|
|
This chapter provides information on the Cisco 4000 series routers. The information is organized into the following sections:
http://www.cisco.com. For more information, see the chapter "Documentation" at the end of the catalog.
The Cisco 4000 series consists of the Cisco 4000, Cisco 4000-M, Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, Cisco 4700, and Cisco 4700-M routers. Although the Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500, and Cisco 4700 routers are no longer orderable, they are still supported. The Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500, and Cisco 4700 routers have been replaced by the Cisco 4000-M, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700-M routers.
The Cisco 4000 series routers run Cisco IOS software, Cisco's industry-leading networking software that provides a variety of feature sets. You can choose a feature set that supports your specific protocol environment. Cisco IOS software assures robust, reliable internetworks by supporting both LAN and WAN protocols, optimizing WAN services, and controlling internetwork access. In addition, Cisco IOS software allows centralized, integrated, and automated installation and management of internetworks.
The Cisco 4000 series routers offer Flash EPROM technology as a standard feature. Flash EPROMs enable you to distribute new software releases from a central location. After the software is distributed, the routers can reboot from programs stored in local Flash memory.
All models provide a configurable modular router platform by using network processor modules (NPMs)---individual removable cards used for external network connections. Because the router's modules support many variations of protocols, line speeds, and transmission media, the Cisco 4000 series can accommodate all types of network computing environments. As Cisco introduces new modules, the Cisco 4000 series can be upgraded to keep pace with technological advances.

A new one-port 100BaseTX Fast Ethernet NPM is now available for the Cisco 4000 series and is introduced in this catalog. See Table 127 for configuration information and Figure 36 for an illustration of this new NPM.
The Cisco 4000 series routers can support combinations of up to three of the following NPMs:
Figure 33 shows the front panel and Figure 34 shows the rear panel of Cisco 4000 series router.
Figure 33 : Cisco 4000 Series Front Panel
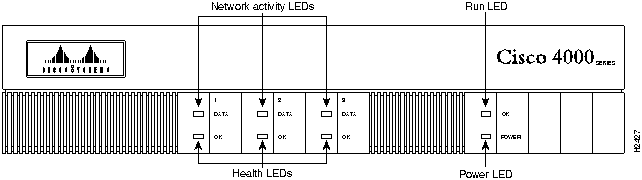
Figure 34 : Cisco 4000 Series Rear Panel
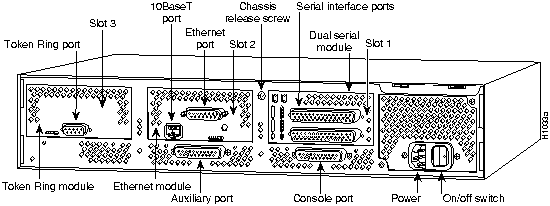
Table 125 : Cisco 4000 Series Summary of Features
| Characteristic | Cisco 4000-M | Cisco 4500-M | Cisco 4700-M1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported network interfaces | Ethernet
Token Ring FDDI Serial ISDN BRI Channelized E1/T1 ISDN PRI |
Ethernet
Token Ring FDDI Serial ISDN BRI Channelized E1/T1 ISDN PRI ATM OC-3c ATM DS-3 ATM E3 |
Ethernet
Token Ring FDDI Serial ISDN BRI Channelized E1/T1 ISDN PRI ATM OC-3c ATM DS-3 ATM E3 |
| Slots available for modules | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Choice of software feature sets2 | |||
| Cisco IOS Release
10.2 to 11.1 |
IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality3 IP/IPX Routing3 IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality3 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality4 Desktop Desktop with IBM base functionality3 Enterprise 5 Enterprise/APPN4 |
IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality3 IP/IPX Routing3 IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality3 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality4 Desktop Desktop with IBM base functionality 3 Enterprise5 Enterprise/APPN4 |
IP Routing
IP Routing with IBM base functionality3 IP/IPX Routing3 IP/IPX Routing with IBM base functionality2 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality4 Desktop Desktop with IBM base functionality 3 Enterprise5 Enterprise/APPN4 |
| Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
IP
IP Plus IP Plus 40 IP Plus 56 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 40 Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) Plus 56 IP/IPX/APPN with IBM base functionality Enterprise Enterprise Plus Enterprise Plus 40 Enterprise Plus 56 Enterprise/APPN Plus Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 |
| Processor type | 40-MHz 68030 | 100-MHz IDT Orion RISC | 133-MHz IDT Orion RISC |
| Flash memory | 4 MB standard, expandable to
8 MB |
4 MB standard, expandable to
8 or 16 MB |
4 MB standard, expandable to
8 or 16 MB |
| Main memory | 8 MB standard, expandable to
16 or 32 MB |
8 MB standard, expandable to
16 or 32 MB |
16 MB standard, expandable to
32 or 64 MB |
| Shared memory | 4 MB6 standard, expandable to 16 MB | 4 MB standard, expandable to
8 or 16 MB |
4 MB standard, expandable to
8 or 16 MB |
| Nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM) | 128 KB | 128 KB | 128 KB |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7"
(8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm) |
3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7"
(8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm) |
3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7"
(8.6 x 44.7 x 43.4 cm) |
| Weight (average shipping) | 24 lb (10.9 kg) | 24 lb (10.9 kg) | 24 lb (10.9 kg) |
| Agency approvals | UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2 | UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B,
VCCI Class 2 |
UL 1950, CSA 22.2, TÜV-GS mark, EN 60950, FCC Class A, Canadian DOC Class A, VDE Class B, EN 55022 Class B,
VCCI Class 2 |
Table 126 : Cisco 4000 Series Environmental Specifications
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Consumption | 200W (682 Btu/hour) |
| Input | 100 to 240 VAC |
| Frequency | 47 to 63 Hz |
| Current rating | 3.0A @ 100V; 1.5A @ 240V |
| Operating temperature range | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
| Nonoperating temperature range | --40 to 185°F (--40 to 85°C) |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 5 to 95% |

Cisco 4000 series routers have the following standard features:
The network processor modules available for the Cisco 4000 series routers and their hardware options are described in the following sections:
Cisco 4000 series routers support combinations of up to three network processor modules (NPMs). Table 127 describes the maximum number of each module supported by a specific system and the minimum Cisco IOS software release required for each module.
