|
|
This chapter provides information on the Cisco 7500 series routers. The information is organized into the following sections:
http://www.cisco.com. For more information, see the chapter "Documentation" at the end of the catalog.
The Cisco 7500 series is Cisco's premier high-end platform of multiprotocol routers, which include the Cisco 7505, the Cisco 7507, and the Cisco 7513. These systems combine Cisco Systems' proven software technology with exceptional reliability, availability, serviceability, and performance features to meet the requirements of today's most mission-critical internetworks. The Cisco 7500 series provides information system professionals with the flexibility they need to meet the constantly changing requirements at the core and distribution points of the internetwork.
The Cisco 7505 features a high-speed Cisco Extended Bus (CyBus), and the Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 feature dual CyBuses. Network interfaces reside on modular interface processors, which provide a direct connection between the CyBus and the external network. The Cisco 7505 uses the RSP1, and the Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 use the RSP2.
The Cisco 7500 series runs the industry-leading networking software, Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) software. Cisco IOS software assures robust, reliable internetworks by supporting both LAN and WAN protocols, optimizing WAN services, and controlling internetwork access. In addition, Cisco IOS software allows centralized, integrated, and automated installation and management of internetworks.
The Cisco 7500 series offers software feature sets and feature licenses, which allows you to select the package that best meets your needs. You can select from six feature sets, which can be enhanced with additional feature licenses. If requirements change in the future, you can upgrade to a higher level feature set and add another feature license.
The Cisco 7505 contains five slots (one slot for the RSP1, and four slots for interface processors); the Cisco 7507 contains seven slots (two slots for RSPs, and five slots for interface processors); and the Cisco 7513 contains thirteen slots (two slots for RSPs, and eleven slots for interface processors). The interface processor types follow:

* Older versions of these boards may be eligible for the Investment Protection Program. See the chapter "Interface Processors and Port Adapters for the Cisco 7000 Family."
The reliability, availability, and serviceability features of the Cisco 7500 series include the following:
Figure 3 : Cisco 7505---Front View
Figure 4 : Cisco 7505---Interface Processor View
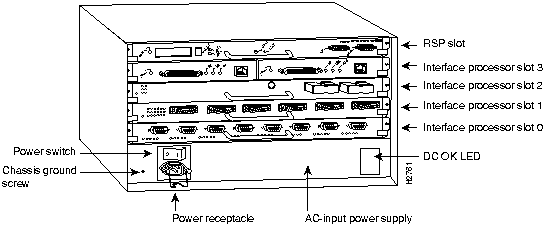
Figure 5 : Cisco 7507---Front View
Figure 6 : Cisco 7507---Interface Processor View
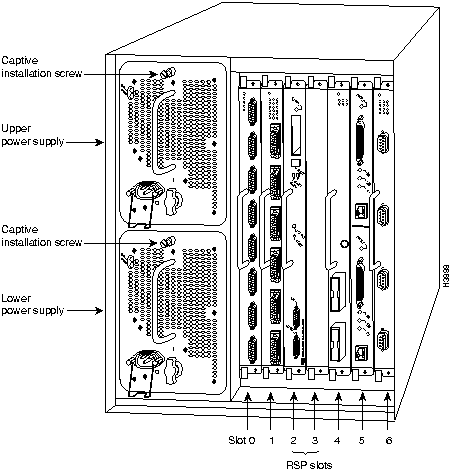
Figure 7 : Cisco 7513---Front View
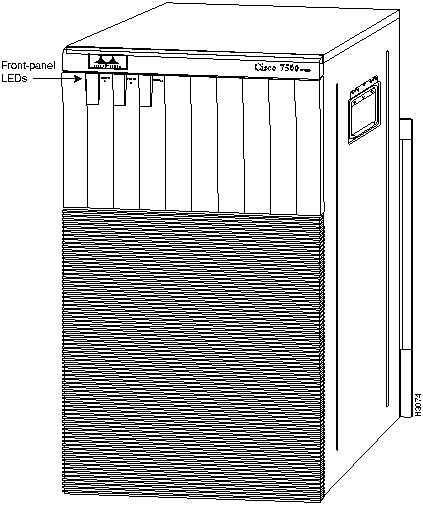
Figure 8 : Cisco 7513---Interface Processor View
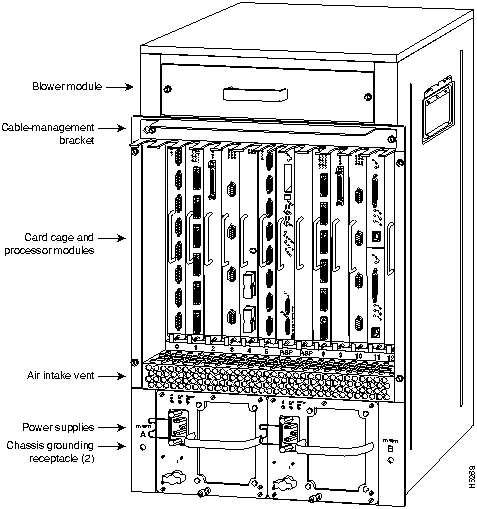
Table 54 : Cisco 7500 Series Summary of Features
| Characteristics | Cisco 7505 | Cisco 7507 | Cisco 7513 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported network interfaces | Ethernet 10BaseT, AUI, and 10BaseFL1
Fast Ethernet (100BaseT and MII) Token Ring FDDI HSSI Serial ATM Multichannel on T1 or E1 lines ISDN PRI IBM channel |
Ethernet 10BaseT, AUI, and 10BaseFL1
Fast Ethernet (100BaseT and MII) Token Ring FDDI HSSI Serial ATM Multichannel on T1 or E1 lines ISDN PRI IBM channel |
Ethernet 10BaseT, AUI, and 10BaseFL1
Fast Ethernet (100BaseT and MII) Token Ring FDDI HSSI Serial ATM Multichannel on T1 or E1 lines ISDN PRI IBM channel |
| Power supplies | 1 | 22 | 22 |
| Interface processor slots | 4 | 5 | 11 |
| Software options---for Cisco IOS Release 11.1, 11.0 software feature sets3 | IP routing
IP/IPX Routing and IBM4 IP/IPX Routing, IBM, and APPN4 Desktop and IBM Desktop and IBM APPN5 Enterprise and IBM Enterprise, IBM and APPN |
IP routing
