the remote PIX Firewall's outside network interface.
pixfirewall(config)# no linkpath
remote_global
IP address from the global address pool.
key
The encryption key. Version 2 PIX Firewall supports one Private Link encryption key. The encryption key can be up to 56 bits in length (14 hexadecimal digits); for example, fadebac.
pixfirewall(config)# no lnko 16.17.18.19 1a2b3c4d
dest_net
The IP address of the destination network on the inside interface of the remote PIX Firewall of a Private Link.
netmask
Specifies a subnet mask to apply to dest_net.
remote_global
IP address in the global pool of the remote PIX Firewall in a Private Link environment.
pixfirewall(config)# no lnkopath 1.2.3.0 255.255.255.255.0 5.6.7.8
global_id
A number in the range of 1 to 10 previously specified with the global command. Specify 0 to indicate that no address translation be used with ip_address.
ip_address
IP address of the network to which the global pool pertains.
netmask
Network mask for ip_address. You can use 0.0.0.0 to allow access to everyone.
pixfirewall(config)# no nat
num
A tag number for the access list.
permit
Use if supplied in the outbound command. The permit keyword allows the access list to access the specified IP address and port.
deny
Use if supplied in the outbound command. The deny keyword denies the access list access to the specified IP address and port.
ip_address
The IP address for this access list entry.
netmask
The network mask for comparing with the IP address; 255.255.255.0 causes the access list to apply to an entire class C address. 0.0.0.0 disables all access.
port
A port or range of ports that the access list is permitted or denied access to.
pixfirewall(config)# no outbound
inside
Modifies RIP behavior on the inside interface.
outside
Modifies RIP behavior on the outside interface.
default
Disables the default route broadcast on the specified interface.
passive
Disables passive RIP on either the inside or outside interface.
pixfirewall(config)# no rip outside default
dest_net_ip [static]
inside|outside
Specifies either the inside or outside
dest_net_ip
The destination network IP address.
static
Remove a static route entry.
pixfirewall(config)# no route inside 192.168.42.0
contact
Indicates that you are supplying your name or that of the PIX Firewall system administrator.
location
Indicates that you are specifying your PIX Firewall location.
host
Indicates that you are specifying the IP address of the SNMP server.
text
When used with contact, your name or that of the PIX Firewall system administrator. When used with location, your PIX Firewall location. If the location name contains spaces, surround the string in single quotes; for
example, 'building 42'.
ip_address
When used with host, the IP address of the SNMP server.
pixfirewall(config)# no snmp-server
global_ip
The registered IP address to be used from the global pool.
local_ip
The local IP address from the inside network.
pixfirewall(config)# no static
ip_address
SYSLOG host IP address.
facility
Eight facilities LOCAL0(16) through LOCAL7(23); the default is LOCAL4(20). Hosts file the messages based on the facility number in the message. Refer to the syslog output command for more information on the facilities.
level
Message type; sets the level above which PIX Firewall suppresses messages to the SYSLOG hosts. Setting the level to 3, for example, allows messages with levels 0, 1, 2, and 3 to display. The default is 3. The levels are:
pixfirewall(config)# no syslog console
ip_address netmask
ip_address
The IP address or network of a host that is authorized to access the PIX Firewall Telnet management interface.
netmask
The netmask for the network specified in this Telnet command. Use a network IP address to enable access to all in the subnet; for example if you set netmask to 255.255.255.0, all systems in the subnet can access the firewall over Telnet. If you set netmask to 255.255.255.255, only the IP address you specify can access the firewall.
pixfirewall(config)# no telnet 192.168.42.2 255.255.255.255
num
A tag number for the access list.
permit
Allow the access list to access the specified IP address and port.
deny
Deny the access list access to the specified IP address and port.
ip_address
The IP address for this access list entry.
netmask
The network mask for comparing with the IP address; 255.255.255.0 causes the access list to apply to an entire class C address. 0.0.0.0 indicates all access.
port
A port or range of ports that the access list is permitted or denied access to.