Table 127 : NPM Configurations---Cisco 4000 Series
| Type | Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M | Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700-M1 | Minimum Cisco IOS Software Release Required | Product Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-port 10BaseT Ethernet | 3 | -- | 9.14(1) | NP-1E |
| 1-port 100BaseTX Fast Ethernet | -- | 2 | 11.1(5) | NP-1FE |
| 2-port 10BaseT Ethernet | 3 | 3 | 9.14(1) | NP-2E |
| 6-port 10BaseT Ethernet | -- | 3 | 10.3(6) | NP-6E |
| 1-port Token Ring | 3 | 3 | 9.14(5) | NP-1RV2 |
| 2-port Token Ring | 3 | 3 | 9.14(5) | NP-2R |
| 1-port single attachment multimode FDDI | 12 | 2 | 9.14(1) | NP-1F-S-M |
| 1-port dual attachment multimode FDDI | 12 | 2 | 9.14(1) | NP-1F-D-MM |
| 1-port dual attachment single-mode FDDI | 12 | 2 | 9.14(3) | NP-1F-D-SS |
| 2-port serial | 3 | 3 | 9.14(6) | NP-2T |
| 4-port serial | 3 | 3 | 10.1 | NP-4T |
| 4-port ISDN BRI | 2 | 2 | 10.2 | NP-4B3 |
| 8-port ISDN BRI | 1 | 2 | 10.2 | NP-8B3 |
| 1-port channelized T1/ISDN PRI | 1 | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CT1 |
| 1-port channelized E1/ISDN PRI, unbalanced | 1 | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CE1U |
| 1-port channelized E1/ISDN PRI, balanced | 1 | 2 | 10.3(4) | NP-CE1B |
| 4-port serial E1/G.703, unbalanced | 3 | 3 | 10.2(4) | NP-4GU |
| 4-port serial E1/G.703, balanced | 3 | 3 | 10.2(4) | NP-4GB |
| 1-port single-mode ATM OC-3c | -- | 1 | 10.3(4) | NP-1A-SM |
| 1-port multimode ATM OC-3c | -- | 1 | 10.3(4) | NP-1A-MM |
| 1-port ATM DS-3 | -- | 2 | 11.0(5) | NP-1A-DS3 |
| 1-port ATM E3 | -- | 1 | 11.0(5) | NP-1A-E3 |
Figure 35 through Figure 53 show the Cisco 4000 series network processor modules.