IP/IPX Routing and IBM4 IP/IPX Routing, IBM, and APPN4 Desktop and IBM Desktop and IBM APPN5 Enterprise and IBM Enterprise, IBM and APPN |
IP routing
IP/IPX Routing and IBM4 IP/IPX Routing, IBM, and APPN4 Desktop and IBM Desktop and IBM APPN5 Enterprise and IBM Enterprise, IBM and APPN |
| Software options---for Cisco IOS Release 11.2
software feature sets6 |
IP routing
IP and Encryption 40 IP and Encryption 56 Desktop Desktop and Encryption 40 Desktop and Encryption 56 Enterprise Enterprise and Encryption 40 Enterprise and Encryption 56 Enterprise and APPN Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 40 Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 56 Desktop/IBM/APPN |
IP routing
IP and Encryption 40 IP and Encryption 56 Desktop Desktop and Encryption 40 Desktop and Encryption 56 Enterprise Enterprise nd Encryption 40 Enterprise and Encryption 56 Enterprise and APPN Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 40 Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 56 Desktop/IBM/APPN |
IP routing
IP and Encryption 40 IP and Encryption 56 Desktop Desktop and Encryption 40 Desktop and Encryption 56 Enterprise Enterprise nd Encryption 40 Enterprise and Encryption 56 Enterprise and APPN Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 40 Enterprise/APPN and Encryption 56 Desktop/IBM/APPN |
| PCMCIA Flash memory card
(optional, 2 slots available) |
8 MB expandable to 40 MB (8, 16, or 20 MBs per card) | 8 MB expandable to 40 MB (8, 16, or 20 MBs per card) | 8 MB expandable to 40 MB (8, 16, or 20 MBs per card) |
| Processor type | MIPS RISC | MIPS RISC | MIPS RISC |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 10.5 x 17.5 x 17.0'' (26.67 x 44.45 x 43.18 cm)
Chassis depth including power cord and cable management brackets is 19'' (48.26 cm) |
19.25 x 17.5 x 25.1" (48.90 x 44.45 x 63.75 cm)
Chassis depth including power cable is 28" (71.12 cm) |
33.75 x 17.5 x 22" (85.73 x 44.45 x 55.88 cm)
Chassis width including rack-mount flanges is 18.93 in (48.1 cm) Chassis depth including power cord and cable management fixture is 24 in (60.96 cm) |
| Weight | Chassis only (including power supply and fan array): 46 lb (20.87 kg)
Chassis fully configured with 1 RSP1 and 4 interface processors: 70 lb (31.75 kg) |
Chassis only: 76 lb (34.47 kg)
Chassis fully configured with 1 RSP2 and 5 interface processors, and 2 power supplies: 143.5 lb (64.63 kg) |
Chassis with blower module: ~75 lbs (34.02 kg)
Chassis with blower module and one power supply: ~100 lbs (45.36 kg) Chassis with blower module and two power supplies: ~125 lbs (56.7 kg) Chassis with blower module, two power supplies, and all slots filled: ~160 lbs (72.58 kg) Each processor module weighs ~2.5 lbs (1.13 kg) |
| High-speed backplane | 5-slot, one 1.067-gigabits per second (Gbps) CyBus: 4 interface processor slots, and 1 RSP1 slot | 7-slot, two 1.067-Gbps CyBuses: 5 interface processor slots, and 2 RSP2 slots | 13-slot, two 1.067-Gbps CyBuses: 11 interface processor slots, and 2 RSP2 slots |
Table 55 : Cisco 7505 Environmental Specifications
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Power dissipation | 600W maximum configuration with AC-input power supply
600W maximum configuration with DC-input power supply |
| Heat dissipation | 715W (2440 British thermal units [Btus]/hr) |
| Power distribution | 75 amps (A) maximum @ +5 VDC1, 15A maximum @ +12 VDC,
3A maximum @ --12 VDC, 5A maximum @ +24 VDC |
| AC-input rating | 100 to 240 volts AC (VAC2), wide input with power factor corrector (PFC);
9A maximum @ 100 VAC, 4A maximum @ 240 VAC (at 600W) |
| Frequency | 50 to 60 Hz |
| DC-input rating | --40 volts DC (VDC) minimum in North America (--56 VDC in European Community)
--48 VDC nominal in North America (--60 VDC in European Community) --52 VDC maximum in North America (--72 VDC in European Community) 20A maximum @ --48 VDC, and 16A maximum @ --60 VDC |
| DC-input cable | 10 AWG3; recommended minimum wire gauge (customer provided) |