pixfirewall(config)# outbound 11 deny 192.168.1.49 255.255.255.255 80
pixfirewall(config)# apply 11 outgoing_src
pixfirewall(config)# outbound 12 deny 192.168.146.201 255.255.255.255 80
pixfirewall(config)# outbound 12 deny 192.168.146.202 255.255.255.255 80
pixfirewall(config)# apply 12 outgoing_dest
password
A password of up to 16 alphanumeric characters, which is not case sensitive. PIX Firewall converts the password to all lowercase.
pixfirewall# passwd athensge0rg1a
pixfirewall# show passwd
ping
inside|outside
ip_address
ip_address
The IP address of a host on the inside or outside networks.
pixfirewall(config)# ping inside 192.168.42.54
192.168.42.54 response received - nnMs
192.168.42.54 response received - nnMs
192.168.42.54 response received - nnMs
pixfirewall# reload
Proceed with reload?[confirm] n
Rebooting...
inside
Modifies RIP behavior on the inside interface.
outside
Modifies RIP behavior on the outside interface.
default
Causes the PIX Firewall to broadcast a default route to the inside network.
passive
Enables passive RIP on either the inside or outside interface. The PIX Firewall listens for RIP routing broadcasts and uses that information to populate its routing tables.
pixfirewall(config)# show rip
rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
no rip inside default
pixfirewall(config)# rip inside default
pixfirewall(config)# show rip
rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
rip inside default
route
inside|outside
dest_net_ip netmask gateway_ip metric
inside|outside
Specifies the interface.
dest_net_ip
The destination network IP address. Use 0.0.0.0 to specify a default route.
netmask
Specifies a network mask to apply to dest_net_ip. Use 0.0.0.0 to specify a default route.
gateway_ip
Specifies the IP address of the gateway router (the next hop address for this route).
metric
Specifies the number of hops to dest_net_ip. If you are not sure, enter 1. Your network administrator can supply this information or you can use a traceroute command to obtain the number of hops (such as the traceroute command provided with Cisco TCP/IP Suite 100 for Windows).
pixfirewall(config)# route inside 192.168.42.0 255.255.255.255.0 192.168.88.1 1
pixfirewall(config)# route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.1.1 1
pixfirewall> show
actkey
age
apply
arp
auth
auth-user
auth-server
blocks
conduit
configure
failover
global
http
hw
interface
ip
link
linkpath
lnko
lnkopath
memory
nat
outbound
passwd
processes
rip
route
snmp-server
static
syslog
telnet
timeout
version
who
xlate
Display activation key
Age PIX Private Link keys
Apply outbound lists
ARP table manipulation
User Authorization Enable/Disable
Maintain IP to Authorization lists
Maintain Authorization Server lists
System buffer utilization
Add/remove conduits to static translations
Configure from terminal, floppy, or memory
Administer Failover
Enter global network addresses
Add authorized IP addresses for http access to PIX
Hardware identification
Interface configuration
Set network number
Establish an encrypted PIX Private Link
Set the network paths for Private Links
Establish an encrypted PIX Private Link (OLD)
Set the network paths for Private Links (OLD)
System memory utilization
Create outbound lists
Administer Address Translations
Modify telnet login password
Display processes
RIP table
Set the network default router
Administer SNMP daemon
Reserve a local to global address translation table entry
Log messages to syslog server
Add authorized IP addresses for telnet access to PIX
Set the maximum idle time for translation and connection slots
Display PIX system software version
Show active administration sessions on PIX
Display current translation and connection slot information
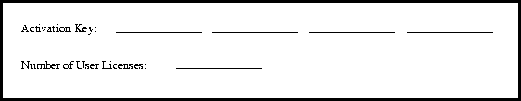
pixfirewall> show actkey
Activation Key: 0xfadebacc 0x42424242 0xa1b2c3d4 0xe5f6a1b2
Connections: 16384
pixfirewall> show age
Private Link Key Aging: 10 minutes
number
View access lists by an identification number previously created with the outbound command.
outgoing_src
View access lists by the source address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall.
outgoing_dest
View access lists by the destination address on packets traversing the PIX Firewall.
pixfirewall> show apply
apply 1 outgoing_src
inside
PIX Firewall inside network interface ARP table.