Figure 35 : One-Port 10BaseT Ethernet
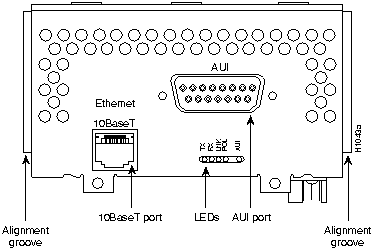
Figure 36 : One-Port 100BaseTX Fast Ethernet

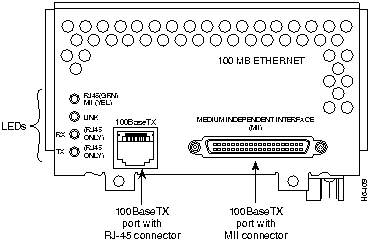
Figure 37 : Two-Port 10BaseT Ethernet
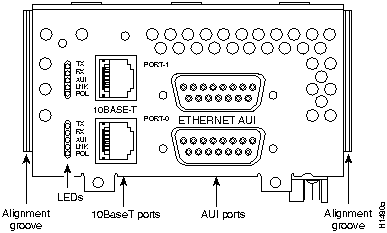
Figure 38 : Six-Port 10BaseT Ethernet
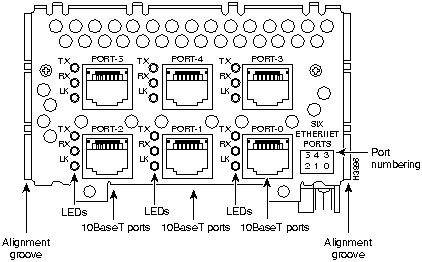
Figure 39 : One-Port Token Ring
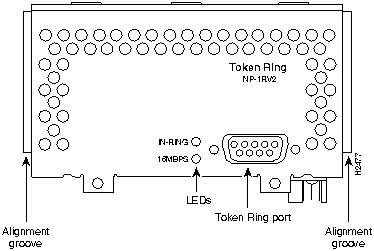
Figure 40 : Two-Port Token Ring
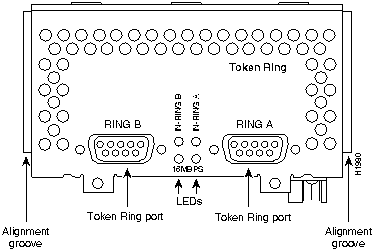
Figure 41 : One-Port Single Attachment Multimode FDDI
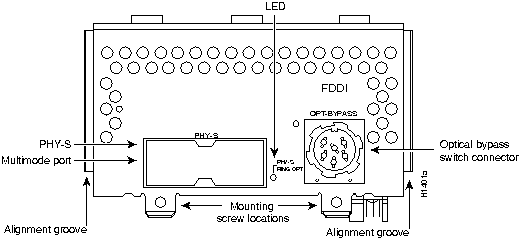
Figure 42 : One-Port Dual Attachment Multimode FDDI
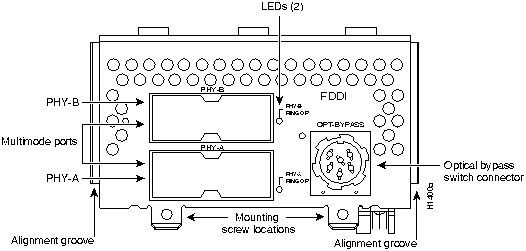
Figure 43 : One-Port Dual Attachment Single-Mode FDDI
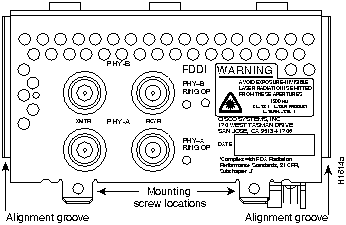
Figure 44 : Two-Port Serial
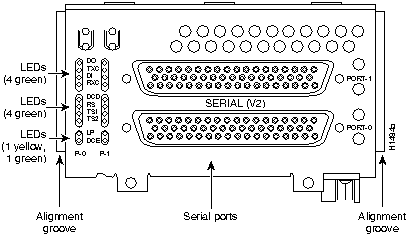
Figure 45 : Four-Port Serial
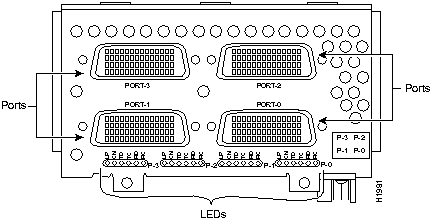
Figure 46 : Four-Port ISDN BRI
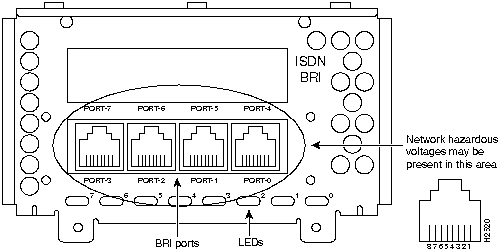
Figure 47 : Eight-Port ISDN BRI
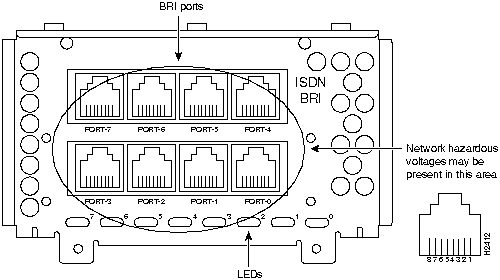
Figure 48 : One-Port Channelized T1/ISDN PRI
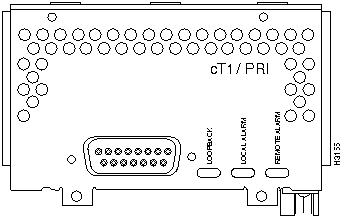
Figure 49 : One-Port Channelized E1/ISDN PRI Balanced/Unbalanced
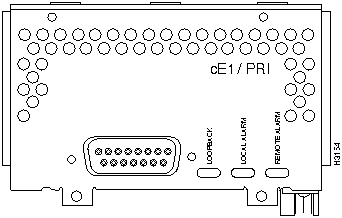
Figure 50 : Four-Port Serial E1/G.703 Balanced/Unbalanced
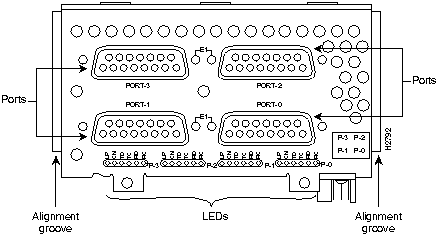
Figure 51 : One-Port Single-Mode ATM OC-3c
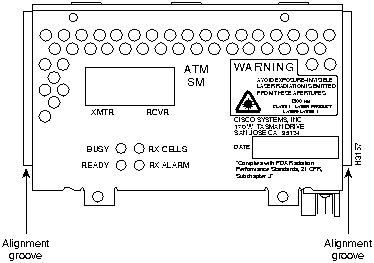
Figure 52 : One-Port Multimode ATM OC-3c
Figure 53 : One-Port ATM DS-3/E3
All Cisco 4000 series routers share the same physical design. Each router offers three slots for LAN or WAN connectivity and uses the same optional NPMs and software features for compatibility and investment protection. Three different types of memory are available for the Cisco 4000 series---main memory, shared memory, and system Flash memory. Each type of memory serves a different purpose in routing the packet from one interface to another. The benefit of this architecture is that the system can read program instructions or routing table data from main memory at the same time as it is moving packets between interfaces (using shared memory), thus increasing overall system performance and lowering network latency.