| DC-input hold-up time | 10 milliseconds (ms) of output after the DC input has been interrupted |
| Airflow | Side-to-side through the chassis using a variable-speed, 6-fan array |
| Temperature | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C), operating; --4 to 149°F (--20 to 65°C), nonoperating |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 10 to 90% |
| Agency approvals | Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2-No. 950, EN60950, EN41003, AUSTEL TS001, AS/NZS 3260, IEC 801-2, 3, 4, 5, and 6
EMI: FCC Class A, VCCI Class II, and CISPR 22 B (EN 55022) Conducted Emissions |
Table 56 : Cisco 7507 Environmental Specifications
| Description | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Power supply | 700W maximum (AC-input and DC-input power supplies) |
| Power dissipation | 626W maximum configuration, 530W typical with maximum configuration |
| Heat dissipation | 1200W (4100 Btu/hr) |
| AC current rating | 12A maximum @100 VAC1, 6A maximum @240 VAC with the chassis fully configured |
| Input voltage | 100 to 240 VAC wide input with power factor corrector (PFC) |
| Frequency | 50 to 60 Hz (hertz) autoranging |
| DC-input power | 1000 watts (W) |
| DC-input voltage | --40 volts direct current (VDC2) minimum
--48 VDC nominal --72 VDC maximum |
| DC-input cable | 8 AWG3 wire (customer provided) |
| DC voltages supplied and steady state maximum current ratings | +5.2V @ 100 amps (A)
+12V @ 15A --12V @ 3A +24V @ 5A |
| DC-input power supply hold-up time specification | 10 milliseconds (ms) of output after the input has been interrupted |
| Airflow | 140 cfm (cubic feet per minute) through the system blower |
| Temperature | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C), operating; --4 to 149°F (--20 to 65°C), nonoperating |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 10 to 90% |
| Agency approvals | Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2-950, EN60950, EN41003, AUSTEL TS001, AS/NZS 3260
EMI: FCC Class A, EN55022 Class B, VCCI Class 2 |
Table 57 : Cisco 7513 Environmental Specifications
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Power dissipation | 1200W with a maximum configuration and one AC-input power supply
1200W with a maximum configuration and one DC-input power supply 1700W nominal with a maximum configuration and two AC- or DC-input power supplies |
| Heat dissipation | 1600W (5461 Btu/hr) |
| AC-input voltage and current | 100 VAC1 @ 16 amps (A) maximum2 wide input with power factor correction (PFC)
240 VAC @ 7A maximum |
| Frequency | 50 to 60 Hz |
| AC-input cable | 12 AWG3, with three leads, an IEC-320 receptacle on the power supply end, and a country-dependent plug on the power source end |
| DC-input voltage and current | --48 VDC4 nominal, at 35 amps (A) in North America
(--60 VDC at 35A in the E.C.) |
| DC-input cable | 8 AWG recommended minimum, with three conductors rated for at least 194°F (90°C) (customer provided) |
| DC voltages supplied and maximum, steady-state current (AC- and DC-input) | +5.2 VDC @ 75 A
+12 VDC @ 15A --12 VDC @ 3A +24 VDC @ 5A |
| Airflow and noise level | Through chassis by variable-speed blower; 62 to 70 dBA |
| Temperature | 32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C), operating; --4 to 149°F (--20 to 65°C), nonoperating |
| Humidity (noncondensing) | 10 to 90% |
| Agency approvals | Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2-950, EN60950, EN41003, AUSTEL TS001, AS/NZS 3260 EMI: FCC Class A, EN60555-2, EN55022 Class B, VDE 0878 Part 3, 30 Class B Immunity: EN55101/2 (ESD), EN55101/3 (RFI), EN55101/4 (Burst), EN55101/5 (Surge), EN55101/6 (Conducted), IEC77B (AC Disturbance) |

The Cisco 7500 series base system includes the following standard features:

Options for the Cisco 7500 series include interface processors, memory, serial cables, software feature sets, software feature licenses, a second power supply (Cisco 7507 and 7513 only), accessories, and upgrades for the Route Switch Processor.