outside
PIX Firewall outside network interface ARP table.
ip_address
IP address.
mac_address
Hardware MAC address for the ARP table entry.
alias
Permanent ARP entry.
pixfirewall> show arp
inside 192.168.89.113 0020.af29.51b0
14400 seconds (4 hours).
pixfirewall> show arp timeout
arp timeout 14400 seconds
inside
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on your local network (inside the PIX Firewall).
outside
Specifies that you require authentication for connections originating on the outside of the PIX Firewall.
pixfirewall# show auth
auth outside
auth inside
type
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+.
server_ip
The IP address of the authentication server.
skey
An alphanumeric keyword of up to 127 characters defined by what the authentication server accepts. This is a public key between the client and server for encrypting data between them. The skey value must be the same on both the client and server systems.
pixfirewall> show auth-server
auth-server radius 192.168.89.106 ski
type
Authentication type: radius or tacacs+.
ip_address
IP address from which or to which access is authenticated. If you want every system in your network to authenticate to this type of server, use 0.0.0.0 for the IP address. You can specify a network IP address by entering zero in each octet of the host portion of the IP address; for example, for a class C address, code 0 in the last octet, such as 192.168.42.0.
netmask
Network mask of ip_address. Always specify a specific mask value. If you want to limit authentication to a single IP address use 255 in each octet; for example, 255.255.255.255.
pixfirewall> show auth-user
auth-user radius 192.168.89.0 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall> show blocks
SIZE MAX LOW CNT
4 1600 1598 1600
80 100 94 97
256 80 79 80
1550 800 791 800
64000 16 16 16
global_ip
The IP address from the global pool associated with this conduit.
port
Destination port number into which connections are permitted on the inside machine. Port values are defined by RFC 1700.
protocol
tcp or udp.
ip_address
IP address (host or network) from which to permit incoming connections (0.0.0.0 is any host).
netmask
Network mask of ip_address.
pixfirewall> show conduit
conduit 192.168.42.1 80 tcp 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall# show config
:Saved
... config commands ...
:End
pixfirewall> show failover
Failover On
This host: Secondary - Active
Other host: Secondary - Standby
Cable status: 0x2 - My side not connected
Outside Interface
this host: Rx cnt 0 Uptime 12975
other host: Rx cnt 0 Uptime 0
Inside Interface
this host: Rx cnt 0 Uptime 12975
other host: Rx cnt 0 Uptime 0
pixfirewall> show global
global 1 192.168.88.1-192.168.88.7
pixfirewall> show http
192.168.89.111 255.255.255.255
192.168.89.113 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall> show hw
Hardware ID: 0x52c 0x1bf 19126
pixfirewall> show interface
ethernet outside is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is i82557 ethernet, address is 00a0.c90a.eb4d
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit half duplex
798 packets input, 35112 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
798 packets output, 35112 bytes, 0 underruns
ethernet inside is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is i82557 ethernet, address is 00a0.c90a.eb43
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit half duplex
1071 packets input, 71410 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 232 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
1071 packets output, 71410 bytes, 0 underruns
pixfirewall> show ip address
inside ip address 1.2.3.4 mask 255.255.255.0
outside ip address 5.6.7.8 mask 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall> show link
Foreign IP KeyID Key
192.168.42.2 1 0x00000000002222
2 0x00000000001111
3 0x00000000003333
4 0x00000000004444
20 out, 20 in
pixfirewall> show linkpath
Foreign IP Foreign Network Mask
192.168.31.33
11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
pixfirewall> show lnko
Foreign IP Local IP Key
1.2.3.4 5.6.7.8 fadebac
pixfirewall>
pixfirewall> show lnkopath
Foreign IP Foreign Network Mask
1.2.3.4 5.6.7.8 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall>
pixfirewall> show nat
nat 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
pixfirewall> show memory
nnnnnnnn bytes total, nnnnnnn bytes free
pixfirewall> show outbound
outbound 1 permit 192.168.42.1 255.255.255.255 80-80
outbound 2 deny 192.168.42.1 255.255.255.255 80-80
pixfirewall# passwd moo
pixfirewall# show passwd
Password moo
pixfirewall> show processes
PC SP STATE Runtime SBASE StackProcess
8000139e 8024ad00 80005354 940 80249d1c 36/4096 arp_timer
...