Factors That Affect Memory Requirements
You can change memory configurations in the Cisco 4000 series to accommodate internetworking demands. The memory requirements are driven by the following three factors:
This section provides basic guidelines for selecting memory options.
Main DRAM Memory
The Cisco 4000 series runs from an image stored in main DRAM. This memory is also used by the system for tables and stacks. The amount of main memory required is determined by the size of the image and by the configuration of the internetwork. Cisco regularly publishes product bulletins that detail what memory is required for any particular Cisco IOS feature subset, and also releases documentation that specifies what memory is needed.
Shared DRAM Memory
The Cisco 4000 series routers use shared DRAM (also known as packet memory) for handling user data. The recommended amount of shared memory is determined by the type and number of physical or virtual interfaces supported by the router. Other factors that impact the amount of required shared memory are the type of routing selected and the degree of throughput to the various interfaces.
Flash Memory
The Cisco 4000 series software images are stored and compressed in Flash memory. Flash memory is more reliable than traditional diskette-resident system software and provides maximum availability and easy software upgrades and maintenance. The Cisco 4000 series products are shipped with 4 MB of system Flash, which leaves room for future image growth. If you want to store two images in a single router, you should upgrade to the 8-MB option. In this way, the router is used as a TFTP server for other Cisco routers.
The following types of memory are also used in the Cisco 4000 series, but they are not critical components that drive the minimum memory requirements for the system.
System Boot Flash
The Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700 store their Boot images in the system Flash memory. The standard configuration of 4 MB is sufficient for use on these platforms. Currently no upgrades are offered.
XBoot Flash
The Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700 store a small software image in XBoot Flash memory. This software image is used to boot the Cisco IOS software across a network. However, it is used as a last resort in case the system Boot Flash fails. XBoot Flash memory is also used for updating the existing image in the system boot Flash. You cannot configure the amount of XBoot Flash memory.
Boot EPROM
The Boot image is stored in ROM on the Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M routers. The XBoot Flash equivalent for the Cisco 4000 is called RXBoot, which resides within the Boot EPROM (as opposed to residing in different modules on the Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 routers). The Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M Boot EPROMs are 2 MB.
The Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 simplify the process of upgrading software images. Rather than changing the EPROMs when you want to load a new image, you can simply download a new image using TFTP into the onboard Flash memory.
ROMMON
The ROMMON performs initialization tasks in the Cisco 4000 series. It performs power diagnostics and sets variables after checking memory sizes. After this is completed, the main image is booted (as a default) from system Boot Flash (for the Cisco 4500 and the Cisco 4700) and from the Boot EPROM (for the Cisco 4000). If you have configured you system to boot from XBoot, ROMMON boots from the secondary image. You cannot configure the amount of ROMMON memory available.
The standard configuration for shared DRAM is 4 MB for the Cisco 4000 series. This is sufficient for most configurations with fewer than 24 physical or virtual interfaces. For routers with 24 or more interfaces or B channels (for example, NP-9B, CT1, and CE1), upgrading to a minimum of 8 MB of shared memory is recommended
Table 128 and Table 129 list the minimum shared memory requirements for NPMs used in Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500, and Cisco 4700 series routers.