The system requires at least one Route Switch Processor (RSP), which can be ordered in three ways: as part of an initial system, as a spare, or as an upgrade. The RSP can be ordered with your choice of 32-, 64-, or 128-MB DRAM and one or two Flash memory cards, which are available in 8-, 16-, or 20-MB densities. The price of an RSP includes 32 MB of DRAM and an 8-MB Flash memory card. For more information about the Flash memory card, see a later section "Flash Memory Cards."
Table 58 lists RSP product numbers, and Table 59 lists RSP DRAM product numbers.
Table 58 : Cisco 7500 Series Route Switch Processors
| Description | Product Numbers |
|---|---|
| Cisco 7505 Route Switch Processor (installed in system) | RSP1 |
| Cisco 7505 Route Switch Processor (spare) | RSP1=1 |
| Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 Route Switch Processor (installed in system) | RSP2 |
| Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 Route Switch Processor (spare) | RSP2=1 |
| RSP2 spare console cable | CAB-RSP2CON= |
| RSP2 spare auxiliary cable | CAB-RSP2AUX= |
Table 59 : Cisco 7500 Series Route Switch Processor DRAM s
| Description | Product Numbers | SIMM Quantity | SIMM Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-RSP-8M= | 2 | 4-MB SIMMs |
| 16-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-RSP-16M= | 2 | 8-MB SIMMs |
| 32-MB DRAM (installed in system) | MEM-RSP-32M | 2 | 16-MB SIMMs |
| 32-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-RSP-32M= | 2 | 16-MB SIMMs |
| 64-MB DRAM (installed in system) | MEM-RSP-64M | 2 | 32-MB SIMMs |
| 64-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-RSP-64M= | 2 | 32-MB SIMMs |
| 128-MB DRAM (installed in system) | MEM-RSP-128M | 4 | 32-MB SIMMs |
| 128-MB DRAM (spare) | MEM-RSP-128M= | 4 | 32-MB SIMMs |
The RSP1 is the main system processor module for the Cisco 7505. It combines all of the routing and high-speed switching functions of the separate Route Processor (RP) and Switch Processor (SP), which are used in Cisco 7000 series routers. Because the RSP1 combines the RP and SP functions, four slots are available for interface processors. The RSP1 contains the CPU and system memory components for the Cisco 7505.
Cisco IOS software images reside in Flash memory, which is located either on the RSP1, in the form of a single in-line memory module (SIMM), or on up to two Flash memory cards. Storing software images in Flash memory enables you to download and boot from upgraded images remotely. This eliminates the need for removal and replacement of ROM devices when updating software. For more information about the RSP1's Flash memory card, see a later section "Flash Memory Cards."
The RSP1 uses a software-controlled configuration register, so it is not necessary to remove the RSP1 to configure jumpers. There are no user-configurable jumpers on the RSP1.
Table 60 summarizes the memory components of the RSP1.
Table 60 : Cisco 7500 Series RSP1 Memory Components
| Type | Size | Quantity | Description |
| DRAM | 32 to
128 MB |
2 to 4 | 8-, 16-, or 32-MB SIMMs (based on maximum DRAM required, user configurable) |
| NVRAM | 128 KB | 1 | Nonvolatile EPROM for the system configuration file1 |
| Flash SIMM | 8 MB | 1 | Contains the Cisco IOS BOOT images on the RSP1 (standard) |
| Flash memory card | 8, 16, and
20 MB2 |
Up to 2 | Contains the Cisco IOS images on up to two PCMCIA cards (user configurable) |
| ROM monitor | 256 KB | 1 | EPROM for the ROM monitor program |
The RSP2 is a system processor module for the Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513. The RSP2 contains the system CPU and system memory components. It maintains and executes the management functions that control the system.