inside
Shows RIP configuration on the inside interface.
outside
Shows RIP configuration on the outside interface.
default
Causes the PIX Firewall to broadcast a default route to the outside network.
passive
Enables passive RIP on the inside interface. The PIX Firewall listens for RIP routing broadcasts and uses that information to populate its routing tables.
pixfirewall> show rip
rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
no rip inside default
inside|outside
The inside or outside interface.
dest_net_ip
The destination network IP address. 0.0.0.0 specifies a default route.
netmask
Specifies a network mask to apply to dest_net_ip. 0.0.0.0 specifies a default route.
gateway_ip
Specifies the IP address of the gateway router (the next hop IP address).
metric
Specifies the number of hops to dest_net_ip.
pixfirewall> show route
outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.42.42 1 OTHER static
inside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.41.10 1 OTHER static
contact
Your name or that of the PIX Firewall system administrator.
location
Your PIX Firewall location.
host
One or more IP addresses of hosts to which SNMP traps are being sent.
pixfirewall(config)# show snmp-server
pixfirewall(config)# show snmp-server host
snmp-server host 192.168.42.54
pixfirewall(config)# snmp-server contact 'arthur dent'
pixfirewall(config)# snmp-server location 'building 42, earth'
pixfirewall(config)# show snmp-server
snmp-server host 192.168.42.54
snmp-server location 'building 42, earth'
snmp-server contact 'arthur dent'
pixfirewall(config)#
pixfirewall> show static
static 10.1.1.5 192.168.42.2
pixfirewall> show syslog
OUTPUT ON (20.6)
CONSOLE OFF
<162> Secondary: Switching to ACTIVE.
<162> Secondary: Disabling Failover.
pixfirewall> show telnet
192.168.42.42 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall(config)# show timeout
timeout xlate 24:00:00 conn 12:00:00
pixfirewall> show version
PIX Version 3.pv.nnn
ip_address
An optional IP address to limit the listing to one IP address or to a network IP address.
pixfirewall# show who
2: From 192.168.2.2
1: From 192.168.1.3
0: On console
pixfirewall#
global_ip
The registered IP address to be used from the global pool.
local_ip
The local IP address from the inside network.
pixfirewall# show xlate
Global 192.168.88.7 Local 192.168.89.207 static
Global 192.168.88.11 Local 192.168.89.215
out 192.168.88.207:23 in 192.168.89.215:1284 idle 0:00:00 Bytes 436
Global 192.168.88.12 Local 192.168.89.11
contact
Indicates that you are supplying your name or that of the PIX Firewall system administrator.
location
Indicates that you are specifying your PIX Firewall location.
host
Indicates that you are specifying an IP address of a host to which SNMP traps should be sent. You can specify a maximum of 5 host IP addresses.
text
When used with contact, specify your name or that of the PIX Firewall system administrator. When used with location, specify your PIX Firewall location. If the location name contains spaces, surround the string in single quotes; for example, 'building 42'.
ip_address
When used with host, the IP address of a host to which SNMP traps should be sent. You can specify a maximum of 5 host IP addresses.
pixfirewall(config)# snmp-server location `building 42, sector 54'
global_ip
The registered IP address to be used from the global pool.
local_ip
The local IP address from the inside network.
pixfirewall(config)# static
pixfirewall(config)# syslog console
pixfirewall(config)# no syslog console
ip_address
The IP address or network of a host that is authorized to receive SYSLOG messages.
pixfirewall(config)# syslog host 192.168.0.99
pixfirewall(config)# no syslog host 192.168.0.99
facility
Eight facilities LOCAL0(16) through LOCAL7(23); the default is LOCAL4(20). Hosts file the messages based on the facility number in the message.
level
Message type; sets the level above which PIX Firewall suppresses messages to the SYSLOG hosts. Setting the level to 3, for example, allows messages with levels 0, 1, 2, and 3 to display. The default is 3. The levels are:
In addition, PIX Firewall sends SYSLOG messages only to a single file on the receiving system.