Table 128 : Minimum Shared Memory Required---Cisco 4000
| Network Processor
Module |
Minimum Shared Memory |
|---|---|
| 1E, 2E, 2T, 2R | 0.1 MB |
| 2E, 2T | 0.2 MB |
| 2R, 4T, 4B | 0.4 MB |
| 8B, 1P | 1.0 MB |
| 1F | 2.0 MB |
Table 129 : Minimum Shared Memory Required---Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700
| Network Processor
Module |
Minimum Shared Memory |
|---|---|
| 1E | 0.2 MB |
| 2E, 2T | 0.4 MB |
| 2R, 4T, 4B, 4G | 0.6 MB |
| 6E | 1.2 MB |
| 8B, 1P | 1.2 MB |
| 1F, 1A | 2 MB |
| 21F | 3 MB (2 FDDI NPMs in one Cisco 4500 or Cisco 4700) |
| FE | 1.5 MB |
The Cisco 4000 series offers the hardware and power supply options listed in Table 130 and Table 131. If a product number ends with an equal sign (=), the item can be ordered only as a spare. If a product number does not end with an equal sign, the item can be ordered as a spare or as a configurable part of a system order.
Table 130 : Cisco 4000 Series Hardware Options
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Network Processor Modules (NPMs) | See Table 127. |
| Cisco 4000 Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| Additional 4-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4000-4F= |
| 8-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4000-8F= |
| 16-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4000-16F= |
| 4-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4000-4S= |
| 16-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4000-16D= |
| Cisco 4000-M Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| 4- to 8-MB Flash memory factory upgrade | MEM-4000M-4U8F |
| Additional 4-MB Flash memory | MEM-4000M-4F= |
| 4- to 16-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4000M-4U16S |
| 16-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4000M-16S= |
| 8- to 16-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4000M-8U16D |
| 16-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4000M-16D= |
| 8- to 32-MB main memory factory upgrade | MEM-4000M-8U32D |
| 32-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4000M-32D= |
| Cisco 4500 Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| Additional 4-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4500-4F= |
| 16-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4500-16S= |
| 32-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4500-32D= |
| Cisco 4500-M Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| 4- to 8-MB Flash memory factory upgrade | MEM-4500M-4U8F |
| 8-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4500M-8F= |
| 4- to 16-MB Flash memory factory upgrade | MEM-4500M-4U16F |
| 16-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4500M-16F= |
| 4- to 8-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4500M-4U8S |
| 8-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4500M-8S= |
| 4- to 16-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4500M-4U16S |
| 16-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4500M-16S= |
| 16- to 32-MB main memory factory upgrade | MEM-4500M-16U32D |
| 32-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4500M-32D= |
| Cisco 4700 Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| 8-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4700-8F= |
| 16-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4700-16F= |
| 8-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4700-8S= |
| 16-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4700-16S= |
| 32-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4700-32D= |
| Cisco 4700-M Memory | |
| Boot ROM upgrade | BOOT-4000= |
| 4- to 8-MB Flash memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-4U8F |
| 8-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-8F= |
| 4- to 16-MB Flash memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-4U16F |
| 16-MB Flash memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-16F= |
| 4- to 8-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-4U8S |
| 8-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-8S= |
| 4- to 16-MB shared memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-4U16S |
| 16-MB shared memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-16S= |
| 16- to 32-MB main memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-16U32D |
| 32-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-32D= |
| 16- to 64-MB main memory factory upgrade | MEM-4700M-16U64D |
| 64-MB main memory field upgrade | MEM-4700M-64D= |
| Kits | |
| Blank NPM filler card | ACS-NPPN= |
| Telco/wall-mount kit | ACS-NPWM |
| 19" rack-mount kit | ACS-NPRM |
Table 131 : Cisco 4000 Series Power Supply Options
| Model | Description | Product Number |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco 4000-M | AC power supply | CISCO4000-M |
| Cisco 4000-DC-M | --48 VDC power supply | CISCO4000-DC-M |
| Cisco 4500-M | AC power supply | CISCO4500-M |
| Cisco 4500-DC-M | --48 VDC power supply | CISCO4500-DC-M |
| Cisco 4700-M | AC power supply | CISCO4700-M |
| Cisco 4700-DC-M | --48 VDC power supply | CISCO4700-DC-M |
Table 132 lists the cables you can use with the NPMs. For cable illustrations, refer to the sections "Specifications" and "ATM Cable Specifications" in the chapter "Cables and Transceivers" later in this catalog.