Cisco IOS images reside in Flash memory, which is located either on a SIMM on the RSP2 or on up to two Flash memory cards. Storing Cisco IOS images in Flash memory enables you to download and boot from upgraded images remotely. This eliminates removal and replacement of ROM devices for software updates. (For more information about the RSP2 Flash memory card, see the following section, "Flash Memory Cards.")
Table 61 summarizes memory components of the RSP2.
Table 61 : Cisco 7500 Series RSP2 Memory Components
| Type | Size | Quantity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRAM | 32 to
128 MB |
2 to 4 | 8-, 16-, or 32-MB SIMMs (based on maximum DRAM required, user configurable) |
| NVRAM | 128 KB | 1 | Nonvolatile EPROM for the system configuration file1 |
| Flash SIMM | 8 MB | 1 | Contains the Cisco IOS BOOT images on the RSP2 |
| Flash memory cards | 8, 16, and
20 MB2 |
Up to 2 | Contains the Cisco IOS images on up to two PCMCIA cards (user configurable) |
| ROM monitor | 256 KB | 1 | EPROM for the ROM monitor program |
Flash memory cards can be used to store and boot Cisco IOS images and/or system configurations. A Cisco 7500 series router can also be used as a TFTP server, with the Flash card memory used to store other files such as software and microcode images for other systems. Cisco recommends using one card for image storage, and another for configurations. The number of system images that can be stored on the card depends both on the Flash card size and the file size.
The Flash memory card is available in 8-, 16-, or 20-MB densities. The card is an Intel Series 2+ Flash memory card, which conforms with the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA) format. The Flash memory card that is shipped with the system contains a software image; the same Flash memory card that is ordered as a spare is shipped blank and must be formatted before use. Table 62 provides a description of each Cisco 7500 series Flash memory card along with its corresponding product number.
Table 62 : Cisco 7500 Series Flash Memory Cards
| Description | Product Number |
|---|---|
| 8-MB Flash memory card (default, shipped with RSP) | MEM-RSP-FLC8M |
| 8-MB Flash memory card (spare) | MEM-RSP-FLC8M=1 |
| 16-MB Flash memory card (installed in system)2 | MEM-RSP-FLC16M |
| 16-MB Flash memory card (spare) | MEM-RSP-FLC16M=1 |
| 20-MB Flash memory card (installed in system) | MEM-RSP-FLC20M |
| 20-MB Flash memory card (spare) | MEM-RSP-FLC20M=1 |
Interface processors for the Cisco 7500 series are described in the chapter "Interface Processors and Port Adapters for the Cisco 7000 Family."
Before you order a spare chassis, read the following sections:
Table 63 lists spare chassis assemblies.
Table 63 : Cisco 7500 Series Chassis Assemblies
| System1 | Product Number |
|---|---|
| Cisco 7505 chassis and AC-input power supply. Includes blower, rack-mount kit, and cable management bracket. | CHAS-7505= |
| Cisco 7505 chassis and DC-input power supply. Includes blower, rack-mount kit, and cable management bracket. | CHAS-7505-DC= |
| Cisco 7507 chassis and AC-input power supply. Includes blower and rack-mount kit. | CHAS-7507= |
| Cisco 7507 chassis and DC-input power supply. Includes blower and rack-mount kit. | CHAS-7507-DC= |
| Cisco 7513 chassis and AC-input power supply. Includes blower and rack-mount kit. | CHAS-7513= |
| Cisco 7513 chassis and AC-input power supply. Includes blower and rack-mount kit. | CHAS-7513-DC= |
Table 64 provides product numbers for single power supplies ordered as part of an initial system or a spare.
Table 64 : Cisco 7500 Series Single Power Supplies
| Description | Product Numbers |
|---|---|
| Cisco 7505 AC-input power supply (spare) | PWR/5-AC=1 |
| Cisco 7505 DC-input power supply (installed in system) | PWR/5-DC1 |
| Cisco 7505 DC-input power supply (spare) | PWR/5-DC=1 |
| Cisco 7507 AC-input power supply (installed in system, default) | PWR/72 |
| Cisco 7507 AC-input power supply (spare) | PWR/7-AC=2 |
| Cisco 7507 DC-input power supply (installed in system) | PWR/7-DC2 |
| Cisco 7507 DC-input power supply (spare) | PWR/7-DC=2 |
| Cisco 7513 AC-input power supply (installed in system, default) | PWR-7513 |
| Cisco 7513 AC-input power supply (spare) | PWR-7513-AC= |
| Cisco 7513 DC-input power supply option (installed in system) | PWR-7513-DC |
| Cisco 7513 DC-input power supply option (spare) | PWR-7513-DC= |
The Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 support dual power supplies. (This option is not available for the Cisco 7505.) The optional additional power supply system provides dual load-sharing for protection against system interruption should one power supply system or one source of power fail. Table 65 provides product numbers for dual power supplies that are ordered as part of an initial system.