# mkdir /var/log/pix
# touch /var/log/pix/name
In the syslog.conf file, you code each selector and action pair for the messages you want to receive. For example, if you want to receive messages in a file called pixfirewall for message priorities 0, 1, 2, and 3, and you use the default LOCAL4 facility, the syslog.conf statements would be:
Message Priority
UNIX syslog.conf File Keyword
0 --- Emergency
local
n.emerg
1 --- Immediate action
local
n.alert
2 --- Critical condition
local
n.crit
3 --- Error
local
n.err
4 --- Warning
local
n.warning
5 --- Notice
local
n.notice
6 --- Information
local
n.info
7 --- Debug
local
n.debug
# PIX Firewall SYSLOG messages (formerly A.S. violations)
local4.emerg /var/log/pix/pixfirewall
local4.alert /var/log/pix/pixfirewall
local4.crit /var/log/pix/pixfirewall
local4.error /var/log/pix/pixfirewall
This configuration directs PIX Firewall SYSLOG message to the specified file. Alternatively, if you want the message sent to the logging host console or emailed to a system administrator, refer to the UNIX syslog.conf(4) manual page.
Entries in /etc/syslog.conf must obey these rules:
# cat /etc/syslog.pid
92
# kill -HUP 92
The first command lists the SYSLOG process ID. This number may vary by system. The second command sends SYSLOG the HUP signal to cause it to restart.
pixfirewall(config)# syslog output 23.4
Oct 15 12:55:03 pix-in PIX out of connections!
Oct 15 12:54:28 pix-in conn end faddr 192.168.42.42 fport 4457 gaddr 10.10.10.1 laddr 10.10.10.2
Oct 15 13:04:02 pix-in deny tcp out 192.168.96.14 in 10.10.10.42 flags SYN ACK
Oct 15 13:37:44 pix-in conns 16384 conns_used 0 xlate 254 xlate_used 1
Oct 15 13:47:21 pix-in PIX logged in from 10.10.42.112
pixfirewall(config)# syslog
ip_address netmask
ip_address
The IP address or network of a host that is authorized to access the PIX Firewall Telnet management interface.
netmask
The netmask for the network specified in this Telnet command. Use any valid mask, or a network IP address to enable access to all in the subnet; for example if you set netmask to 255.255.255.0, all systems in the subnet can access the firewall over Telnet. If you set netmask to 255.255.255.255, only the IP address you specify can access the firewall.
pixfirewall(config)# telnet 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall(config)# telnet 192.168.1.4 255.255.255.255
pixfirewall(config)# telnet 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall(config)# show telnet
192.168.1.3 255.255.255.255
192.168.1.4 255.255.255.255
192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
pixfirewall(config)# no telnet 192.168.1.3
pixfirewall(config)# show telnet
192.168.1.4 255.255.255.255
192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
xlate hh:mm:ss
Idle time until a translation slot is cleared (default value is
24 hours).
conn hh:mm:ss
Idle time until a connection slot is cleared (default value is
12 hours).
pixfirewall(config)# show timeout
timeout xlate 24:00:00 conn 12:00:00
pixfirewall(config)# timeout xlate 5:0:0
pixfirewall(config)# timeout conn 2:0:0
pixfirewall(config)# show timeout
timeout xlate 5:00:00 conn 2:00:00
pixfirewall(config)# timeout xlate 0:10:0 conn 0:5:0
pixfirewall(config)# show timeout
timeout xlate 0:10:00 conn 0:05:00
pixfirewall(config)# timeout xlate 0:0:12345
pixfirewall(config)# show timeout
timeout xlate 3:25:45 conn 0:05:00
pixfirewall(config)#
ip_address
An optional IP address to limit the listing to one IP address or to a network IP address.
pixfirewall# who
2: From 192.168.2.2
1: From 192.168.1.3
0: On console
pixfirewall#
pixfirewall# write erase
pixfirewall# reload
pixfirewall# write floppy
pixfirewall# write memory
pixfirewall# write terminal
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()