Table 132 : Cisco 4000 Series Cables
| Description | Product Number |
| Serial Cables for One-Port Channelized T1/E1/PRI NPM | |
| MIP-CT1: DSX1 to CSU DB-15 straight-through cable | CAB-7KCT1DB15 |
| MIP-CT1: DSX1 to CSU DB-15 null modem cable | CAB-7KCT1NULL |
| E1 for 75-ohm, unbalanced connections (with BNC connectors) | CAB-E1-BNC |
| E1 for 120-ohm, balanced connections (with DB-15 connector) | CAB-E1-DB15 |
| E1 for 120-ohm, balanced connections (with Twinax connector) | CAB-E1-TWINAX |
| E1 ISDN PRI cable, 10' (3 m) | CAB-E1-PRI |
| Serial Cables for Two-Port Serial NPM | |
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NP232T |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NP232C |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NP449T |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NP449C |
| EIA/530 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NP530 |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NPX21T |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NPX21C |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NPV35TV2 |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-NPV35CV2 |
| Serial Cables for Four-Port Serial NPM | |
| EIA/TIA-232 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232MT |
| EIA/TIA-232 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-232FC |
| EIA/TIA-449 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449MT |
| EIA/TIA-449 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-449FC |
| EIA/530 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-530MT |
| X.21 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21MT |
| X.21 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-X21FC |
| V.35 male DTE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35MT |
| V.35 female DCE interface, 10' (3 m) | CAB-V35FC |
| Cables for Four-Port E1/G.703 NPM | |
| E1 cable, BNC E1, 75 ohm, unbalanced, 10' (3 m) | CAB-E1-BNC-3M |
| E1 cable, Twinax 120 ohm, balanced, 10' (3 m) | CAB-E1-TWINAX-3M |
| ATM Cables | |
| RG-59 coaxial cable with BNC connectors | CAB-ATM-DS3/E3 |
The Cisco IOS software available for the Cisco 4000 series router is described in the following sections:
The Cisco 4000 series routers support the following software releases:
Traditional software packaging is no longer included in the base price of the Cisco 4000 series. Cisco IOS Release 10.0 it is still orderable for the Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M routers. Table 136 lists the product numbers for traditional software packaging for Cisco IOS Release 10.0. (Product numbers beginning with SF- are not orderable for the Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M routers. For these routers, you can only order software as spares.) Table 137 describes the contents of each traditional software feature license.
With the introduction of Cisco IOS Release 11.2, feature sets have been updated to make it easier to select the exact feature sets you need. Feature sets names are simplified and are more consistent across Cisco hardware platforms. In addition, you can add options to the standard feature set offerings. These options provide additional features and value based on the hardware platform selected. Cisco also continues to offer specialized feature sets for key applications.

The Cisco 4000 series offers the following types of feature sets:
Cisco IOS images with 40-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) support may legally be distributed to any party eligible to receive Cisco IOS software. 40-bit DES is not a cryptographically strong solution and should not be used to protect sensitive data.
Cisco IOS images with 56-bit DES are subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) controls and have a limited distribution. Images to be installed outside the U.S. require an export license. Orders may be denied or subject to delays due to U.S. Government regulations. Please contact your sales representative or distributor for more information, or send e-mail to export@cisco.com.
The new feature set tables use the following conventions to identify features:
| Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500 and Cisco 4700 Feature Sets | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | IP Routing | IP/IPX/
IBM/ APPN1 |
IP/IPX Routing2 | Desktop
(IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) |
Enterprise3 | |||||||||||||||
| Cisco IOS Release | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 |
| LAN Support | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 24 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)5 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Novell IPX6 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Source-route bridging7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Services | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ATM LAN emulation: DECnet routing and Banyan VINES support
(Cisco 4500 and 4700 only)8 |
Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Simple Server Redundancy Protocol (SSRP)
(Cisco 4500 and 4700 only) |
Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: Rate queues for SVC per subinterface | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: UNI 3.1 signaling for ATM
(Cisco 4500 and 4700 only) |
Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay SVC Support (DTE) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay traffic shaping | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for CPP and PPP | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ISDN9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PPP10 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMDS | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Switched 56 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| X.2511 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| WAN Optimization | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header12, link and payload compression13 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IP Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| BGP414 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EGP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Named IP Access Control List | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NHRP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSPF Not-So-Stubby-Areas (NSSA) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| OSPF On Demand Circuit (RFC 1793) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Other Routing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AURP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NLSP15 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| RTMP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| SRTP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Management | ||||||||||||||||||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration16 | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RMON events and alarms | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- | Plus | X | -- | -- | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Kerberos V client support | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Lock and key | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Network layer encryption (export controlled 40-bit and 56-bit DES)17 | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| RADIUS | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- |
| Router authentication | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| TACACS+18 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IBM Support (Optional) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| APPN (optional)3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Bisync19 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Caching and filtering | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DLSw+ 20 | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| Frame Relay SNA support (RFC 1490) | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA) Server | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NetView Native Service Point | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| QLLC19 | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | Plus | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Response Time Reporter (RTR) | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | Plus | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SDLC integration | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization
via local acknowledgment |
Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB21, 22 | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | -- | |
| SRT | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | Plus | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Protocol Translation | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rlogin | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| Remote Node23 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ARAP 1.0/2.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Asynchronous master interfaces | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| ATCP24 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| CPPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| CSLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DHCP | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- | X | X | X | X | -- |
| IP pooling | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPX and ARAP on virtual asynch interfaces | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| IPXCP12 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| MacIP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NASI25 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| NetBEUI over PPP | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- |
| PPP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SLIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Terminal Services23 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LAT26 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Rlogin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TN3270 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
| X.25 PAD | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Xremote | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X |
Software Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements for Cisco IOS
Adding a feature set may require you to purchase additional memory. Table 134 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Table 135 lists the software feature set product numbers and minimum memory requirements for Cisco IOS Release 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2. The minimum memory requirements listed were chosen for typical branch and remote office applications. If your network is very large, using complex routing protocols, or using RMON, you may need more memory. Configuration analysis and testing are encouraged.