Table 65 : Cisco 7507 and Cisco 7513 Dual Power Supplies
| Description | Product Numbers |
|---|---|
| Cisco 7507 dual AC-input power supply | PWR/7/21 |
| Cisco 7507 dual DC-input power supply | PWR/7/2-DC1 |
| Cisco 7513 dual AC-input power supply | PWR-7513/2 |
| Cisco 7513 dual DC-input power supply | PWR-7513/2-DC |
For international spare AC-input power supply orders, Cisco uses country-specific product numbers, which specify the type of power cord to be included in the order. Table 66 provides international spare power supply product numbers.
Table 66 : Cisco 7500 Series International Spare AC-input Power Supplies
| System | Country | Product Number |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco 7505 | Australia | PWR/5-ACA=1 |
| Europe | PWR/5-ACE=1 | |
| Italy | PWR/5-ACI=1 | |
| United Kingdom | PWR/5-ACU=1 | |
| USA | PWR/5-AC=1 | |
| Cisco 7507 | Australia | PWR/7-ACA=2 |
| Europe | PWR/7-ACE=2 | |
| Italy | PWR/7-ACI=2 | |
| United Kingdom | PWR/7-ACU=2 | |
| USA | PWR/7-AC=2 | |
| Cisco 7513 | Australia | PWR-7513-ACA= |
| Europe | PWR-7513-ACE= | |
| Italy | PWR-7513-ACI= | |
| United Kingdom | PWR-7513-ACU= | |
| USA | PWR-7513-AC= |
Several spare accessories are available for the Cisco 7500 series: a rack-mount kit, cable-management bracket, packing material, fans, air filter, and LED board. Table 67 lists spare accessories.
Table 67 : Cisco 7500 Series Accessories
| Product | Description | Cisco 7505
Product Number |
Cisco 7507
Product Number |
Cisco 7513
Product Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rack-mount kit | Standard EIA 19-inch rack-mount kit, spare | ACS/5-RMK= | ACS-RMK= | ACS-RMK= |
| Cable-management bracket | Cable-management system, spare | ACS/5-CBLM= | -- | ACS-7513CBLM= |
| Spare packaging | Spare packaging material | PKG/5= | PKG/7= | PKG-7513= |
| Fan assembly | Fan or blower assembly | MAS/5-FAN= | MAS/7-FAN= | MAS-7513FAN= |
| Air filter | Air filter for fan assembly | -- | ACS/7-FILTER= | -- |
| LED board | Spare LED board | -- | MAS/7-LED= | -- |
This section describes Cisco IOS software feature sets for the Cisco 7500 series. With feature sets, you can order software combinations that support your particular application. Optional licenses expand the feature sets by providing WAN packet protocol and interdomain routing. To order, select one feature set (there is no default) and one or both of the optional feature licenses.
With the introduction of Cisco IOS Release 11.2, feature sets have been updated to make it easier to select the exact feature sets you need. Feature set names are simplified and are more consistent across Cisco hardware platforms. In addition, you can add options to the standard feature set offerings. These options provide additional features and value based on the hardware platform selected. Cisco also continues to offer specialized feature sets for key applications.

The Cisco 7500 series offers the following types of feature sets:
Cisco IOS images with 40-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) support may legally be distributed to any party eligible to receive Cisco IOS software. 40-bit DES is not a cryptographically strong solution and should not be used to protect sensitive data.
Cisco IOS images with 56-bit DES are subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) controls, and have a limited distribution. Images to be installed outside the U.S. require an export license. Orders may be denied or subject to delays due to U.S. Government regulations. Contact your sales representative or distributor for more information, or send e-mail to export@cisco.com.
The new feature set tables use the following conventions to identify features:
The following tables provide feature set information by product:
Table 68 lists the Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1, and 11.0 feature sets, Table 69 lists feature set product numbers, Table 70 lists optional feature set licenses and their product numbers, and Table 71 lists feature set upgrade product numbers.
Table 68 : Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1, and 11.0 Feature Sets---Cisco 7500 Series
| Cisco 7500 Series Feature Sets | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | IP Routing | IP/IPX/IBM1 | Desktop/IBM2 | Enterprise2 | |||||||
| Cisco IOS Release | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 11.0 |
| LAN Support | |||||||||||
| Apollo Domain | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| AppleTalk 1 and 23 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Banyan VINES | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Concurrent routing and bridging4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet IV | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DECnet V | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| GRE | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Integrated routing and bridging (IRB)5 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| IP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| LAN extension host | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multiring | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Novell IPX6 | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSI | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Transparent and translational bridging7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| XNS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| WAN Services | |||||||||||
| ATM LAN emulation: DECnet routing and Banyan VINES support8 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and
Simple Server Redundancy Protocol (SSRP) |
X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: Rate queues for SVC per subinterface | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| ATM LAN emulation: UNI 3.1 signaling for ATM | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Combinet Packet Protocol (CPP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Dialer profiles | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Half bridge/half router for CPP and PPP | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| HDLC | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ISDN9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| PPP10 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| WAN Optimization | |||||||||||
| Bandwidth-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Custom and priority queuing11 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial backup | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dial-on-demand | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Header12, link and payload compression13 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NetFlow Switching (NFS)14 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Snapshot routing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Weighted fair queuing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IP Routing | |||||||||||
| Enhanced IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Enhanced IGRP Optimizations | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| ES-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| IGRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IS-IS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Named IP Access Control List15 | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| NHRP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| On Demand Routing (ODR) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| OSPF | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| OSPF Not-So-Stubby-Areas (NSSA) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| OSPF On Demand Circuit (RFC 1793) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| PIM | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Policy-based routing | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RIP Version 2 | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| Other Routing | |||||||||||
| AURP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IPX RIP | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| NLSP | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| RTMP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SMRP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRTP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Multimedia and Quality of Service | |||||||||||
| Generic traffic shaping | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Random Early Detection (RED) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Management | |||||||||||
| AutoInstall | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Automatic modem configuration16 | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| HTTP Server | X | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| RMON events and alarms | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| SNMP | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Telnet | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Security | |||||||||||
| Access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Access security | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Extended access lists | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberized login | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | -- |
| Kerberos V client support | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| Lock and Key | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| MD5 routing authentication | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Network layer encryption (export controlled 40-bit and 56-bit DES)17 | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- |
| RADIUS | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| Router authentication | Encrypt | -- | -- | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- | Encrypt | -- | -- |
| TACACS+18 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IBM Support | |||||||||||
| APPN (optional)2 | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| BAN for SNA Frame Relay support | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| Caching and filtering | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DLSW+19, 20 | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Downstream PU concentration (DSPU) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| Frame Relay SNA support (RFC 1490) | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Native Client Interface Architecture (NCIA) Server | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| NetView Native Service Point | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| QLLC | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Response Time Reporter (RTR) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| SDLC integration | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC transport (STUN) | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SDLC-to-LAN conversion (SDLLC) | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SNA and NetBIOS WAN optimization via local acknowledgment | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRB/RSRB21 | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| SRT | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| TG/COS | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | X | X |
| TN3270 Server (CIP only) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | X | -- | -- | X | -- | -- |
| VIP and HSA | |||||||||||
| VIP and HSA22 | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
| VIP223 | X | X | -- | X | -- | X | X | -- | X | X | -- |
Table 69 : Cisco IOS Software Product Numbers---Cisco 7500 Series
| Description | Cisco IOS Release 11.2 | Cisco IOS Release 11.1 | Cisco IOS Release 11.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise | SF75A--11.2.x1
SW75A-11.2.x= |
SF-G75A-11.1.x1
SW-G75A-11.1.x= |
SF-G75A-11.0.x1
SW-G75A-11.0.x= |
| Enterprise and Encryption 40 | SF75AK-11.2.x
SW75AK-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Enterprise and Encryption 56 | SF75AT-11.2.x
SW75AT-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Enterprise, VIP/VIP22 | SF75A--11.2.x
SW75A-11.2.x= |
SF-G75AV-11.1.x | -- |
| Enterprise, APPN3 | SF75AN-11.2.x
SW75AN-11.2.x= |
SF-G75AN-11.1.x
SW-G75AN-11.1.x= |
SF-G75AN-11.0.x
SW-G75AN-11.0.x= |
| Enterprise, APPN, and Encryption 40 | SF75ANK-11.2.