| Product Numbers and
Minimum Memory Requirements |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | |||||
| Feature Set | Product Number | Cisco 4000
Series Model |
Flash | Main
DRAM |
Shared DRAM |
| IP | SF4C-11.2.1
SW4C-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45C-11.2.1
SW45C-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| IP Plus | SF4CP-11.2.1
SW4CP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45CP-11.2.1
SW45CP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| IP Plus 40 | SF4CW-11.2.1
SW4CW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45CW-11.2.1
SW45CW-11.2.1 |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | ||
| IP Plus 56 | SF4CY-11.2.1
SW4CY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45CY-11.2.1
SW45CY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Desktop | SF4B-11.2.1
SW4B-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45B-11.2.1
SW45B-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Desktop Plus | SF4BP-11.2.1
SW4BP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45BP-11.2.1
SW45BP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Desktop Plus 40 | SF4BW-11.2.1
SW4BW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45BW-11.2.1
SW45BW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Desktop Plus 56 | SF4BY-11.2.1
SW4BY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45BY-11.2.1
SW45BY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| IP/IPX/IBM and APPN1 | SF4DSN-11.2.1
SW4DSN-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45DSN-11.2.1
SW45DSN-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 32 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 32 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Enterprise | SF4A-11.2.1
SW4A-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45A-11.2.1
SW45A-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Enterprise Plus | SF4AP-11.2.1
SW4AP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45AP-11.2.1
SW45AP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Enterprise Plus 40 | SF4AW-11.2.1
SW4AW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45AW-11.2.
SW45AW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Enterprise Plus 56 | SF4AY-11.2.1
SW4AY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45AY-11.2.1
SW45AY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus | SF4ANP-11.2.1
SW4ANP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45ANP-11.2.1
SW45ANP-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus 40 | SF4ANW-11.2.1
SW4ANW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45ANW-11.2.1
SW45ANW-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 | SF4ANY-11.2.1
SW4ANY-11.2.1 |
Cisco 4000 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF45ANY-11.2.1
SW45ANY-11.2.1= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | ||
| Product Numbers and Minimum Memory Requirements | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Releases | ||||||||||||||
| 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.2 | |||||||||||
| Feature Set | Product Number | Cisco 4000 Series Model | Flash | Main
DRAM |
Shared DRAM | Flash | Main
DRAM |
Shared DRAM | Flash | Main DRAM | Shared DRAM | Flash | Main
DRAM |
Shared DRAM |
| IP | SF-G4C-xx.x.x
SW-G4C-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45C-xx.x.x
SW-G45C-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP with IBM base | SF-G4CS-xx.x.x
SW-G4CS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45CS-xx.x.x
SW-G45CS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP/IPX | SF-G4D-xx.x.x
SW-G4D-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45D-xx.x.x
SW-G45D-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP/IPX with IBM base | SF-G4DS-xx.x.x
SW-G4DS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45DS-xx.x.x=
SW-G45DS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| IP/IPX with IBM base and APPN | SF-G4DSN-xx.x.x
SW-G4DSN-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| SF-G45DSN-xx.x.x
SW-G45DSN-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop | SF-G4B-xx.x.x
SW-G4B-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | -- | -- | -- | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45B-xx.x.x
SW-G45B-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Desktop with IBM base | SF-G4BS-xx.x.x
SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45BS-xx.x.x
SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise | SF-G4A-xx.x.x
SW-G4A-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 1 MB |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | ||
| SF-G45A-xx.x.x
SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 4 MB | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Enterprise with APPN | SF-G4AN-xx.x.x
SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4000 | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Cisco 4000-M | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| SF-G45AN-xx.x.x
SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
Cisco 4500 | 8 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | 4 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| Cisco 4500-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Cisco 4700 | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| Cisco 4700-M | 8 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | 4 MB | 16 MB | 8 MB | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
Table 136 : Traditional Software Product Numbers---Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000M
| Description | Product Numbers
Cisco IOS Release 10.01 |
|---|---|
| Router software | SF-G4-10.0.x
SW-G4-10.0.x= SF-G4P-10.0.x SW-G4P-10.0.x= |
| Feature: standard | FR-S4-10.0.X
FR-S4-10.0.X= |
| Feature: bridging | FR-B4-10.0.X= |
| Feature: packet switching2 | FR-X4-10.0.X= |
| Feature: protocol translation | FR-P4-10.0.X |
| Category | Protocols/Features | Feature License |
|---|---|---|
| LAN support | IP, Novell IPX, AppleTalk I and II, DECnet IV and V, OSI, XNS, Banyan VINES, Apollo Domain, GRE | Standard |
| Transparent, translational, and source-route bridging, multiring | Bridging option | |
| WAN services | HDLC, PPP1, ISDN2, IPXWAN, Switched 56 | Standard |
| X.25, Frame Relay, SMDS | Packet-switching option | |
| WAN optimization | Header and link compression, dialondemand, dial backup, bandwidthondemand, custom and priority queuing | Standard |
| IP routing | RIP, IGRP, Enhanced IGRP, OSPF, BGP, EGP, ESIS, ISIS | Standard |
| Other routing | IPX RIP, RTMP, SRTP | Standard |
| IBM support | RSRB, SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization via local acknowledgment, SDLC Integration, SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC), SDLC transport (STUN), TG/COS | Bridging option |
| Management | AutoInstall, SNMP, Telnet | Standard |
| Security | Access lists, access security, TACACS | Standard |
| Protocol translation | Telnet, LAT, rlogin, TN3270, X.25 | Protocol translation option |
| Remote node3 | SLIP, CSLIP, PPP, CPPP, IPXCP, MacIP | Standard |
| Terminal services3 | Telnet, rlogin | Standard |
| X.25 PAD, LAT | Protocol translation option |
Cisco IOS Feature Set Upgrades
Cisco IOS Release 11.2 for the Cisco 4000 series allows software upgrades that cross multiple feature sets. This will require you to order multiple feature set licenses. The following is an example:

You have a Cisco 4500-M router running the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 IP Routing (basic) feature set. You want to upgrade to the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 Enterprise/APPN Plus 56 feature set. You are crossing three feature sets: one to get from IP to Enterprise, one to add APPN, and one to add Plus 56 (basic to plus). To complete the upgrade, use the following guidelines:
Table 138 lists Cisco IOS Software upgrade product numbers for the Cisco 4000 series.
Table 138 : Cisco IOS Software Upgrades for Cisco IOS Release 11.2---Cisco 4000 Series
| Feature Set Upgrade1 | Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M
Product Numbers |
Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and
Cisco 4700-M Product Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Plus | FL4-P= | FL45-P= |
| Plus 40 | FL4-W= | FL45-W= |
| Plus 56 | FL4-Y= | FL45-Y= |
| APPN | FL4-APPN= | FL45-APPN= |
| IP to Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) | FL4-CB= | FL45-CB= |
| IP to Enterprise | FL4-CA= | FL45-CA= |
| Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) to Enterprise | FL4-BA= | FL45-BA= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop (IP/IPX/Appletalk/DEC) | FL4-DB= | FL45-DB= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FL4-DA= | FL45-DA= |
Feature sets for Cisco IOS Releases 11.1, 11.0, 10.3, and 10.2 can be upgraded as described in Table 139. To order an upgrade, you must use two product numbers; one represents the upgrade license, and the other represents the software. For example, to upgrade from an IP feature set to an IP feature set with IBM base functionality, order product number FR-G4X-CCS= (the upgrade license) and SW-G4CS-xx.x.x= (the software for a Cisco 4000-M). To upgrade to a feature set with APPN, you must first purchase the upgrade license for the desired feature set and then purchase the upgrade license and upgrade software for the APPN feature set.
| Feature Set Upgrade | Cisco 4000 and Cisco 4000-M
Product Numbers1 |
Cisco 4500, Cisco 4500-M, and
Cisco 4700-M Product Numbers1 |
|---|---|---|
| IP to IP with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-CCS= and SW-G4CS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CCS= and SW-G45CS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX | FR-G4X-CD= and SW-G4D-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CD= and SW-G45D-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-CDS= and SW-G4DS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CDS= and SW-G45DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN | FR-G4X-CDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4DSN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop | FR-G4X-CB= and SW-G4B-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CB= and SW-G45B-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-CBS= and SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CBS= and SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise | FR-G4X-CA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| IP to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-CA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-CSDS= and SW-G4DS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CSDS= and SW-G45DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN | FR-G4X-CSDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4DSN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CSDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-CSBS= and SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CSBS= and SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base functionality to Enterprise | FR-G4X-CSA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CSA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| IP with IBM base functionality to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-CSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-CSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-DDS= and SW-G4DS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DDS= and SW-G45DS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN | FR-G4X-DDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4DSN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DDS=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop | FR-G4X-DB= and SW-G4B-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DB= and SW-G45B-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Desktop with IBM base functionality | FR-G4X-DBS= and SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DBS= and SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise | FR-G4X-DA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-DA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Desktop with IBM base | FR-G4X-DSBS= and SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DSBS= and SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to IP/IPX with IBM base functionality and APPN | FR-G4X-APPN= and SW-G4DSN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-APPN= and SW-G45DSN-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Enterprise | FR-G4X-DSA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DSA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| IP/IPX with IBM base to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-DSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-DSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Desktop with IBM base | FR-G4X-BBS= and SW-G4BS-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-BBS= and SW-G45BS-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise | FR-G4X-BA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-BA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-BA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-BA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop with IBM base to Enterprise | FR-G4X-BSA= and SW-G4A-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-BSA= and SW-G45A-xx.x.x= |
| Desktop with IBM base to Enterprise and APPN | FR-G4X-BSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G4AN-xx.x.x= | FR-G4X-BSA=, FR-G4X-APPN=, and SW-G45AN-xx.x.x= |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.