SW75ANK-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Enterprise, APPN, and Encryption 56 | SF75ANT-11.2.x
SW75ANT-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Enterprise, APPN, VIP/VIP22 | SF75AN-11.2.x
SW75AN-11.2.x= |
SF-G75ANV-11.1.x | -- |
| Desktop, IBM | SF75BS-11.2.x
SW75BS-11.2.x= |
SF-G75BS-11.1.x
SW-G75BS-11.1.x= |
SF-G75BS-11.0.x
SW-G75BS-11.0.x= |
| Desktop, IBM, and Encryption 40 | SF75BSK-11.2.x
SW75BSK-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Desktop, IBM, and Encryption 56 | SF75BST-11.2.x
SW75BST-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| Desktop, IBM, VIP/VIP22 | SF75BS-11.2.x
SW75BS-11.2.x= |
SF-G75BSV-11.1.x | -- |
| Desktop, IBM, APPN, VIP/VIP22 | SF75BSN-11.2.x
SW75BSN-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| IP/IPX, IBM4 | -- | SF-G75DS-11.1.x
SW-G75DS-11.1.x= |
SF-G75DS-11.0.x
SW-G75DS-11.0.x= |
| IP/IPX 4, IBM, VIP/VIP22 | -- | SF-G75DSV-11.1.x | -- |
| IP/IPX4, IBM, APPN | -- | SF-G75DSN-11.1.x
SW-G75DSN-11.1.x= |
SF-G75DSN-11.0.x
SW-G75DSN-11.0.x= |
| IP/IPX4, IBM, APPN, VIP/VIP22 | -- | SF-G75DSNV-11.1.x | -- |
| IP only | SF75C-11.2.x
SW75C-11.2.x= |
SF-G75C-11.1.x
SW-G75C-11.1.x= |
SF-G75C-11.0.x
SW-G75C-11.0.x= |
| IP and Encryption 40 | SF75CK-11.2.x
SW75CK-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| IP and Encryption 56 | SF75CT-11.2.x
SW75CT-11.2.1= |
-- | -- |
| IP, VIP/VIP22 | SF75C-11.2.x
SW75C-11.2.1= |
SF-G75CV-11.1.x | -- |
Table 70 : Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1, and 11.0 Feature Licenses---Cisco 7500 Series
| Category | Features | Product Number |
|---|---|---|
| WAN packet protocols | X.25, X.25 switching, Frame Relay, SMDS, Frame Relay switching, Switched 56, ATM DXI, SMDS over ATM
In Cisco IOS Release 11.2 only: all of the above plus Frame Relay SVC support (DTE) and Frame Relay traffic shaping |
FR-WPP75, FR-WPP75= |
| Interdomain routing1 | BGP, EGP for Internet scale routing
In Cisco IOS Release 11.2 only: all of the above plus BGP42 |
FR-IR75, FR-IR75= |
| NetFlow Switching | NetFlow Switching | FR-NF75
FR-NF75= |
| CIP (or CIP2) support3 | TCP/IP offload feature for CIP (or CIP2) | FR-CIP-TCPOFF, FR-CIP-TCPOFF= |
| SNA support feature for CIP (or CIP2) SNA | FR-CIP-CSNA, FR-CIP-CSNA= | |
| VIP/VIP2 support | Included automatically with VIP order | -- |
Cisco IOS Feature Set Upgrades
Cisco IOS Release 11.2 for the Cisco 7500 series allows software upgrades that cross multiple feature sets. This will require you to order multiple feature set licenses. The following is an example:

You have a Cisco 7513 router running the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 IP Routing (basic) feature set. You want to upgrade to the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 Enterprise and Encryption 40 feature set. You are crossing two feature sets: one to get from IP to Enterprise and one to add Encryption 40 (basic to encryption). To complete the upgrade, use the following guidelines:
Cisco IOS Release 11.1 and 11.0 follow the same upgrade guidelines as described for Cisco IOS Release 11.2. Use the applicable product numbers listed in Table 71. Unless otherwise noted, these upgrades are available for Cisco IOS Release 11.2, 11.1 and 11.0.
Table 71 : Cisco IOS Software Upgrades---Cisco 7500 Series
| Feature Set Upgrade | Product Number |
|---|---|
| IP to IP/IPX and IBM Base Upgrade | FR75-CDS= |
| IP to Desktop and IBM Base Upgrade | FR75-CBS= |
| IP to Enterprise Upgrade | FR75-CA= |
| IP/IPX and IBM to Desktop and IBM Upgrade1 | FR75-DSBS= |
| IP/IPX and IBM to Enterprise Upgrade1 | FR75-DSA= |
| Desktop and IBM to Enterprise Upgrade | FR75-BSA= |
| RSP1, RSP2, and RSP7000 IOS Encryption 40 Upgrade2 | FR75-40 |
| RSP1, RSP2, and RSP7000 IOS Encryption 40 Upgrade2 | FR75-56= |
| APPN Upgrade3 | SW-G75NU-11.0.x= |
| APPN Upgrade4 | SW-G75NU-11.1.x= |
| IP/IPX and IBM and APPN to Enterprise and APPN Upgrade3 | SW-G75DNNU-11.0.x= |
| IP/IPX and IBM and APPN to Enterprise and APPN Upgrade4 | SW-G75DNNU-11.1.x= |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.